文章目录
- 什么是协程
- suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn
- suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn存在的问题
- suspendCoroutine
- suspendCancellableCoroutine
引言: 在Kotlin协程中,如何让一个suspned 函数挂起?如何让挂起协程恢复?想必使用过协程的同学都非常清楚那就是调用
suspendCoroutine或者
suspendCancellableCoroutine。使用了这么久,你真的知道他们是怎么回事吗?.
注:本文源码班基于kotlin 1.7.10
什么是协程
先简要回顾一下什么是协程?我们通过协程最基础的API createCoroutine 可以创建一个协程,然后在调用resume 开启协程,startCoroutine创建并直接开启协程。像launch,async 等这些框架API是在基础API上的再次封装,让我们在创建和使用协程时变得更为方便。协程是由一个 suspend函数创建出来的,我们来看一个最原始的创建协程方式:
//第一步创建一个suspend 函数
val suspendFun : suspend () -> Unit = {
//TODO 这里面写上协程要执行的代码,也被称之为协程体
}
//第二步创建一个协程,并传一个协程执行完成后的回调
val continuation = suspendFun.createCoroutine(object :Continuation<Unit>{
override val context: CoroutineContext
get() = EmptyCoroutineContext
//协程执行完成后,会回调该方法,result代表了协程的结果,如果没有返回值就是Unit,如果协程体里面发生异常
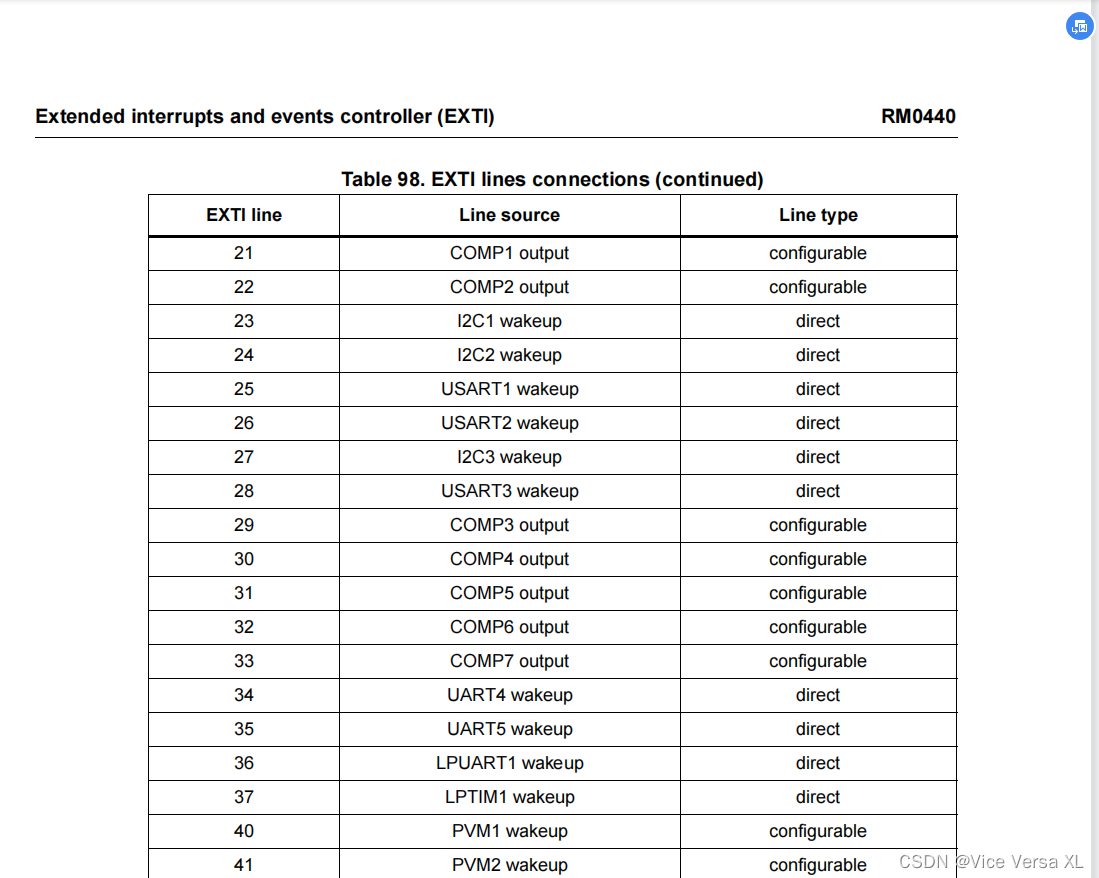
//result里面包含有异常信息
override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Unit>) {
println("协程执行完毕")
}
})
//第三步开启一个协程
continuation.resume(Unit)
被创建出来的协程continuation到底是一个什么东西呢?通过createCoroutine源码发现:
@SinceKotlin("1.3")
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
public fun <R, T> (suspend R.() -> T).createCoroutine(
receiver: R,
completion: Continuation<T>
): Continuation<Unit> =
SafeContinuation(createCoroutineUnintercepted(receiver, completion).intercepted(), COROUTINE_SUSPENDED)
这里面做了三件事:
第一:createCoroutineUnintercepted(receiver, completion) 创建了一个协程,”Unintercepted“说明了创建出来的这个协程是不被调度器协程(DispatchedContinuation)所包含或者代理的,这个就是我们真正执行代码的协程,我把它称之为原始协程。
第二:调用原始协程的intercepted(),该方法会通过我们在创建协程时指定的调度器创建一个DispatchedContinuation,它里面包含了原始协程和调度器,如果我们没有指定调度器intercepted()返回原始协程自己。
第三步:创建一个SafeContinuation,它持有了intercepted()返回的对象,设置了调度器就是DispatchedContinuation,没有设置就是原始协程。

原始协程是被createCoroutineUnintercepted创建出来的,那到底创建出来的是一个什么东西呢?
public actual fun <T> (suspend () -> T).createCoroutineUnintercepted(
completion: Continuation<T>
): Continuation<Unit> {
val probeCompletion = probeCoroutineCreated(completion)
return if (this is BaseContinuationImpl)
create(probeCompletion)
else
createCoroutineFromSuspendFunction(probeCompletion) {
(this as Function1<Continuation<T>, Any?>).invoke(it)
}
}
在createCoroutineUnintercepted里面this是该函数的接收者是一个suspend () -> T,其实就是我们在上面定义的suspned函数:
val suspendFun : suspend () -> Unit = {
//TODO 这里面写上协程要执行的代码,也被称之为协程体
}
在kotlin协程中,suspend () -> T 函数类型的父类都是SuspendLambda。而SuspendLambda又继承至ContinuationImpl,ContinuationImpl又继承至BaseContinuationImpl,BaseContinuationImpl又实现了Continuation接口。因此在createCoroutineUnintercepted会调用suspend () -> T 的create函数来创建我们的原始协程。create函数定义在什么地方呢?是父类SuspendLambda中还是ContinuationImpl或者还是BaseContinuationImpl中呢?它里面又是如何实现呢?都不是,craete函数编译器为我们生成的。当我们在代码定义一个suspend函数类型的时候(注意是函数类型不是suspend函数)编译器会为我们生成一个类,该类继承至SuspendLambda,把我们原本要执行的代码(协程体代码)给放到一个叫invokeSuspend函数中,并且为该类生成create函数,在create函数中new一个该类的实例对象返。
如果有对这个比较感兴趣的同学可以在IDEA中把kotlin代码编译后的字节码转成java代码查看。
到此我们知道了我们的原始协程原来是一个由kotlin编译器为我们生成的一个继承了SuspendLambda的子类。知道了原始协程为何物后,协程是如何开启的呢?是怎么执行到我们协程体代码里面的呢?在前面说过,编译器会把我们协程体要执行的代码放到生成的类中的invokeSuspend函数中,因此我们只需要知道什么时候调用invokeSuspend就行。在上面代码中的第三步调用了SafeContinuation的resume函数,SafeContinuation中会调用DispatchedContinuation的resumeWith函数,在DispatchedContinuation中又会通过调度器去调用原始协程的resumeWith函数。原始协程的resumeWitht函数在BaseContinuationImpl中定义的:
internal abstract class BaseContinuationImpl(
public val completion: Continuation<Any?>?
) : Continuation<Any?>, CoroutineStackFrame, Serializable {
public final override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any?>) {
var current = this
var param = result
while (true) {
probeCoroutineResumed(current)
with(current) {
val completion = completion!!
val outcome: Result<Any?> =
try {
//在这里调用了编译器生成的类的invokeSuspend,
//invokeSuspend中就是协程体的代码
val outcome = invokeSuspend(param)
if (outcome === COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) return
Result.success(outcome)
} catch (exception: Throwable) {
Result.failure(exception)
}
releaseIntercepted()
if (completion is BaseContinuationImpl) {
current = completion
param = outcome
} else {
completion.resumeWith(outcome)
return
}
}
}
}
xxxxx
}
在BaseContinuationImpl的resumeWith中调用了invokeSuspend,这样就执行到我们自己写的协程体要执行的代码里面了。
回顾了一大堆,是想说明一个事情,不管是协程第一次执行,还是后面协程从挂起函数恢复都要调用我们原始协程的
resumeWith函数才行。协程内部的执行(invokeSuspend内部)是一个状态机,每一次调用invokeSuspend都会给状态机设置一个不同的状态,使其执行invokeSuspend中不同分支的代码。至于协程状态机的原理不在本文讨论之中,不然就偏题了。
我们什么时候需挂起协程?被挂起的协程什么时候恢复?当我们不能立马返回结果的时候,需要把协程挂起,等结果准备好了后通过调用协程的resume函数进行恢复。那协程怎样才能挂起呢?答案就是在suspend函数中返回一个标识(COROUTINE_SUSPENDED),当协程看到这个标识后就知道协程需要被挂起了,恢复协程的时候需要调用协程的resume函数,那我么怎么才能在suspend函数中拿到协程这个对象呢?只有拿到协程这个对象才能调用其resume函数。说到这里,想必很多同学都知道调用suspendCoroutine函数啊,对,没错,当我们需要把我们的suspend函数挂起的,稍后再恢复的时候,我们可以有三种方式:
- suspendCoroutine
- suspendCancellableCoroutine
- suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn
其中suspendCoroutine和 suspendCancellableCoroutine两个内部都是调用了suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn来实现:
public suspend inline fun <T> suspendCoroutine(crossinline block: (Continuation<T>) -> Unit): T {
contract { callsInPlace(block, InvocationKind.EXACTLY_ONCE) }
//直接调用了suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn
return suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn { c: Continuation<T> ->
val safe = SafeContinuation(c.intercepted())
block(safe)
safe.getOrThrow()
}
}
public suspend inline fun <T> suspendCancellableCoroutine(
crossinline block: (CancellableContinuation<T>) -> Unit
): T = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn { uCont -> //同样的直接调用
val cancellable = CancellableContinuationImpl(uCont.intercepted(), resumeMode = MODE_CANCELLABLE)
cancellable.initCancellability()
block(cancellable)
cancellable.getResult()
}
当我们想去看suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn的源码的时候,发现无论如何都找不到源码了,很正常,因为suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn是有编译器在编译代码的时时候生成的。所以你找不到很正常。因此搞懂suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn的前提下再回过头来看另外两个就简单了。
suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn
佛说世间万物皆有其因果,任何一个东西的诞生都是有其原因的,在日常开发中,我们经常有这样的需求,调用一个函数获得一个想要的数据,有时候这个数据不能立马获得,比如本地缓存没有,需要从网络下载,这时候就需要把协程挂起,等数据回来了后再把协程恢复,如果本地有就直接返回,简而言之就是有可能会挂起,也有可能不会挂起直接返回结果。因此要让一个suspend函数能满足这种要求,那需要具备两个条件:1.我们需要再suspend函数中拿到协程对象,用于恢复协程的时候使用,2.suspend函数的返回值只能是Any类型,因为挂起的时候返回COROUTINE_SUSPENDED,不需要挂起的事后返回数据真实的类型。
针对条件一,我们知道每一个增加了suspned关键字标识的函数在编译后,函数参数中都会多一个Continuation的参数。这个参数就是我们的原始协程,但问题的关键是我们是在编码阶段的时候需要拿到协程。所以条件一靠我们自己是搞不定的。
针对条件2,虽然比较好满足,在我们定义函数的时候,把返回值改成Any即可,但是也同样带来一个问题,获得该函数的结果后,我们还需要人为去判断然后转换成我们需要的数据类型,如果真实这样,协程的代码得有多恶心,那我想估计没几个人愿意使用kotlin协程了。
于是这些kotlin的天才们想了一个招,他们说,你不是想在suspend函数中要拿到协程对象吗?我有啊,我给你,你只要按照我的要求你随便定义一个函数类型的变量,或者重新再写一个非susnpend函数。
如果是定义一个变量: 那么这个变量的类型必须为一个函数类型`Continuation<T>) -> Any?`,该函数接收一个`Continuation`作为参数,泛型参数`T`代表了真正需要返回真实数据类型,函数返回值类型为`Any`,给这个变量赋值一个`lambda`表达式,把你原本要写在`suspend`函数的代码放在这个`lambda`表达式里面。
如果是定义一个非suspend函数:那么这个函数的类型同样为Continuation<T>) -> Any?,你把原来要写在suspend函数里面的代码放在这个非suspend函数里面。
上面两种方式,其本质是一样的,都是一个函数类型,定义好后,kotlin说我给你提供一个叫某某的函数,我这个某某函数接收一个函数类型为``Continuation) -> Any?的参数,我这个函数的返回值为泛型T(代表了你要的结果的真实类型)。你在你需要挂起的suspned中直接调用我们这个某某函数,把你定义的函数类型变量或者非suspend函数的引用传给我,我在我的某某`函数中去调用你传进来的函数,把协程对象传过去,再把计算的结果返回给你suspend函数。这样就达到了想要的目的,既能获得协程对象,又能在需要挂起的时候返回挂起表示,不需要挂起的时候返回具体结果。
听起来如果觉得有点抽象,没关系,我们写一段代码演示一下,比如你现在有一个需求,获得一个Int类型数据,如果这个数据之前被计算出来了就直接返回,如果没有就需要重新计算,计算比较耗时,需要把协程挂起,计算完成把结果缓存起来以便下次直接使用,
故事原本是这样的,我们把代码写在suspend函数中:
suspend fun calculate(): Any?{
//先不要关心cache是一个啥,只需要知道它可以缓存结果就行
var result = cache.get()
//如果没有缓存就需要开一个子线程去计算,让该函数挂起
if(result == null){
thread {
Thread.sleep(10000)
val result = 1 + 2
cache.put(result)
//计算完成了后调用协程的resume函数让协程恢复。并把计算完成的结果交给协程。
//但是问题来了,contination在源码阶段是那拿不到的。
contination.resume(result) //error
}
//返回COROUTINE_SUSPENDED的目的是让协程挂起。
return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}else{
//如果有缓存,直接返回
return result
}
}
虽然calculate函数返回值可以是真实的数据也可以是挂起标识,但是我们拿不到协程对象啊,于是乎我们按照kotlin的要求来,整一个变量,于是你又开始写:
val calculateFun : (Continuation<Int>) -> Any? = { contination ->
var result = cache.get()
if(result == null){
thread {
Thread.sleep(10000)
val result = 1 + 2
cache.put(result)
contination.resume(result)
}
COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}else{
result
}
}
然后kotlin给你提供了一个某某函数,这个函数叫suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn:
inline suspend fun <T> suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn(block: (Continuation<T>) -> Any?) : T{
//由于suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn是在编译期间生成的,因此continuation是能拿到的。
val continuation = xxxx //
return block(continuation)
}
这样,你的calculate就可以改为:
suspend fun calculate() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<Int>(calculateFun)
//为了省去定义calculateFun的环节,因此可以简化为:
suspend fun calculate() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<Int> { contination ->
var result = cache.get()
if(result == null){
thread {
Thread.sleep(10000)
val result = 1 + 2
cache.put(result)
contination.resume(result)
}
COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}else{
result
}
}
这就达到了能获取到Continuation的目的,再加上 suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn还是一个inline函数,在编译过后会内联到调用者里面,因此也不存在性能开销。
suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn存在的问题
kotlin提供的这个suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn从名字就可以看出来,你既可以挂起该函数,也可以直接return。意思如果你需要挂起时就返回COROUTINE_SUSPENDED,不需要挂起时就返回正确的结果。这个函数名里面还有一个’Unintercepted‘ 意思就是我们拿到的协程是不包含调度器的,也就是是说调用其resume函数时是不会走调度器的,这样也就存在一个问题,在什么线程里调用的resume,接下里协程就恢复在什么线程里面了,这也就导致了我们平时使用时很少直接使用suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn而是使用另外两个替代品suspendCoroutine 和suspendCancellableCoroutine。
我们写一段代码来验证一下看看通过suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn挂起后协程恢复在什么线程:
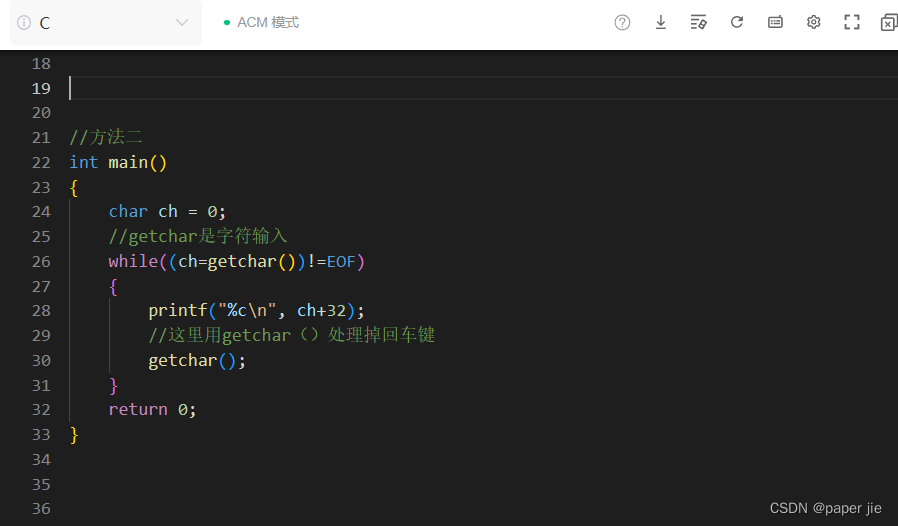
fun main() {
//第一步创建一个suspend 函数
val suspendFun : suspend () -> Unit = {
log("协程开始执行")
val result = testSuspendResumeThread()
log("协程恢复后的结果: $result")
}
//第二步创建一个协程
val continuation = suspendFun.createCoroutine(object :Continuation<Unit>{
override val context: CoroutineContext
get() = EmptyCoroutineContext
override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Unit>) {
log("协程执行完毕")
}
})
//第三步开启一个协程
continuation.resume(Unit)
Thread.sleep(100000)
}
suspend fun testSuspendResumeThread() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {con ->
//开一线程模拟耗时操作
thread(name = "子线程") {
Thread.sleep(1000)
//结束后恢复协程
con.resume("over")
}
return@suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}
输出结果:
00:06:22:865[ main ] 协程开始执行
00:06:23:896[ 子线程 ] 协程恢复后的结果: over
00:06:23:897[ 子线程 ] 协程执行完毕
从输出的结果来看,的确如我们所料,协程被恢复在了子线程。那有没有办法可以让协程恢复在原来的线程环境里面呢?可能有的同学已经开始在想了,我们是不是可以用学学源码里面的做法,调用协程的intercepted函数,获得一个DispatchedContinuation,调用DispatchedContinuation的resume函数呢?有这个想法说明你对协程原理有一定了解了,很可惜,intercepted函数我们调用不了。
suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn除了存在协程恢复后线程的问题,其实还有两个问题:
第一个:不算问题的问题,那就是我们写代码的时候需要自己去判断是不是需要挂起,需要挂起的时候返回值需要通过协程的resume函数传回到协程调用的地方,然后在lambda中 return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED。不要挂起的时候值可以直接return结果。貌似看上去很合理啊,逻辑清晰,思路简单,但是对于kotlin这个最求极致简单,语法糖丰富的一种语言,怎么能容忍这样没有营养的代码存在。
第二个:suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn使用不当容易造成一些奇怪的问题,比如在需要挂起的时候忘记写return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED,或者既调用resuem把值传回协程里面,又直接return了值,我们先看忘记return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED的情况,还是以上面的代码为基础,稍微改动一下:
suspend fun testSuspendResumeThread() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {con ->
thread(name = "子线程") {
Thread.sleep(1000)
con.resume("over")
}
//忘记写 return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}
还有一个地方需要改一下,给调用testSuspendResumeThread的地方try catch一下,为什么要try Catch,那是因为我知道这里会发生异常。不try catch也行,也不会因为异常导致进程终止,协程体内发生的异常会在BaseContinuationImpl的resumeWith函数中被协程内部捕获,然后交给协程的completion的resumeWith函数,在本例中由于我们采用了协程基础API创建的协程,在createCoroutine的时候传了一个简单的匿名内部类作为协程的completion,在其resumeWith中没有对收到的异常做任何处理,
注意:如果我们采用协程框架提供的api创建协程时,协程的completion收到异常后,如果创建协程时指定了异常处理器就交给指定的异常处理器处理,如果没有指定就交给默认异常处理器处理,默认异常处理器处理就是抛出异常,进程终止。
val suspendFun : suspend () -> Unit = {
log("协程开始执行")
try { //增加了try cacht
val result = testSuspendResumeThread()
log("协程恢复后的结果: $result")
}catch (e : Exception){
log(e) //打印异常信息
}
}
输出结果:
00:46:57:354[ main ] 协程开始执行
//类型转换异常,Thread不能转换成Strin类型。
00:46:57:397[ main ] 捕获异常:java.lang.ClassCastException: class kotlin.concurrent.ThreadsKt$thread$thread$1 cannot be cast to class java.lang.String (kotlin.concurrent.ThreadsKt$thread$thread$1 is in unnamed module of loader 'app'; java.lang.String is in module java.base of loader 'bootstrap')
00:46:57:397[ main ] 协程执行完毕
00:46:58:401[ 子线程 ] 协程恢复后的结果: over //协程执行完后又打印了 ’over‘,
Exception in thread "子线程" java.lang.NullPointerException
at kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.ContinuationImpl.releaseIntercepted(ContinuationImpl.kt:118)
at kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.BaseContinuationImpl.resumeWith(ContinuationImpl.kt:39)
at com.m.k.coroutine.example.TextExceptionKt$testSuspendResumeThread$2$thread$1.invoke(TextException.kt:44)
at com.m.k.coroutine.example.TextExceptionKt$testSuspendResumeThread$2$thread$1.invoke(TextException.kt:42)
at kotlin.concurrent.ThreadsKt$thread$thread$1.run(Thread.kt:30)
从输出的结果看出以下几个问题:
问题1:try catch处 捕获到一个异常(ClassCastException),协程内部还抛出了一个异常(NullPointerException)。
问题2: “协程执行完毕” 先于 “协程恢复后的结果: over” 被输出。
就因为忘记返回 COROUTINE_SUSPENDED 导致了一些列问题,如果我告诉你,给我们创建协程指定一个调度器后抛出异常又不一样了。
**问题3:**会由原来的NullPointerException变成了ClassCastException.比如:
//第二步创建一个协程
val continuation = suspendFun.createCoroutine(object :Continuation<Unit>{
override val context: CoroutineContext
//原来get返回的是一个EmptyCoroutineContext,现在给他指定一个默认调度器,让协程运行在线程池里面
get() = Dispatchers.Default
override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Unit>) {
log("协程执行完毕")
}
})
其他代码不变的情况下,看看输出结果:
00:52:28:676[ DefaultDispatcher-worker-1 ] 协程开始执行
//trc catch捕获到的异常没变,Thread不能转换成Strin类型。
00:52:28:731[ DefaultDispatcher-worker-1 ] 捕获异常:java.lang.ClassCastException: class kotlin.concurrent.ThreadsKt$thread$thread$1 cannot be cast to class java.lang.String (kotlin.concurrent.ThreadsKt$thread$thread$1 is in unnamed module of loader 'app'; java.lang.String is in module java.base of loader 'bootstrap')
00:52:28:732[ DefaultDispatcher-worker-1 ] 协程执行完毕 //同样优先于 “协程恢复后的结果: over”
//协程内部抛出的异常由原来的NullPointerException变成了ClassCastException
//这儿的这个ClassCastException和上面的那个ClassCastException不是同一个。
Exception in thread "子线程" java.lang.ClassCastException: class kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.CompletedContinuation cannot be cast to class kotlinx.coroutines.internal.DispatchedContinuation (kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.CompletedContinuation and kotlinx.coroutines.internal.DispatchedContinuation are in unnamed module of loader 'app')
at kotlinx.coroutines.CoroutineDispatcher.releaseInterceptedContinuation(CoroutineDispatcher.kt:147)
at kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.ContinuationImpl.releaseIntercepted(ContinuationImpl.kt:118)
at kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.BaseContinuationImpl.resumeWith(ContinuationImpl.kt:39)
at com.m.k.coroutine.example.TextExceptionKt$testSuspendResumeThread$2$thread$1.invoke(TextException.kt:44)
at com.m.k.coroutine.example.TextExceptionKt$testSuspendResumeThread$2$thread$1.invoke(TextException.kt:42)
at kotlin.concurrent.ThreadsKt$thread$thread$1.run(Thread.kt:30)
00:52:29:731[ 子线程 ] 协程恢复后的结果: over
**问题四:**打印两次结果。
我们接着在看看另一种情况,既调用resum又直接返回了结果:
suspend fun testSuspendResumeThread() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {con ->
val thread = thread(name = "子线程") {
Thread.sleep(1000)
con.resume("over")
}
//把我们要的结果`over`直接返回了
return@suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn "over"
}
看看输出结果:
01:01:16:180[ DefaultDispatcher-worker-1 ] 协程开始执行
01:01:16:203[ DefaultDispatcher-worker-1 ] 协程恢复后的结果: over //第一次打印
01:01:16:204[ DefaultDispatcher-worker-1 ] 协程执行完毕
01:01:17:205[ 子线程 ] 协程恢复后的结果: over //第二次打印
//协程内部抛出的异常和上面新增调度器后抛出的异常是同一个异常。
Exception in thread "子线程" java.lang.ClassCastException: class kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.CompletedContinuation cannot be cast to class kotlinx.coroutines.internal.DispatchedContinuation (kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.CompletedContinuation and kotlinx.coroutines.internal.DispatchedContinuation are in unnamed module of loader 'app')
at kotlinx.coroutines.CoroutineDispatcher.releaseInterceptedContinuation(CoroutineDispatcher.kt:147)
at kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.ContinuationImpl.releaseIntercepted(ContinuationImpl.kt:118)
at kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.BaseContinuationImpl.resumeWith(ContinuationImpl.kt:39)
at com.m.k.coroutine.example.TextExceptionKt$testSuspendResumeThread$2$thread$1.invoke(TextException.kt:44)
at com.m.k.coroutine.example.TextExceptionKt$testSuspendResumeThread$2$thread$1.invoke(TextException.kt:42)
at kotlin.concurrent.ThreadsKt$thread$thread$1.run(Thread.kt:30)
有没有发现,打印了两次’over’。少了一个异常,在我们try里面没有发生类型转换异常了,如果你不知道协程内部运行原理,肯定会一头雾水,这都什么东西?怎么会这样?
不要着急,接下里我们就一个一个的把问题都解决了,听我慢慢到来,不管是忘记写COROUTINE_SUSPENDED 还是既调用resume又直接return结果,他们出问题的原因是一样的。在lambda表达式中不明确return的时候,默认会把最后一行的代码的结果作为返回值。我们回头看看上面的忘记写COROUTINE_SUSPENDED的时候的代码:
suspend fun testSuspendResumeThread() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {con ->
thread(name = "子线程") {
Thread.sleep(1000)
con.resume("over")
}
//忘记写 return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}
这个lambda最后一个代码的结果是啥?没错,就是Thread对象。thrad函数开启一个线程后会返回Thred对象。所以以上代码等效于如下:
suspend fun testSuspendResumeThread() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {con ->
val thread = thread(name = "子线程") {
Thread.sleep(1000)
con.resume("over")
}
return@suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn thread
}
我们要求在不挂起的情况下真实数据的返回值类型通过suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn函数的泛型参数指定了是String,你要么返回一个String 要么就返回一个挂起标识COROUTINE_SUSPENDED,你现在给我来个Thread类型,在编译后的协程体代码里面优先判断返回值是不是挂起标识,如果是,协程挂起,如果不是会把结果强转成泛型参数指定类型,此处为String,所以协try catch 捕获到了一个Thread不能转换成Strin类型的异常。是不是合情合理。
ok第一个异常问题搞清楚原因了。继续找第二个异常的问题的原因,在说原因之前,你得先知道一个结论,一个协程在什么时候被认为执行完成,一个协程被认为执行完成的条件是协程体最后一行代码被执行了并且里面的所有子协程都执行完成。有了这个结论后我们继续看我们的代码执行流程,以下面代码为基础:
fun main() {
//第一步创建一个suspend 函数
val suspendFun : suspend () -> Unit = {
log("协程开始执行")
try {
val result = testSuspendResumeThread()
log("协程恢复后的结果: $result")
}catch (e : Exception){
log("捕获异常:$e")
}
}
//第二步创建一个协程,用一个匿名内部类作为协程的comletion。也就是协程执行完后的回调
val continuation = suspendFun.createCoroutine(object :Continuation<Unit>{
override val context: CoroutineContext
get() = EmptyCoroutineContext //没有指定调度器
//由于上面的异常已经被try catch了,这里就收不到了
override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Unit>) {
log("协程执行完毕")
}
})
//第三步开启一个协程
continuation.resume(Unit)
Thread.sleep(100000)
}
suspend fun testSuspendResumeThread() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {con ->
val thread = thread(name = "子线程") {
Thread.sleep(1000)
con.resume("over")
}
return@suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn thread
}
在我们创建的协程里面,调用testSuspendResumeThread,开启一个子线程后,里面立马返回了Thread对象,所以协程不会被挂起,继续执行,try cache 就捕获到了类型转换异常,打印出异常信息后,协程体里面就没有其他代码了,并且也没有任何其他子协程,因此我们创建的协程就执行完成了,我们的协程体里面的代码是被BaseContinuationImpl中的resumeWith函数里面的invokeSuspend调用的,协程执行完成后,resumeWith还会执行其他剩余操作:
internal abstract class BaseContinuationImpl(
public val completion: Continuation<Any?>?
) : Continuation<Any?>, CoroutineStackFrame, Serializable {
public final override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any?>) {
var current = this
var param = result
while (true) {
probeCoroutineResumed(current)
with(current) {
val completion = completion!!
val outcome: Result<Any?> =
try {
//在这里调用了编译器生成的类的invokeSuspend,可以理解为调用创建的
//协程体里面的代码。由于我们在协程题里面try cache了异常,因此
//异常不会被这里的try cache捕获到。协程体里面的代码全部执行完成
//outcome为Unit,接着就会走下面的releaseIntercepted()
val outcome = invokeSuspend(param)
if (outcome === COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) return
Result.success(outcome)
} catch (exception: Throwable) {
//如果我们不在协程体里面try catch异常,异常会被这里捕获。存入到Result中
//这个Result被赋值给outcome,最终会被下面的completion.resumeWith(outcome)调用。
//既然发了异常就不能藏着,必须得让外界知道。
Result.failure(exception)
}
//协程体里面代码执行完成后,继续执行releaseIntercepted
releaseIntercepted()
if (completion is BaseContinuationImpl) {
current = completion
param = outcome
} else {
//completion就是我们调用createCoroutine时传进去的那个匿名对象。
//这一行的代码的代用打印了”协程执行完毕“,
// 协程没有返回值outcome里面就是Unit,如果协程体内发生未被捕获的异常,outcome
//里面就会包含被上面try catch的异常。
completion.resumeWith(outcome)
return
}
}
}
}
xxxxx
}
进入到协程的releaseIntercepted里面:
protected override fun releaseIntercepted() {
//由于没有指定调度器,因此intercepted =this。 this就是我们创建的那个原始协程,BaseContinuationImpl对象
val intercepted = intercepted
//因此if条件不满足,不会走进去
if (intercepted != null && intercepted !== this) {
context[ContinuationInterceptor]!!.releaseInterceptedContinuation(intercepted)
}
//把CompletedContinuation赋值给intercepted,记住这里是关键
this.intercepted = CompletedContinuation
}
//这个函数在创建协程的时候会调用。因此有了intercepted = this
public fun intercepted(): Continuation<Any?> =
//如果没有指定调度器,返回this,并把this赋值给intercepted
intercepted ?: (context[ContinuationInterceptor]?.interceptContinuation(this) ?: this)
.also { intercepted = it }
到这里,一切正常,由于testSuspendResumeThread返回值不是COROUTINE_SUSPENDED而是一个Thread对象,协程没有被挂起,因为返回类型的错误倒是捕获了一个异常后协程快速的执行完成了,一秒钟后,在testSuspendResumeThread开启的子线程调用了协程的resume函数:
public inline fun <T> Continuation<T>.resume(value: T): Unit =
resumeWith(Result.success(value))
resume为Continuation的扩展函数,直接调用了协程的resumeWith,因此也就调用到了BaseContinuationImpl的resumeWith函数,并且把 结果"over" 传到了 BaseContinuationImpl的resumeWith函数里面,继续看resumeWith里面做了什么:
public final override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any?>) {
var current = this
var param = result
while (true) {
probeCoroutineResumed(current)
with(current) {
val completion = completion!!
val outcome: Result<Any?> =
try {
//第一步:
//param里面包含了结果"over",再次调用了我们创建的协程体里面的代码
//所以才有了协程执行完后才又打印了'over'的输出,这也就解释了上面提到的两个问题中的
//第二个问题:"协程执行完毕" 先于 "协程恢复后的结果: over" 被输出。
//这一次不会抛出类型转换异常了,协程体里面代码正常执行完毕,outcome 为Unit.
//为什么返回值为Unit,因为我们创建的就是一个没有返回值的的协程。
val outcome = invokeSuspend(param)
if (outcome === COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) return
Result.success(outcome)
} catch (exception: Throwable) {
Result.failure(exception)
}
//第二步:继续调用releaseIntercepted
releaseIntercepted()
if (completion is BaseContinuationImpl) {
current = completion
param = outcome
} else {
completion.resumeWith(outcome)
return
}
}
}
}
xxxxx
}
又走到了协程的releaseIntercepted函数里面:
protected override fun releaseIntercepted() {
//在前一次releaseIntercepted调用的时候intercepted被赋值为了CompletedContinuation
val intercepted = intercepted
//if条件满足。this为我们原始协程BaseContinuationImpl对象。
if (intercepted != null && intercepted !== this) {
//我们创建写的时候没有指定调度器,因此 context[ContinuationInterceptor] 为null.
//这就是协程内部抛出NullPointerException的原因。
context[ContinuationInterceptor]!!.releaseInterceptedContinuation(intercepted)
}
this.intercepted = CompletedContinuation
}
到目前我只,我们提出的前两个问题:
1. try catch处 捕获到一个异常(`ClassCastException`),协程内部还抛出了一个异常(`NullPointerException`)。
2. ` 协程执行完毕` 先于 `协程恢复后的结果: over` 被输出。
都找到愿原因了。别着急,还没完呢。前面不是说了,给创建的协程指定了一个调度器后,协程内部抛出的异常又不是NullPointerException,而是ClassCastException。这个问题的原因也是出在第二次调用releaseIntercepted这流程里面。其他地方执行流程都不变,我们重新回顾依稀两次调用releaseIntercepted。
第一次:
protected override fun releaseIntercepted() {
//由于指定了调度器,因此intercepted为DispatchedContination
val intercepted = intercepted
//if条件满足,会走进去
if (intercepted != null && intercepted !== this) {
//拿到调度器CoroutineDispatcher,由于指定了调度器,因此不会为空。
context[ContinuationInterceptor]!!.releaseInterceptedContinuation(intercepted)
}
//把CompletedContinuation赋值给intercepted
this.intercepted = CompletedContinuation
}
代码进入到了CoroutineDispatche的releaseInterceptedContinuation里面:
public final override fun releaseInterceptedContinuation(continuation: Continuation<*>) {
//第一次continuation为DispatchedContination,转换没有问题,
val dispatched = continuation as DispatchedContinuation<*>
dispatched.release()
}
第一次顺利执行完成,第二次执行releaseIntercepted的时候:
protected override fun releaseIntercepted() {
//第一次执行后 intercepted = CompletedContinuation
val intercepted = intercepted
//if条件满足,会走进去
if (intercepted != null && intercepted !== this) {
//拿到调度器CoroutineDispatcher,此时intercepted为CompletedContinuation
context[ContinuationInterceptor]!!.releaseInterceptedContinuation(intercepted)
}
//把CompletedContinuation赋值给intercepted
this.intercepted = CompletedContinuation
}
再次进入CoroutineDispatche的releaseInterceptedContinuation里面:
public final override fun releaseInterceptedContinuation(continuation: Continuation<*>) {
//第二次continuation为CompletedContinuation,出现类型转换异常,
val dispatched = continuation as DispatchedContinuation<*>
dispatched.release()
}
回头看看前面的输出结果中是不是输出的CompletedContinuation不是DispatchedContinuation的一个类型转换异常。这下问题3也找到原因了。
经过前面3个问题的分析,问题4两次打印的问题是不是就呼之欲出了,在testSuspendResumeThread中直接返回结果"over"协程不会被挂起有了第一次打印。一秒后,子线程调用协程的resuem再次把结果"over"传到了协程体里面就有了第二次打印。
在kotlin源码的的注释中也写到,不建议在suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn里面直接调用协程的resume,这里所说的直接调用是指的同步调用,也就是说在同一个线程里面调用,同一个线程栈里面调用,比如:
suspend fun testSuspendResumeThread() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {con ->
con.resume("over")
}
这也相对于:
suspend fun testSuspendResumeThread() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {con ->
con.resume("over")
return@suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn Unit
}
至于这样写了会出现什么问题?想必经过前面的学习,你应该知道了。第一:Unit不能转成String的类型异常,第二,没有指定调度器会协程内部会抛出空指针异常,指定了调度器会抛出类型转换异常。
总结:
suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn存在的问题如下:
- 调用
suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn挂起后协程不会被恢复到原来的线程环境里面执行剩余代码。- 使用不当会造成各种异常。
经过这么一分析,suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn存在这么多问题,那为什么还要发明他呢?存在即合理,suspendCoroutine和suspendCancellableCoroutine中用到了他,并且还把suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn存在的问题完美解决了。
suspendCoroutine
有了前面suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn的经验,从命名上就可以知道suspendCoroutine他要做的事情是挂起协程,不支持直接返回,从源头上杜绝你使用不当造成suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn中retun错存在的问题。那你肯定会想,如果我的需求是有可能挂起也有可能不需要挂起直接返回怎么办呢?难道koltin协程的开发者就这么傻吗?想不到这么简单需求的问题吗?显然是不可能的,看似不支持直接返回,必须挂起,实际上是可以直接返回的。使用suspendCoroutine时,不管是挂起还是不需要挂起,想要把结果返回,都要通过调用continuation.resume这种方式,并且suspendCoroutine还完美绝了挂起恢复后的线程问题。它是怎么做到的呢?我们先看源码:
public suspend inline fun <T> suspendCoroutine(crossinline block: (Continuation<T>) -> Unit): T {
contract { callsInPlace(block, InvocationKind.EXACTLY_ONCE) }
return suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn { c: Continuation<T> ->
/**
* 第一步:拿到协程,c 这个c为原始协程。
* 第二步:通过c.intercepted()拿到原始协程的调度器协程DispatchedContinuation,
* DispatchedContinuation也是一个Continuation,它里面包含了原始协程和一个调度器
* 第三步:创建一个SafeContinuation,把DispatchedContinuation放进去。
* 第四步:block为我们的lambda表达式,执行block的事后使用SafeContinuation代替了原始协程。
*/
val safe = SafeContinuation(c.intercepted())
//block中返回任何东西都对suspendCoroutine最终的返回值没有任何影响
//这里就杜绝了 suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn返回不当的问题。
//但是suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn总归需要有返回值的,那么怎么办呢?
//kotlin开发者们帮你做了。通过 safe.getOrThrow()把值返回出去。
block(safe)
/**
*
*
* suspendCoroutine的返回值有两种情况:
* 第一:在safe.getOrThrow()这行代码执行之前如果在block代码中调用了
* SafeContinuation的resume,那么safe.getOrThrow()的结果就是resume时传进去的值。
* 这样suspendCoroutine就直接把结果返回出去了,调用suspendCoroutine的函数
* 就不会被挂起了。
* 第二:在执行safe.getOrThrow()这行代码的时候,SafeContinuation的resume还没被调用,那么
* safe.getOrThrow()的结果就是COROUTINE_SUSPENDED。调用suspendCoroutine的函数就
* 会被挂起。
*
*
* 是不是很巧妙的就解决了返回值不当问题。既能满足挂起返回OROUTINE_SUSPENDED又能满足不需要
* 挂起时返回需要的数据。
*
* 同时通过c.intercepted()拿到了原始协程的调度器协程,让挂起的协程恢复在原来的线程环境里面。
*/
safe.getOrThrow()
}
}
所以当我们在使用suspendCoroutine函数后,收到的Continuation并不是我们原始协程,而是经过层层包装的协程,他们之间的关系如下:

原来我们想要在suspend函数中使用Continuation,可以通过suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn,现在kotlin又提供了一个函数叫suspendCoroutine,通过它我们也可以拿到Continuation,我们又多了一种在suspned函数中获取Continuation的方式:

在suspendCoroutine中kotlin为我们把原始协程进行了层层包装,最终我么拿到的Continuatin就变成了SafeContinuation.当我们在代码中调用resume时也就变成了调用SafeContinuation的resume。这样做目的是什么呢?这样做用两个重要的目的:
**第一:安全(Safe):**这儿的安全是指resume只能调用一次。不能多次调用resume,多次调用会抛出一个 IllegalStateException("Already resumed")
**第二:线程切换:**使用suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn时拿到的Continuation为原始协程,调用它的resume被恢复后的协程所运行的线程不受协程调度器控制了,而是由调用resume函数所在的线程决定。因此为了让协程被恢复在原来的线程里面。为了解决这个问题,suspendCoroutine 传给我们的协程不再是原始协程,而是SafeContinuation。所以在恢复一个协程时我们调用SafeContinuation的resume,SafeContinuation中调用DispatchedContinuation的resume,在DispatchedContinuation中用调度器去执行原始协程的resume调用操作。这样就达到了让原始协程被恢复在其原来的线程环境里面。
SafeContinuation中的安全除了上面提到的,还有一个安全作用就是解决了suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn使用不当的各种异常问题
suspendCoroutine函数的签名:
public suspend inline fun <T> suspendCoroutine(crossinline block: (Continuation<T>) -> Unit): T
我们代码是写在block函数里面的,但是blocK的函数是没有返回值的,也就是说不管你在block代码块return任何东西都没有任何意义。这样就杜绝了像在使用suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn时返回不当的各种异常,我们一个简单的例子来看看到底是怎么做到的?
fun main() {
GlobalScope.launch {
val result = test("kotlin coroutine")
println( result)
}
Thread.sleep(100000)
}
suspend fun test(arg : String) = suspendCoroutine<String> { con ->
//此处没有任何耗时操作。直接调用resume。协程会挂起吗?
con.resume("Hello $arg by resume ")
}
在跟进去看SafeContinuation的resume是怎么做到之前,先看看suspendCoroutine里面是怎么做的:
public suspend inline fun <T> suspendCoroutine(crossinline block: (Continuation<T>) -> Unit): T {
contract { callsInPlace(block, InvocationKind.EXACTLY_ONCE) }
return suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn { c: Continuation<T> ->
//创建好一个SafeContinuation后
val safe = SafeContinuation(c.intercepted())
//调用block函数,也就是执行上面 con.resume("Hello $arg by resume ")这一行代码
block(safe)
safe.getOrThrow()
}
}
resume函数Continuationde的扩展函数:
public inline fun <T> Continuation<T>.resume(value: T): Unit =
resumeWith(Result.success(value))
进入到SafeContinuation的resumeWith函数:
public actual override fun resumeWith(result: Result<T>) {
while (true) { // lock-free loop
//根据result决定,这个result是个什么呢?
val cur = this.result // atomic read
when {
cur === UNDECIDED -> if (RESULT.compareAndSet(this, UNDECIDED, result.value)) return
cur === COROUTINE_SUSPENDED -> if (RESULT.compareAndSet(this, COROUTINE_SUSPENDED, RESUMED)) {
delegate.resumeWith(result)
return
}
else -> throw IllegalStateException("Already resumed")
}
}
}
看看这个resut是在什么时候初始化的。
internal actual class SafeContinuation<in T>
internal actual constructor(
private val delegate: Continuation<T>,
initialResult: Any?
) : Continuation<T>, CoroutineStackFrame {
//在suspendCoroutine中调用该构造函数,这个构造函数又调用主构造函数,
internal actual constructor(delegate: Continuation<T>) : this(delegate, UNDECIDED)
//初始值就可以知道了为 UNDECIDED
private var result: Any? = initialResult
}
所以在执行resumeWith的时候result的值为UNDECIDED。ok 接着继续:
public actual override fun resumeWith(result: Result<T>) {
while (true) { // lock-free loop
//cur == UNDECIDED
val cur = this.result
when {
/**
* 这个RESULT.compareAndSet操作就是一个CAS操作,意思就是如果this.result原来的值
* 为UNDECIDED,那么就把result.value(这个result.value就是我们在外面调用resume时传的那个值)
* 赋值给this.result,并返回true,相当于把resume调用时传进来的值保存在了this.result这个变量中。
*
* 如果this.result原来的值不为UNDECIDED就return false.
*
* 所以此处就会把外面调用resume时传进来的值保存在了this.result变量中,然后就return 出去了。
* 也就是说们上面con.resume("Hello $arg by resume ")这一行代码只是把”Hello $arg by resume“
* 保存在了this.result中,并没有去做唤醒原始协程的操作。
*/
cur === UNDECIDED -> if (RESULT.compareAndSet(this, UNDECIDED, result.value)) return
cur === COROUTINE_SUSPENDED -> if (RESULT.compareAndSet(this, COROUTINE_SUSPENDED, RESUMED)) {
delegate.resumeWith(result)
return
}
else -> throw IllegalStateException("Already resumed")
}
}
}
在resumeWith中把值保存了后,就直接return了。这个时候在回到suspendCoroutine中,block就执行完了。执行下一行代码safe.getOrThrow():
@PublishedApi
internal actual fun getOrThrow(): Any? {
var result = this.result
//在上面resumeWith中,this.result值已经被设置为了 ”Hello $arg by resume“
if (result === UNDECIDED) {
if (RESULT.compareAndSet(this, UNDECIDED, COROUTINE_SUSPENDED)) return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
result = this.result // reread volatile var
}
return when {
result === RESUMED -> COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
result is Result.Failure -> throw result.exception
else -> result //所以最终走到这里,把”Hello $arg by resume“返回出去了
}
}
所以最终suspendCoroutine方法中:
public suspend inline fun <T> suspendCoroutine(crossinline block: (Continuation<T>) -> Unit): T {
contract { callsInPlace(block, InvocationKind.EXACTLY_ONCE) }
return suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn { c: Continuation<T> ->
//创建好一个SafeContinuation后
val safe = SafeContinuation(c.intercepted())
//调用block函数,也就是执行上面 con.resume("Hello $arg by resume ")这一行代码
block(safe)
/**
* 所以最后safe.getOrThrow()的结果为"Hello $arg by resume“,作为
* suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn的返回值返回到
* suspendCoroutine中,在suspendCoroutine中又把结果返回到调用它的test函数中。
* 最终test函数直接把这个结果返回出去了。从而实现了没有挂起直接返回结果。
*/
safe.getOrThrow()
}
}
如果在test中需要挂起又是怎么一个流程呢?
suspend fun test(arg : String) = suspendCoroutine<String> { con ->
//开启一个子线程模拟耗时操作
thread {
Thread.sleep(1000)
//耗时完成后,调用resume恢复协程
con.resume("Hello $arg by resume ")
}
}
同样在suspendCoroutine函数中:
public suspend inline fun <T> suspendCoroutine(crossinline block: (Continuation<T>) -> Unit): T {
contract { callsInPlace(block, InvocationKind.EXACTLY_ONCE) }
return suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn { c: Continuation<T> ->
//创建好一个SafeContinuation后
val safe = SafeContinuation(c.intercepted())
//调用block函数,开启线程后,block就执行完了。
block(safe)
//因此调用safe.getOrThrow()的时候,resume还没有调用。
safe.getOrThrow()
}
}
先调用getOrThrow():
@PublishedApi
internal actual fun getOrThrow(): Any? {
var result = this.result
//这个时候this.result的值还是初始值为UNDECIDED
if (result === UNDECIDED) {
//把this.result值设置为COROUTINE_SUSPENDED,然后返回COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
if (RESULT.compareAndSet(this, UNDECIDED, COROUTINE_SUSPENDED)) return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
result = this.result
}
return when {
result === RESUMED -> COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
result is Result.Failure -> throw result.exception
else -> result
}
}
getOrThrow()返回了COROUTINE_SUSPENDED,因此,suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn把COROUTINE_SUSPENDED返回给了suspendCoroutine,把``suspendCoroutine又把COROUTINE_SUSPENDED作为结果返回到了test中。最终test的返回结果就是COROUTINE_SUSPENDED,这样test`函数就被协程挂起了。
耗时操作执行完成后在,再调用resume的时候:
public actual override fun resumeWith(result: Result<T>) {
while (true) {
//在调用getOrThrow时 this.result值被设置为了COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
val cur = this.result
when {
cur === UNDECIDED -> if (RESULT.compareAndSet(this, UNDECIDED, result.value)) return
//通过compareAndSet把this.result设置为RESUMED
cur === COROUTINE_SUSPENDED -> if (RESULT.compareAndSet(this, COROUTINE_SUSPENDED, RESUMED)) {
//delegate为创建SafeContinuation是传的DispatchedContinuation
//在DispatchedContinuation的resumeWith中会用协程的调度器去把原始协程恢复
//从而让挂起的协程恢复在原来的线程环境里面。
delegate.resumeWith(result)
return
}
else -> throw IllegalStateException("Already resumed")
}
}
}
suspendCoroutine的整个流程就差不多完事了。
suspendCancellableCoroutine
这个和suspendCoroutine在使用行为上基本一致,只是它多了一个可支持取消的功能。
public suspend inline fun <T> suspendCancellableCoroutine(
crossinline block: (CancellableContinuation<T>) -> Unit
): T =
suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn { uCont ->
val cancellable = CancellableContinuationImpl(uCont.intercepted(), resumeMode = MODE_CANCELLABLE)
cancellable.initCancellability()
block(cancellable)
cancellable.getResult()
}
从他的源码中可以看出它里面不是使用的SafeContinuation。而是CancellableContinuationImpl。我们拿到这个CancellableContinuationImpl后可以调用他的invokeOnCancellation注册一个协程取消的监听。一遍再协程取消时取消我们的耗时任务。
此处就在过多分析。感兴趣的可以自行研究。
kotlin 还有一个internal的suspendCancellableCoroutineReusable函数,这个函数和suspendCancellableCoroutine很像,重在一个Resuable。意思即使它不用每次都重新重建CancellableContinuationImpl对象