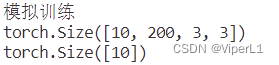本文实验的部分代码参考
Hyperspectral-Classification![]() https://github.com/eecn/Hyperspectral-Classification如果对dataloader的工作原理不太清楚可以参见
https://github.com/eecn/Hyperspectral-Classification如果对dataloader的工作原理不太清楚可以参见
[Pytorch]DataSet和DataLoader逐句详解![]() https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37878740/article/details/129350390?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37878740/article/details/129350390?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
一、原理解析
常见的高光谱数据维.mat格式,由数据文件和gt(ground-truth)文件组成,图像数据和标签数据。这里以印度松数据为例,图像数据的尺寸为145*145*200,标签数据的尺寸为145*145*1。
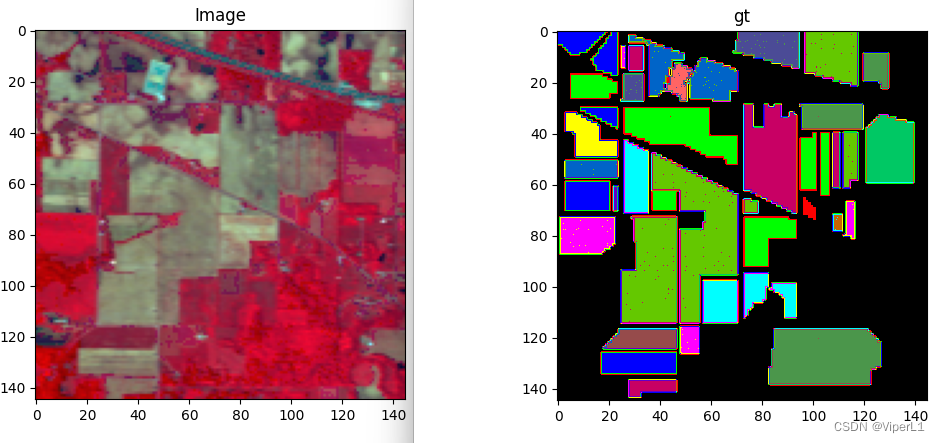
本文的实验代码主要思想如下:
①获取高光谱数据集和gt标签集
②按一定比例将数据集切割为训练集、测试集、验证集
③将训练集和验证集装入dataloader
二、获取高光谱数据
# 解析高光谱数据
def get_dataset(target_folder,dataset_name):
palette = None
# 拼接文件路径
folder = target_folder + '/' + dataset_name
# 打开数据文件
if dataset_name == 'IndianPines':
img = open_file(folder + '/Indian_pines_corrected.mat')
img = img['indian_pines_corrected'] #选择矩阵
rgb_bands = (43, 21, 11) # AVIRIS sensor
gt = open_file(folder + '/Indian_pines_gt.mat')['indian_pines_gt']
# 设置标签
label_values = ["Undefined", "Alfalfa", "Corn-notill", "Corn-mintill",
"Corn", "Grass-pasture", "Grass-trees",
"Grass-pasture-mowed", "Hay-windrowed", "Oats",
"Soybean-notill", "Soybean-mintill", "Soybean-clean",
"Wheat", "Woods", "Buildings-Grass-Trees-Drives",
"Stone-Steel-Towers"]
ignored_labels = [0]
# 设置背景标签
nan_mask = np.isnan(img.sum(axis=-1))
img[nan_mask] = 0
gt[nan_mask] = 0
ignored_labels.append(0)
# 数据格式转换
ignored_labels = list(set(ignored_labels))
img = np.asarray(img, dtype='float32')
data = img.reshape(np.prod(img.shape[:2]), np.prod(img.shape[2:]))
data = preprocessing.minmax_scale(data)
img = data.reshape(img.shape)
return img, gt, label_values, ignored_labels, rgb_bands, palette这里仅适配了印度松,有其他数据集需求的可以自行修改内部的参数。
该函数会从.mat文件中获取图像文件和gt文件,并将相关信息打包返回,其中,读取文件的函数为:open_file(.)
# 打开高光谱文件
def open_file(dataset):
_, ext = os.path.splitext(dataset)
ext = ext.lower()
# 根据格式不同打开文件
if ext == '.mat':
return io.loadmat(dataset)
elif ext == '.tif' or ext == '.tiff':
return imageio.imread(dataset)
elif ext == '.hdr':
img = spectral.open_image(dataset)
return img.load()
else:
raise ValueError("Unknown file format: {}".format(ext))在主函数中调用如下:
DataSetName = 'IndianPines'
target_folder = 'Dataset'
img, gt, LABEL_VALUES, IGNORED_LABELS, RGB_BANDS,
palette = get_dataset(target_folder,DataSetName)
二、DataSet类
在使用DataSet类加载数据集前,我们需要将数据集进行随机划分,这里直接调用了原项目的sample_gt(.)函数对gt进行分割。
def sample_gt(gt, train_size, mode='random'):
indices = np.nonzero(gt)
X = list(zip(*indices)) # x,y features
y = gt[indices].ravel() # classes
train_gt = np.zeros_like(gt)
test_gt = np.zeros_like(gt)
if train_size > 1:
train_size = int(train_size)
if mode == 'random':
train_indices, test_indices = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(X, train_size=train_size, stratify=y)
train_indices = [list(t) for t in zip(*train_indices)]
test_indices = [list(t) for t in zip(*test_indices)]
train_gt[tuple(train_indices)] = gt[tuple(train_indices)]
test_gt[tuple(test_indices)] = gt[tuple(test_indices)]
elif mode == 'fixed':
print("Sampling {} with train size = {}".format(mode, train_size))
train_indices, test_indices = [], []
for c in np.unique(gt):
if c == 0:
continue
indices = np.nonzero(gt == c)
X = list(zip(*indices)) # x,y features
train, test = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(X, train_size=train_size)
train_indices += train
test_indices += test
train_indices = [list(t) for t in zip(*train_indices)]
test_indices = [list(t) for t in zip(*test_indices)]
train_gt[train_indices] = gt[train_indices]
test_gt[test_indices] = gt[test_indices]
elif mode == 'disjoint':
train_gt = np.copy(gt)
test_gt = np.copy(gt)
for c in np.unique(gt):
mask = gt == c
for x in range(gt.shape[0]):
first_half_count = np.count_nonzero(mask[:x, :])
second_half_count = np.count_nonzero(mask[x:, :])
try:
ratio = first_half_count / second_half_count
if ratio > 0.9 * train_size and ratio < 1.1 * train_size:
break
except ZeroDivisionError:
continue
mask[:x, :] = 0
train_gt[mask] = 0
test_gt[train_gt > 0] = 0
else:
raise ValueError("{} sampling is not implemented yet.".format(mode))
return train_gt, test_gt主函数调用如下:
#--训练集占比
SAMPLE_PERCENTAGE = 0.1
#--数据集划分
train_gt, test_gt = sample_gt(gt,SAMPLE_PERCENTAGE,mode='random')
train_gt, val_gt = sample_gt(train_gt, 0.95, mode='random')随后将划分好的数据集放入DataSet类中,DataSet类共计9个参数,分别代表:
data-高光谱数据集;
gt-标签集;
patch_size-邻居个数(即感受野,影响提取的每个块大小);
ignored_labels - 需要忽略的类别;
flip_augmentation - 是否使用随机折叠;
radiation_augmentation - 是否使用随机噪声;
mixture_augmentation - 是否对光谱进行随机混合
center_pixel - 设置为True以仅考虑中心像素的标签
supervision - 训练模式,可选'full'-全监督 或 'semi'-半监督DataSet如下:
# 高光谱dataset类
class HyperX(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self,data,gt,patch_size,ignored_labels,flip_augmentation,radiation_augmentation,mixture_augmentation,center_pixel,supervision):
super().__init__()
self.data = data
self.label = gt
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.ignored_labels = ignored_labels
self.flip_augmentation = flip_augmentation
self.radiation_augmentation = radiation_augmentation
self.mixture_augmentation = mixture_augmentation
self.center_pixel = center_pixel
supervision = supervision
# 监督模式
if supervision == 'full':
mask = np.ones_like(gt)
for l in self.ignored_labels:
mask[gt == l] = 0
# 半监督模式
elif supervision == 'semi':
mask = np.ones_like(gt)
x_pos, y_pos = np.nonzero(mask)
p = self.patch_size // 2
self.indices = np.array([(x,y) for x,y in zip(x_pos, y_pos) if x > p-1 and x < data.shape[0] - p and y > p-1 and y < data.shape[1] - p])
self.labels = [self.label[x,y] for x,y in self.indices]
np.random.shuffle(self.indices)
@staticmethod #静态方法
def flip(*arrays):
horizontal = np.random.random() > 0.5
vertical = np.random.random() > 0.5
if horizontal:
arrays = [np.fliplr(arr) for arr in arrays]
if vertical:
arrays = [np.flipud(arr) for arr in arrays]
return arrays
@staticmethod
def radiation_noise(data, alpha_range=(0.9, 1.1), beta=1/25):
alpha = np.random.uniform(*alpha_range)
noise = np.random.normal(loc=0., scale=1.0, size=data.shape)
return alpha * data + beta * noise
def mixture_noise(self, data, label, beta=1/25):
alpha1, alpha2 = np.random.uniform(0.01, 1., size=2)
noise = np.random.normal(loc=0., scale=1.0, size=data.shape)
data2 = np.zeros_like(data)
for idx, value in np.ndenumerate(label):
if value not in self.ignored_labels:
l_indices = np.nonzero(self.labels == value)[0]
l_indice = np.random.choice(l_indices)
assert(self.labels[l_indice] == value)
x, y = self.indices[l_indice]
data2[idx] = self.data[x,y]
return (alpha1 * data + alpha2 * data2) / (alpha1 + alpha2) + beta * noise
# 获得长度数据
def __len__(self):
return len(self.indices)
# 获得元素
def __getitem__(self, i):
x,y = self.indices[i]
x1,y1 = x-self.patch_size // 2, y-self.patch_size // 2
x2,y2 = x1+self.patch_size, y1+self.patch_size
data = self.data[x1:x2,y1:y2]
label = self.label[x1:x2,y1:y2]
# 选择数据增强模式
if self.flip_augmentation and self.patch_size > 1: #
data, label = self.flip(data, label)
if self.radiation_augmentation and np.random.random() < 0.1:
data = self.radiation_noise(data)
if self.mixture_augmentation and np.random.random() < 0.2:
data = self.mixture_noise(data, label)
# mat->np->tensor
data = np.asarray(np.copy(data).transpose((2, 0, 1)), dtype='float32')
label = np.asarray(np.copy(label), dtype='int64')
data = torch.from_numpy(data)
label = torch.from_numpy(label)
# 提取中心标签
if self.center_pixel and self.patch_size > 1:
label = label[self.patch_size // 2, self.patch_size // 2]
# 使用不可见光谱时删除未使用部分
elif self.patch_size == 1:
data = data[:, 0, 0]
label = label[0, 0]
# 进行3D卷积时增加一维
if self.patch_size > 1:
data = data.unsqueeze(0)
return data,labeldataset_collate:
def HyperX_collate(batch):
datas = []
labels = []
for data, label in batch:
datas.append(data)
labels.append(label)
datas = np.array(datas)
labels = np.array(labels)
return datas, labels在主函数中调用如下:
# 调用dataset
train_dataset = HyperX(img, train_gt,patch_size,IGNORED_LABELS,True,True,True,True,'full')
val_dataset = HyperX(img, val_gt,patch_size,IGNORED_LABELS,True,True,True,True,'full')
# 调用dataloader
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset,batch_size=batch_size,pin_memory=True,shuffle=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset,batch_size=batch_size,pin_memory=True,shuffle=True)三、数据展示
# 可视化展示
for item in train_dataset:
img,label = item
img = torch.squeeze(img,0) #除去第0维度
img = img.permute(1,2,0) #调整通道位置
print('tensor尺寸:{}'.format(img.shape))
img = img.numpy() #转换为numpy
view1 = spy.imshow(data=img, bands=RGB_BANDS, title="train") # 图像显示
print('标签编号:{}'.format(label.numpy()))邻居个数patch_size设置为9,运行后得到如下结果:
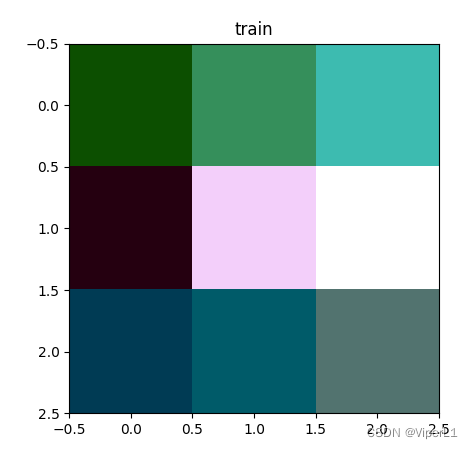
![]()
四、模拟训练
print("模拟训练")
for epoch in range(3):
step = 0
for data in train_loader:
imgs, labels = data
print(imgs.shape)
print(labels.shape)
img = imgs[0]
img = torch.squeeze(img,0).permute(1,2,0).numpy() #通道调整和numpy转换
view1 = spy.imshow(data=img, bands=RGB_BANDS, title="train") # 图像显示
step=step+1
input("按任意键继续")测试结果如下: