介绍
java.util中的工具类,提供数组相关的常用操作,排序、比较、填充、二分查找等功能
该类还包含一个静态内部类ArrayList,其中add、remove、clear方法都是没有实现的。
常量&变量
/**
* The minimum array length below which a parallel sorting
* algorithm will not further partition the sorting task. Using
* smaller sizes typically results in memory contention across
* tasks that makes parallel speedups unlikely.
* 并行排序的最小数组长度8192,数组长度小于这个数则不再划分数组
* 数组长度较小会导致排序的任务竞争内存导致效率降低
*/
private static final int MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN = 1 << 13;
/**
* Tuning parameter: list size at or below which insertion sort will be
* used in preference to mergesort.
* To be removed in a future release.
* 小于等于这个值时,使用插入排序优先于归并排序。在未来的版本将被废弃
*/
private static final int INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD = 7;
构造方法
// Suppresses default constructor, ensuring non-instantiability.
//私有构造函数,确保不会进行实例化
private Arrays() {}
内部类
NaturalOrder
/**
* A comparator that implements the natural ordering of a group of
* mutually comparable elements. May be used when a supplied
* comparator is null. To simplify code-sharing within underlying
* implementations, the compare method only declares type Object
* for its second argument.
*
* Arrays class implementor's note: It is an empirical matter
* whether ComparableTimSort offers any performance benefit over
* TimSort used with this comparator. If not, you are better off
* deleting or bypassing ComparableTimSort. There is currently no
* empirical case for separating them for parallel sorting, so all
* public Object parallelSort methods use the same comparator
* based implementation.
* 实现一组相互比较元素的自然排序的比较器。可在提供的比较器为空时使用。
*/
static final class NaturalOrder implements Comparator<Object> {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public int compare(Object first, Object second) {
return ((Comparable<Object>)first).compareTo(second);
}
static final NaturalOrder INSTANCE = new NaturalOrder();
}
LegacyMergeSort
/**
* Old merge sort implementation can be selected (for
* compatibility with broken comparators) using a system property.
* Cannot be a static boolean in the enclosing class due to
* circular dependencies. To be removed in a future release.
* 经典的归并排序,不过它即将被废弃了,只是用来兼容老的排序方法,
*/
static final class LegacyMergeSort {
private static final boolean userRequested =
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.security.action.GetBooleanAction(
"java.util.Arrays.useLegacyMergeSort")).booleanValue();
}
ArrayList
/**
* @serial include
*/
private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements RandomAccess, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2764017481108945198L;
private final E[] a;
ArrayList(E[] array) {
a = Objects.requireNonNull(array);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return a.length;
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
return a.clone();
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
int size = size();
if (a.length < size)
return Arrays.copyOf(this.a, size,
(Class<? extends T[]>) a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(this.a, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
@Override
public E get(int index) {
return a[index];
}
@Override
public E set(int index, E element) {
E oldValue = a[index];
a[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
@Override
public int indexOf(Object o) {
E[] a = this.a;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
if (a[i] == null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
if (o.equals(a[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (E e : a) {
action.accept(e);
}
}
@Override
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
E[] a = this.a;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = operator.apply(a[i]);
}
}
@Override
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
Arrays.sort(a, c);
}
}
常用方法
void rangeCheck(int arrayLength, int fromIndex, int toIndex)
/**
* Checks that {@code fromIndex} and {@code toIndex} are in
* the range and throws an exception if they aren't.
* 私有方法,检查是否越界,超出范围抛出异常
*/
private static void rangeCheck(int arrayLength, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(fromIndex);
}
if (toIndex > arrayLength) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(toIndex);
}
}
sort
对于int[]、byte[]、long[]等基本类型数组的排序,使用DualPivotQuicksort类进行排序,可选范围。
注意这个类改动了双轴快排的策略,使用了其他的排序方法,查看其源码可以知道还使用了计数排序、插入排序、归并排序。很多会导致其他版本快排退化到O(n^2)的数据集使用这个类仍能保证O(nlogn)
单轴快排和双轴快排
- 快排的思想是分治,方法是递归
- 单轴快排只有一个划分点,对点两侧的区间进行递归
- 双轴快排有两个划分点,将区间分为三段,效率会高一些
/**
* Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* 按照数字顺序排列指定的int数组。
*/
public static void sort(int[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the array into ascending order. The range
* to be sorted extends from the index {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, to
* the index {@code toIndex}, exclusive. If {@code fromIndex == toIndex},
* the range to be sorted is empty.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element, inclusive, to be sorted
* @param toIndex the index of the last element, exclusive, to be sorted
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromIndex > toIndex}
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code fromIndex < 0} or {@code toIndex > a.length}
* 按升序排列int数组的指定范围。
*/
public static void sort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* 按照数字顺序排列指定的long数组。
*/
public static void sort(long[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the array into ascending order. The range
* to be sorted extends from the index {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, to
* the index {@code toIndex}, exclusive. If {@code fromIndex == toIndex},
* the range to be sorted is empty.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element, inclusive, to be sorted
* @param toIndex the index of the last element, exclusive, to be sorted
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromIndex > toIndex}
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code fromIndex < 0} or {@code toIndex > a.length}
* 按升序排列long数组的指定范围。
*/
public static void sort(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* 按照数字顺序排列指定的short数组。
*/
public static void sort(short[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the array into ascending order. The range
* to be sorted extends from the index {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, to
* the index {@code toIndex}, exclusive. If {@code fromIndex == toIndex},
* the range to be sorted is empty.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element, inclusive, to be sorted
* @param toIndex the index of the last element, exclusive, to be sorted
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromIndex > toIndex}
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code fromIndex < 0} or {@code toIndex > a.length}
* 按升序排列short数组的指定范围。
*/
public static void sort(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* 按照数字顺序排列指定的char数组。
*/
public static void sort(char[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the array into ascending order. The range
* to be sorted extends from the index {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, to
* the index {@code toIndex}, exclusive. If {@code fromIndex == toIndex},
* the range to be sorted is empty.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element, inclusive, to be sorted
* @param toIndex the index of the last element, exclusive, to be sorted
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromIndex > toIndex}
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code fromIndex < 0} or {@code toIndex > a.length}
* 按升序排列char数组的指定范围。
*/
public static void sort(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* 按照数字顺序排列指定的byte数组。
*/
public static void sort(byte[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the array into ascending order. The range
* to be sorted extends from the index {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, to
* the index {@code toIndex}, exclusive. If {@code fromIndex == toIndex},
* the range to be sorted is empty.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element, inclusive, to be sorted
* @param toIndex the index of the last element, exclusive, to be sorted
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromIndex > toIndex}
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code fromIndex < 0} or {@code toIndex > a.length}
* 按升序排列byte数组的指定范围。
*/
public static void sort(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order.
*
* <p>The {@code <} relation does not provide a total order on all float
* values: {@code -0.0f == 0.0f} is {@code true} and a {@code Float.NaN}
* value compares neither less than, greater than, nor equal to any value,
* even itself. This method uses the total order imposed by the method
* {@link Float#compareTo}: {@code -0.0f} is treated as less than value
* {@code 0.0f} and {@code Float.NaN} is considered greater than any
* other value and all {@code Float.NaN} values are considered equal.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* 按升序排列float数组的指定范围。
*/
public static void sort(float[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the array into ascending order. The range
* to be sorted extends from the index {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, to
* the index {@code toIndex}, exclusive. If {@code fromIndex == toIndex},
* the range to be sorted is empty.
*
* <p>The {@code <} relation does not provide a total order on all float
* values: {@code -0.0f == 0.0f} is {@code true} and a {@code Float.NaN}
* value compares neither less than, greater than, nor equal to any value,
* even itself. This method uses the total order imposed by the method
* {@link Float#compareTo}: {@code -0.0f} is treated as less than value
* {@code 0.0f} and {@code Float.NaN} is considered greater than any
* other value and all {@code Float.NaN} values are considered equal.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element, inclusive, to be sorted
* @param toIndex the index of the last element, exclusive, to be sorted
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromIndex > toIndex}
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code fromIndex < 0} or {@code toIndex > a.length}
* 按升序排列float数组的指定范围。
*/
public static void sort(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order.
*
* <p>The {@code <} relation does not provide a total order on all double
* values: {@code -0.0d == 0.0d} is {@code true} and a {@code Double.NaN}
* value compares neither less than, greater than, nor equal to any value,
* even itself. This method uses the total order imposed by the method
* {@link Double#compareTo}: {@code -0.0d} is treated as less than value
* {@code 0.0d} and {@code Double.NaN} is considered greater than any
* other value and all {@code Double.NaN} values are considered equal.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* 按照数字顺序排列指定的double数组。
*/
public static void sort(double[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the array into ascending order. The range
* to be sorted extends from the index {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, to
* the index {@code toIndex}, exclusive. If {@code fromIndex == toIndex},
* the range to be sorted is empty.
*
* <p>The {@code <} relation does not provide a total order on all double
* values: {@code -0.0d == 0.0d} is {@code true} and a {@code Double.NaN}
* value compares neither less than, greater than, nor equal to any value,
* even itself. This method uses the total order imposed by the method
* {@link Double#compareTo}: {@code -0.0d} is treated as less than value
* {@code 0.0d} and {@code Double.NaN} is considered greater than any
* other value and all {@code Double.NaN} values are considered equal.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element, inclusive, to be sorted
* @param toIndex the index of the last element, exclusive, to be sorted
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromIndex > toIndex}
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code fromIndex < 0} or {@code toIndex > a.length}
* 按升序排列double数组的指定范围。
*/
public static void sort(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified array of objects into ascending order, according
* to the {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} of its elements.
* All elements in the array must implement the {@link Comparable}
* interface. Furthermore, all elements in the array must be
* <i>mutually comparable</i> (that is, {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must
* not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1}
* and {@code e2} in the array).
*
* <p>This sort is guaranteed to be <i>stable</i>: equal elements will
* not be reordered as a result of the sort.
*
* <p>Implementation note: This implementation is a stable, adaptive,
* iterative mergesort that requires far fewer than n lg(n) comparisons
* when the input array is partially sorted, while offering the
* performance of a traditional mergesort when the input array is
* randomly ordered. If the input array is nearly sorted, the
* implementation requires approximately n comparisons. Temporary
* storage requirements vary from a small constant for nearly sorted
* input arrays to n/2 object references for randomly ordered input
* arrays.
*
* <p>The implementation takes equal advantage of ascending and
* descending order in its input array, and can take advantage of
* ascending and descending order in different parts of the the same
* input array. It is well-suited to merging two or more sorted arrays:
* simply concatenate the arrays and sort the resulting array.
*
* <p>The implementation was adapted from Tim Peters's list sort for Python
* (<a href="http://svn.python.org/projects/python/trunk/Objects/listsort.txt">
* TimSort</a>). It uses techniques from Peter McIlroy's "Optimistic
* Sorting and Information Theoretic Complexity", in Proceedings of the
* Fourth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, pp 467-474,
* January 1993.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @throws ClassCastException if the array contains elements that are not
* <i>mutually comparable</i> (for example, strings and integers)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException (optional) if the natural
* ordering of the array elements is found to violate the
* {@link Comparable} contract
* 根据元素的自然顺序,将指定的对象数组按升序排序。
*/
public static void sort(Object[] a) {
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a);
else
ComparableTimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the specified array of objects into
* ascending order, according to the
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} of its
* elements. The range to be sorted extends from index
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, to index {@code toIndex}, exclusive.
* (If {@code fromIndex==toIndex}, the range to be sorted is empty.) All
* elements in this range must implement the {@link Comparable}
* interface. Furthermore, all elements in this range must be <i>mutually
* comparable</i> (that is, {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must not throw a
* {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and
* {@code e2} in the array).
*
* <p>This sort is guaranteed to be <i>stable</i>: equal elements will
* not be reordered as a result of the sort.
*
* <p>Implementation note: This implementation is a stable, adaptive,
* iterative mergesort that requires far fewer than n lg(n) comparisons
* when the input array is partially sorted, while offering the
* performance of a traditional mergesort when the input array is
* randomly ordered. If the input array is nearly sorted, the
* implementation requires approximately n comparisons. Temporary
* storage requirements vary from a small constant for nearly sorted
* input arrays to n/2 object references for randomly ordered input
* arrays.
*
* <p>The implementation takes equal advantage of ascending and
* descending order in its input array, and can take advantage of
* ascending and descending order in different parts of the the same
* input array. It is well-suited to merging two or more sorted arrays:
* simply concatenate the arrays and sort the resulting array.
*
* <p>The implementation was adapted from Tim Peters's list sort for Python
* (<a href="http://svn.python.org/projects/python/trunk/Objects/listsort.txt">
* TimSort</a>). It uses techniques from Peter McIlroy's "Optimistic
* Sorting and Information Theoretic Complexity", in Proceedings of the
* Fourth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, pp 467-474,
* January 1993.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element (inclusive) to be
* sorted
* @param toIndex the index of the last element (exclusive) to be sorted
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromIndex > toIndex} or
* (optional) if the natural ordering of the array elements is
* found to violate the {@link Comparable} contract
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex < 0} or
* {@code toIndex > a.length}
* @throws ClassCastException if the array contains elements that are
* not <i>mutually comparable</i> (for example, strings and
* integers).
* 对指定对象升序排列的数组的指定范围内,根据natural ordering的元素。
* 根据元素的自然顺序,将对象数组指定范围按升序排序。
*/
public static void sort(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
else
ComparableTimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, null, 0, 0);
}
/**
* Sorts the specified array of objects according to the order induced by
* the specified comparator. All elements in the array must be
* <i>mutually comparable</i> by the specified comparator (that is,
* {@code c.compare(e1, e2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException}
* for any elements {@code e1} and {@code e2} in the array).
*
* <p>This sort is guaranteed to be <i>stable</i>: equal elements will
* not be reordered as a result of the sort.
*
* <p>Implementation note: This implementation is a stable, adaptive,
* iterative mergesort that requires far fewer than n lg(n) comparisons
* when the input array is partially sorted, while offering the
* performance of a traditional mergesort when the input array is
* randomly ordered. If the input array is nearly sorted, the
* implementation requires approximately n comparisons. Temporary
* storage requirements vary from a small constant for nearly sorted
* input arrays to n/2 object references for randomly ordered input
* arrays.
*
* <p>The implementation takes equal advantage of ascending and
* descending order in its input array, and can take advantage of
* ascending and descending order in different parts of the the same
* input array. It is well-suited to merging two or more sorted arrays:
* simply concatenate the arrays and sort the resulting array.
*
* <p>The implementation was adapted from Tim Peters's list sort for Python
* (<a href="http://svn.python.org/projects/python/trunk/Objects/listsort.txt">
* TimSort</a>). It uses techniques from Peter McIlroy's "Optimistic
* Sorting and Information Theoretic Complexity", in Proceedings of the
* Fourth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, pp 467-474,
* January 1993.
*
* @param <T> the class of the objects to be sorted
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param c the comparator to determine the order of the array. A
* {@code null} value indicates that the elements'
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} should be used.
* @throws ClassCastException if the array contains elements that are
* not <i>mutually comparable</i> using the specified comparator
* @throws IllegalArgumentException (optional) if the comparator is
* found to violate the {@link Comparator} contract
* 根据指定的比较器对指定的对象数组进行排序。
*/
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
sort(a);
} else {
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, c);
else
TimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, c, null, 0, 0);
}
}
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the specified array of objects according
* to the order induced by the specified comparator. The range to be
* sorted extends from index {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, to index
* {@code toIndex}, exclusive. (If {@code fromIndex==toIndex}, the
* range to be sorted is empty.) All elements in the range must be
* <i>mutually comparable</i> by the specified comparator (that is,
* {@code c.compare(e1, e2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException}
* for any elements {@code e1} and {@code e2} in the range).
*
* <p>This sort is guaranteed to be <i>stable</i>: equal elements will
* not be reordered as a result of the sort.
*
* <p>Implementation note: This implementation is a stable, adaptive,
* iterative mergesort that requires far fewer than n lg(n) comparisons
* when the input array is partially sorted, while offering the
* performance of a traditional mergesort when the input array is
* randomly ordered. If the input array is nearly sorted, the
* implementation requires approximately n comparisons. Temporary
* storage requirements vary from a small constant for nearly sorted
* input arrays to n/2 object references for randomly ordered input
* arrays.
*
* <p>The implementation takes equal advantage of ascending and
* descending order in its input array, and can take advantage of
* ascending and descending order in different parts of the the same
* input array. It is well-suited to merging two or more sorted arrays:
* simply concatenate the arrays and sort the resulting array.
*
* <p>The implementation was adapted from Tim Peters's list sort for Python
* (<a href="http://svn.python.org/projects/python/trunk/Objects/listsort.txt">
* TimSort</a>). It uses techniques from Peter McIlroy's "Optimistic
* Sorting and Information Theoretic Complexity", in Proceedings of the
* Fourth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, pp 467-474,
* January 1993.
*
* @param <T> the class of the objects to be sorted
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element (inclusive) to be
* sorted
* @param toIndex the index of the last element (exclusive) to be sorted
* @param c the comparator to determine the order of the array. A
* {@code null} value indicates that the elements'
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} should be used.
* @throws ClassCastException if the array contains elements that are not
* <i>mutually comparable</i> using the specified comparator.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromIndex > toIndex} or
* (optional) if the comparator is found to violate the
* {@link Comparator} contract
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex < 0} or
* {@code toIndex > a.length}
* 根据指定的比较器对指定的对象数组的指定范围进行排序。
*/
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
} else {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c);
else
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c, null, 0, 0);
}
}
mergeSort
Arrays 在对 Object 数组进行排序是会使用到 legacyMergeSort 和 ComparableTimSort.sort,其中 legacyMergeSort 调用的就是 mergeSort 方法
/**
* Src is the source array that starts at index 0
* Dest is the (possibly larger) array destination with a possible offset
* low is the index in dest to start sorting
* high is the end index in dest to end sorting
* off is the offset to generate corresponding low, high in src
* To be removed in a future release.
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})mergeSort
private static void mergeSort(Object[] src,
Object[] dest,
int low,
int high,
int off) {
int length = high - low;
// Insertion sort on smallest arrays
//需要排序的长度小于7 使用插入排序
if (length < INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD) {
for (int i=low; i<high; i++)
//倒序遍历
for (int j=i; j>low &&
//左侧的值比遍历到的值大,交换位置
((Comparable) dest[j-1]).compareTo(dest[j])>0; j--)
swap(dest, j, j-1);
return;
}
// Recursively sort halves of dest into src
int destLow = low;
int destHigh = high;
low += off;
high += off;
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
//将数组分成两部分进行排序
mergeSort(dest, src, low, mid, -off);
mergeSort(dest, src, mid, high, -off);
// If list is already sorted, just copy from src to dest. This is an
// optimization that results in faster sorts for nearly ordered lists.
//两个数组排完序,如果左侧数组的最大值小于右侧数组的最小值,说明整体有序
if (((Comparable)src[mid-1]).compareTo(src[mid]) <= 0) {
//拷贝
System.arraycopy(src, low, dest, destLow, length);
return;
}
// Merge sorted halves (now in src) into dest
//否则进行归并排序
for(int i = destLow, p = low, q = mid; i < destHigh; i++) {
if (q >= high || p < mid && ((Comparable)src[p]).compareTo(src[q])<=0)
dest[i] = src[p++];
else
dest[i] = src[q++];
}
}
parallelSort
对基本类型的并行排序,以int[]为例。提供范围排序
/**
* Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order.
*
* @implNote The sorting algorithm is a parallel sort-merge that breaks the
* array into sub-arrays that are themselves sorted and then merged. When
* the sub-array length reaches a minimum granularity, the sub-array is
* sorted using the appropriate {@link Arrays#sort(int[]) Arrays.sort}
* method. If the length of the specified array is less than the minimum
* granularity, then it is sorted using the appropriate {@link
* Arrays#sort(int[]) Arrays.sort} method. The algorithm requires a
* working space no greater than the size of the original array. The
* {@link ForkJoinPool#commonPool() ForkJoin common pool} is used to
* execute any parallel tasks.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
*
* @since 1.8
* 这个排序算法是个将数组划分为几个子数组分别排序然后合并的并行排序-合并过程。
* 当子数组长度达到最小粒度,或者数组小于设定的最小粒度,
* 使用类似Arrays.sort()的方法(DualPivotQuickSort)来进行排序。
* 这个算法需要一个不大于原数组大小的额外空间,使用ForkJoin common pool
* ForkJoinPool#commonPool())来执行并行的排序任务
*/
public static void parallelSort(int[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
//如果数组长度小于分组的最小粒度或者只有一个执行线程,使用DualPivotQuicksort
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
//g表示粒度,参数4、5、6分别为排序数组开始位置,需要排序的长度和额外空间的开始位置
//g = n / (p << 2)不可小于最小粒度,否则使用最小粒度
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJInt.Sorter
(null, a, new int[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
equals
以int为例
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if the two specified arrays of ints are
* <i>equal</i> to one another. Two arrays are considered equal if both
* arrays contain the same number of elements, and all corresponding pairs
* of elements in the two arrays are equal. In other words, two arrays
* are equal if they contain the same elements in the same order. Also,
* two array references are considered equal if both are <tt>null</tt>.<p>
*
* @param a one array to be tested for equality
* @param a2 the other array to be tested for equality
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the two arrays are equal
*/
public static boolean equals(int[] a, int[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
//存在null,则false
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
//依次比较
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
deepEquals
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if the two specified arrays are <i>deeply
* equal</i> to one another. Unlike the {@link #equals(Object[],Object[])}
* method, this method is appropriate for use with nested arrays of
* arbitrary depth.
*
* <p>Two array references are considered deeply equal if both
* are <tt>null</tt>, or if they refer to arrays that contain the same
* number of elements and all corresponding pairs of elements in the two
* arrays are deeply equal.
*
* <p>Two possibly <tt>null</tt> elements <tt>e1</tt> and <tt>e2</tt> are
* deeply equal if any of the following conditions hold:
* <ul>
* <li> <tt>e1</tt> and <tt>e2</tt> are both arrays of object reference
* types, and <tt>Arrays.deepEquals(e1, e2) would return true</tt>
* <li> <tt>e1</tt> and <tt>e2</tt> are arrays of the same primitive
* type, and the appropriate overloading of
* <tt>Arrays.equals(e1, e2)</tt> would return true.
* <li> <tt>e1 == e2</tt>
* <li> <tt>e1.equals(e2)</tt> would return true.
* </ul>
* Note that this definition permits <tt>null</tt> elements at any depth.
*
* <p>If either of the specified arrays contain themselves as elements
* either directly or indirectly through one or more levels of arrays,
* the behavior of this method is undefined.
*
* @param a1 one array to be tested for equality
* @param a2 the other array to be tested for equality
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the two arrays are equal
* @see #equals(Object[],Object[])
* @see Objects#deepEquals(Object, Object)
* @since 1.5
* 深入比较,即比较多维数组。deepHashcode和deepToString也是如此。
*/
public static boolean deepEquals(Object[] a1, Object[] a2) {
if (a1 == a2)
return true;
if (a1 == null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a1.length;
//长度不同直接false
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Object e1 = a1[i];
Object e2 = a2[i];
if (e1 == e2)
continue;
if (e1 == null)
return false;
// Figure out whether the two elements are equal
//递归比较,记录是否相等
boolean eq = deepEquals0(e1, e2);
if (!eq)
return false;
}
return true;
}
asList
返回固定大小的ArrayList,这个是Arrays内部类,注意在使用时和java.util.ArrayList的区别。这个方法和Collection.toArray方法充当了数组和集合的桥梁
/**
* Returns a fixed-size list backed by the specified array. (Changes to
* the returned list "write through" to the array.) This method acts
* as bridge between array-based and collection-based APIs, in
* combination with {@link Collection#toArray}. The returned list is
* serializable and implements {@link RandomAccess}.
*
* <p>This method also provides a convenient way to create a fixed-size
* list initialized to contain several elements:
* <pre>
* List<String> stooges = Arrays.asList("Larry", "Moe", "Curly");
* </pre>
*
* @param <T> the class of the objects in the array
* @param a the array by which the list will be backed
* @return a list view of the specified array
*/
@SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("varargs")
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}
binarySearch
二分查找,显然数组必须是有序的,否则结果不确定了。如果数组里面有多个相同的,不能保证找到哪一个
以int为例
/**
* Searches the specified array of ints for the specified value using the
* binary search algorithm. The array must be sorted (as
* by the {@link #sort(int[])} method) prior to making this call. If it
* is not sorted, the results are undefined. If the array contains
* multiple elements with the specified value, there is no guarantee which
* one will be found.
*
* @param a the array to be searched
* @param key the value to be searched for
* @return index of the search key, if it is contained in the array;
* otherwise, <tt>(-(<i>insertion point</i>) - 1)</tt>. The
* <i>insertion point</i> is defined as the point at which the
* key would be inserted into the array: the index of the first
* element greater than the key, or <tt>a.length</tt> if all
* elements in the array are less than the specified key. Note
* that this guarantees that the return value will be >= 0 if
* and only if the key is found.
*/
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) {
//调用私有方法
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
/**
* Searches a range of
* the specified array of ints for the specified value using the
* binary search algorithm.
* The range must be sorted (as
* by the {@link #sort(int[], int, int)} method)
* prior to making this call. If it
* is not sorted, the results are undefined. If the range contains
* multiple elements with the specified value, there is no guarantee which
* one will be found.
*
* @param a the array to be searched
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element (inclusive) to be
* searched
* @param toIndex the index of the last element (exclusive) to be searched
* @param key the value to be searched for
* @return index of the search key, if it is contained in the array
* within the specified range;
* otherwise, <tt>(-(<i>insertion point</i>) - 1)</tt>. The
* <i>insertion point</i> is defined as the point at which the
* key would be inserted into the array: the index of the first
* element in the range greater than the key,
* or <tt>toIndex</tt> if all
* elements in the range are less than the specified key. Note
* that this guarantees that the return value will be >= 0 if
* and only if the key is found.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if {@code fromIndex > toIndex}
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code fromIndex < 0 or toIndex > a.length}
* @since 1.6
*/
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
我们可以看到到最后都会调用binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key)方法。
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
// 定义数组开始位置
int low = fromIndex;
// 定义数组结束位置
int high = toIndex - 1;
// 开始位置 <= 结束位置
while (low <= high) {
// 数组mid位置值
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
//下标mid位置的值
int midVal = a[mid];
//小于搜索的值
if (midVal < key)
//二分 查找后面的部分
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
//二分 查找前面的部分
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found 找到了
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found. 没找着,保证为负
}
当出现重复元素时会取哪个下标
从源码可分析出查找的过程:
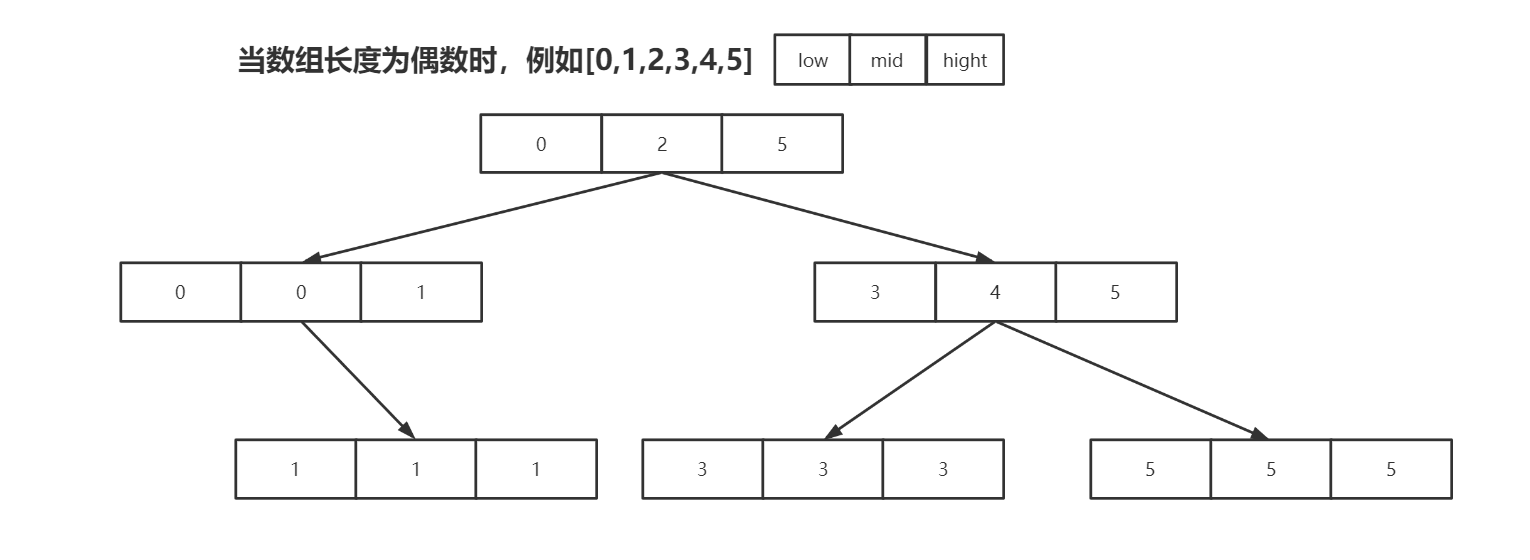
第一次循环:[0,1,2,3,4,5]二分为[0,1],[3.4.5] mid为2
第二次循环:[0,1] 二分为[0],[1] mid为 0 [3,4,5]二分为[3] ,[5] ,mid为4 此时搜索0或4,直接返回
第三次循环:剩下[1],[3],[5],此时搜索1,3或5,直接返回
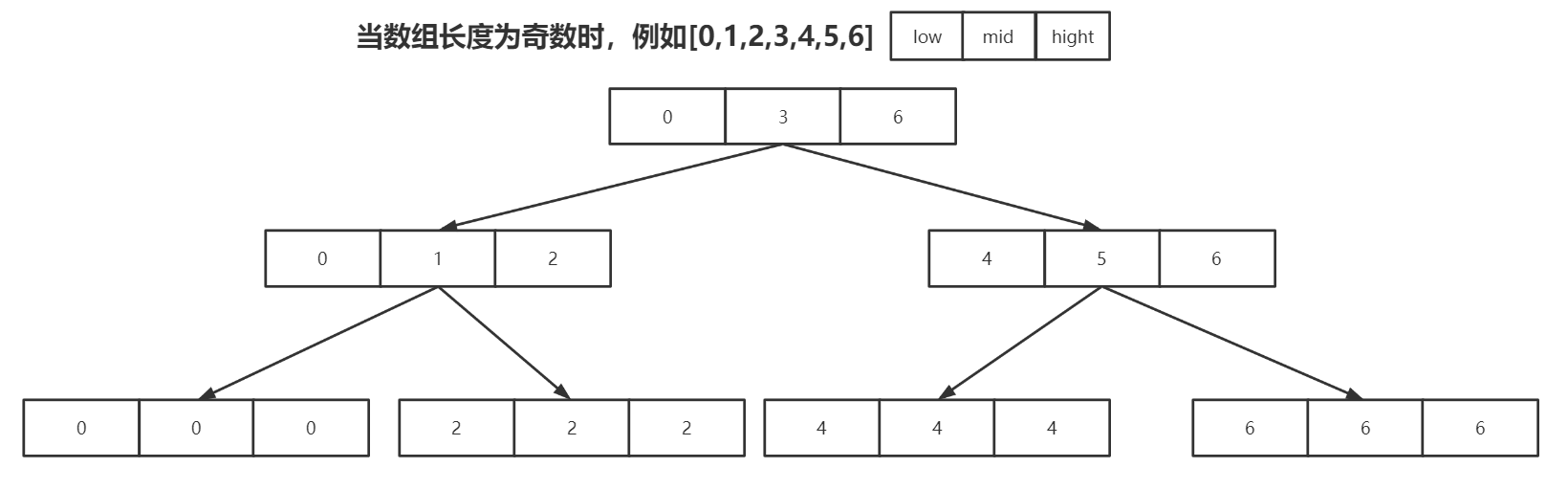
那么,如果出现重复元素时
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println("当前数组长度为奇数时:");
int[] sort = new int[]{10,10,30,40,50,60,70};
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,10);
System.out.println("10的下标为:"+index);
sort = new int[]{10,20,20,40,50,60,70};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,20);
System.out.println("20的下标为:"+index);
sort = new int[]{10,20,30,30,50,60,70};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,30);
System.out.println("30的下标为:"+index);
sort = new int[]{10,20,30,40,40,60,70};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,40);
System.out.println("40的下标为:"+index);
sort = new int[]{10,20,30,40,50,50,70};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,50);
System.out.println("50的下标为:"+index);
sort = new int[]{10,20,30,40,40,60,60};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,60);
System.out.println("60的下标为:"+index);
System.out.println("--------------");
System.out.println("当前数组长度为偶数时:");
sort = new int[]{10,10,30,40,50,60};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,10);
System.out.println("10的下标为:"+index);
sort = new int[]{10,20,20,40,50,60};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,20);
System.out.println("20的下标为:"+index);
sort = new int[]{10,20,30,30,50,60};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,30);
System.out.println("30的下标为:"+index);
sort = new int[]{10,20,30,40,40,60};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,40);
System.out.println("40的下标为:"+index);
sort = new int[]{10,20,30,40,50,50};
index = Arrays.binarySearch(sort,50);
System.out.println("50的下标为:"+index);
}
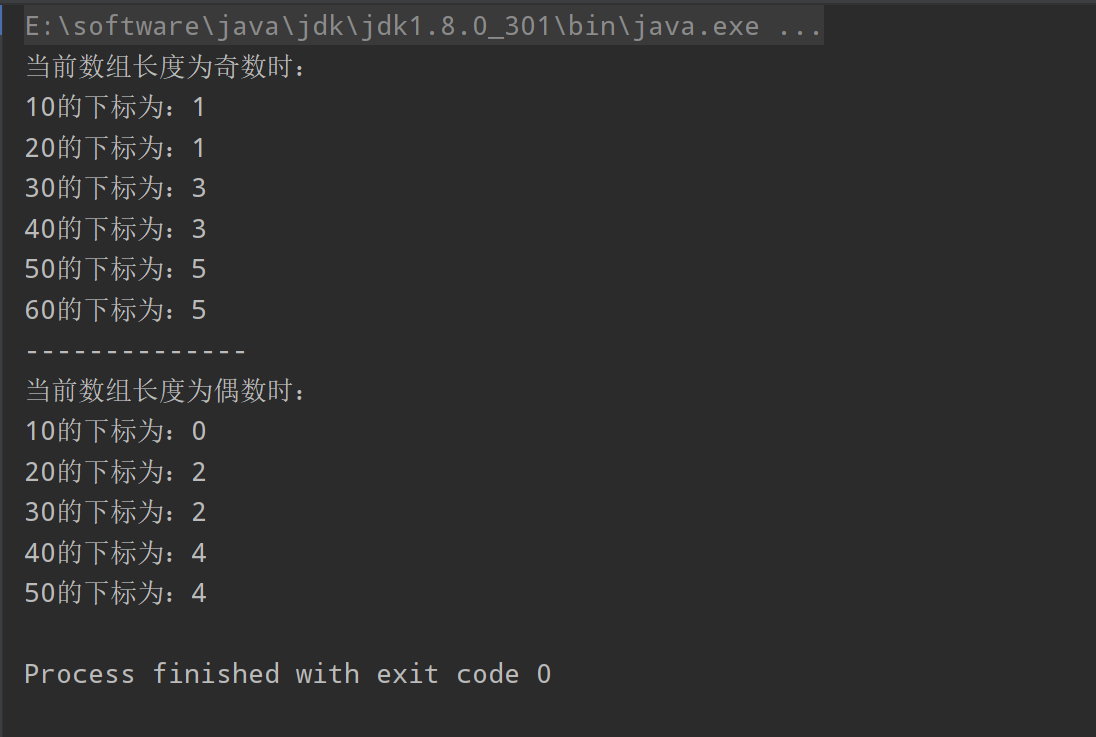
现在我们可以得出结论,
- 当数组长度为奇数时,数组中有重复元素,Arrays.binarySearch()会优先返回奇数且靠近当前区间中间的下标
- 当数组长度为偶数时,数组中有重复元素,Arrays.binarySearch()会优先返回偶数且靠近当前区间中间的下标