文章目录
- 【LeetCode热题100】打卡第19天:最大数组和&跳跃游戏
- ⛅前言
- 最大数组和
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
- 跳跃游戏
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
【LeetCode热题100】打卡第19天:最大数组和&跳跃游戏
⛅前言
大家好,我是知识汲取者,欢迎来到我的LeetCode热题100刷题专栏!
精选 100 道力扣(LeetCode)上最热门的题目,适合初识算法与数据结构的新手和想要在短时间内高效提升的人,熟练掌握这 100 道题,你就已经具备了在代码世界通行的基本能力。在此专栏中,我们将会涵盖各种类型的算法题目,包括但不限于数组、链表、树、字典树、图、排序、搜索、动态规划等等,并会提供详细的解题思路以及Java代码实现。如果你也想刷题,不断提升自己,就请加入我们吧!QQ群号:827302436。我们共同监督打卡,一起学习,一起进步。
博客主页💖:知识汲取者的博客
LeetCode热题100专栏🚀:LeetCode热题100
Gitee地址📁:知识汲取者 (aghp) - Gitee.com
Github地址📁:Chinafrfq · GitHub
题目来源📢:LeetCode 热题 100 - 学习计划 - 力扣(LeetCode)全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
PS:作者水平有限,如有错误或描述不当的地方,恳请及时告诉作者,作者将不胜感激
最大数组和
🔒题目
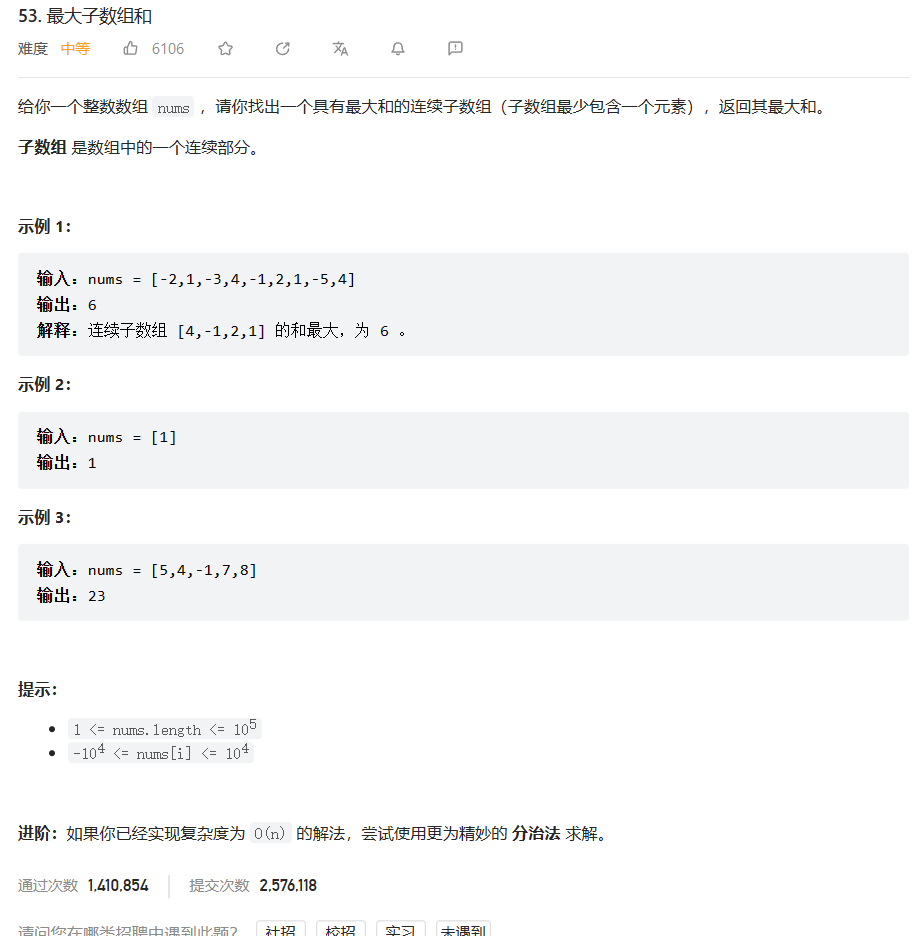
原题链接:53. 最大子数组和
🔑题解
-
解法一:暴力(内存超限,210个数据通过200个)
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Collectors; /** * @author ghp * @title 最大数组和 */ class Solution { public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { List<Integer> list = Arrays.stream(nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList()); for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { int sum = nums[i]; for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) { sum += nums[j]; list.add(sum); } } return Collections.max(list); } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 2 n ) O(2^n) O(2n)
其中 n n n 为数组中元素的个数
不出所料,对于元素个数较少的情况,是可以通过的,但是遇到长度较大的时候会出现内存超限!
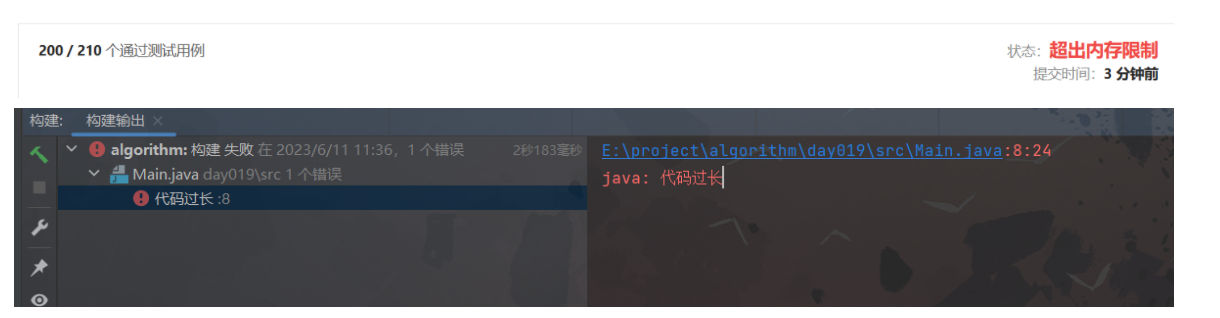
备注:Java规定一个方法编译后的字节码大小不能超过 65535 字节,这个长度在一般情况下都是够用的,但碰到极端情况就不行了
/** * @author ghp * @title 最大数组和 */ class Solution { public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] > max){ max = nums[i]; } } for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { int sum = nums[i]; for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) { sum += nums[j]; if (sum>max){ max = sum; } } } return max; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
其中 n n n 为数组中元素的个数
这样写内存不超限了,但是时间超限!
-
解法二:动态规划
主要思路:因为我们是要求数组连续元素之和的最大值,所以每次我们在遍历数组时,有两种选择的可能性,要么是选择当前元素,要么是选择之前求的和加上当前元素。这样我们就可以得到一个递推式: M a t h . m a x ( s u m + n u m s [ i ] , n u m s [ i ] ) Math.max(sum+nums[i], nums[i]) Math.max(sum+nums[i],nums[i]),这里需要注意,我们要需要有一个变量来记录这个过程中出现的最大值,所以还应当有: M a t h . m a x ( m a x , s u m ) Math.max(max, sum) Math.max(max,sum)
/** * @author ghp * @title 最大数组和 */ class Solution { public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { sum = Math.max(sum+nums[i], nums[i]); max = Math.max(max, sum); } return sum; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
其中 n n n 为数组中元素的个数
-
解法三:
跳跃游戏
🔒题目
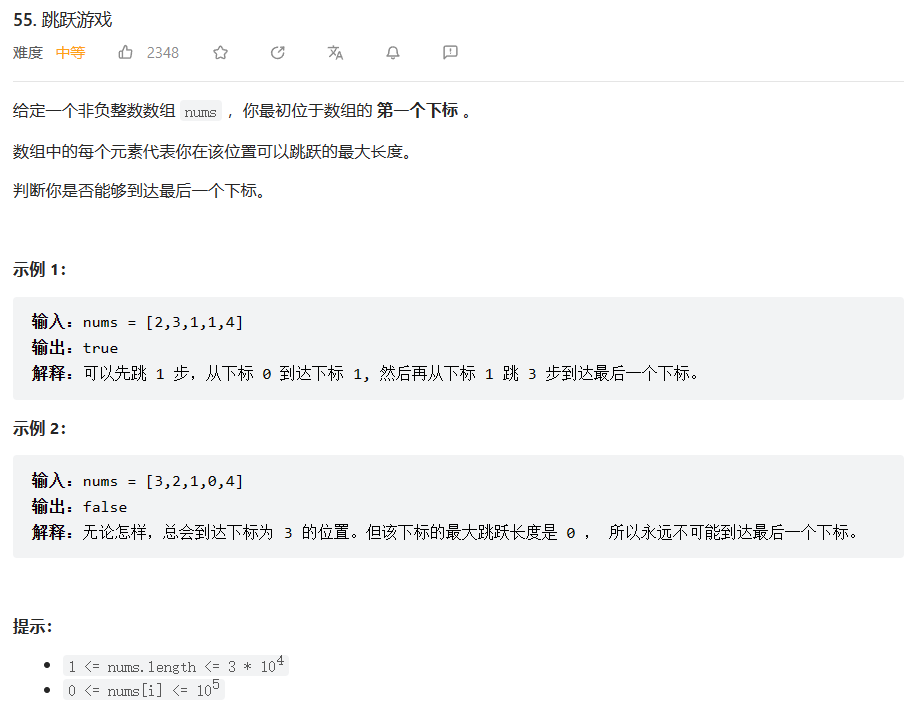
原题链接:55.跳跃游戏
🔑题解
- 解法一:BFS(时间超限)
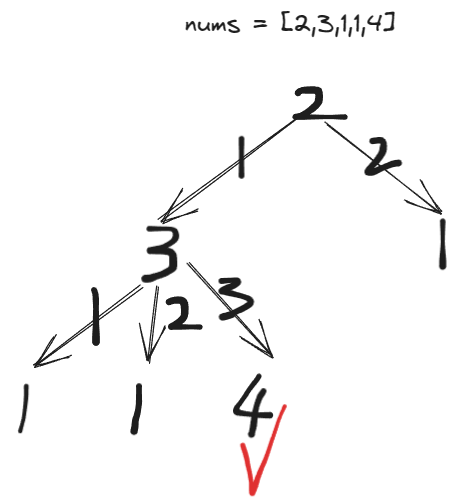
主要不断进行搜索遍历,然后因为这相当于是一个带权的树,只要树的权值之和等于数组长度-1,就说明数组的最后一个元素可达。否则就不可达。
/**
* @author ghp
* @title 跳跃游戏
*/
class Solution {
static boolean f = false;
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int path = 0;
bfs(nums, path);
return f;
}
private void bfs(int[] nums, int path) {
if (path >= nums.length - 1) {
// 当前可达距离>=数组最大长度,说明可到达最后一个元素,结束递归
f = true;
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= nums[path]; i++) {
// 遍历下一层
bfs(nums, path + i);
}
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ! ) O(n!) O(n!)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
其中 n n n 为数组中元素的个数
-
解法二:贪心
通过不断迭代,计算出当前可达的最大长度,只要最大长度超过数组的长度,就可以达到数组中的最后一个元素
/** * @author ghp * @title 跳跃游戏 */ class Solution { public boolean canJump(int[] nums) { int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (i <= max){ // 当前距离是能够到达的 // 更新最大距离 max = Math.max(max, i + nums[i]); if (max >= nums.length-1){ // 最大距离已经超过了数组的长度,所以可以到达最后一个元素 return true; } } } return false; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
其中 n n n 为数组中元素的个数






![[安卓广播入门][1]Android Studio接收系统广播](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8f61ee7b528141c0aff292dcb63d5bdc.png)