1. 无向图的联通分量个数

1.1 联通分量个数
无向图的联通分量个数是指图中无法通过边连接到其他分量的顶点集合的个数。可以通过深度优先搜索或广度优先搜索来计算无向图的联通分量个数。
1.2 记录联通分量
(1)多个联通量的数:
7 6
0 1
0 2
1 3
1 4
2 3
2 6
5
(2)查询联通分量个数代码
public class CC {
private Graph G; // 顶点数
private boolean [] visited; // 边数
private int cccount = 0; // 联通分量个数
public CC(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++ ){
if (!visited[v]){
dfs(v);
cccount++;
}
}
}
private void dfs(int v){
visited[v] = true;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!visited[w]) {
dfs(w);
}
}
}
public int count(){
return cccount;
}
}
结果:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph("cc.txt");
CC cc = new CC(graph);
System.out.println(cc.count());
}
执行结果:
2
Process finished with exit code 0在CC类中,私有成员变量G表示图对象,visited表示顶点访问标记数组,cccount表示联通分量个数。在dfs方法中的递归过程中,会一直深入到无法再继续深入为止,然后回溯到上一层顶点,继续搜索其他未访问过的顶点。每次完成dfs(v)的递归调用后,联通分量个数cccount加1,表示找到了一个新的联通分量。
1.3 记录每个顶点所属联通分量
将boolean[] visited改为int[] visited,并使用visited数组来记录每个顶点所属的联通分量ID,进行如下修改:
- 在构造函数CC中,将
visited数组的类型修改为int[],并初始化数组元素为-1,表示尚未分配联通分量ID。 - 在dfs方法中,将
visited[v]设置为cccount,表示顶点v属于当前联通分量ID。 - 在count方法中,返回
cccount。 - 添加一个新的方法
getComponentID(int v),用于获取顶点v所属的联通分量ID。
/**CC类用于计算无向图的联通分量个数。
* @author wushaopei
* @create 2023-06-03 21:49
*/
public class CC_INT {
private Graph G; // 顶点数
private int [] visited; // 边数
private int cccount = 0; // 联通分量个数
public CC_INT(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new int[G.V()]; // 初始化顶点访问标记数组,默认为false
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++){
visited[i] = -1;
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++ ){
if (visited[v] == -1){
dfs(v, cccount);
cccount++; // 搜索完成后,联通分量个数加1
}
}
}
private void dfs(int v, int ccid){
visited[v] = ccid;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (visited[w] == -1) {
dfs(w, ccid);
}
}
}
public int count(){
return cccount;
}
public boolean isConnected(int v, int w){
G.validateVertex(v);
G.validateVertex(w);
return visited[v] == visited[w];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph("cc.txt");
CC_INT cc = new CC_INT(graph);
System.out.println(cc.isConnected(0,5));
}
}
测试顶点是否属于同一个联通量上:
false
返回每个联通分量中的顶点列表:
public ArrayList<Integer>[] components(){
ArrayList<Integer>[] res = new ArrayList[cccount];
for (int i = 0; i < cccount; i ++)
res[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
res[visited[v]].add(v);
return res;
}这段代码是在CC类中添加了一个新的方法components(),用于返回每个联通分量中的顶点列表。
执行结果:
0 : 0 1 2 3 4 6
1 : 5
Process finished with exit code 02. 路径问题
如果两个顶点在同一个联通分量中,那么它们之间一定存在路径。联通分量是指图中的一组顶点,这些顶点之间可以相互连通,通过边进行路径的传递。
单源路径问题是指在给定的图中,找到从单个源顶点到其他所有顶点的路径。下面是使用广度优先搜索(BFS)来解决单源路径问题的步骤:
public class SingleSourcePath {
private Graph G; // 图对象
private int s; // 源顶点
private boolean[] visited; // 记录顶点是否访问过
private int[] pre; // 记录每个顶点在路径中的前一个顶点
public SingleSourcePath(Graph G, int s){
G.validateVertex(s);
this.G = G;
this.s = s;
visited = new boolean[G.V()]; // 初始化visited数组,默认所有顶点未访问
pre = new int[G.V()]; // 初始化pre数组,默认所有顶点前一个顶点为-1
for (int i = 0; i < pre.length; i++) {
pre[i] = -1;
}
dfs(s, s); // 调用深度优先搜索方法,从源顶点s开始遍历图
}
private void dfs(int v, int parent){
visited[v] = true; // 标记当前顶点为已访问
pre[v] = parent; // 设置当前顶点的前一个顶点为parent
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!visited[w]) {
dfs(w, v); // 递归遍历当前顶点的未访问过的邻接顶点
}
}
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int t){
G.validateVertex(t); // 验证目标顶点t的有效性
return visited[t]; // 返回目标顶点t是否与源顶点s相连
}
public Iterable<Integer> path(int t){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (!isConnectedTo(t)) return res; // 若目标顶点t与源顶点s不相连,则返回空路径
int cur = t;
while (cur != s){
res.add(cur); // 将当前顶点加入路径中
cur = pre[cur]; // 更新当前顶点为其前一个顶点
}
res.add(s); // 将源顶点s加入路径中
Collections.reverse(res); // 反转路径列表,得到从源顶点s到目标顶点t的路径
return res; // 返回路径列表
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph("cc.txt");
SingleSourcePath sspath = new SingleSourcePath(graph, 0);
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + sspath.path(6)); // 打印从顶点0到顶点6的路径
}
}在构造函数中,使用深度优先搜索(DFS)从源顶点s开始遍历图,并记录每个顶点在路径中的前一个顶点。通过isConnectedTo(t)方法可以判断目标顶点t是否与源顶点s相连,通过path(t)方法可以获取从源顶点s到目标顶点t的路径。在path(t)方法中,根据记录的前一个顶点信息
3. 从v开始遍历,看是否可以达到t
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
/**
* @author wushaopei
* @create 2023-06-03 21:49
*/
public class Path {
private Graph G; // 图对象
private int s; // 源顶点
private int t;
private boolean[] visited; // 记录顶点是否访问过
private int[] pre; // 记录每个顶点在路径中的前一个顶点
public Path(Graph G, int s, int t){
G.validateVertex(s);
this.G = G;
this.s = s;
this.t = t;
visited = new boolean[G.V()]; // 初始化visited数组,默认所有顶点未访问
pre = new int[G.V()]; // 初始化pre数组,默认所有顶点前一个顶点为-1
for (int i = 0; i < pre.length; i++) {
pre[i] = -1;
}
dfs(s, s); // 调用深度优先搜索方法,从源顶点s开始遍历图
for (boolean e: visited)
System.out.print(e + " ");
System.out.println();
}
private boolean dfs(int v, int parent){
visited[v] = true; // 标记当前顶点为已访问
pre[v] = parent; // 设置当前顶点的前一个顶点为parent
if (v == t) return true;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!visited[w]) {
if (dfs(w, v)) // 递归遍历当前顶点的未访问过的邻接顶点
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean isConnected(){
return visited[t]; // 返回目标顶点t是否与源顶点s相连
}
public Iterable<Integer> path(){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (!isConnected()) return res; // 若目标顶点t与源顶点s不相连,则返回空路径
int cur = t;
while (cur != s){
res.add(cur); // 将当前顶点加入路径中
cur = pre[cur]; // 更新当前顶点为其前一个顶点
}
res.add(s); // 将源顶点s加入路径中
Collections.reverse(res); // 反转路径列表,得到从源顶点s到目标顶点t的路径
return res; // 返回路径列表
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph("cc.txt");
Path sspath = new Path(graph, 0, 6);
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + sspath.path()); // 打印从顶点0到顶点6的路径
Path sspath2 = new Path(graph, 0, 6);
System.out.println("0 -> 1 : " + sspath2.path()); // 打印从顶点0到顶点6的路径
}
}
上述代码,新增了一个顶点目标顶点t作为构造函数的参数,用于指定要寻找路径的目标顶点。将isConnectedTo()方法更名为isConnected(),用于判断源顶点s和目标顶点t是否相连。在dfs()方法中,增加了一个判断条件if (v == t) return true;,当当前顶点v等于目标顶点t时,直接返回true,表示找到了源顶点到目标顶点的路径。
在main()方法中,创建了一个新的Path对象sspath2,用于寻找从顶点0到顶点1的路径。
这个版本的代码在功能上与前一个版本基本相同,不同之处在于可以指定目标顶点,且通过isConnected()方法判断源顶点和目标顶点是否相连,而不再需要单独调用path()方法来判断路径是否存在。
4. 检测无向图中的环
/**
* @author wushaopei
* @create 2023-06-04 22:53
*/
import java.util.*;
public class CycleDetection {
private Graph G; // 图对象
private boolean[] visited; // 记录顶点是否访问过
private boolean hasCycle; // 是否存在环
public CycleDetection(Graph G) {
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
hasCycle = false;
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (!visited[v]) {
if (dfs(v, v)) {
hasCycle = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
// 从顶点v开始,判断图中是否有环
private boolean dfs(int v, int parent) {
visited[v] = true;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!visited[w]) {
if (dfs(w, v)) return true;
} else if (w != parent) {
// 如果顶点w已经被访问过,并且w不是当前顶点v的父节点,说明存在环
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean hasCycle() {
return hasCycle;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph("cc.txt");
CycleDetection cycleDetection = new CycleDetection(graph);
System.out.println("Has cycle: " + cycleDetection.hasCycle());
Graph graph2 = new Graph("cc2.txt");
CycleDetection cycleDetection2 = new CycleDetection(graph2);
System.out.println("Has cycle: " + cycleDetection2.hasCycle());
}
}
检测的数cc.txt、cc2.txt:
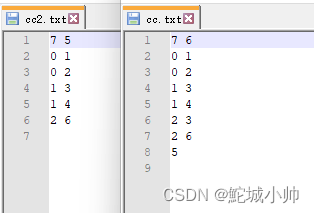
检测结果:
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:50987', transport: 'socket'
Has cycle: true
Has cycle: false
Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:50987', transport: 'socket'
Process finished with exit code 05. 二分图
5.1 概述
二分图,也称为二部图或二分图,是一种特殊的图结构。它的顶点集可以分为两个互不相交的子集,使得同一个子集内的顶点之间没有边相连。换句话说,可以用两种颜色对顶点进行着色,使得任意一条边的两个顶点颜色不相同。
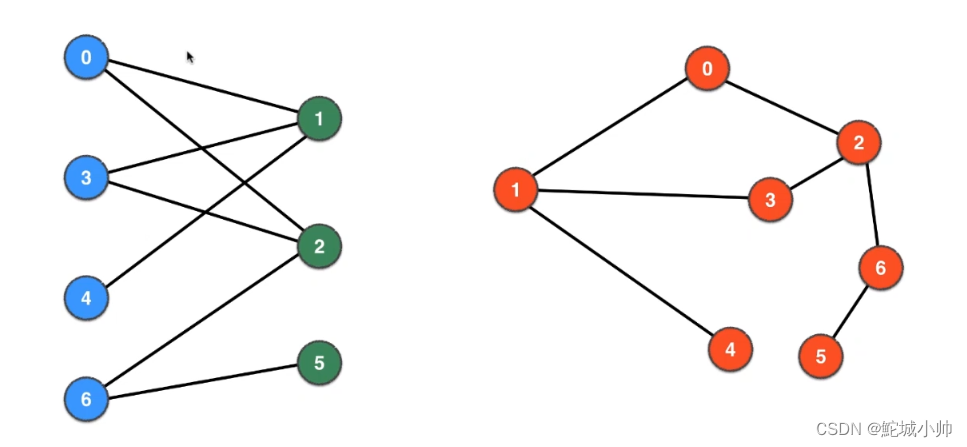
二分图具有许多应用,例如任务分配、时间表调度、匹配问题等。在计算机科学中,判断一个图是否为二分图是一个重要的问题。
二分图的判断可以使用多种算法,其中一种常见的算法是使用深度优先搜索(DFS)或广度优先搜索(BFS)。
染色
染色是判断图是否为二分图的常用方法之一。该方法基于以下原理:如果一个图是二分图,那么可以用两种颜色对图的顶点进行染色,使得相邻顶点的颜色不同。
二分图检测
下面是一个用DFS判断无向图是否为二分图的代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @author wushaopei
* @create 2023-06-03 21:49
*/
public class BipartitionDetection {
private Graph G; // 顶点数
private boolean [] visited; // 边数
private int[] colors;
private boolean isBipartite = true;
public BipartitionDetection(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
colors = new int[G.V()];
for (int i = 0; i < G.V(); i ++)
colors[i] = -1;
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++ ){
if (!visited[v]){
if (!dfs(v, 0))
isBipartite = false;
}
}
}
private boolean dfs(int v, int color){
visited[v] = true;
colors[v] = color;
for (int w : G.adj(v)) {
if (!visited[w]) {
if (!dfs(w, color == 0? 1:0)) return false;
}
else if (colors[v] == colors[w]) return false;
}
return true;
}
public boolean isBipartite(){
return isBipartite;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph("cc.txt");
BipartitionDetection bipartitionDetection = new BipartitionDetection(graph);
System.out.println(bipartitionDetection.isBipartite());
}
}
以上代码使用DFS进行图的遍历,并在遍历过程中对顶点进行染色。初始时,将第一个顶点的颜色设为0,然后递归地遍历该顶点的邻接顶点,并将它们染色为与当前顶点颜色不同的颜色(0或1)。如果发现某个顶点的邻接顶点已经被访问过,并且颜色与当前顶点相同,则图不是二分图,返回false。如果遍历结束后没有发现冲突,则图是二分图,返回true。
使用染色法进行二分图的判断具有简单直观的思路,时间复杂度为O(V+E),其中V为顶点数,E为边数。该方法在实际应用中也有较好的效果。
6. 扩展
DFS还有图同构、NP难等知识点。