构造函数
Guaranteed initialization with the constructor使用构造函数保证初始化
• If a class has a constructor, the compiler automatically calls that constructor at the point an object is created, before client programmers can get their hands on the object.
• The name of the constructor is the same as the name of the class.

构造函数:
1、没有返回类型
2、会被自动调用
Constructors with arguments有参构造函数
• The constructor can have arguments to allow you to specify how an object is created, give it initialization values, and so on.
Tree(int i) {…}
Tree t(12);Constructor1.cpp
struct X{
int i;
X(int i);
void prt();
};
X::X(int i){
this -> i = i;
}
X::prt(){
cout << i << endl;
}
int main(){
X a; //无参构造,相当于a.X()
X a(1);//有参构造,相当于a.X(1)
X a=1; //变量初始化,相当于X a(1)
int m(10);// 相当于 m = 1;
a.prt();
}想要i的值固定
struct X{
int i = 100;
X();
void prt();
};
//X::X(){
// i = 100;
//}
X::prt(){
cout << i << endl;
}
int main(){
X a; //无参构造,相当于a.X()
a.prt();
}
//C++11会后才有这个特性:在成员变量定义的时候给初始值//也可以采用构造函数的方式给成员变量赋初始值
X::X(){
i = 100;
}default意思:缺省;默认
缺省构造函数:没有参数的构造函数,可以是程序员定义的或者程序员没写时编译器提供的
普通构造函数:有参数的构造函数 X(int i);
如果没有无参构造函数,只有有参构造函数,则创建对象需要传入有参构造函数的参数
struct X{
int i = 100;
X(int i);
void prt();
};
X::X(int i){
this -> i = i;
}
X::prt(){
cout << i << endl;
}
int main(){
X a; //会报错
X a(1);//需要传入参数
a.prt();
}如果没有定义有参构造函数,创建对象时就不能加参数
struct X{
int i = 100;
X();
void prt();
};
X::X(){
i = 100;
}
X::prt(){
cout << i << endl;
}
int main(){
X a; //正确
X a(1);//会报错
a.prt();
}int main(){
X b[10];//每个数组元素的i值为100
//如果想给数组元素对象的成员变量赋值
X b[10](7)//不对
X b[10] ={1,2,3,4,5}//不对,因为只提供了5个值,数组元素一共有十个
}The default constructor默认构造函数
• A default constructor is one that can be called with
no arguments.
struct Y {
float f;
int i;
Y(int a);
};
Y y1[] = { Y(1), Y(2), Y(3) }; //OK,每个元素类型都是Y,没有给大小,根据大括号内动态决定
Y y2[2] = { Y(1) };//错误,大括号内只有一个,要有两个
Y y3[7];//不行,结构体内含有参构造函数,创建对象就必须传入参数
Y y4;//不行,因为结构体内含有参构造函数,创建对象就必须传入参数“auto” default constructor
• If you have a constructor, the compiler ensures that construction always happens.
• If (and only if) there are no constructors for a class (struct or class), the compiler will automatically create one for you.
The destructor析构函数
• In C++, cleanup is as important as initialization and is therefore guaranteed with the destructor.
• The destructor is named after the name of the class
with a leading tilde (~). The destructor never has any
arguments.
struct Y {
public:
~Y();
};struct X{
X(int i);
void prt();
~X();
};
X::X(int i){
this -> i = i;
}
X::prt(){
cout << i << endl;
}
X::~X(){
cout << "~X()" << i << endl;
}
int main(){
X a(7);
X b(11);
a.prt();
b.prt();
}
/*
输出:
7
11
~X()11 // b的析构
~X()7 // a的析构
*/先构造的后析构,因为可能后面的对象会用到前面的对象,所以先构造的不能先析构。
//代码复杂一些
int main(){
X a(7);
{
X b(11);
}
a.prt();
//b.prt();
}
/*
输出:
~X()11 //b被析构,因为出了大括号这个生存期
7
~X()7 // a的析构
*/说明析构发生在离开大括号的时候
Storage allocation
• The compiler allocates all the storage for a scope at the opening brace of that scope.
• The constructor call doesn’t happen until the sequence point where the object is defined.
Examlpe: Nojump.cpp
class X{
private:
char* buf;
public:
X(){buf = new char[1024];};
~X(){delete buf;}
}
X::X(){}
void f(int i){
if(i < 10){
goto jump1;
}
X x1;
jump1;
switch(i){
case 1:
X x2;
break;
case 2:
X x3;
break;
}
}
/*
如果i小于10,goto跳转到jump1,一旦进入到f函数,本地变量就被分配了空间,
但是此时x1的构造函数不会执行,程序结束时,由于析构函数找不到要delete的buf
同理,switch的大括号规定了x2和x3的生命周期,一旦进入就给他们分配了空间,但由于case,x2或x3可能不会在对应的case下执行构造函数,最后析构的时候也会有问题。
解决方法:
1、不用goto
2、不用switch
*/Aggregate initialization聚合体初始化
• int a[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
• int b[6] = {5};
• int c[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
– sizeof c / sizeof *c
• struct X { int i; float f; char c; };
– X x1 = { 1, 2.2, 'c' };
• X x2[3] = { {1, 1.1, 'a'}, {2, 2.2, 'b'} };
• struct Y { float f; int i; Y(int a); };
• Y y1[] = { Y(1), Y(2), Y(3) };Defifinition of a class
• In C++, separated .h and .cpp files are used to define one class.
• Class declaration and prototypes in that class are in the header file (.h).
• All the bodies of these functions are in the source file (.cpp).
compile unit
• The compiler sees only one .cpp file, and generates .obj file。一个.cpp文件是一个编译单元,编译器在编译的时候只看见这一个.cpp文件
• The linker links all .obj into one executable file
• To provide information about functions in other .cpp files, use .h
The header fifiles
• If a function is declared in a header file, you must include the header file everywhere the function is used and where the function is defined.
• If a class is declared in a header file, you must include the header file everywhere the class is used and where class member functions are defined.
Header = interface
• The header is a contract (契约)between you and the
user of your code.
• The compile enforces the contract by requiring you to declare all structures and functions before they
Structure of C++ program

Declarations vs Defifinitions
• A .cpp file is a compile unit
• Only declarations are allowed to be in .h
• extern variables
• function prototypes
• class/struct declaration
#include
• #include is to insert the included file into the .cpp file at where the #include statement is.
• #include “xx.h”:first search in the current directory, then the directories declared somewhere
• #include <xx.h>:search in the specified directories
• #include <xx>:same as #include <xx.h>
Standard header fifile structure
防止多次声明
#ifndef HEADER_FLAG
#define HEADER_FLAG
// Type declaration here...
#endif // HEADER_FLAGTips for header
1. One class declaration per header file
2. Associated with one source file in the same
prefix of file name.
3. The contents of a header file is surrounded with #ifndef #define #endif
Clock display

Abstract
• Abstraction is the ability to ignore details of parts to focus attention on a higher level of a problem.
• Modularization is the process of dividing a whole into well-defined parts, which can be built and examined separately, and which interact in well-defined ways.
Modularizing the clock display
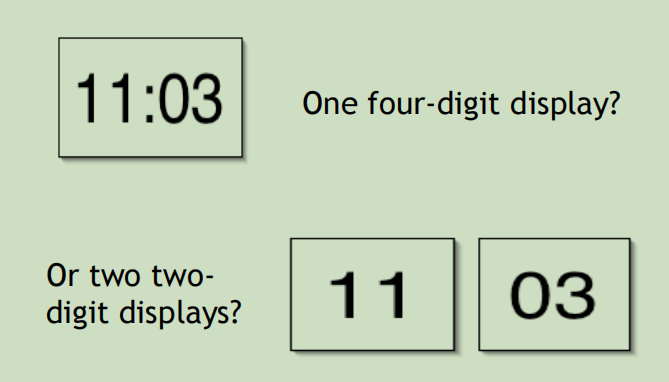
NumberDisplay.h
#ifndef __NUMBER_DISPLAY__
#define __NUMBER_DISPLAY__
struct NumberDisplay{
int value = 0;
int limit = 0; //上界
NumberDisPlay(int limit);
int setValue(int value);
int getValue();
bool increase();
};
#endifNumberDisplay.cpp
#include "NumberDisplay.h"
NumberDisplay::NumberDisPlay(int limit){
this -> limit = limit;
}
void NumberDisPlay::setValue(int value){
this -> value = value;
}
int NumberDisPlay::getvalue(){
return value;
}
bool NumberDisPlay::increase(){
value++;
if(value == limit){
value = 0; //当值达到上限时,重新置零
return true;
}
return false;
}main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "NumberDisPlay"
using namespace std;
int main(){
NumberDisPlay n(10);
n.setValue(2);
for(int i = 0; i < 15; i++){
if(n.increase()){
cout << "-------------" << endl;
}
cout << n.getValue() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
输出:
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
------------------
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
*/Clock.h
#ifndef __CLOCK_H__
#define __CLOCK_H__
#include "NumberDisPlay.h"
struct Clock{
// NumberDisplay hour(24);编译会报错
// NumberDisplay minute(60);
//类内初始值只能放在花括号里,或放在等号右边,记住不能使用圆括号
NumberDisplay hour=24;
NumberDisplay minute=60;
void dida();
int getTime()
}
#endifClock.cpp
#include "Clock.h"
void Clock::dida(){
if(minute.increase()){
hour.increase();
}
}
int Clock::getTime(){
return hour.getValue() *100 + minute.getValue();
}main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "NumberDisPlay"
#include "Clock.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
// NumberDisPlay n(10);
// n.setValue(2);
// for(int i = 0; i < 15; i++){
// if(n.increase()){
// cout << "-------------" << endl;
// }
// cout << n.getValue() << endl;
// }
Clock clk;
for(int i = 0; i < 123; i++){
clk.dida();
cout << clk.getTime() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
类内初始值只能放在花括号里,或放在等号右边,记住不能使用圆括号。
类外部创建对象时可以用圆括号,表示使用有参构造函数。