目录
一、链表概述
二、模拟实现链表
1、结点
2、遍历链表
3、获取链表的长度
4、添加元素
(1)、头插法
(2)、尾插法
(3)、在指定位置插入元素
5、删除元素
(1)、删除第一次出现值为key的结点
(2)、删除所有值为key的结点
6、清空链表
三、常见笔试题
1、单链表转置
2、获取单链表的中间结点
3、获取倒数第K个结点
4、合并两个有序链表
一、链表概述
链表:存储结构上并非连续,元素之间靠指针连接的线性表。
链表可以分为是否带头节点的链表、是否为循环链表、是否为双向链表,但是不带头的单向链表使用较多,本文也是对不带头的单向链表进行详解。
二、模拟实现链表
1、结点
链表是有多个结点组成,结点的成员变量有data和next,结点类为链表类的内部类。
class Node{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int data){
this.data=data;
}
}2、遍历链表
定义一个结点指向链表的首元结点,逐个进行遍历,直至链表中某个结点的next为空。
//遍历链表
public void display() {
if(head==null){
return;
}
Node cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
System.out.print(cur.data+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
}
3、获取链表的长度
与遍历链表相似,只是需要设置一个计数器,来求出链表的长度。
public int size() {
int count=0;
Node cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return count;
}
4、添加元素
(1)、头插法
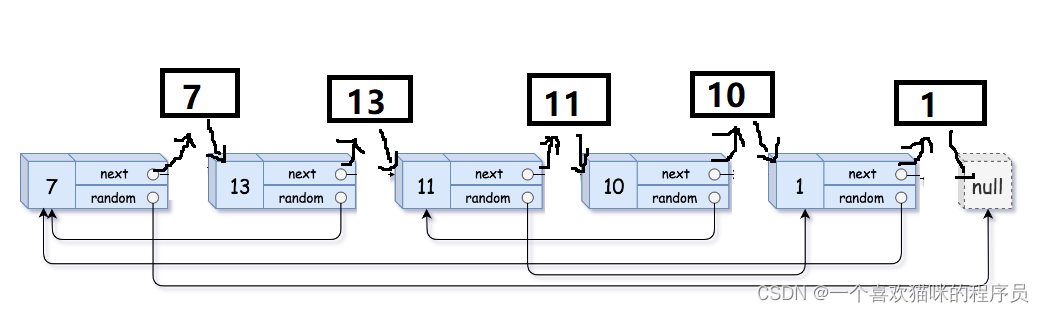
将待添加的元素插入到链表首部,需要将待插的元素封装为一个结点,将该结点的next指向链表的首部,再将链表的首部指向该结点,那么该结点为链表的首元结点。
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node node=new Node(data);
node.next=head;
head=node;
}(2)、尾插法
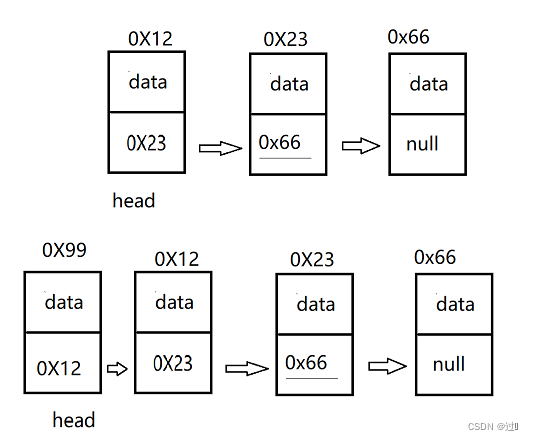
将需要插入的元素封装为一个结点,遍历整个链表,让链表的最后一个结点的next指向新增的结点即可。
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
Node node=new Node(data);
if(head==null){
head=node;
return;
}
Node cur=head;
while(cur.next!=null){
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=node;
}(3)、在指定位置插入元素
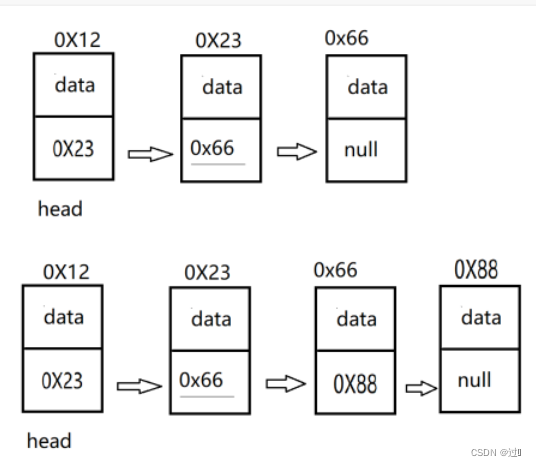
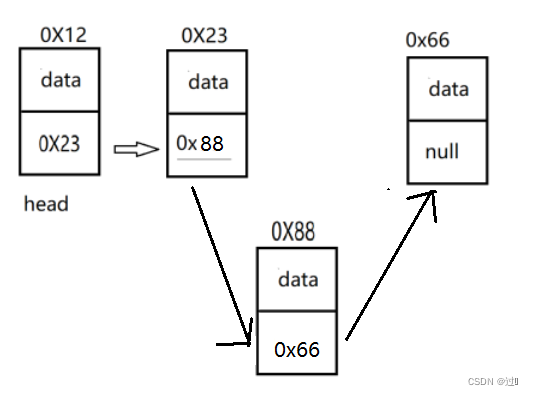
可以再定义一个方法获取指定位置的结点,以此得到指定位置的前一个结点,然后新增结点的next为前一个结点的next, 前一个结点的next为新增结点。
//获取指定位置的结点
public Node indexNode(int index){
if(index<0||index>size()){
throw new PosException("位置不合法!");
}
int count=0;
Node cur = head;
while(count!=index){
cur=cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public boolean addIndex(int index, int data) {
if(index==0){
addFirst(data);
return true;
}
if(index==size()){
addLast(data);
return true;
}
if(index<0||index>size()){
throw new PosException("位置不合法!");
}
Node cur=indexNode(index-1);
Node node=new Node(data);
node.next=cur.next;
cur.next=node;
return true;
}5、删除元素
(1)、删除第一次出现值为key的结点
首先对特殊情况(链表为空,链表的首元结点为要删除的节点,直接将首元结点指向其下一个结点) 处理,然后找到key结点的前一个结点,让其的next指向next.next。
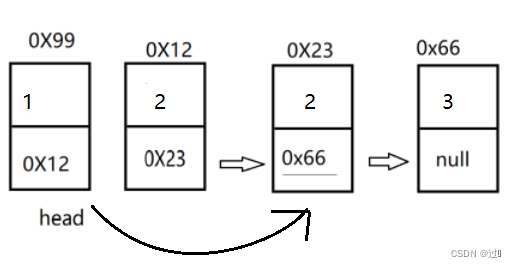
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
if(head==null){
return;
}
Node cur=head;
if(cur.data==key&&cur.next==null){
head=null;
return;
}
while(cur.next!=null){
if(cur.next.data==key){
cur.next=cur.next.next;
return;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
System.out.println("链表中不存在"+key+"元素");
}(2)、删除所有值为key的结点
首先仍需对特殊情况进行处理(与上述类似),采用双指针,开始时,pre和cur都指向首元结点, 当cur继续像后遍历时,若值为key,则pre.next=cur.next,否则pre=cur。
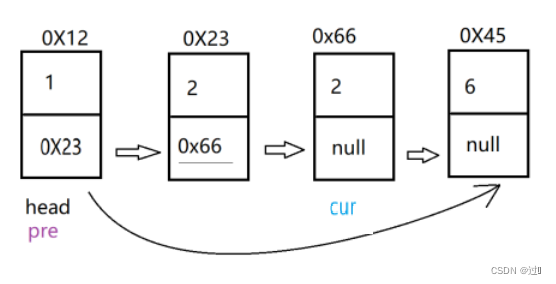
//删除所有值为key的结点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if(head==null){
return;
}
while(head.data==key){
if(head.next==null){
head=null;
}
head=head.next;
}
Node pre=head;
Node cur=head.next;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.data==key){
pre.next=cur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}else{
pre=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
/*if(head.data==key){
if(head.next==null){
head=null;
}
head=head.next;
}*/
}6、清空链表
直接将首元结点置为null即可。
public void clear() {
head=null;
}三、常见笔试题
1、单链表转置
对链表为空和链表只有一个首元结点进行处理,定义一个结点cur指向首元结点的next,然后利用头插法的思想,将所有的元素进行转置。
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur=head.next;
head.next=null;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode node=cur.next;
cur.next=head;
head=cur;
cur=node;
}
return head;
}2、获取单链表的中间结点
同样需要对特殊情况进行处理,之后不再赘述,利用快慢指针的思想,在进行遍历时,slow向后走一步,fast向后走两步,这里需要考虑到链表长度为奇数和偶数的情况,对于奇数的
情况是fast.next==null,对于偶数的情况是fast==null,故将while的循环条件写为(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null)。
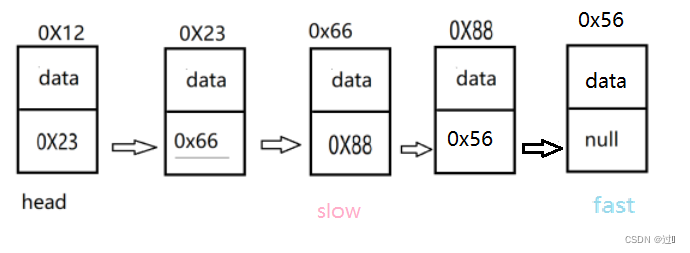
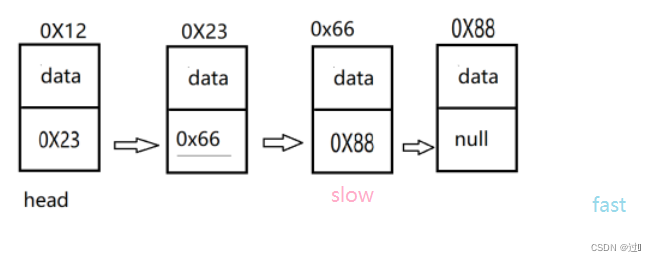
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode slow=head.next;
ListNode fast=head.next.next;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}3、获取倒数第K个结点
依旧采用快慢指针的思想,首先对k的合法性进行判断,先将fast和slow都指向head,然后将fast指向其后的k个结点,最后进行while循环,fast和slow继续向后进行遍历,循环条件为fast!=null,循环结束后slow指向倒数第k个结点。
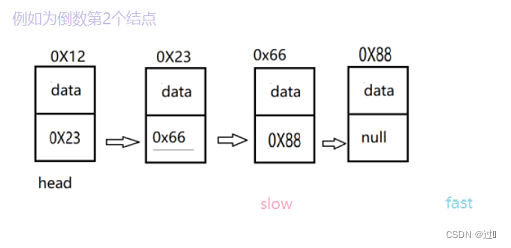
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(k<=0){
return null;
}
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
int count=0;
while(count<k){
if(fast==null){
return null;
}
fast=fast.next;
count++;
}
while(fast!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next;
}
return slow;
}4、合并两个有序链表
需要定义一个新的首元结点,再定义一个结点cur指向该结点然后对两个链表进行遍历,循环条件为两个链表不为空,较小的结点添加到cur结点之后,遍历完成后,若还有链表没有遍历完,则cur.next指向未遍历完链表的首元结点。最后将新链表的首元结点进行删除。
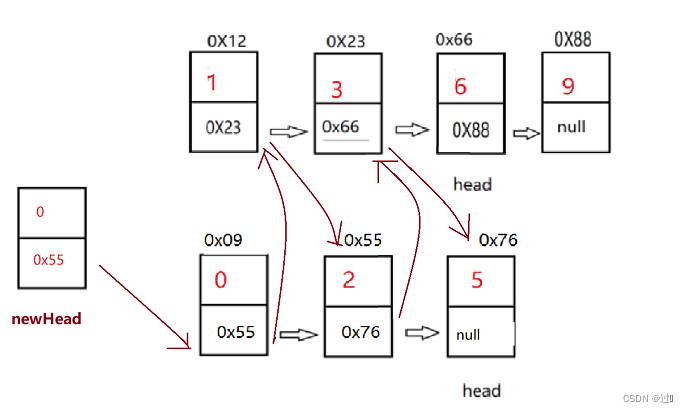
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode newHead=new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur=newHead;
while(list1!=null&&list2!=null){
if(list1.val<list2.val){
cur.next=list1;
list1=list1.next;
}else{
cur.next=list2;
list2=list2.next;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
if(list1!=null){
cur.next=list1;
}
if(list2!=null){
cur.next=list2;
}
newHead=newHead.next;
return newHead;
}5、判断链表是否为回文
首先需要找到中间结点,然后从中间结点的后一个改变指向,进行翻转,最后进行遍历。
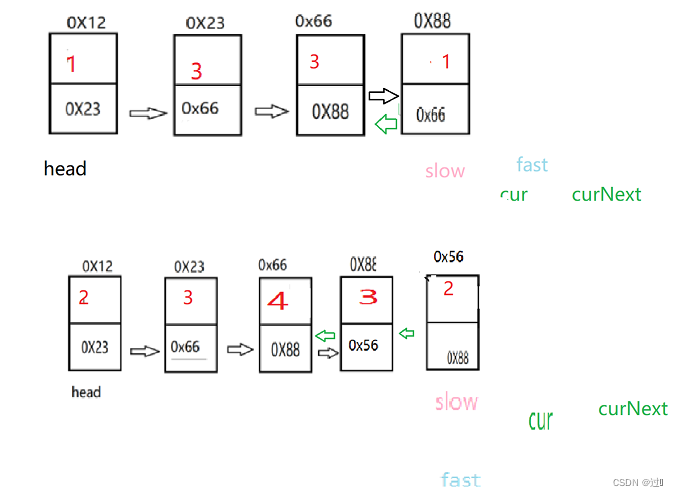
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return false;
}
if(head.next==null){
return true;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
//1、寻找中间结点
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
//2.翻转
ListNode cur=slow.next;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=slow;
slow=cur;//注意:此处不能写slow=slow.next,因为slow后面结点的next指向已发生改变
cur=curNext;
}
//3.判断
while(head!=slow){
if(head.val!=slow.val){
return false;
}
if(head.next==slow){
return true;
}
head=head.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return true;
}

![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django基于JEE平台springboot技术的订餐系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/771a87d894a249eaacbc3b0dfd07c0b5.png)


![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django绿色生鲜](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5a87e446a45a4dbb8f9a36002216f493.png)
![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计酒店管理系统(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7a1e8274ca0b4a3db69f7007dafc6d4e.png)
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计打印助手平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4b43ce51576b42378c09cc1a8b2f127c.png)
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计基于springboot的旅游景点管理系统的设计与实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/59babe8ae1cb47beb7c71590a29e3c6a.png)


![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django人事系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/26db9ae57ed14027b99d499358d5b11e.png)