nginx.conf 配置文件
基本说明
Nginx 的配置文件位置
- 文件位置
安装目录\conf\nginx.conf
安装目录\nginx.conf
- 两个文件是一样的
多说一句:使用/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx 启动Nginx ,默认用的是安装目录\nginx.conf 配置文件
作用:完成对Nginx 的各种配置,包括端口,并发数,重写规则等
nginx.conf 组成
-
全局块
-
events 块
-
http 块
nginx.conf 详细文档
- 地址: 文档:https://blog.csdn.net/liuchang19950703/article/details/110792007
- 文档: Nginx 配置文件nginx.conf 详解.docx
- 详细内容
#Nginx 用户及组:用户组。window 下不指定
#user nobody;
#工作进程:数目。根据硬件调整,通常等于CPU 数量或者2 倍于CPU。
worker_processes 1;
#错误日志:存放路径。
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid(进程标识符):存放路径
pid /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid;
#一个进程能打开的文件描述符最大值,理论上该值因该是最多能打开的文件数除以进程数。
#但是由于nginx 负载并不是完全均衡的,所以这个值最好等于最多能打开的文件数。
#LINUX 系统可以执行sysctl -a | grep fs.file 可以看到linux 文件描述符。
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
events {
#使用epoll 的I/O 模型。linux 建议epoll,FreeBSD 建议采用kqueue,window 下不指定。
use epoll;
#单个进程最大连接数(最大连接数=连接数*进程数)
worker_connections 1024;
#客户端请求头部的缓冲区大小。这个可以根据你的系统分页大小来设置,
#一般一个请求头的大小不会超过1k,不过由于一般系统分页都要大于1k,所以这里设置为分页大小。
#client_header_buffer_size 4k;
}
http {
#设定mime 类型,类型由mime.type 文件定义
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#日志格式设置
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#用了log_format 指令设置了日志格式之后,需要用access_log 指令指定日志文件的存放路径
#记录了哪些用户,哪些页面以及用户浏览器、ip 和其他的访问信息
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#access_log logs/host.access.404.log log404;
#服务器名字的hash 表大小
server_names_hash_bucket_size 128;
#客户端请求头缓冲大小。
#nginx 默认会用client_header_buffer_size 这个buffer 来读取header 值,
#如果header 过大,它会使用large_client_header_buffers 来读取。
#如果设置过小HTTP 头/Cookie 过大会报400 错误nginx 400 bad request
#如果超过buffer,就会报HTTP 414 错误(URI Too Long)
#nginx 接受最长的HTTP 头部大小必须比其中一个buffer 大
#否则就会报400 的HTTP 错误(Bad Request)
#client_header_buffer_size 32k;
#large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
#隐藏ngnix 版本号
#server_tokens off;
#忽略不合法的请求头
#ignore_invalid_headers on;
#让nginx 在处理自己内部重定向时不默认使用server_name 设置中的第一个域名
#server_name_in_redirect off;
#客户端请求体的大小
#client_body_buffer_size 8m;
#开启文件传输,一般应用都应设置为on;若是有下载的应用,则可以设置成off 来平衡网络I/O 和磁盘的I/O 来降低系统负
载
sendfile on;
#告诉nginx 在一个数据包里发送所有头文件,而不一个接一个的发送。
#tcp_nopush on;
#tcp_nodelay off 会增加通信的延时,但是会提高带宽利用率。在高延时、数据量大的通信场景中应该会有不错的效果
#tcp_nodelay on,会增加小包的数量,但是可以提高响应速度。在及时性高的通信场景中应该会有不错的效果
tcp_nodelay on;
#长连接超时时间,单位是秒
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip 模块设置,使用gzip 压缩可以降低网站带宽消耗,同时提升访问速度。
#gzip on; #开启gzip
#gzip_min_length 1k; #最小压缩大小
#gzip_buffers 4 16k; #压缩缓冲区
#gzip_http_version 1.0; #压缩版本
#gzip_comp_level 2; #压缩等级
#gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml text/javascript application/json application/x-javascript application/xml
application/xml+rss;#压缩类型
#负载均衡
#max_fails 为允许请求失败的次数,默认为1
#weight 为轮询权重,根据不同的权重分配可以用来平衡服务器的访问率。
# upstream myServer{
# server 192.168.247.129:8080 max_fails=3 weight=2;
# server 192.168.247.129:8081 max_fails=3 weight=4;
# }
#server {
# listen 80;
#
# #IP/域名可以有多个,用空格隔开
# server_name 192.168.247.129;
# #server_name www.test.com;
#
# #charset koi8-r;
#
# #access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#
# #反向代理配置,
# #将所有请求为www.test.com 的请求全部转发到upstream 中定义的目标服务器中。
# location / {
#
# #此处配置的域名必须与upstream 的域名一致,才能转发。
# proxy_pass http://myServer;
# #proxy_pass http://192.168.247.129:8080;
#
# proxy_connect_timeout 20; #nginx 跟后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时)
#
# #client_max_body_size 10m; #允许客户端请求的最大单文件字节数
# #client_body_buffer_size 128k; #缓冲区代理缓冲用户端请求的最大字节数
# #proxy_send_timeout 300; #后端服务器数据回传时间(代理发送超时)
# #proxy_read_timeout 300; #连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间(代理接收超时)
# #proxy_buffer_size 4k; #设置代理服务器(nginx)保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小
# #proxy_buffers 4 32k; #proxy_buffers 缓冲区,网页平均在32k 以下的话,这样设置
# #proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; #高负荷下缓冲大小(proxy_buffers*2)
# #proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; #设定缓存文件夹大小,大于这个值,将从upstream 服务器传
#
# root html;
#
# #定义首页索引文件的名称
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#
# #动静分离静态资源走linux 动态资源走tomcat
# # 注意/source/image/下面寻找资源
# location /image/ {
# root /source/;
# autoindex on;
# }
#
#
# # 出现50x 错误时,使用/50x.html 页返回给客户端
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# root html;
# }
#}
#下面是配置生产环境中既支持HTTP 又支持HTTPS,保证用户在浏览器中输入HTTP 也能正常访问
# SSL 证书配置
ssl_certificate cert/yphtoy.com.pem; #加密证书路径
ssl_certificate_key cert/yphtoy.com.key; #加密私钥路径
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; #加密协议
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; #加密访问缓存设置,可以大大提高访问速度
ssl_session_timeout 10m; #加密访问缓存过期时间
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; #加密算法
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; #是否由服务器决定采用哪种加密算法
# 负载均衡
upstream api_upstream
{
server 127.0.0.1:8080 max_fails=3 weight=1;
server 127.0.0.1:8081 max_fails=3 weight=1;
}
#api 接口(兼容HTTP)
server{
listen 80;
server_name api.test.com;
# 301 重定向跳转到HTTPS 接口
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
#api 接口(兼容HTTPS)
server{
listen 443 ssl;
server_name api.test.com;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://api_upstream;
#语法: proxy_cookie_path oldpath replacepath;
#oldpath 就是你要替换的路径replacepath 就是要替换的值
#作用:同一个web 服务器下面多个应用之间能获取到cookie
proxy_cookie_path /api/ /;
#服务端接收的请求头Cooke 值不变
proxy_set_header Cookie $http_cookie;
}
}
#管理后台端(兼容HTTP)
server{
listen 80;
server_name manage.test.com;
# 301 重定向跳转到HTTPS 接口
return 301 https://$server_name/$request_uri;
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html{
root html
}
}
#管理后台端(兼容HTTPS)
server{
listen 443 ssl;
server_name manage.test.com;
location / {
root /home/test/web/dist
index /index.html;
#语法:try_files 【$uri】【$uri/】【参数】
#当用户请求https://manage.test.com/login 时,
#一.如果配置了上面的默认index,会依次请求
#1./home/test/web/dist/login 查找有没有login 这个文件,没有的话
#2./home/test/web/dist/index.html 有就直接返回
#二.如果没有配置了上面的默认index 或者配置了没有找到对应的资源,会依次请求
#1./home/test/web/dist/login 查找有没有login 这个文件,没有的话
#2./home/test/web/dist/login/ 查找有没有login 这个目录,没有的话
#3.请求https://manage.test.com/index.html nginx 内部做了一个子请求
#三.总的来说,index 的优先级比try_files 高,请求会先去找index 配置,这里最后一个参数必须存在
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
#解决跨域问题
#允许跨域请求地址(*表示全部,但是无法满足带cookie 请求,因为cookie 只能在当前域请求)
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin $http_origin;
#允许接收cookie 和发送cookie
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials 'true';
#允许请求的方法
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'GET,POST,DELETE,PUT,OPTIONS';
#允许请求头(Content-Type:请求数据/媒体类型x-requested-with:判断请求是异步还是同步自定义header 比如token)
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Headers $http_access_control_request_headers;
#浏览器缓存请求头信息,1800 秒内,只会有1 次请求,不会出现"OPTIONS"预请求,节约资源
#add_header Access-Control-Max-Age '1800';
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
return 204;
}
#服务端HttpServletRequest 可以获得用户的真实ip
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
#服务端HttpServletRequest 可以获得用户的真实ip 和经过的每一层代理服务器的ip
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
#服务端接收的请求头Host 值不变
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Nginx-Proxy true;
}
}
}
nginx.conf 讲解
一张图说明nginx.conf 结构
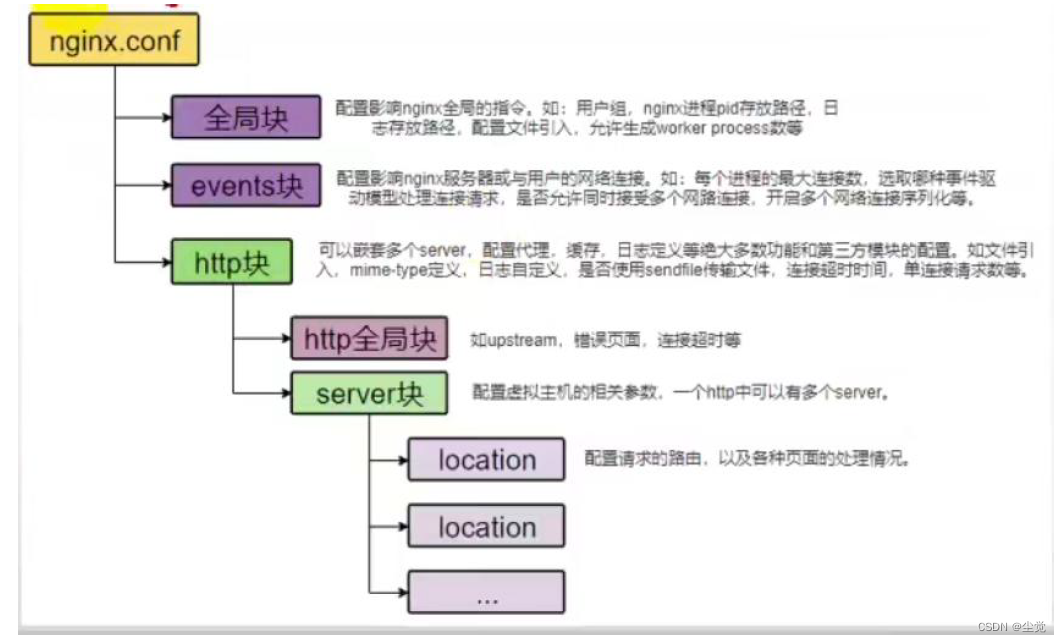
看一下/usr/local3/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
全局块
说明
- 从配置文件开始到events 块之间的内容
- 主要会设置一些影响nginx 服务器整体运行的配置指令,主要包括配置运行Nginx服务器的用户(组)、允许生成的worker process 数,进程PID 存放路径、日志存放路径和类型以及配置文件的引入等
简单分析
这是Nginx 服务器并发处理服务的关键配置,worker_processes 值越大,可以支持的并发处理量也越多,但是会受到硬件、软件等设备的制约
配置举例:
worker_processes 1;
events 块
说明
- events 块涉及的指令主要影响Nginx 服务器与用户的网络连接
- 常用的设置包括是否开启对多work process 下的网络连接进行序列化,是否允许同时接收多个网络连接,选取哪种事件驱动模型来处理连接请求,每个work process 可以同时支持的最大连接数等
简单分析
1、上述例子就表示每个work process 支持的最大连接数为1024, 这部分的配置对Nginx 的性能影响较大,在实际中应根据实际情况配置
配置举例
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http 块
说明
- 这是Nginx 服务器配置中最复杂的部分,代理、缓存和日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置都在这里
- http 块也可以包括http 全局块、server 块
http 全局块
http 全局块配置的指令包括文件引入、MIME-TYPE 定义、日志自定义、连接超时时间、单连接请求数上限等
配置举例:
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#开启文件传输
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
}
server 块
- 这块和虚拟主机有密切关系,虚拟主机从用户角度看,和一台独立的硬件主机是完全一样的,该技术的产生是为了节省互联网服务器硬件成本。
- 每个http 块可以包括多个server 块,而每个server 块就相当于一个虚拟主机。
- 每个server 块也分为全局server 块,以及可以同时包含多个location 块。
全局server 块
最常见的配置是本虚拟机主机的监听配置和本虚拟主机的名称或IP 配置
location 块
一个server 块可以配置多个location 块
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
4. 小结: 这块的主要作用是基于Nginx 服务器接收到的请求字符串( 例如server_name/uri-string),对虚拟主机名称(也可以是IP 别名) 之外的字符串(例如前面的/uri-string)进行匹配,对特定的请求进行处理。比如地址定向、数据缓存和应答控制等功能,还有许多第三方模块的配置也在这里进行。