目录
🤔常见集合算法:
🙂1.set_intersection 容器交集
代码示例:
运行结果:
🙂2.set_union 容器并集
图解:
代码示例:
运行结果:
🙂 3.set_difference 容器差集
图解:
代码示例:
运行结果:
结束!
🤔常见集合算法:
🙂1.set_intersection 容器交集
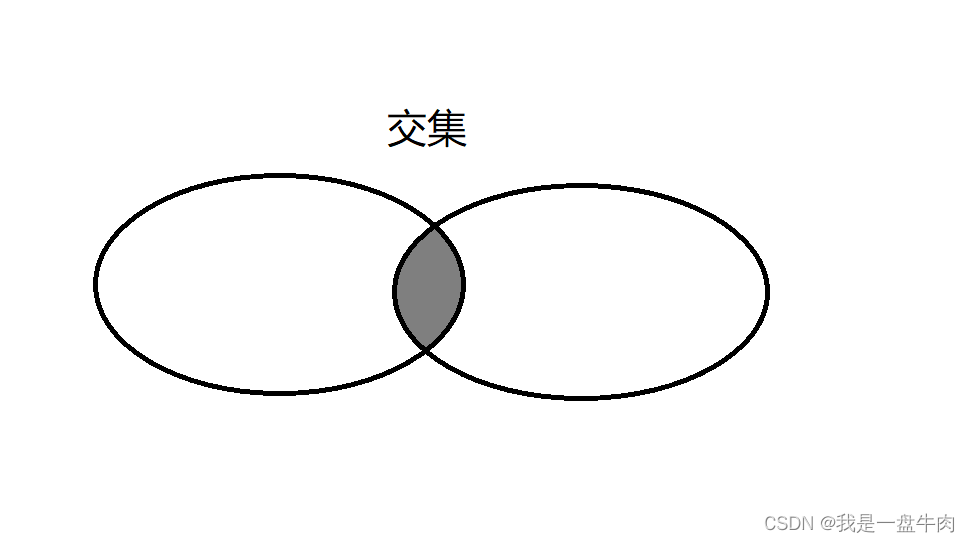
set_intersection是STL中的一个算法函数,用于求两个已经有序的集合的交集,并将结果输出到一个目标容器中。set_intersection函数的声明方式如下:
template<class InputIt1, class InputIt2, class OutputIt>
OutputIt set_intersection(InputIt1 first1, InputIt1 last1,
InputIt2 first2, InputIt2 last2,
OutputIt d_first);first1和last1:表示第一个有序集合的起始和结束迭代器first2和last2:表示第二个有序集合的起始和结束迭代器d_first:表示输出结果的容器的起始迭代器
📖函数返回值为输出结果容器的结束迭代器。
set_intersection函数会将两个集合的交集元素依据元素的大小关系依次复制到目标容器中,并返回目标容器的迭代器。
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void print(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> d1 = { 10, 20, 30, 40,};
vector<int> d2 = { 30, 40, 50, 60 };
vector<int> d3(100); // 向量容量设为100
auto iter = set_intersection(d1.begin(), d1.end(), d2.begin(), d2.end(), d3.begin());
cout << "d1: ";
for_each(d1.begin(), d1.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "d2: ";
for_each(d2.begin(), d2.end(), print);
cout << endl;
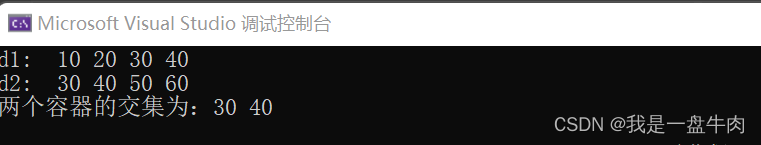
cout << "两个容器的交集为:";
for_each(d3.begin(), iter, print); // 只输出交集部分
cout << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:
🙂2.set_union 容器并集
图解:
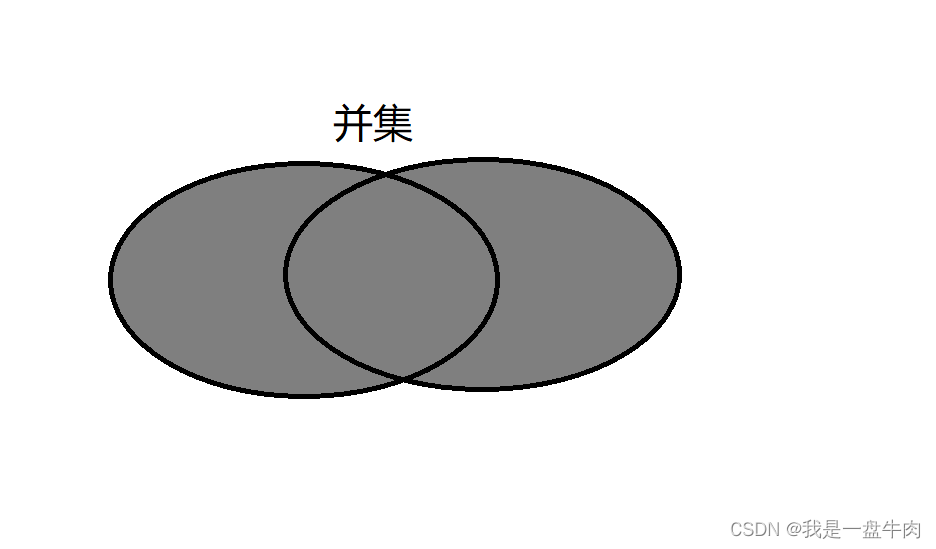
set_union是STL中的一个算法函数,用于求两个已经有序的集合的并集,并将结果输出到一个目标容器中。set_union函数的声明方式如下:
template<class InputIt1, class InputIt2, class OutputIt>
OutputIt set_union(InputIt1 first1, InputIt1 last1,
InputIt2 first2, InputIt2 last2,
OutputIt d_first);first1和last1:表示第一个有序集合的起始和结束迭代器first2和last2:表示第二个有序集合的起始和结束迭代器d_first:表示输出结果的容器的起始迭代器
📖函数返回值为输出结果容器的结束迭代器。
set_union函数会将两个集合的所有元素依据元素的大小关系依次复制到目标容器中,并排除重复的元素,返回目标容器的迭代器。
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void print(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> d1 = { 10, 20, 30, 40,};
vector<int> d2 = { 10,30, 40, 50, 60 };
vector<int> d3(100); // 向量容量设为100
auto iter = set_union(d1.begin(), d1.end(), d2.begin(), d2.end(), d3.begin());
cout << "d1: ";
for_each(d1.begin(), d1.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "d2: ";
for_each(d2.begin(), d2.end(), print);
cout << endl;
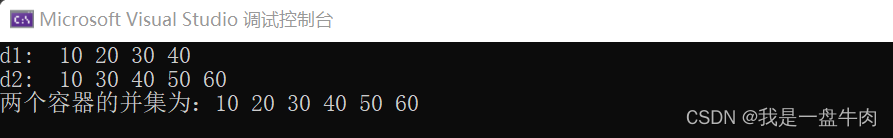
cout << "两个容器的并集为:";
for_each(d3.begin(), iter, print); // 只输出并集部分
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
🙂 3.set_difference 容器差集
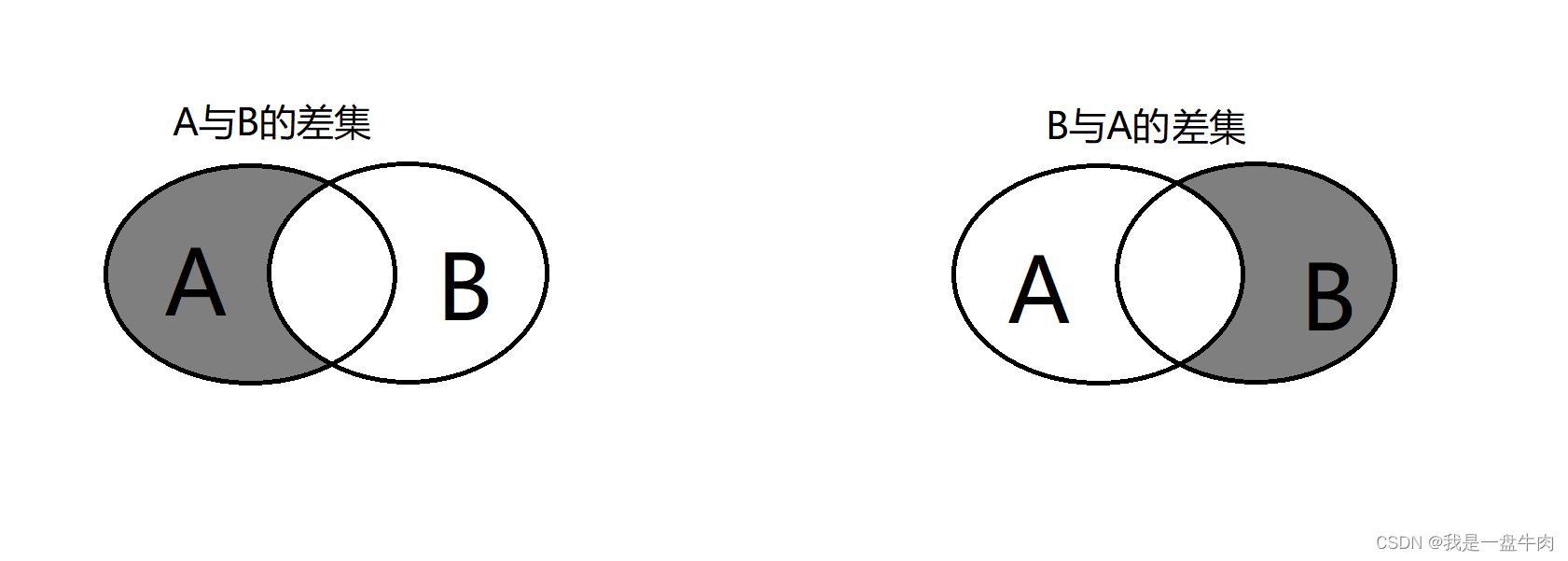
在数学中,对于两个集合A和B,A与B的差集(也称为相对补集)指的是由所有属于A但不属于B的元素组成的集合,记作A-B。
例如,对于集合A={1,2,3,4,5}和集合B={4,5,6,7,8},则A与B的差集为{1,2,3}。
B与A的差集所有属于B但不属于A的元素组成的集合{6,7,8},记作B-A。
在计算机科学中,集合的差集操作同样应用广泛,例如在关系型数据库设计中,可以使用集合的差集操作来实现多表之间的联接操作。在C++的STL中,set_difference是一个常见的集合算法,可用于计算两个有序容器的差集。
图解:
set_difference是STL中的一个算法函数,用于求两个已经有序的集合的差集,并将结果输出到一个目标容器中。set_difference函数的声明方式如下:
template<class InputIt1, class InputIt2, class OutputIt>
OutputIt set_difference(InputIt1 first1, InputIt1 last1,
InputIt2 first2, InputIt2 last2,
OutputIt d_first);
参数说明:
first1和last1:表示第一个有序集合的起始和结束迭代器first2和last2:表示第二个有序集合的起始和结束迭代器d_first:表示输出结果的容器的起始迭代器
📖函数返回值为输出结果容器的结束迭代器。
set_difference函数会将属于第一个集合但不属于第二个集合的所有元素依据元素的大小关系依次复制到目标容器中,返回目标容器的迭代器。
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void print(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> d1 = { 10, 20, 30, 40, };
vector<int> d2 = { 10,30, 40, 50, 60 };
vector<int> d3(100); // 向量容量设为100
auto iter = set_difference(d1.begin(), d1.end(), d2.begin(), d2.end(), d3.begin());
cout << "d1: ";
for_each(d1.begin(), d1.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "d2: ";
for_each(d2.begin(), d2.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "两个容器的差集为:";
for_each(d3.begin(), iter, print); // 只输出差集部分
cout << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果: