前言
关于流本质的问题,其实从我刚开始学习C++的时候,就已经存在了。当时找了不少的资料,不过一直处于那种知其然而不知其所以然的状态,关于流的本质问题我还是一直没有搞通,始终就是懵懵懂懂的。
不过在今天,我在一时兴起又在查阅流相关资料的时候,突然发现我貌似能够理解了它,因此用此篇博客来记录一下。
有一点需要事先声明一下,以下的内容,皆是我自己的理解,由于个人知识积累及阅历的原因,可能会存在一些不足,如果发现有错误,还请读者予以斧正。
流的理解
流的本质是一种对象。
流是介于数据和程序之间的一个中转设备。
因为流的存在,使得我们可以不需要直接操作数据,而是通过操作流的方式间接对数据进行操作。
流的优势
统一操作标准。
无论对于何种数据,以及数据的类型如何,只要将这个数据和流关联起来,那么我们就可以不用考虑数据到底是如何存储的,只需要按照流的操作标准来进行操作即可,这就是统一了操作标准。
上面说到,流的本质是一个对象,因此对于流而言,存在着许多的方法,这些方法为我们操作数据提供了统一的接口,对我们甚至可以做到在不更改代码的前提下,操作不同的数据。
C++中流的分类
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-0KxVaOJC-1686041257286)(C:\Users\hp\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230417223450379.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d3b4e058e1e546769bbdcb2bf5e3db00.png)
C++中流主要分为三类:
- IO流: 输入输出流,iostream
- 文件流: 对于文件的操作,fstream
- 字符串流: 主要实现对于字符串的操作,stringstream
IO流
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6YJmhysV-1686041257287)(C:\Users\hp\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230417223559721.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fc818bfffd2345eb8402c94daf2e8120.png)
这三者在本质上还是一样的,都是抽象出方法,只不过操作的对象不同罢了。以下贴出这几个类之间的关系图:

由上图可见,为什么说可以像使用cin/cout的方式去使用fstream,因为fstream本身是继承自iostream的。
字符串流sstream
基本概念
用内存中的string类型变量作为输入和输出的对象.。
特点:
- 与标准输入输出流相同,能够进行文本与二进制之间的相互转换。
- 向string存数据⇔ \Leftrightarrow⇔cout 二进制转为ASCII。
- 从string取数据⇔ \Leftrightarrow⇔cin ASCII转为二进制。
- 无需打开关闭。
- 能够存放各种类型数据。
使用
#include <sstream>
ostringstream ostr;//输出流
istringstream istr;//输入流
stringstream str;//输入/输出流
sstring头文件定义了三个类型来支持内存IO操作,这些类型可以向string写入数据,从string读取数据,就像string是一个IO流一样。
istringstream从string读取数据,ostringstream向string写入数据,stringstream既可以向string写入数据也可以向string读取数据。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-u0qXk7ik-1686041257289)(C:\Users\hp\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230417221021687.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7a3e9f1c990e46e79ed3b7777be2b1bf.png)
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
class Stream {
public:
Stream() {}
Stream(std::string& str)
:str_(str)
{}
~Stream() {};
//输出流
void OsStringStream();
//输入流
void IsStringStream();
//输入输出流
void StringStringStream();
protected:
std::string str_;
};
#include"stream.h"
void Stream::OsStringStream() {
std::ostringstream oss(str_);
std::cout << oss.str() << std::endl;
}
void Stream::IsStringStream() {
std::string line;
std::istringstream iss(str_);
std::getline(iss, line);
std::cout << line << std::endl;
//创建输入流
std::istringstream str;
//拷贝字符串到输入流中
str.str("bye bye");
//用str_str返回str.str()的拷贝
std::string str_str = str.str();
std::cout << str_str << std::endl;
}
void Stream::StringStringStream() {
std::stringstream ss1(str_);
std::cout << ss1.str() << std::endl;
}
#include"stream.h"
int main() {
std::string str("ni hao");
Stream stream(str);
stream.IsStringStream();
stream.OsStringStream();
stream.StringStringStream();
return 0;
}
文件流fstream

程序运行时,产生的数据都属于临时数据,程序一旦运行结束都会被释放,通过文件可以将数据持久化,C++对文件操作需要包含头文件 < f s t r e a m > 。文本类型分为两种:
(1)文本文件:文件以文本的ASCII码的形式存储在计算机中。
(2)二进制文件:文件以文本的二进制形式存储在计算机中,用户一般不能直接读懂他们。
操作文件三大类:
-
ofstream:写
-
ifstream:读
-
fstream:读写
文本文件
写文件
步骤如下:
- 包含头文件:#include< fstream>
- 创建流对象:ofstream ofs;
- 打开文件:ofs.open(“文件路径”,打开方式);
- 写数据:ofs<<“写入的数据”;
- 关闭文件:ofs.close();
打开方式:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-yhqK8uDz-1686041257289)(C:\Users\hp\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230417223237070.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0b1e126df80145dfa33f5bec6ef35674.png)
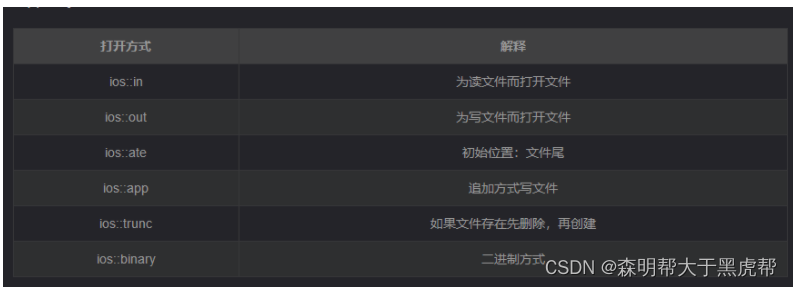
注:文件打开方式可以配合使用,利用|操作符。
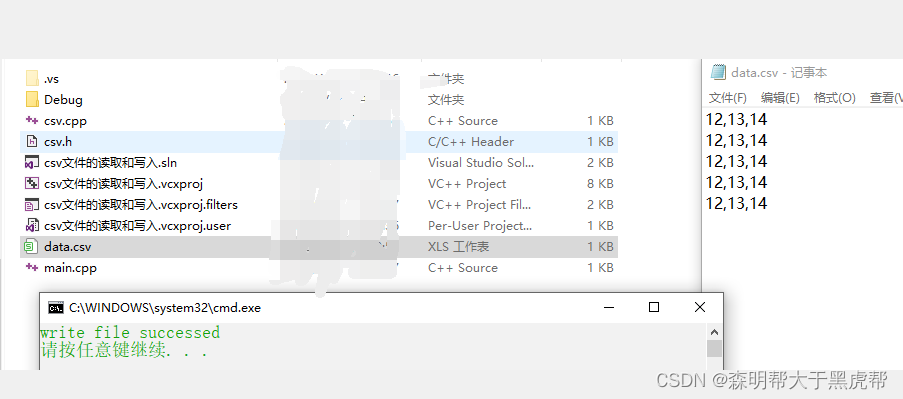
void Csv::WriteCsvFile() {
//std::ofstream out_file("data.csv", std::ios::out); //std::ios::out 文件不存在则创建文件,有文件则清空文件
std::ofstream out_file;
out_file.open("data.csv", std::ios::out);
if (!out_file) {
std::cout << "open file failed" << std::endl;
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
out_file << 12 << ",";
out_file << 13 << ",";
out_file << 14 << std::endl;
}
out_file.close();
std::cout << "write file successed" << std::endl;
}
读文件
步骤如下:
- 包含头文件:#include< fstream>
- 创建流对象:ifstream ifs;
- 打开文件,并判断文件是否打开成功:ifs.open(“文件路径”,打开方式);
- 读数据:四种读取方式
- 关闭文件:ifs.close();

#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
class Csv {
public:
Csv() {}
~Csv() {}
void ReadCsvFile();
void WriteCsvFile();
};
#include"csv.h"
void Csv::ReadCsvFile() {
//std::ifstream in_file("data.csv", std::ios::in);
std::ifstream in_file;
in_file.open("data.csv", std::ios::in);
if (!in_file) {
std::cout << "open fill failed" << std::endl;
}
int num = 0;
std::string line;
std::string file;
while (std::getline(in_file, line)) {
std::string file;
// 将整行字符串line读入到字符串流iss中
std::istringstream iss(line);
std::getline(iss, file, ',');
//将刚刚读取的字符串转换成int
std::cout << std::atoi(file.c_str()) << " ";
std::getline(iss, file, ',');
std::cout << std::atoi(file.c_str()) << " ";
std::getline(iss, file, ',');
std::cout << std::atoi(file.c_str()) << std::endl;
num++;
}
std::cout << "读取了" << num << "行" << std::endl;
if (5 == num) {
std::cout << "read file success" << std::endl;
}
in_file.close();
}
void Csv::WriteCsvFile() {
//std::ofstream out_file("data.csv", std::ios::out);
std::ofstream out_file;
out_file.open("data.csv", std::ios::out);
if (!out_file) {
std::cout << "open file failed" << std::endl;
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
out_file << 12 << ",";
out_file << 13 << ",";
out_file << 14 << std::endl;
}
out_file.close();
std::cout << "write file successed" << std::endl;
}
#include"csv.h"
int main() {
Csv csv;
csv.WriteCsvFile();
csv.ReadCsvFile();
return 0;
}
每个文件流都有一个默认的文件模式,ifstream关联的文件默认以in模式打开,ofstream关联的文件默认以out模式打开,fstream关联的文件默认以in和out模式打开。
ofstream out; // 未指定文件打开模式
out.open("test.txt"); // 模式隐含设置为输出和截断
out.close(); // 关闭out
out.open("test2.txt",ofstream::app); //模式为输出和追加
out.close(); //关闭out