Pandas的groupby用法说明
1、功能说明
按官方文档说明groupby功能,可以参考与SQL中的分组操作进行理解。
By “group by” we are referring to a process involving one or more of the following steps:
- Splitting the data into groups based on some criteria.
- Applying a function to each group independently.
- Combining the results into a data structure.
主要三步: - 按条件数据分组
- 每个独立分组数据应用函数处理
- 结果合并到数据结构中
数据处理、使用:
Aggregation: 聚合,sum mean std max min var 等
Transformation:转换,可以标准化数据,处理空值
Filtration:过滤,基于分组函数过滤数据,如sum mean
下面先介绍分组,然后是聚合,转换和过滤
2、数据分组
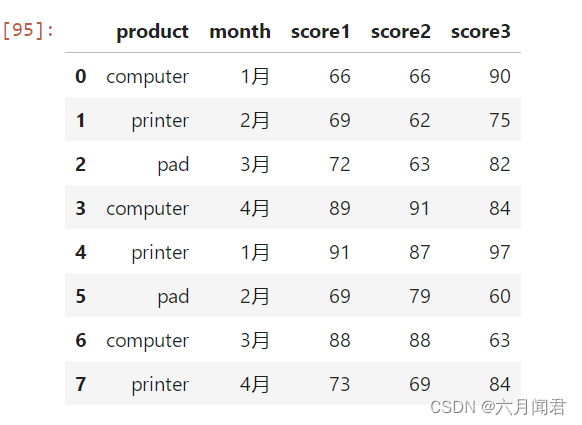
(1)数据准备
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
"product": ['computer','printer','pad','computer','printer','pad','computer','printer'],
"month": ['1月','2月','3月','4月','1月','2月','3月','4月'],
"score1": np.random.randint(60,100,8),
"score2": np.random.randint(60,100,8),
"score3": np.random.randint(60,100,8)
})
df
(2)分组
groupby首先要指定分组原则,groupby函数的第一步,其常用参数包括:
by,分组字段,可以是列名/series/字典/函数,常用为列名
- axis,指定切分方向,默认为0,表示沿着行切分
- as_index,是否将分组列名作为输出的索引,默认为True;当设置为False时相当于加了reset_index功能
- sort,与SQL中groupby操作会默认执行排序一致,该groupby也可通过sort参数指定是否对输出结果按索引排序
按 product 分组:
df.groupby('product',as_index=False)
注意 df.groupby(‘product’,as_index=False) 是一个分组对象,并非一个dataframe ,开始的时候有些不易理解。
总结:
groupby的过程就是将原有的DataFrame按照groupby的字段,划分为若干个分组子DataFrame,被分为多少个组就有多少个分组子DataFrame。
在groupby之后的一系列操作(如agg、apply等),均是基于子DataFrame的操作。
理解了这点,就基本理解Pandas中groupby对象操作的主要原理。
<pandas.core.groupby.generic.DataFrameGroupBy object at 0x7f6a16ccdfd0>
看一下分组对象内容
name group都可以随意命名,name对应分组列。
for name, group in df.groupby('product'):
print(name)
print(group)
运行结果,对理解分组对象就比较容易了:
computer
product month score1 score2 score3
0 computer 1月 66 66 90
3 computer 4月 89 91 84
6 computer 3月 88 88 63
pad
product month score1 score2 score3
2 pad 3月 72 63 82
5 pad 2月 69 79 60
printer
product month score1 score2 score3
1 printer 2月 69 62 75
4 printer 1月 91 87 97
7 printer 4月 73 69 84
(3)组合分组
按 product month 两列分组:
for name, group in df.groupby(['product','month']):
print(name)
print(group)
name 就是两个值分组,结果如下:
('computer', '1月')
product month score1 score2 score3
0 computer 1月 66 66 90
('computer', '3月')
product month score1 score2 score3
6 computer 3月 88 88 63
('computer', '4月')
product month score1 score2 score3
3 computer 4月 89 91 84
('pad', '2月')
product month score1 score2 score3
5 pad 2月 69 79 60
('pad', '3月')
product month score1 score2 score3
2 pad 3月 72 63 82
('printer', '1月')
product month score1 score2 score3
4 printer 1月 91 87 97
('printer', '2月')
product month score1 score2 score3
1 printer 2月 69 62 75
('printer', '4月')
product month score1 score2 score3
7 printer 4月 73 69 84
或者用list函数,显示一下groupby对象内容。
list(df.groupby(['product','month']))
(4)first tail nth
分组后的第一组分组数据
computer printer pad 第一次出现的数据:
df.groupby('product').first(1)

tail 和 last 就是最后一组分组数据。
tail包括所有列
df.groupby('product').tail(1)
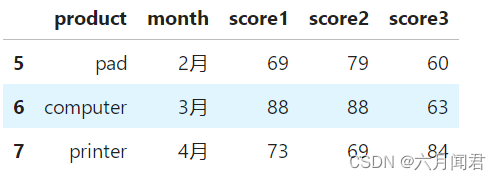
last只包括数据列。
df.groupby('product').last(1)
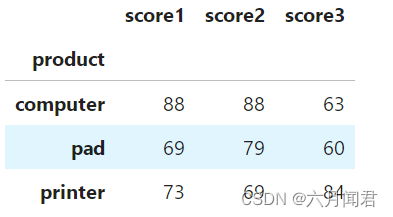
nth函数就是显示第N组分组数据,可以方便从分组的中间部分查询数据。
显示第3组分组数据,从0开始。本例就是最后一组分组数据,没有pad产品。
df.groupby('product').nth(2)
df.groupby('product').nth(1)
中间一组分组数据,效果如下:

3、聚合 Aggregation
(1)单列agg聚合
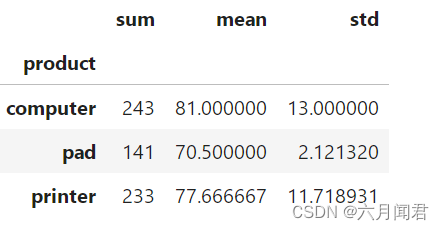
df.groupby('product')['score1'].agg([np.sum, np.mean, np.std])
score1的求和,均值和标准差,效果如下:
(2)多列聚合
df.groupby('product').agg({'score1':np.sum, 'score2':np.mean, 'score3':np.std})
效果如下:
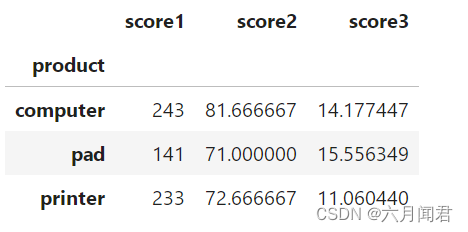
对应SQL 可以类比,更容易理解:
select sum(score1),mean(score2),std(score3) from df group by product ;
(3)多列多聚合计算
df.groupby('product').agg({'score1':[np.sum,np.max], 'score2':[np.mean,np.min], 'score3':[np.std,np.var]})
效果如下:

(4) apply
apply函数是一个应用非常广泛的转换函数,例如:面向series对象,apply函数的处理粒度是series的每个元素(标量);面向dataframe对象,apply函数的处理粒度是dataframe的一行或一列(series对象);而现在面向groupby后的group对象,其处理粒度则是一个分组(子dataframe对象)
例如:计算两列的均值差
df.groupby('product').apply(lambda x: x['score3'].mean()-x['score1'].mean())
结果如下:
product
computer -2.000000
pad 0.500000
printer 7.666667
dtype: float64
4、转换 Transformation
每一条数据求得相应的结果,同一组内的样本会有相同
的值,通过索引一一对应。
df.groupby('product')['score1'].transform('mean')
结果如下:
0 81.000000
1 77.666667
2 70.500000
3 81.000000
4 77.666667
5 70.500000
6 81.000000
7 77.666667
Name: score1, dtype: float64
通过transform直接将聚合运算结果增加一个新列 。score1的平均值,增加一个新列。
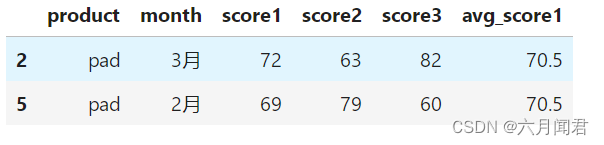
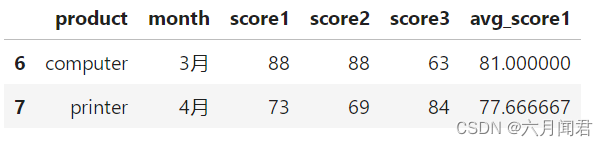
df['avg_score1'] = df.groupby('product')['score1'].transform('mean')
对应computer产品,都是同一个值,效果如下:

transform和agg所不一样的地方,对agg而言,会计算得到不同产品对应的均值并直接返回,但对transform而言,则会对每一条数据求得相应的结果,同一组内的样本会有相同的值,组内求完均值后会按照原索引的顺序返回结果 。
本例的索引就是01234567 。
5、过滤 Filtration
通过聚合函数进行条件筛选,类似SQL中的having 子句。
df.groupby('product').filter(lambda x: x['score1'].mean()>80)
效果如下:

df.groupby('product').filter(lambda x: x['score3'].mean()<75)
结果如下: