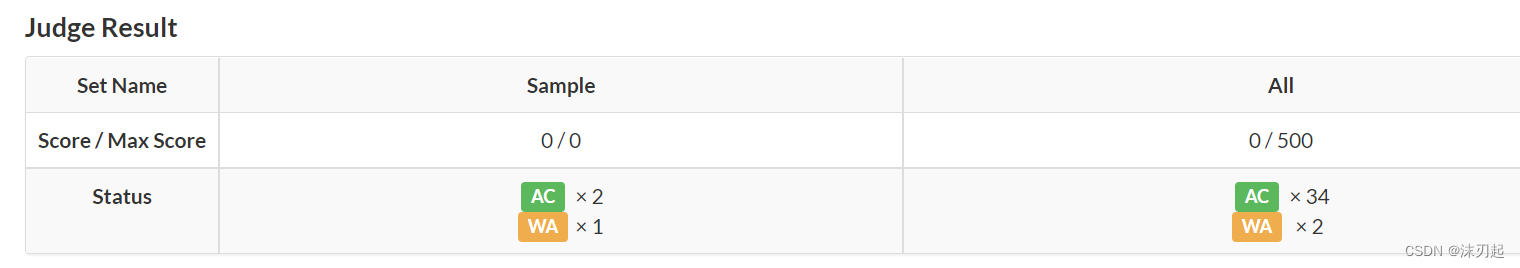
目录
一、前言
二、实践与代码
1.电亮LED1
2.熄灭LED1
3.翻转LED电平
4.LED1与LED2交替闪烁
5.LED1呼吸灯
三、程序代码
一、前言
本篇内容属于新大陆物联网Lora模块开发,使用给定的Lora基础例程,并在其基础上开发完成,并可为其他版本的Lora学习提供思路。
二、实践与代码
1.电亮LED1

2.熄灭LED1

3.翻转LED电平

4.LED1与LED2交替闪烁
在其为我们提供的led_light.c文件中,定义了关于闪烁的方法:
#define HELF_SECOND 50
uint16_t helfSecondCnt = 0;
bool isLed1Lighted = true;
bool isHelfSecondLedBlinkEnable = false;
void blinkPerHelfSecond() {
if (!isHelfSecondLedBlinkEnable)
return;
helfSecondCnt ++;
if (helfSecondCnt > HELF_SECOND) {
helfSecondCnt = 0;
isLed1Lighted = !isLed1Lighted;
}
if (isLed1Lighted) {
GpioWrite( &Led1, 0 );
GpioWrite( &Led2, 1 );
}
else {
GpioWrite( &Led1, 1 );
GpioWrite( &Led2, 0 );
}
}
void startLedBlink() {
isHelfSecondLedBlinkEnable = true;
GpioWrite( &Led1, 1 );
GpioWrite( &Led2, 1 );
}
void stopLedBlink() {
isHelfSecondLedBlinkEnable = false;
GpioWrite( &Led1, 1 );
GpioWrite( &Led2, 1 );
}
通过对上述的代码分析,我们可以得知,如果我们想开启闪烁,我们首先先需要调用startLedBlink()函数,随后我们需要在主函数中一直调用blinkPerHelfSecond(),即可实现闪烁效果。
由代码可知,当blinkPerHelfSecond()函数调用50次后,LED将会翻转电平,因此我们只需要控制调用的间隔时间,即可完成固定时间闪烁。

上述代码,通过每10ms调用一次blinkPerHelfSecond()函数,实现了每0.5s交替闪烁的效果。
5.LED1呼吸灯
同样是在led_light.c中,也定义了关于呼吸灯的方法:
#define LED_ILLUMINATION_LEVEL 8
#define LED_LEVEL_TIMER LED_ILLUMINATION_LEVEL/2
#define DEVIDE_VALUE 16
uint8_t levelCount = LED_ILLUMINATION_LEVEL;
uint8_t led_levet_timer = LED_LEVEL_TIMER;
uint8_t devideCount = DEVIDE_VALUE;
uint8_t level = 1;
uint8_t timeTic = 0;
bool isUprise = true;
bool isLed1BreathEnable = false;
bool isLed2BreathEnable = false;
void setBreathLedArg(uint8_t levelCnt, uint8_t levelUpDevide){
levelCount = levelCnt;
led_levet_timer = levelCount/2;
devideCount = levelUpDevide;
}
void resetLedPwm() {
timeTic = 0;
if (isLed1BreathEnable)
GpioWrite( &Led1, 0 );
if (isLed2BreathEnable)
GpioWrite( &Led2, 0 );
}
void pwmLevelUp() {
static unsigned long led_level_tick = 0;
led_level_tick++;
if (led_level_tick > led_levet_timer) {
led_level_tick = 0;
if (isUprise)
level++;
else
level--;
if (level > levelCount) {
level = levelCount;
isUprise = false;
} else if (level == 0) {
isUprise = true;
}
}
}
void pwm() {
timeTic++;
if (timeTic > level) {
if (isLed1BreathEnable)
GpioWrite( &Led1, 1 );
if (isLed2BreathEnable)
GpioWrite( &Led2, 1 );
}
if (timeTic > levelCount) {
resetLedPwm();
}
}
uint8_t timeDevice = 0;
void breathLed() {
timeDevice++;
if (timeDevice >= devideCount) {
timeDevice = 0;
pwmLevelUp();
}
pwm();
}
void switchLed1Breath() {
isLed1BreathEnable = !isLed1BreathEnable;
}
void switchLed2Breath() {
isLed2BreathEnable = !isLed2BreathEnable;
}
void startLedBreath() {
isLed1BreathEnable = true;
isLed2BreathEnable = true;
GpioWrite( &Led1, 1 );
GpioWrite( &Led2, 1 );
}
void stopLedBreath() {
isLed1BreathEnable = false;
isLed2BreathEnable = false;
GpioWrite( &Led1, 1 );
GpioWrite( &Led2, 1 );
}
根据上面代码,我们可知使用setBreathLedArg()函数进行初始化,其第一个参数为亮度的分级,建议为100,第二个为亮度等级变化的调用次数,推荐为50,随后使用startLedBreath()开启呼吸灯,然后只需要在主程序内一直调用breathLed()函数。switchLed1Breath函数可以与startLedBreath()用法相似,可以单独开启某个呼吸灯的呼吸标志位。

三、程序代码
/**
* Main application entry point.
*/
int main( void )//任务4
{
Init();
startLedBlink();
while( 1 )
{
HAL_Delay(10);
blinkPerHelfSecond();
}
}
int main( void )//任务5
{
Init();
setBreathLedArg(100,50);
switchLed1Breath();
while( 1 )
{
breathLed();
}
}