✨博主:命运之光
✨专栏:算法基础学习

目录
DFS与BFS\树与图
✨DFS
✨BFS
🍓宽搜流程图如下:
🍓宽搜流程:
🍓广搜模板
✨树与图
🍓树是特殊的图(连通无环的图)
🍓树与图的存储:
🍓用宽搜框架来搜索图:
前言:算法学习笔记记录日常分享,需要的看哈O(∩_∩)O,感谢大家的支持!
DFS与BFS\树与图
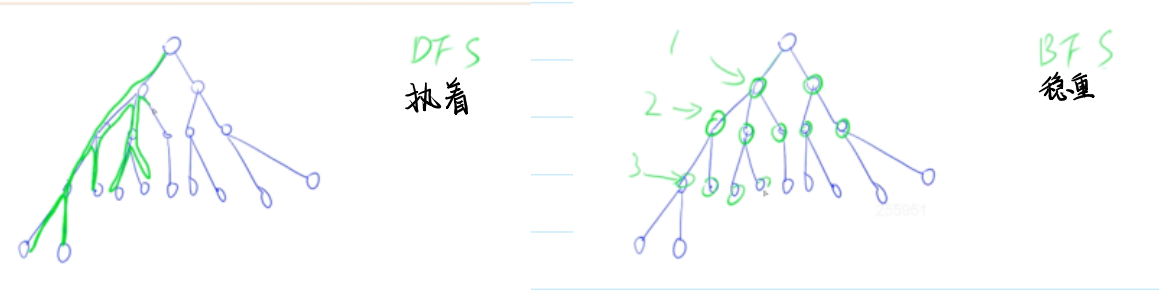
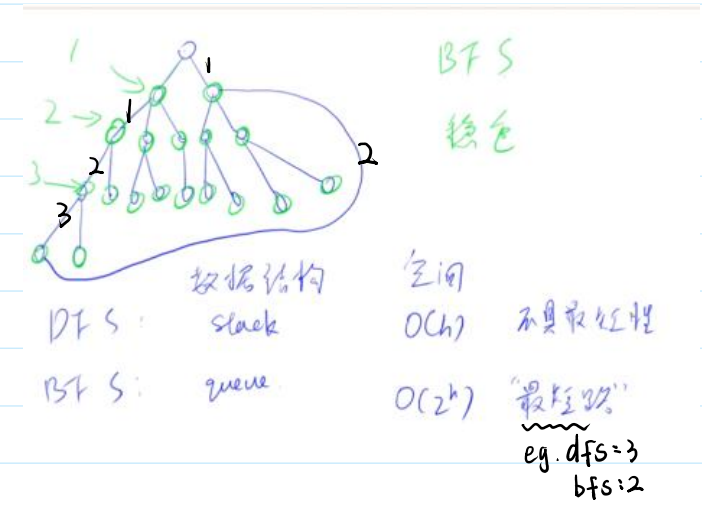
✨DFS
//回溯,剪枝
当使用深度优先搜索(DFS)回溯算法来搜索图时,我们需要考虑以下几个步骤:
- 初始化数据结构:创建一个栈(通常使用先进后出的原则)来存储待探索的节点,以及一个集合(通常使用哈希集合或集合)来记录已访问的节点。
- 将起始节点放入栈中,并将其标记为已访问。
- 进入循环,直到栈为空:
-
- 从栈中取出一个节点。
- 检查该节点是否为目标节点。如果是,则搜索完成,返回结果。
- 如果不是目标节点,则将其所有未访问过的邻居节点加入栈,并标记为已访问。
- 继续下一轮循环。
- 如果循环结束时仍未找到目标节点,则图中不存在目标节点。

剪枝:可以提前判断当前方案一定不合法,就不用往下搜
✨BFS

🍓宽搜流程图如下:

🍓宽搜流程:

🍓广搜模板
q.push(初始状态);
while(q.empty()){
a=q.front();
q.pop();
for(枚举a的所有可达状态v){
if(本状态v合法){
执行标记操作;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
连通块问题:
例题:全球变暖
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=1005;
bool v[N][N],book[N*N];
char a[N][N];
int n,w[N][N],s,cnt;
int dx[4]={-1,0,1,0};
int dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};
typedef struct node
{
int x,y;
}node;
queue<node>q;
bool check(int x,int y)
{
if(x<1||x>n||y<1||y>n)
return false;
return true;
}
bool judge(int x,int y)
{
if(check(x+1,y)&&a[x+1][y]=='.')
return false;
if(check(x,y+1)&&a[x][y+1]=='.')
return false;
if(check(x-1,y)&&a[x-1][y]=='.')
return false;
if(check(x,y-1)&&a[x][y-1]=='.')
return false;
return true;
}
void bfs()
{
while(!q.empty())
{
node head,tail;
head=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
tail.x=head.x+dx[i];
tail.y=head.y+dy[i];
if(check(tail.x,tail.y)&&a[tail.x][tail.y]=='#'&&w[tail.x][tail.y]==0)
{
w[tail.x][tail.y]=cnt;
q.push(tail);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]=='#'&&w[i][j]==0)
{
cnt++;
w[i][j]=cnt;
node tmp={i,j};
q.push(tmp);
bfs();
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]=='#')
{
if(judge(i,j))
{
book[w[i][j]]=true;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)
{
if(book[i]==true)
{
s++;
}
}
cout<<cnt-s;
return 0;
}问题2:
两个BFS
例题:Fire
/*
预处理:预处理出火传染到(i,j)点的最早时间
人在去想要走到(i,j)点时,到(i,j)点的时刻一定要小于火最早到(i,j)的s时刻
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=1000+5;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef struct Node{
int x,y;
int t;
}Node;
int t,n,m;
int ti[N][N];//ti[i][j]是火最早到(i,j)的时间
char a[N][N];
queue<Node> fq,q;
bool vis[N][N];
int _next[4][2]={{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1}};
bool judge(int x,int y)
{
if(x<1||x>n||y<1||y>m)
return false;
return true;
}
void FireBFS()
{
Node _new;
while(!fq.empty())
{
Node tp=fq.front();
fq.pop();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
_new.x=tp.x+_next[i][0];
_new.y=tp.y+_next[i][1];
if(judge(_new.x,_new.y)&&a[_new.x][_new.y]=='.'&&ti[_new.x][_new.y]==INF)
{
_new.t=tp.t+1;
ti[_new.x][_new.y]=_new.t;
fq.push(_new);
}
}
}
}
int ManBFS(){
Node _new;
while(!q.empty()){
Node tp=q.front();
q.pop();
if(tp.x==1||tp.x==n||tp.y==1||tp.y==m){
return tp.t+1;
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
_new.x=tp.x+_next[i][0];
_new.y=tp.y+_next[i][1];
if(judge(_new.x,_new.y)&&a[_new.x][_new.y]=='.'&&!vis[_new.x][_new.y]){
_new.t=tp.t+1;
if(_new.t<ti[_new.x][_new.y]){
vis[_new.x][_new.y]=true;
q.push(_new);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
void init(){
memset(ti,0x3f,sizeof(ti));
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
while(!fq.empty())
fq.pop();
while(!q.empty())
q.pop();
}
int main(){
cin>>t;
while(t--){
init();
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
cin>>a[i][j];
if(a[i][j]=='F'){
Node tmp={i,j,0};
ti[i][j]=0;
fq.push(tmp);
}
else if(a[i][j]=='J'){
Node tmp={i,j,0};
vis[i][j]=true;
q.push(tmp);
}
}
}
FireBFS();
int ans=ManBFS();
if(ans==-1)
cout<<"IMPOSSIBLE"<<endl;
else
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
/*
2
4 4
####
#JF#
#..#
#..#
3 3
###
#J.
#.F
*/✨树与图
🍓树是特殊的图(连通无环的图)


🍓树与图的存储:
树是一种特殊的图,与图的存储方式相同。
对于无向图中的边ab,存储两条有向边a->b, b->a。
因此我们可以只考虑有向图的存储。
(1) 邻接矩阵:g[a][b] 存储边a->b
(2) 邻接表:
// 对于每个点k,开一个单链表,存储k所有可以走到的点。h[k]存储这个单链表的头结点
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
// 添加一条边a->b
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
// 初始化
idx = 0;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);树与图的遍历:
时间复杂度 O(n+m)O(n+m), nn 表示点数,mm 表示边数
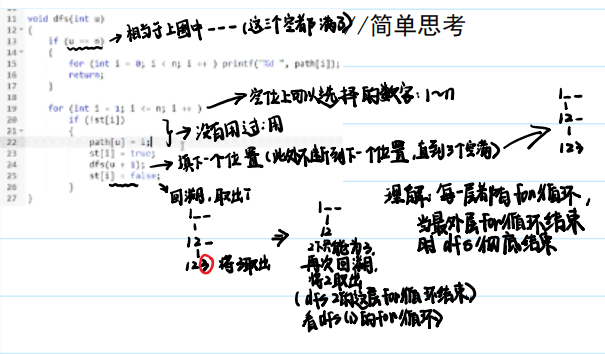
(1) 深度优先遍历

int dfs(int u)
{
st[u] = true; // st[u] 表示点u已经被遍历过
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j]) dfs(j);
}
}(2) 宽度优先遍历

queue<int> q;
st[1] = true; // 表示1号点已经被遍历过
q.push(1);
while (q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j])
{
st[j] = true; // 表示点j已经被遍历过
q.push(j);
}
}
}🍓用宽搜框架来搜索图:
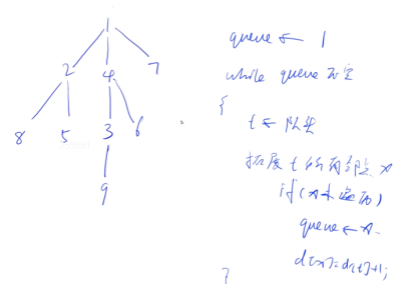
当使用宽度优先搜索(BFS)框架搜索图时,我们可以按照以下步骤进行操作:
- 选择一个起始节点,并将其添加到队列中,同时将其标记为已访问。
- 重复以下步骤直到队列为空:
-
- 从队列中取出一个节点作为当前节点。
- 检查当前节点是否满足搜索条件。如果是,则返回结果或执行相应操作。
- 遍历当前节点的所有相邻节点。
- 对于每个未被访问的相邻节点,将其添加到队列中,并将其标记为已访问。
- 如果队列为空且没有找到满足条件的节点,则搜索结束,可以返回相应的结果或执行其他操作。
🍓以下是使用宽度优先搜索框架在C++中搜索图的示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
bool bfs(const std::unordered_map<char, std::vector<char>>& graph, char startNode, char targetNode) {
std::queue<char> queue; // 创建一个队列
std::unordered_set<char> visited; // 创建一个集合,用于记录已访问的节点
queue.push(startNode); // 将起始节点放入队列
visited.insert(startNode); // 标记起始节点为已访问
while (!queue.empty()) {
char node = queue.front(); // 从队列中取出一个节点
queue.pop();
if (node == targetNode) // 检查是否为目标节点
return true;
const std::vector<char>& neighbors = graph.at(node); // 获取当前节点的邻居节点
for (char neighbor : neighbors) {
if (visited.find(neighbor) == visited.end()) { // 如果邻居节点未被访问过
queue.push(neighbor); // 将邻居节点加入队列
visited.insert(neighbor); // 标记邻居节点为已访问
}
}
}
return false; // 循环结束,未找到目标节点
}
int main() {
std::unordered_map<char, std::vector<char>> graph = {
{'A', {'B', 'C'}},
{'B', {'D', 'E'}},
{'C', {'F'}},
{'D', {}},
{'E', {'F'}},
{'F', {}}
};
char startNode = 'A';
char targetNode = 'F';
bool result = bfs(graph, startNode, targetNode);
if (result)
std::cout << "The target node '" << targetNode << "' is reachable from the start node '" << startNode << "'.\n";
else
std::cout << "The target node '" << targetNode << "' is not reachable from the start node '" << startNode << "'.\n";
return 0;
}在上述代码中,使用std::unordered_map来表示图的邻接表,其中键是节点,值是该节点的邻居节点列表。还使用std::queue来作为队列存储待探索的节点,std::unordered_set用于记录已访问的节点。
注意,上述代码仅为示例,假设图中的节点标识为字符('A', 'B', 'C'等),您可以根据实际情况进行修改和适应。