一、 多线程并发情况下数据异常回滚解决方案
在需要多个没有前后顺序的数据操作情况下,一般我们可以选择使用并发的形式去操作,以提高处理的速度,但并发情况下,我们使用 @Transactional 还能解决事务回滚问题吗。
例如有下面表结构:
CREATE TABLE `test` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`thread_name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
假如需要进行两个写操作,并且写没有先后顺序之分,我们可以开个线程并发去写,这里以 JdbcTemplate 操作为例,使用其他DB工具也是一样的效果,例如:
@Service
public class TestService {
@Resource
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void test() {
// 放入子线程
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
});
// ....其他操作...
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
// ....其他操作...
}
}
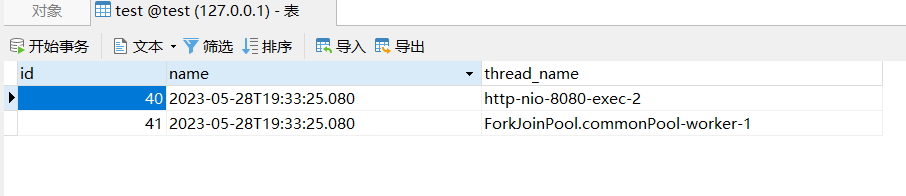
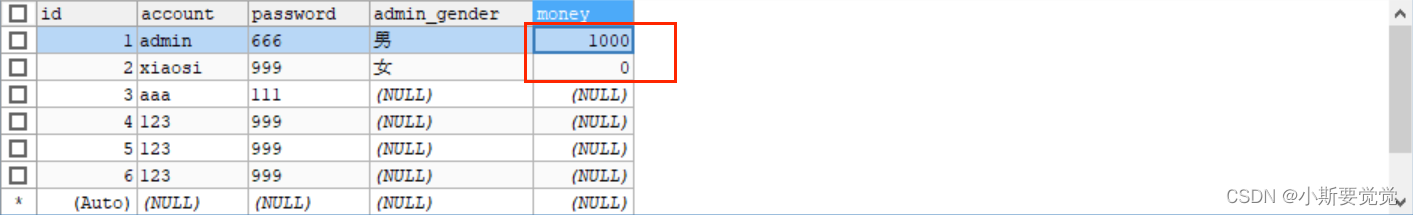
数据库成功写入了两条数据,假如在做其他操作时,发生了异常:
@Service
public class TestService {
@Resource
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void test() {
// 放入子线程
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
});
// ....其他操作...
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
// ....其他操作...
int a = 1 / 0;
}
}
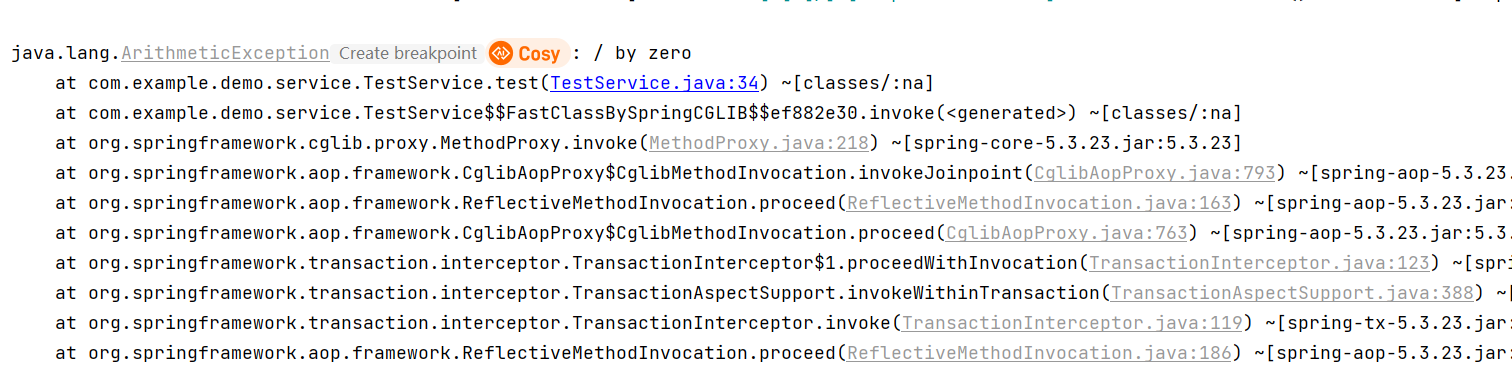
运行后可以看到已经抛出了异常:
查看数据库:

发现还是写入了一条数据,线程中的操作并没有回滚,但主线程的回滚了,既然一个回滚一个没有回滚肯定用的不是同一个数据库连接,这里源码看下 JdbcTemplate 从哪里获取的数据库连接:
进到JdbcTemplate 的 update(String sql, @Nullable Object... args) 方法中:
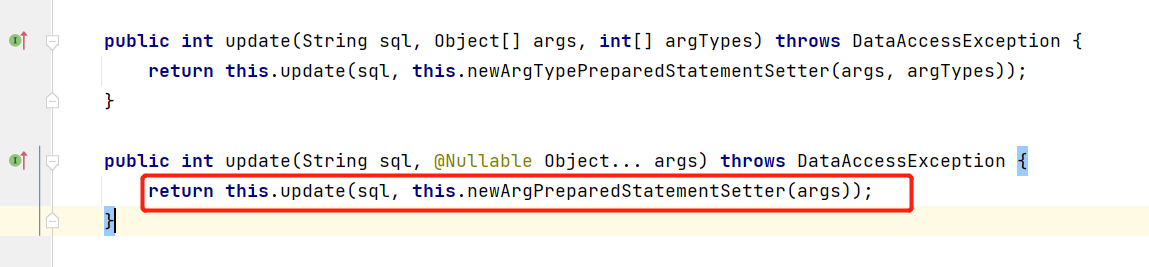
调用了当前类的 update(String sql, @Nullable PreparedStatementSetter pss) 方法中,最终调用的是当前类的 update(final PreparedStatementCreator psc, @Nullable final PreparedStatementSetter pss) 方法:
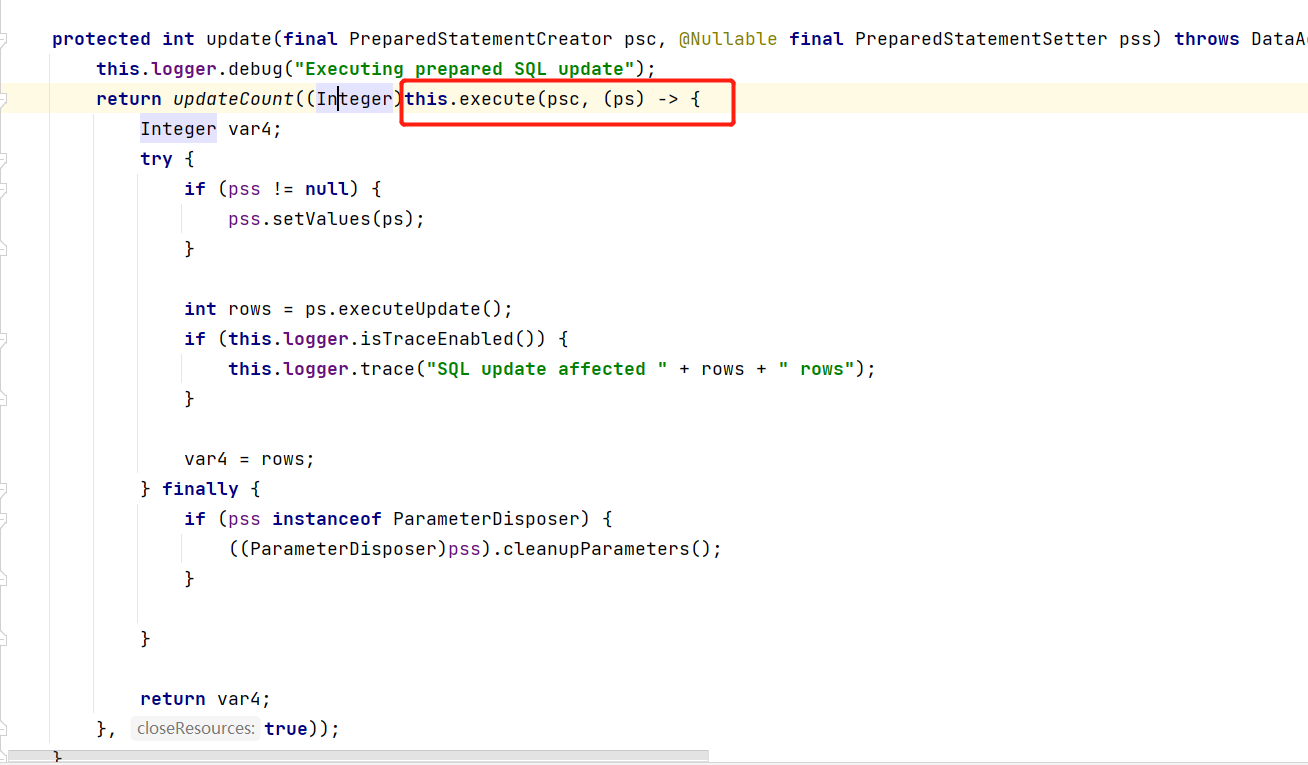
这里主要使用了 execute(StatementCallback<T> action) 方法,进到该方法中:
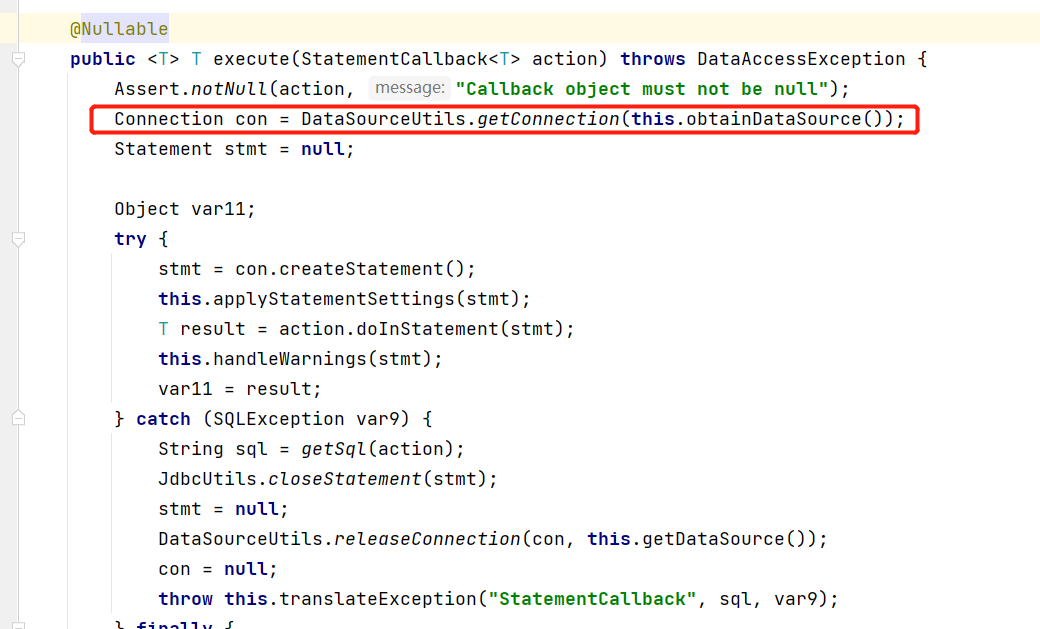
这里可以看出通过 DataSourceUtils.getConnection 方法获取数据库连接,进到该方法中:
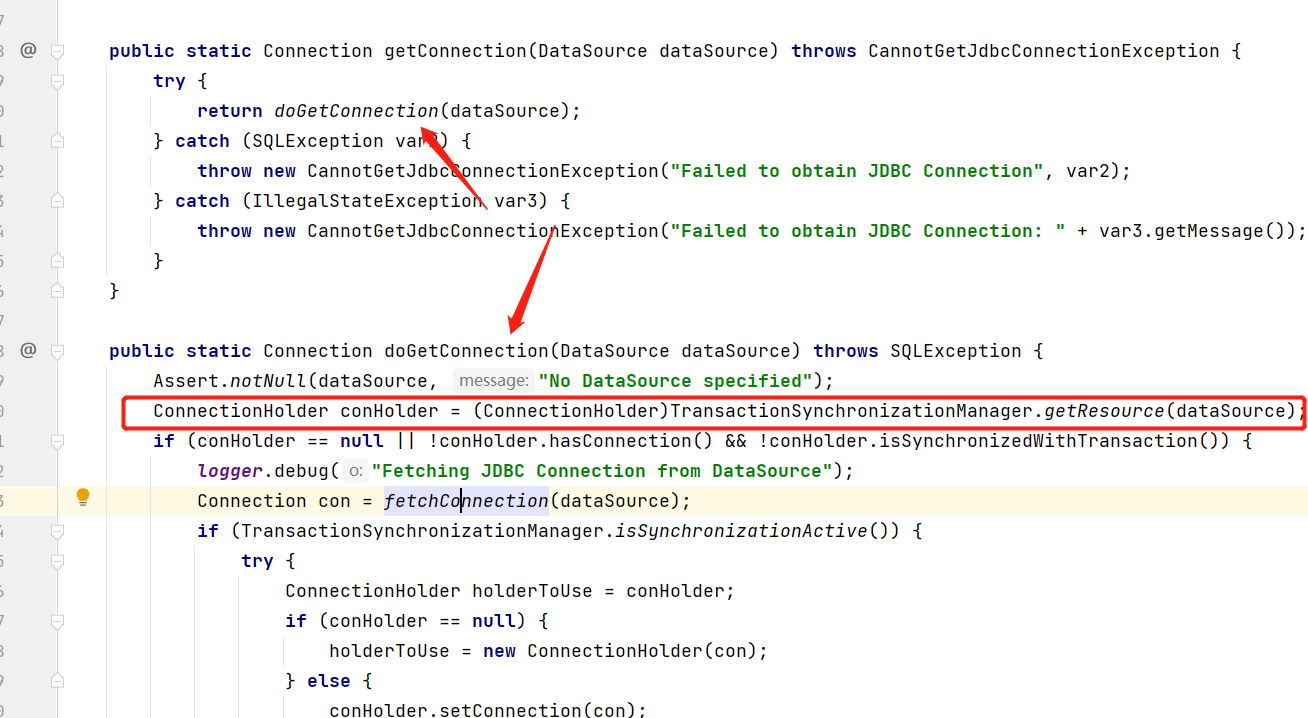
这里看到 TransactionSynchronizationManager 是不是有点熟悉,在本专栏前面讲解@Transactional 声明式事务执行源码分析时,其中开启事务的逻辑中,就是使用 TransactionSynchronizationManager 获取的数据库连接,如果对这部分还不了解,可以看下下面这篇文章:
SpringTx 源码解析 - @Transactional 声明式事务执行原理
其实在String生态中,获取数据库连接基本都默认使用了 TransactionSynchronizationManager。
这里也来看下当 @Transactional 注解情况下开启事务时获取连接的逻辑,在DataSourceTransactionManager 下的 doGetTransaction 方法下:
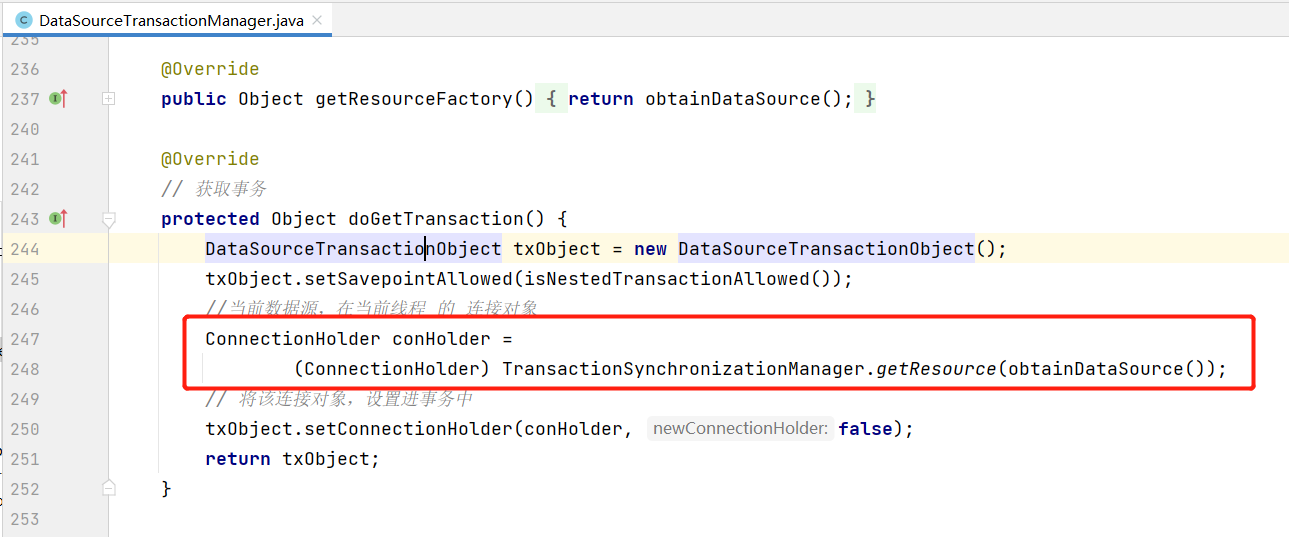
可以看到这里同样也是使用的 TransactionSynchronizationManager 获取连接。
下面看下TransactionSynchronizationManager 都做了啥,进到 getResource 方法:
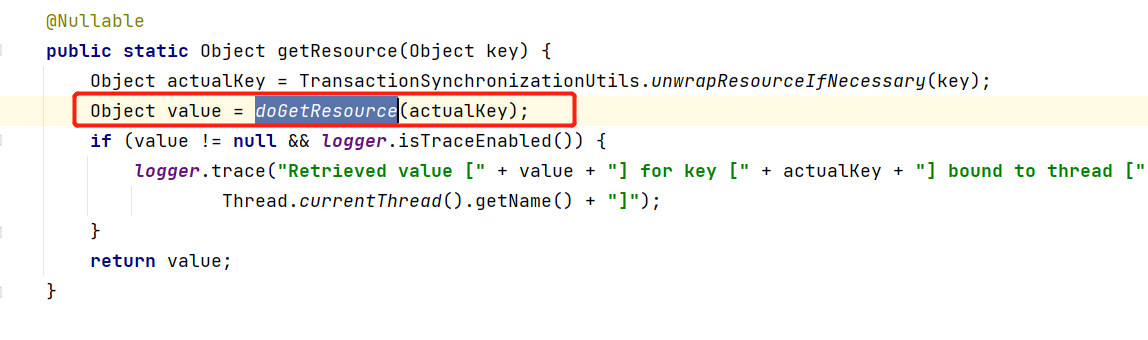
这里又触发了 doGetResource 方法,进入到该方法下:
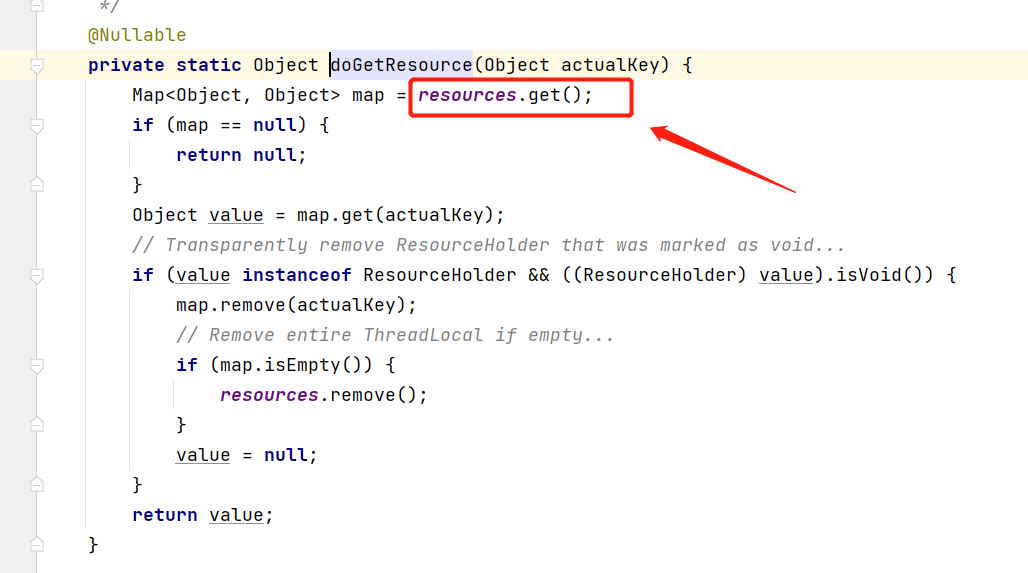
这里明显从 resources 中获取的,看下 resources 到底是个啥:
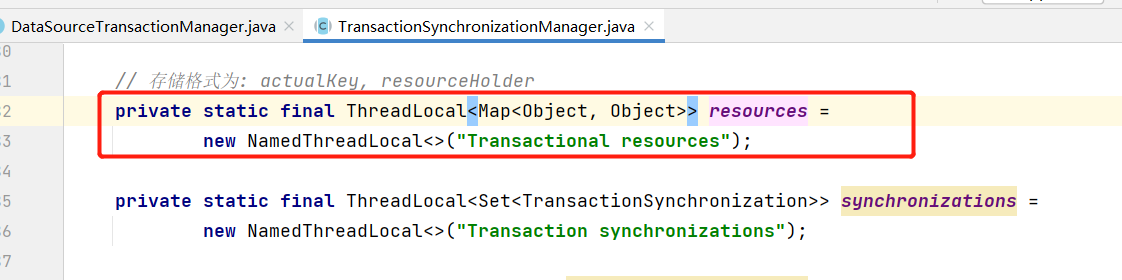
是一个 ThreadLocal ,现在是不是就明白了,在没有多线程的情况下,开启事务时就将拿到的连接放到了当前的 ThreadLocal 中,后面其他组件执行数据操作,同样先从ThreadLocal 中取连接,这样都在一个连接中操作,自然也可以进行回滚,由于上面我们是单独开启了线程,线程中的操作尝试获取 ThreadLocal中的连接,但获取不到,所以只能获取一个新的连接操作,导致了声明事务时的连接和实际操作时的连接不一致,从而无法进行回滚。
现在找到了问题的原因我们怎么解决呢?
既然是因为 ThreadLocal 导致的连接不同,那我们在开启线程时,就给它补充确实的信息,获取连接是用的 TransactionSynchronizationManager ,那添加同样也用 TransactionSynchronizationManager,通过观察 TransactionSynchronizationManager 的 Api,获取连接句柄可以使用 :
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
其中key就是当前数据源,绑定句柄可以使用:
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, conHolder);
移除句柄可以使用 :
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(dataSource);
下面对前面的程序进行改造:
@Service
public class TestService {
@Resource
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Resource
DataSource dataSource;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void test() {
// 获取当前线程的句柄
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
// 放入子线程
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 子线程绑定
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, conHolder);
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
// 解绑
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(dataSource);
});
// ....其他操作...
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
// ....其他操作...
int a = 1 / 0;
}
}
再次运行:
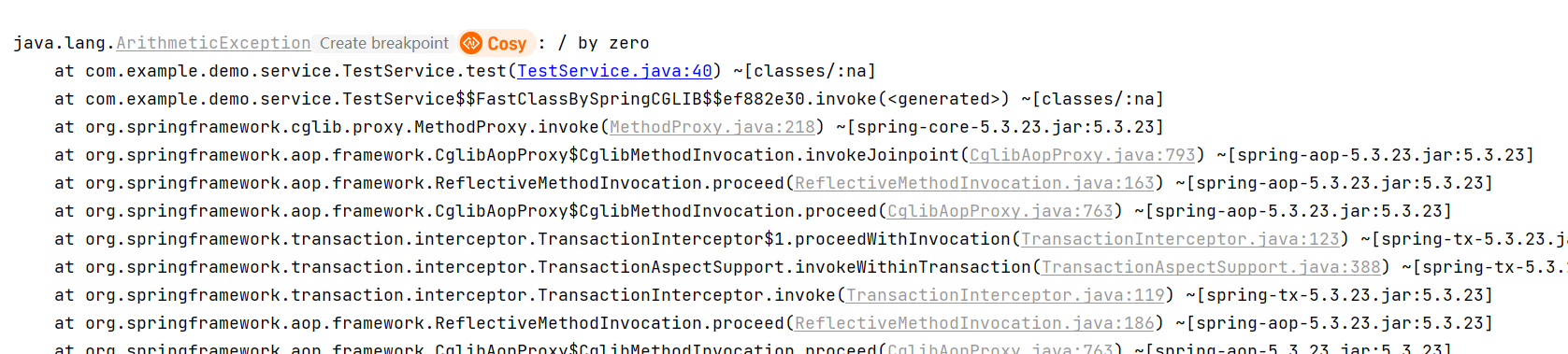
已经出现异常,查看数据库:
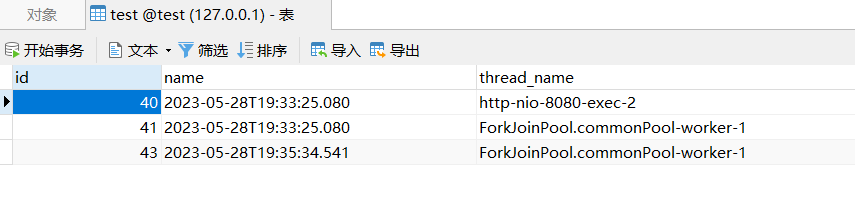
数据成功回滚了!
假入异常是出现在子线程的还可以回滚吗,下面开始实验一下:
@Service
public class TestService {
@Resource
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Resource
DataSource dataSource;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void test() {
// 获取当前线程的句柄
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
// 放入子线程
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 子线程绑定
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, conHolder);
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
int a = 1 / 0;
// 解绑
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(dataSource);
});
// ....其他操作...
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
// ....其他操作...
}
}
运行后,查看数据:
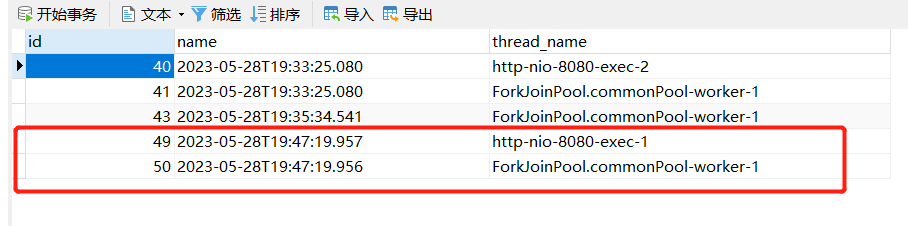
发现没有出现回滚现象,这是因为异常在子线程的 Runnable 中,父线程没有感知到异常,怎么让父线程感知呢,我们可以加个在数据处理最后加个 join ,如果再出现异常就抛到父线程了:
@Service
public class TestService {
@Resource
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Resource
DataSource dataSource;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void test() {
// 获取当前线程的句柄
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
// 放入子线程
CompletableFuture future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 子线程绑定
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, conHolder);
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
int a = 1 / 0;
// 解绑
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(dataSource);
});
// ....其他操作...
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into test(name,thread_name) value(? , ?)"
, new Object[]{LocalDateTime.now().toString(), Thread.currentThread().getName()});
// ....其他操作...
future.join();
}
}
运行后,可以看到异常已经抛出来了:

查看数据库:
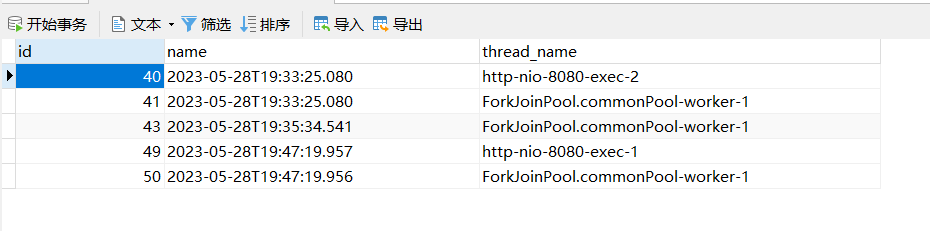
数据也成功回滚了。
二、延伸:MVC 子线程获取 Request 信息
看完上面事务的过程,同理在 MVC 中,加入原本是在主线程跑的,后面有需求需要放在子线程中优化,但是其中有从 ThreadLocal 中获取 Request 信息,此时就可以和上面一个做法解决问题,如:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test3")
public class RequestController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public void test(){
// 获取句柄
ServletRequestAttributes att = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder
.getRequestAttributes();
CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
// 绑定
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(att);
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder
.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
System.out.println(request.getHeader("token"));
// 解绑
RequestContextHolder.resetRequestAttributes();
}).join();
}
}