Dijkstra算法是单源最短路算法,是用来求一个点到其他所有点点最短距离,使用小根堆优化后时间复杂度大概为 O m l o g n Omlogn Omlogn
注意:不可以解决存在负权边的问题
【模板】单源最短路径(标准版)
链接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4779
题目描述
给定一个 n n n 个点, m m m 条有向边的带非负权图,请你计算从 s s s 出发,到每个点的距离。
数据保证你能从 s s s 出发到任意点。
输入格式
第一行为三个正整数
n
,
m
,
s
n, m, s
n,m,s。
第二行起
m
m
m 行,每行三个非负整数
u
i
,
v
i
,
w
i
u_i, v_i, w_i
ui,vi,wi,表示从
u
i
u_i
ui 到
v
i
v_i
vi 有一条权值为
w
i
w_i
wi 的有向边。
输出格式
输出一行 n n n 个空格分隔的非负整数,表示 s s s 到每个点的距离。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
4 6 1
1 2 2
2 3 2
2 4 1
1 3 5
3 4 3
1 4 4
样例输出 #1
0 2 4 3
提示
1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 1 \leq n \leq 10^5 1≤n≤105;
1 ≤ m ≤ 2 × 1 0 5 1 \leq m \leq 2\times 10^5 1≤m≤2×105;
s = 1 s = 1 s=1;
1 ≤ u i , v i ≤ n 1 \leq u_i, v_i\leq n 1≤ui,vi≤n;
0 ≤ w i ≤ 1 0 9 0 \leq w_i \leq 10 ^ 9 0≤wi≤109,
0 ≤ ∑ w i ≤ 1 0 9 0 \leq \sum w_i \leq 10 ^ 9 0≤∑wi≤109。
思路-朴素
- 初始化时,
dist[]数组全部初始化为无穷大,dist[1]=0 - 从圈中选择一个距离最小的点
u,打上标记st[u]=1表示这个点出圈 - 对
u的所有出边进行松弛操作【尝试更新相邻点的最小距离】 - 重复2,3步骤,直到圈内为空
代码- O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
下面代码是用邻接矩阵求1-n的最短路
#include <iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510;
int g[N][N]; //为稠密阵所以用邻接矩阵存储
bool st[N];//用于记录该点的最短距离是否已经确定
int dist[N]; //用于记录每一个点距离第一个点的距离
int n, m;
int Dijkstra()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0; //第一个点到自身的距离为0
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
int u = i; //当前访问的点
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) if (!st[j] && dist[j] < dist[u]) u = j; //寻找距离最小的点
st[u] = true;
//依次更新每个点所到相邻的点路径值
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[u] + g[u][j]);
}
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1; //不存在
return dist[n];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
while (m--)
{
int x, y, z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
g[x][y] = min(g[x][y], z); //如果发生重边的情况则保留最短的一条边
}
cout << Dijkstra() << endl;
return 0;
}
思路-堆优化
算法的主要耗时的步骤是从dist 数组中选出:没有确定最短路径的节点中距离源点最近的点 t。
只是找个最小值而已,没有必要每次遍历一遍dist数组。所以这里可以使用小根堆来维护。
代码- O ( m l o g n ) O(mlogn) O(mlogn)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef struct edge {
int y, w;
} edge;
vector<edge> e[N];
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
int n, m, s;
void Dijkstra() {
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<>> q;
q.push({0, s});
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) dist[i] = 1e18;
dist[s] = 0;
while (q.size()) {
auto [d, x] = q.top();
q.pop();
if (st[x]) continue;
st[x] = true;
for (auto [y, w]: e[x]) {
if (dist[y] > dist[x] + w) {
dist[y] = dist[x] + w;
q.push({dist[y], y});
}
}
}
}
signed main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
cin >> n >> m >> s;
while (m--) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
e[a].push_back({b, c});
}
Dijkstra();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces Alpha Round 20 (Codeforces format)-C. Dijkstra?
题目
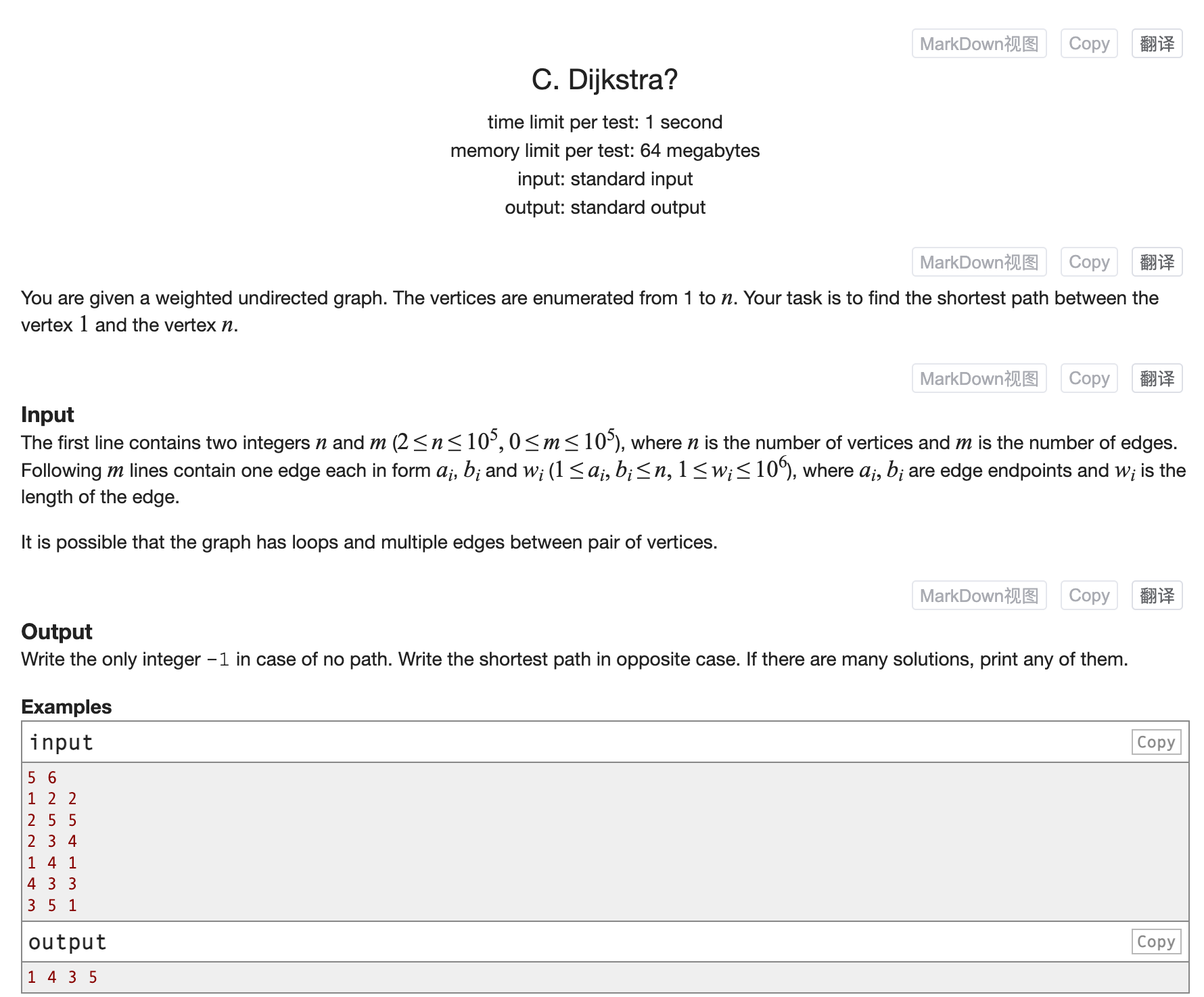
思路
Dijkstra算法的模版题目,这里需要求从1走到n到最短路径长度,
- 可以先跑一遍Dijkstra算法
- 然后从终点开始往前找是从哪个点转移过来的,即满足dist[x]=dist[y]+w,y为x的邻点,w为边权
- 最后需要把路径反转一下
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
typedef struct edge {
int to, w;
} edge;
vector<edge> e[N];
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
int n, m;
void dijkstra() {
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<>> q;
q.push({0, 1});
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
dist[i]=1e18;
}
dist[1] = 0;
while (q.size()) {
auto [distance, x] = q.top();
q.pop();
if (st[x])
continue;
st[x] = true;
for (auto [y, w] : e[x]) {
if (dist[x] + w < dist[y]) {
dist[y] = dist[x] + w;
q.push({dist[y], y});
}
}
}
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
while (m--) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
e[a].push_back({b, c});
e[b].push_back({a, c});
}
dijkstra();
if (dist[n] == 1e18) {
cout << -1 << endl;
} else {
int t = dist[n];
vector<int> path;
path.push_back(n);
int x = n;
while (t != 0) {
for (auto [y, w] : e[x]) {
if (dist[x] == dist[y] + w) {
path.push_back(y);
x = y;
t-=w;
break;
}
}
}
reverse(path.begin(),path.end());
for(auto x:path){
cout<<x<<" ";
}
}
}
signed main() {
int _ = 1;
while (_--)
solve();
return 0;
}