赋值运算符重载实例:Date类
文章目录
- 赋值运算符重载实例:Date类
- 一、构造日期类
- 二、获取某年某月天数以及检查合法
- 1.获取某年某月天数
- 2.检查日期合法
- 3.打印日期类
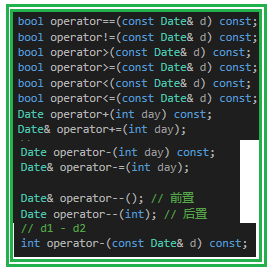
- 三、不同运算符的重载
- (1)== ; !=
- (2)> ; >= ; < ; <=
- (3)+ ; += ; - ; -=
- (4)前置++/-- ; 后置++/--
- (5)流插入重载;流提取重载
- 四、Date菜单
- (1)日期加/减天数
- (2)日期减日期
- (3)日期-》判断周几
- 五、总源码
- (1)Date.h
- (2)Date.cpp
- (3)Test.cpp
- 总结
一、构造日期类
构造会频繁调用,所以直接放在类里面定义作为inline
代码如下(示例):
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
/*if (!CheckDate())
{
Print();
cout << "刚构造的日期非法" << endl;
}*/
assert(CheckDate());
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
接下来我们要运算符重载以下运算符!
二、获取某年某月天数以及检查合法
1.获取某年某月天数
这里也会频繁调用,所以直接放在类里面定义作为inline,这里获取要判断闰年!
代码如下(示例):
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int days[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
int day = days[month];
if (month == 2
&& ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
day += 1;
}
return day;
}
2.检查日期合法
代码如下(示例):
bool CheckDate()
{
if (_year >= 1
&& _month > 0 && _month < 13
&& _day > 0 && _day <= GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
3.打印日期类
代码如下(示例):
void Date::Print() const
{
//_year = 1;
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
三、不同运算符的重载
(1)== ; !=
代码如下(示例):
bool Date::operator== (const Date& d) const
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
// d1 != d2
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this == d);
}
(2)> ; >= ; < ; <=
代码如下(示例):
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{
if ((_year > d._year)
|| (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)
|| (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{
return (*this > d) || (*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this > d);
}
(3)+ ; += ; - ; -=
在 += 或者 -=的时候要注意判断日期是否合法:例如day必须>0,年不能>12
代码如下(示例):
// d1 + 100
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{
//Date ret(*this);
Date ret = *this;
ret += day;
return ret;
}
// d2 += d1 += 100
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
// d1 - d2
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
int flag = 1;
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
(4)前置++/-- ; 后置++/–
注意:前置++/–是先++后使用,所以后置时要注意用拷贝构造函数进行拷贝;前置时可以用引用传参
代码如下(示例):
Date& Date::operator++() // 前置
{
//*this += 1;
//return *this;
return *this += 1;
}
Date Date::operator++(int) // 后置
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator--() // 前置
{
return *this -= 1;
}
Date Date::operator--(int) // 后置
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
(5)流插入重载;流提取重载
注意:这里可以使用友元函数—》内部可以使用Date对象访问私有保护成员
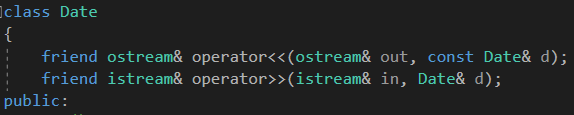
在流提取重载的时候,要注意检查类是否合法!
代码如下(示例):
// 流插入重载
inline ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
// 流提取重载
inline istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
assert(d.CheckDate());
return in;
}
四、Date菜单
代码如下(示例):
Date d1, d2;
int day = 0;
int option = 0;
(1)日期加/减天数
代码如下(示例):
if (option == 1)
{
cout << "请依次输入日期及天数(减天数就输入负数):";
cin >> d1 >> day;
cout << "日期加减天数后的日期:" << d1 + day << endl;
}
(2)日期减日期
代码如下(示例):
else if (option == 2)
{
cout << "请依次输入两个日期:";
cin >> d1 >> d2;
cout << "相差的天数:" << d1 - d2 << endl;
}
(3)日期-》判断周几
这里可以用数组来写明周一到周日,便于观察理解!
代码如下(示例):
else if (option == 3)
{
cout << "请输入日期:";
cin >> d1;
Date start(1, 1, 1);
int n = d1 - start;
int weekDay = 0; // 周一
weekDay += n;
//weekDay += 9;
//cout << "周" << weekDay % 7 + 1 << endl;
cout << WeeDayToStr[weekDay % 7] << endl;
}
五、总源码
(1)Date.h
代码如下(示例):
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
// 一个到底可以重载哪些运算符?-》哪些运算符对这个类型有意义
class Date
{
// 友元函数 -- 这个函数内部可以使用Date对象访问私有保护成员
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:
// 获取某年某月的天数
// 会频繁调用,所以直接放在类里面定义作为inline
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int days[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
int day = days[month];
if (month == 2
&& ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
day += 1;
}
return day;
}
bool CheckDate()
{
if (_year >= 1
&& _month > 0 && _month < 13
&& _day > 0 && _day <= GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// 构造会频繁调用,所以直接放在类里面定义作为inline
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
/*if (!CheckDate())
{
Print();
cout << "刚构造的日期非法" << endl;
}*/
assert(CheckDate());
}
void Print() const;
bool operator==(const Date& d) const;
bool operator!=(const Date& d) const;
bool operator>(const Date& d) const;
bool operator>=(const Date& d) const;
bool operator<(const Date& d) const;
bool operator<=(const Date& d) const;
Date operator+(int day) const;
Date& operator+=(int day);
// ++d1;
// d1++;
// 直接按特性重载,无法区分
// 特殊处理,使用重载区分,后置++重载增加一个int参数跟前置构成函数重载进行区分
Date& operator++(); // 前置
Date operator++(int); // 后置
// d1 - 100
Date operator-(int day) const;
Date& operator-=(int day);
Date& operator--(); // 前置
Date operator--(int); // 后置
// d1 - d2
int operator-(const Date& d) const;
//void operator<<(ostream& out);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 流插入重载
inline ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
// 流提取重载
inline istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
assert(d.CheckDate());
return in;
}
(2)Date.cpp
代码如下(示例):
#include "Date.h"
// const int* const ptr;
// void Date::Print(const Date* const this)
void Date::Print() const
{
//_year = 1;
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
// 任何一个类,只需要写一个> == 或者 < ==重载 剩下比较运算符重载复用即可
bool Date::operator== (const Date& d) const
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
// d1 != d2
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this == d);
}
// d1 > d2
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{
if ((_year > d._year)
|| (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)
|| (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{
return (*this > d) || (*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this > d);
}
// d1 + 100
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{
//Date ret(*this);
Date ret = *this;
ret += day;
return ret;
}
// d2 += d1 += 100
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
//Date Date::operator+(int day)
//{
// Date ret = *this;
// // ...
// ret._day += day;
// while (ret._day > GetMonthDay(ret._year, ret._month))
// {
// //...
// }
// return ret;
//}
d1 += 100
//Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
//{
// *this = *this + day;
// return *this;
//}
Date& Date::operator++() // 前置
{
//*this += 1;
//return *this;
return *this += 1;
}
Date Date::operator++(int) // 后置
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{
Date ret = *this;
ret -= day;
return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date& Date::operator--() // 前置
{
return *this -= 1;
}
Date Date::operator--(int) // 后置
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
// d1 - d2
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
int flag = 1;
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
//void Date::operator<<(ostream& out)
//{
// out << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
//}
(3)Test.cpp
代码如下(示例):
#include "Date.h"
//class A
//{
//public:
// A(int a = 0)
// {
// _a = a;
// cout << "A(int a = 0)->" <<_a<< endl;
// }
//
// ~A()
// {
// cout << "~A()->" <<_a<<endl;
// }
//private:
// int _a;
//};
//
//A aa3(3);
//
//void f()
//{
// static int i = 0;
// static A aa0(0);
// A aa1(1);
// A aa2(2);
// static A aa4(4);
//}
//
构造顺序:3 0 1 2 4 1 2
析构顺序:~2 ~1 ~2 ~1 ~4 ~0 ~3
//int main()
//{
// f();
// f();
//
// return 0;
//}
//class A
//{
//public:
// A(int a = 0)
// {
// _a = a;
// cout << "A(int a = 0)->" << _a << endl;
// }
//
// // A aa2(aa1);
// A(const A& aa)
// {
// _a = aa._a;
// cout << "A(const A& aa)->" << _a << endl;
// }
//
// ~A()
// {
// cout << "~A()->" << _a << endl;
// }
//private:
// int _a;
//};
//
//void func1(A aa)
//{
//
//}
//
//void func2(A& aa)
//{
//
//}
//
//A func3()
//{
// static A aa(3);
// return aa;
//}
//
//A& func4()
//{
// static A aa(4);
// return aa;
//}
//
//int main()
//{
// //A aa1(1);
// //A aa2(aa1);
//
// //func1(aa1);
// //func2(aa1);
// func3();
// cout << endl << endl;
// func4();
//
// //int i = 0;
// //int& j = i;
// //cout << typeid(j).name() << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}
//#pragma once
//
//class Time
//{
//public:
// Time()
// {
// _hour = 1;
// _minute = 1;
// _second = 1;
// }
//
// Time& operator=(const Time& t)
// {
// cout << "Time& operator=(const Time& t)" << endl;
// if (this != &t)
// {
// _hour = t._hour;
// _minute = t._minute;
// _second = t._second;
// }
//
// return *this;
// }
//private:
// int _hour;
// int _minute;
// int _second;
//};
//
//class Date
//{
//public:
// // 构造会频繁调用,所以直接放在类里面定义作为inline
// Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
// {
// _year = year;
// _month = month;
// _day = day;
// }
//
// Date(const Date& d)
// {
// cout << "Date(const Date& d)" << endl;
// _year = d._year;
// _month = d._month;
// _day = d._day;
// }
//
// // d1 = d3;
// // d2 = d2;
// //Date& operator=(const Date& d)
// Date operator=(const Date d)
// //{
// // if (this != &d)
// // {
// // _year = d._year;
// // _month = d._month;
// // _day = d._day;
// // }
//
// // return *this;
// //}
//
//private:
// int _year;
// int _month;
// int _day;
//
// // 自定义类型
// Time _t;
//};
//
休息11:17继续
//
这里会发现下面的程序会崩溃掉?这里就需要我们以后讲的深拷贝去解决。
//typedef int DataType;
//class Stack
//{
//public:
// Stack(size_t capacity = 10)
// {
// _array = (DataType*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(DataType));
// if (nullptr == _array)
// {
// perror("malloc申请空间失败");
// return;
// }
//
// _size = 0;
// _capacity = capacity;
// }
//
// void Push(const DataType& data)
// {
// // CheckCapacity();
// _array[_size] = data;
// _size++;
// }
//
// ~Stack()
// {
// if (_array)
// {
// free(_array);
// _array = nullptr;
// _capacity = 0;
// _size = 0;
// }
// }
//
//private:
// DataType *_array;
// size_t _size;
// size_t _capacity;
//};
//
躺赢 -- 构造、拷贝构造、赋值重载、析构默认生成都可以用
//class MyQueue
//{
//private:
// Stack _st1;
// Stack _st2;
//};
//
//void Test()
//{
// Date d1(2022, 7, 24);
// Date d2(d1);
//
// Date d3(2022, 8, 24);
// d2 = d1 = d3; // d1.operator=(&d1, d3)
// d2 = d2;
//
// Stack st1;
// Stack st2;
// st2.Push(1);
// st2.Push(2);
// st1 = st2; // 实现深拷贝赋值解决
//
// int i = 0, j = 1, k = 2;
// k = i = j = 10;
//}
void TestDate1()
{
Date d1(2022, 7, 24);
Date d2(2022, 7, 25);
Date d3(2021, 7, 25);
cout << (d1 < d2) << endl;
cout << (d1 < d3) << endl;
cout << (d1 == d3) << endl;
cout << (d1 > d3) << endl;
}
void TestDate2()
{
//Date d1(2022, 7, 24);
//d1 += 4;
//d1.Print();
//d1 += 40; // 跨月
//d1.Print();
//d1 += 400;// 跨年
//d1.Print();
//d1 += 4000; // 跨闰年
//d1.Print();
Date d1(2022, 7, 24);
/*Date d2 = d1 + 4;
d2.Print();*/
(d1 + 4).Print();
(d1 + 40).Print();// 跨月
(d1 + 400).Print();// 跨年
(d1 + 4000).Print(); // 跨闰年
(d1 + 40000).Print();
Date ret1 = ++d1; // d1.operator++(&d1)
Date ret2 = d1++; // d1.operator++(&d2, 0)
}
void TestDate3()
{
Date d1(2022, 7, 25);
(d1 - 4).Print();
(d1 - 40).Print();// 跨月
(d1 - 400).Print();// 跨年
(d1 - 4000).Print(); // 跨闰年
(d1 - 40000).Print();
Date d2(2022, 7, 25);
Date d3(2023, 2, 15);
cout << d2 - d3 << endl;
cout << d3 - d2 << endl;
Date d4(2000, 2, 15);
cout << d2 - d4 << endl;
cout << d4 - d2 << endl;
}
void TestDate4()
{
/*Date d1(2022, 7, 32);
d1.Print();
Date d2(2022, 2, 29);
d2.Print();
d2++;
d2.Print();*/
Date d1(2022, 7, 25);
Date d2(2022, 7, 26);
cout << d1 << d2;
cin >> d1 >> d2;
cout << d1 << d2;
//d1.operator<<(cout);
//d1 << cout;
//cout << (d1 + 100);
//(d1 + 100).Print();
//(d1 + -100).Print();
}
void TestDate5()
{
const char* WeeDayToStr[] = { "周一", "周二", "周三", "周四", "周五", "周六", "周天" };
Date d1, d2;
int day = 0;
int option = 0;
do {
cout << "*******************************" << endl;
cout << " 1、日期加/减天数 2、日期减日期" << endl;
cout << " 3、日期->周几 -1、退出" << endl;
cout << "*******************************" << endl;
cout << "请选择:>";
cin >> option;
if (option == 1)
{
cout << "请依次输入日期及天数(减天数就输入负数):";
cin >> d1 >> day;
cout << "日期加减天数后的日期:" << d1 + day << endl;
}
else if (option == 2)
{
cout << "请依次输入两个日期:";
cin >> d1 >> d2;
cout << "相差的天数:" << d1 - d2 << endl;
}
else if (option == 3)
{
cout << "请输入日期:";
cin >> d1;
Date start(1, 1, 1);
int n = d1 - start;
int weekDay = 0; // 周一
weekDay += n;
//weekDay += 9;
//cout << "周" << weekDay % 7 + 1 << endl;
cout << WeeDayToStr[weekDay % 7] << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "无此选项,请重新选择" << endl;
}
} while (option != -1);
}
void TestDate6()
{
Date d1(2022, 7, 25);
const Date d2(2022, 7, 25);
d1.Print();
d2.Print();
d1 < d2;
d2 < d1;
}
//int main()
//{
// //TestDate6();
//
// //int i = 0;
// //double d = 1.1;
// //cout << i; // cout.operator<<(i);
// //cout << d; // cout.operator<<(d);
//
// return 0;
//}
class A
{
public:
// 他们是默认成员函数,我们不写编译器会自动生成,自动生成就够用了,所以一般是不需要我们自己写的
// 特殊场景:不想让别人取到这个类型对象的地址
A* operator&()
{
return nullptr;
}
const A* operator&()const
{
return nullptr;
}
void Print() const
{
//_year = 1;
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
/*void Print()
{
_year = 1;
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}*/
private:
int _year; // 年
int _month; // 月
int _day; // 日
};
int main()
{
A d1;
const A d2;
d1.Print();
d2.Print();
cout << &d1 << endl;
cout << &d2 << endl;
return 0;
}
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文介绍赋值运算符重载这一章的实例:Date日期类,以及诸多运算符的重载。
如果我的作品对你有所帮助,记得点赞加关注,谢谢大家!