定义于头文件<map>
| template< class Key, | (1) | |
| namespace pmr { template <class Key, class T, class Compare = std::less<Key>> | (2) | (C++17 起) |
std::map 是有序键值对容器,它的元素的键是唯一的。用比较函数 Compare 排序键。搜索、移除和插入操作拥有对数复杂度。 map 通常实现为红黑树。
在每个标准库使用比较 (Compare) 概念的位置,以等价关系检验唯一性。不精确而言,若二个对象 a 与 b 互相比较不小于对方 : !comp(a, b) && !comp(b, a) ,则认为它们等价(非唯一)。
std::map 满足容器 (Container) 、具分配器容器 (AllocatorAwareContainer) 、关联容器 (AssociativeContainer) 和可逆容器 (ReversibleContainer) 的要求。
观察器
返回用于比较键的函数
std::map<Key,T,Compare,Allocator>::key_comp| key_compare key_comp() const; |
返回用于比较关键的函数对象,它是此容器构造函数参数 comp 的副本。
参数
(无)
返回值
比较关键的函数对象。
复杂度
常数
返回用于在value_type类型的对象中比较键的函数
std::map<Key,T,Compare,Allocator>::value_comp| std::map::value_compare value_comp() const; |
返回比较 std::map::value_type (关键-值 pair )对象的函数对象,它用 key_comp 比较 pair 的第一组分。
参数
(无)
返回值
比较值的函数对象。
复杂度
常数。
非成员函数
按照字典顺序比较 map 中的值
operator==,!=,<,<=,>,>=(std::map)| template< class Key, class T, class Compare, class Alloc > bool operator==( const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& lhs, const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& rhs ); | (1) | |
| template< class Key, class T, class Compare, class Alloc > bool operator!=( const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& lhs, const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& rhs ); | (2) | |
| template< class Key, class T, class Compare, class Alloc > bool operator<( const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& lhs, const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& rhs ); | (3) | |
| template< class Key, class T, class Compare, class Alloc > bool operator<=( const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& lhs, const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& rhs ); | (4) | |
| template< class Key, class T, class Compare, class Alloc > bool operator>( const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& lhs, const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& rhs ); | (5) | |
| template< class Key, class T, class Compare, class Alloc > bool operator>=( const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& lhs, const std::map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& rhs ); | (6) |
比较二个容器的内容。
1-2) 检查 lhs 与 rhs 的内容是否相等,即它们是否拥有相同数量的元素且 lhs 中每个元素与 rhs 的同位置元素比较相等。
3-6) 按字典序比较 lhs 与 rhs 的内容。由等价于 std::lexicographical_compare 的函数进行比较。此比较忽略容器的定序 Compare 。
参数
| lhs, rhs | - | 要比较内容的容器 |
- 为使用重载 (1-2) , T, Key 必须满足可相等比较 (EqualityComparable) 的要求。 | ||
- 为使用重载 (3-6) , Key 必须满足可小于比较 (LessThanComparable) 的要求。顺序关系必须建立全序。 | ||
返回值
1) 若容器内容相等则为 true ,否则为 false
2) 若容器内容不相等则为 true ,否则为 false
3) 若 lhs 的内容按字典序小于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
4) 若 lhs 的内容按字典序小于或等于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
5) 若 lhs 的内容按字典序大于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
6) 若 lhs 的内容按字典序大于或等于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
复杂度
1-2) 若 lhs 与 rhs 的大小不同则为常数,否则与容器大小成线性
3-6) 与容器大小成线性
特化 std::swap 算法
std::swap(std::map)| template< class Key, class T, class Compare, class Alloc > void swap( map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& lhs, map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& rhs ); | (C++17 前) | |
| template< class Key, class T, class Compare, class Alloc > void swap( map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& lhs, map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>& rhs ) noexcept(/* see below */); | (C++17 起) |
为 std::map 特化 std::swap 算法。交换 lhs 与 rhs 的内容。调用 lhs.swap(rhs) 。
参数
| lhs, rhs | - | 要交换内容的容器 |
返回值
(无)
复杂度
常数。
异常
| noexcept 规定: noexcept(noexcept(lhs.swap(rhs))) | (C++17 起) |
擦除所有满足特定判别标准的元素
std::erase_if(std::map)| template< class Key, class T, class Compare, class Alloc, class Pred > | (1) | (C++20 起) |
从容器中擦除所有满足谓词 pred 的元素。等价于
for (auto i = c.begin(), last = c.end(); i != last; ) {
if (pred(*i)) {
i = c.erase(i);
} else {
++i;
}
}
参数
| c | - | 要从中擦除的元素 |
| pred | - | 若应该擦除元素则对它返回 true 的谓词 |
复杂度
线性。
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <map>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
struct Cell
{
int x;
int y;
Cell() = default;
Cell(int a, int b): x(a), y(b) {}
Cell &operator +=(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator +(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator *(const Cell &cell)
{
x *= cell.x;
y *= cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator ++()
{
x += 1;
y += 1;
return *this;
}
bool operator <(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y < cell.y;
}
else
{
return x < cell.x;
}
}
bool operator >(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y > cell.y;
}
else
{
return x > cell.x;
}
}
bool operator ==(const Cell &cell) const
{
return x == cell.x && y == cell.y;
}
};
struct myCompare
{
bool operator()(const int &a, const int &b)
{
return a < b;
}
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Cell &cell)
{
os << "{" << cell.x << "," << cell.y << "}";
return os;
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const std::pair<const int, Cell> &pCell)
{
os << pCell.first << "-" << pCell.second;
return os;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::mt19937 g{std::random_device{}()};
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
auto genKey = []()
{
return std::rand() % 10 + 100;
};
auto generate = []()
{
int n = std::rand() % 10 + 100;
Cell cell{n, n};
return cell;
};
std::map<int, Cell> map1;
for (size_t index = 0; index < 5; index++)
{
//插入以给定的 args 原位构造的新元素到容器。
map1.emplace(genKey(), generate());
}
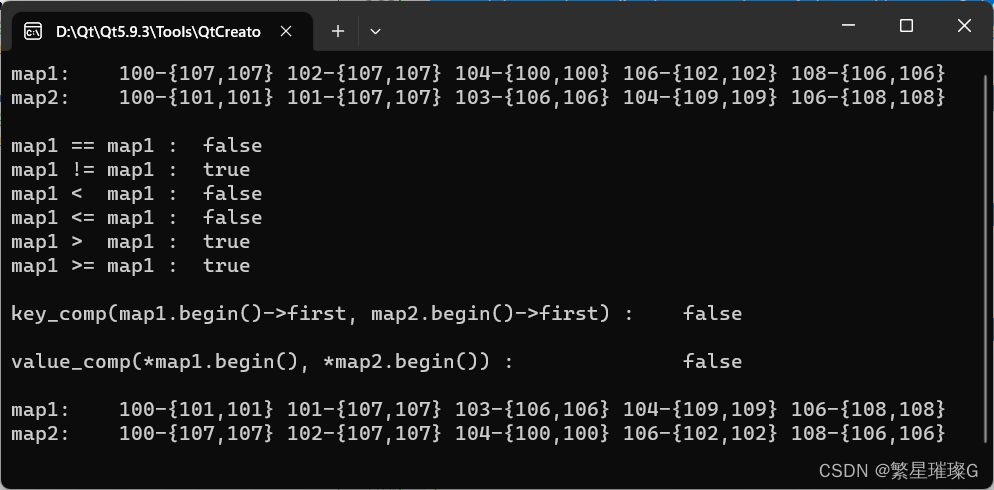
std::cout << "map1: ";
std::copy(map1.begin(), map1.end(),
std::ostream_iterator<std::pair<const int, Cell>>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::map<int, Cell> map2;
for (size_t index = 0; index < 5; index++)
{
//插入以给定的 args 原位构造的新元素到容器。
map2.emplace(genKey(), generate());
}
std::cout << "map2: ";
std::copy(map2.begin(), map2.end(), std::ostream_iterator<std::pair<const int, Cell>>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
//比较二个容器的内容。
//1) 若容器内容相等则为 true ,否则为 false
std::cout << "map1 == map1 : " << (map1 == map2) << std::endl;
//2) 若容器内容不相等则为 true ,否则为 false
std::cout << "map1 != map1 : " << (map1 != map2) << std::endl;
//3) 若 lhs 的内容按字典序小于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
std::cout << "map1 < map1 : " << (map1 < map2) << std::endl;
//4) 若 lhs 的内容按字典序小于或等于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
std::cout << "map1 <= map1 : " << (map1 <= map2) << std::endl;
//5) 若 lhs 的内容按字典序大于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
std::cout << "map1 > map1 : " << (map1 > map2) << std::endl;
//6) 若 lhs 的内容按字典序大于或等于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
std::cout << "map1 >= map1 : " << (map1 >= map2) << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
//返回用于比较关键的函数对象,它是此容器构造函数参数 comp 的副本。
auto key_comp = map2.key_comp();
std::cout << "key_comp(map1.begin()->first, map2.begin()->first) : "
<< key_comp(map1.begin()->first, map2.begin()->first) << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
auto value_comp = map2.value_comp();
std::cout << "value_comp(*map1.begin(), *map2.begin()) : "
<< value_comp(*map1.begin(), *map2.begin()) << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
//为 std::map 特化 std::swap 算法。交换 lhs 与 rhs 的内容。调用 lhs.swap(rhs) 。
std::swap(map1, map2);
std::cout << "map1: ";
std::copy(map1.begin(), map1.end(),
std::ostream_iterator<std::pair<const int, Cell>>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "map2: ";
std::copy(map2.begin(), map2.end(),
std::ostream_iterator<std::pair<const int, Cell>>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}输出