💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
2.1 案例研究II:三种模式下各MES的购入电量及出清电价
2.2 每个MES中的本地负荷和可再生能源(RES)曲线
2.3 案例研究II:每个Mes ( a )电功率和( b )热功率的结果
2.4 案例研究II:3种模式下的变压器功率
2.5 风力资源丰富的MES中RES限功率和EES的功率
2.5 结论
🌈3 Matlab代码+数据+文章详细讲解
🎉4 参考文献
💥1 概述
文献来源:

持续的环境恶化和能源消耗使得各种形式的能源必须得到综合利用。因此,多能源系统(MES)因其提高综合能源效率以及有益于系统经济和环境的能力而受到了极大的关注[1,2]。一方面,MES可以改变能源载体和网络的供需,以及处理可再生能源(RES)的不确定和不稳定的发电输出[3,4]。此外,由于能源互补性,MES具有共同最小化运营成本[5]、提高整体运营效率和提高系统灵活性的未开发潜力。
基于多能源集成的优点,本文建立了一个基于事务控制的双层两级框架,以实现互连多能源系统(MES)之间的最优能源供应。在较低级别,每个MES通过解决成本最小化问题,自主确定其可控资产的最佳设定点,其中采用滚动水平优化来处理负载和可再生能源的随机特征。进一步实现了一种通过放松存储的互补约束来实现优化模型凸化的技术,其数学证明验证了放松的正确性。在上层,协调器负责最小化互连MES的总成本,同时防止变压器过载。该协作问题在一个建议的两阶段事务控制框架中迭代解决,该框架与操作时间要求兼容,同时保留每个MES的可扩展性、信息隐私和操作权限通过对协作自主优化机制进行详细分析的仿真案例验证了所提出框架的有效性。
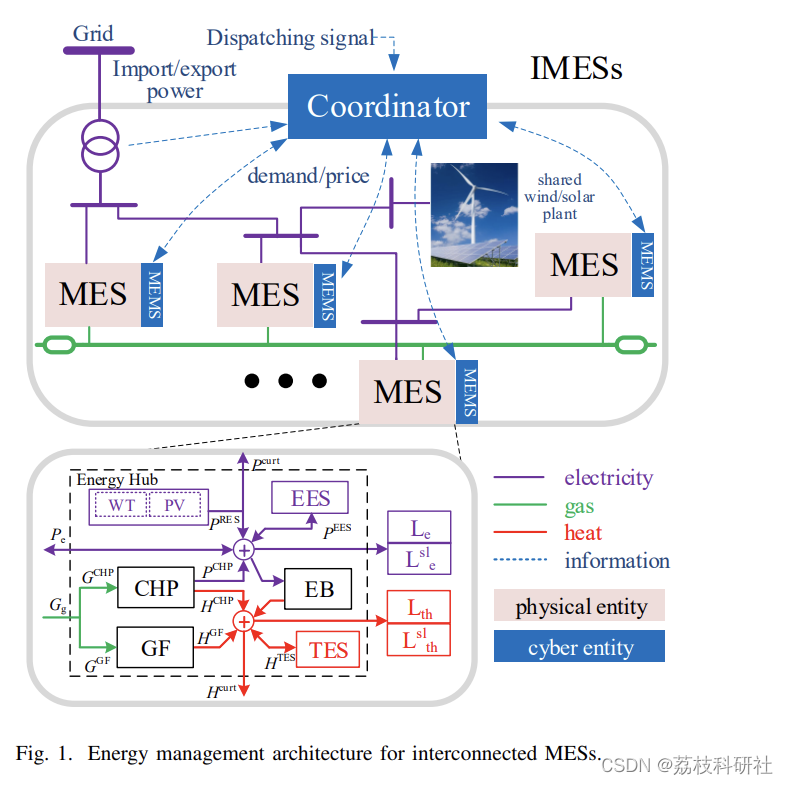
📚2 运行结果
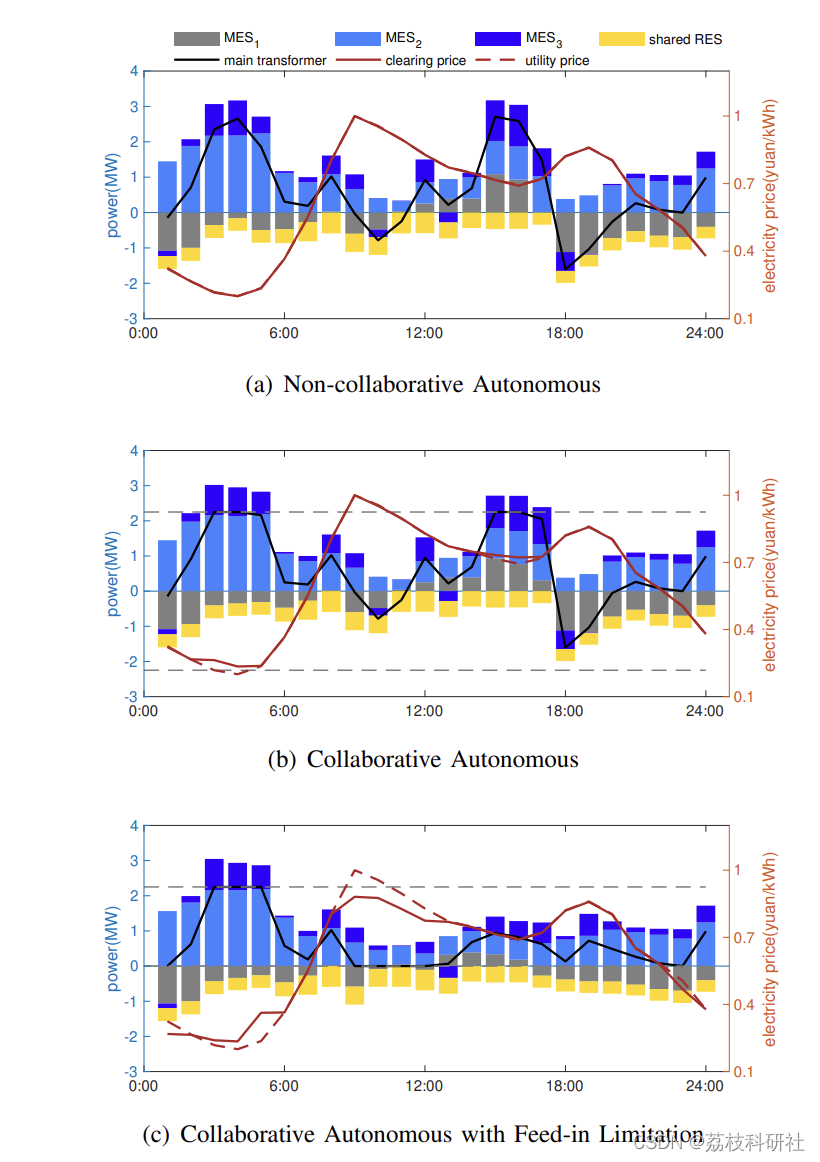
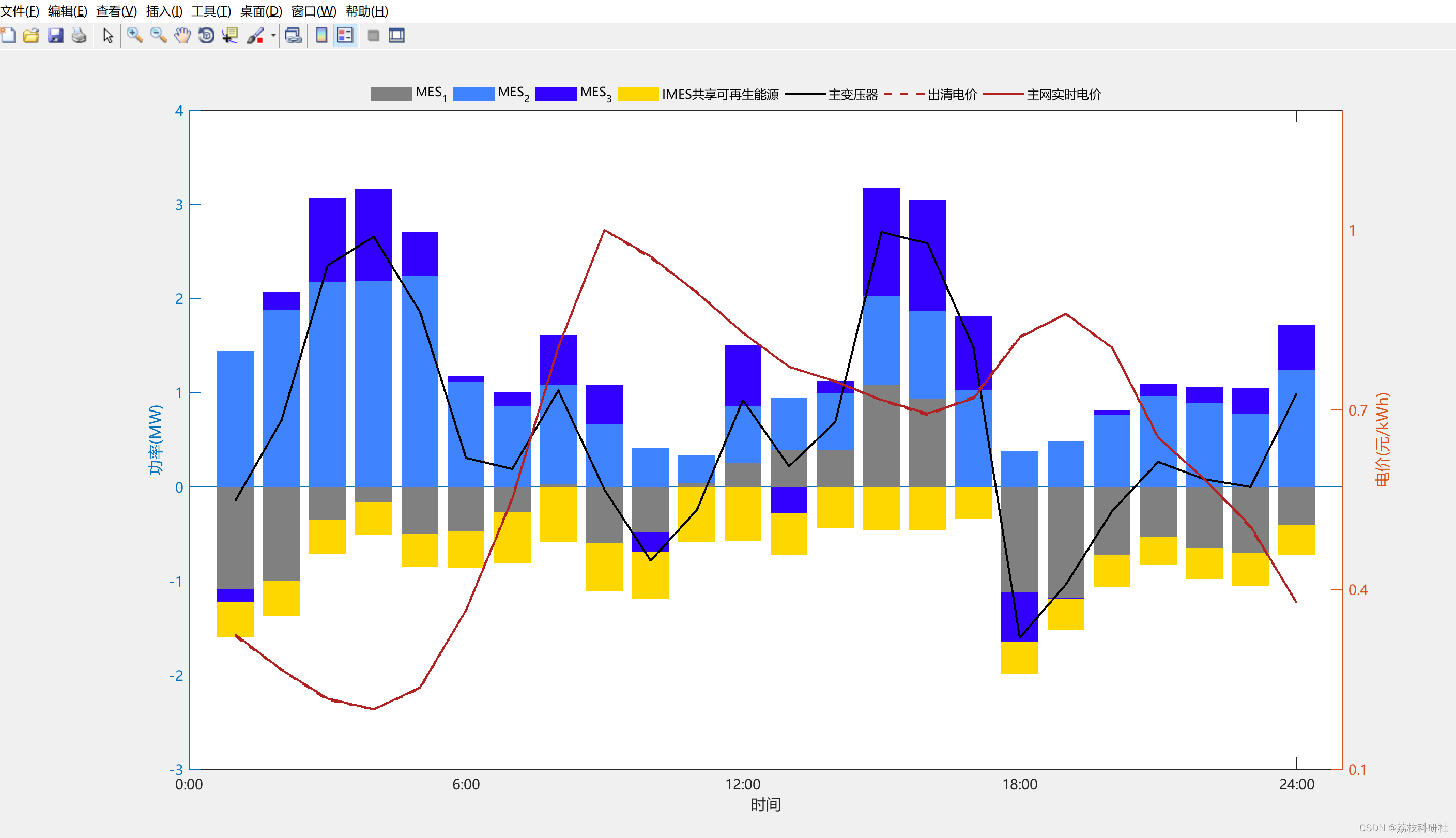
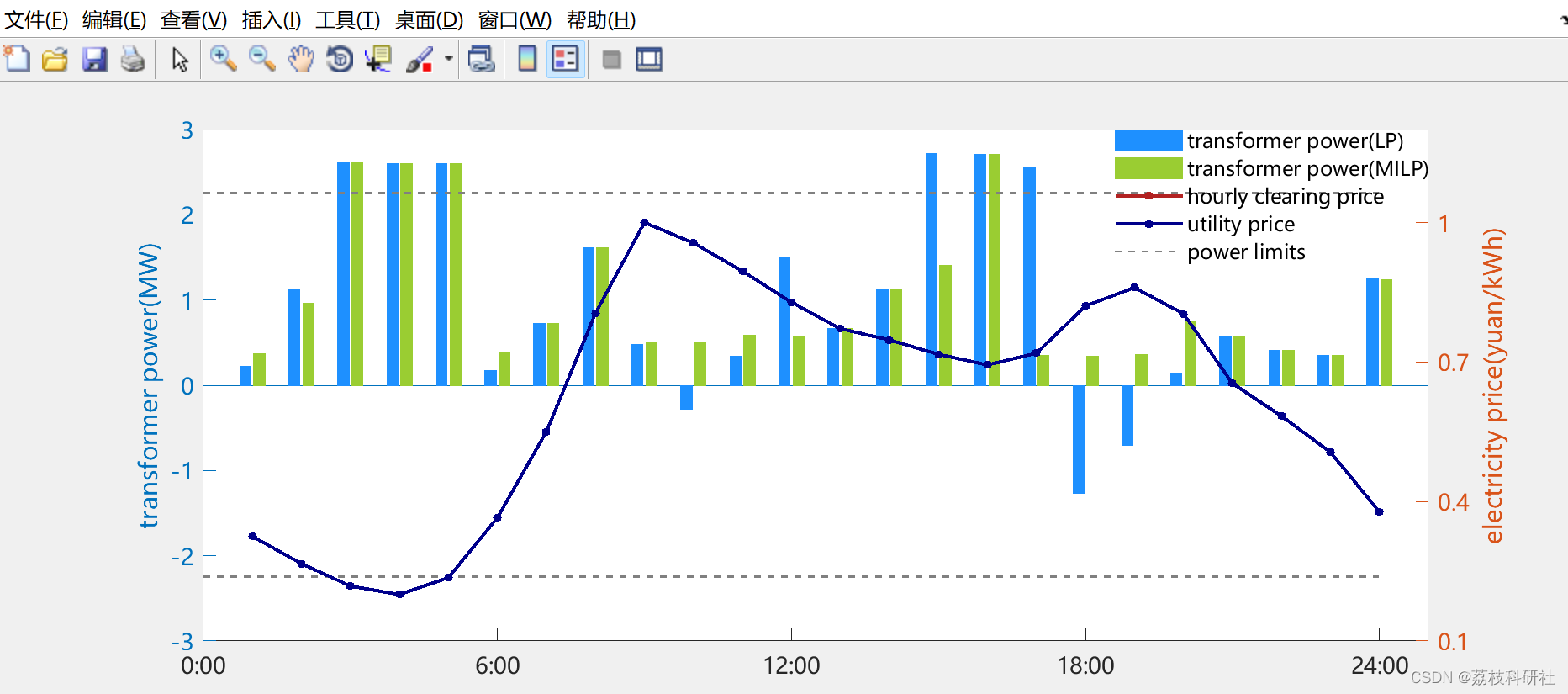
2.1 案例研究II:三种模式下各MES的购入电量及出清电价
原文图:
复现结果图:
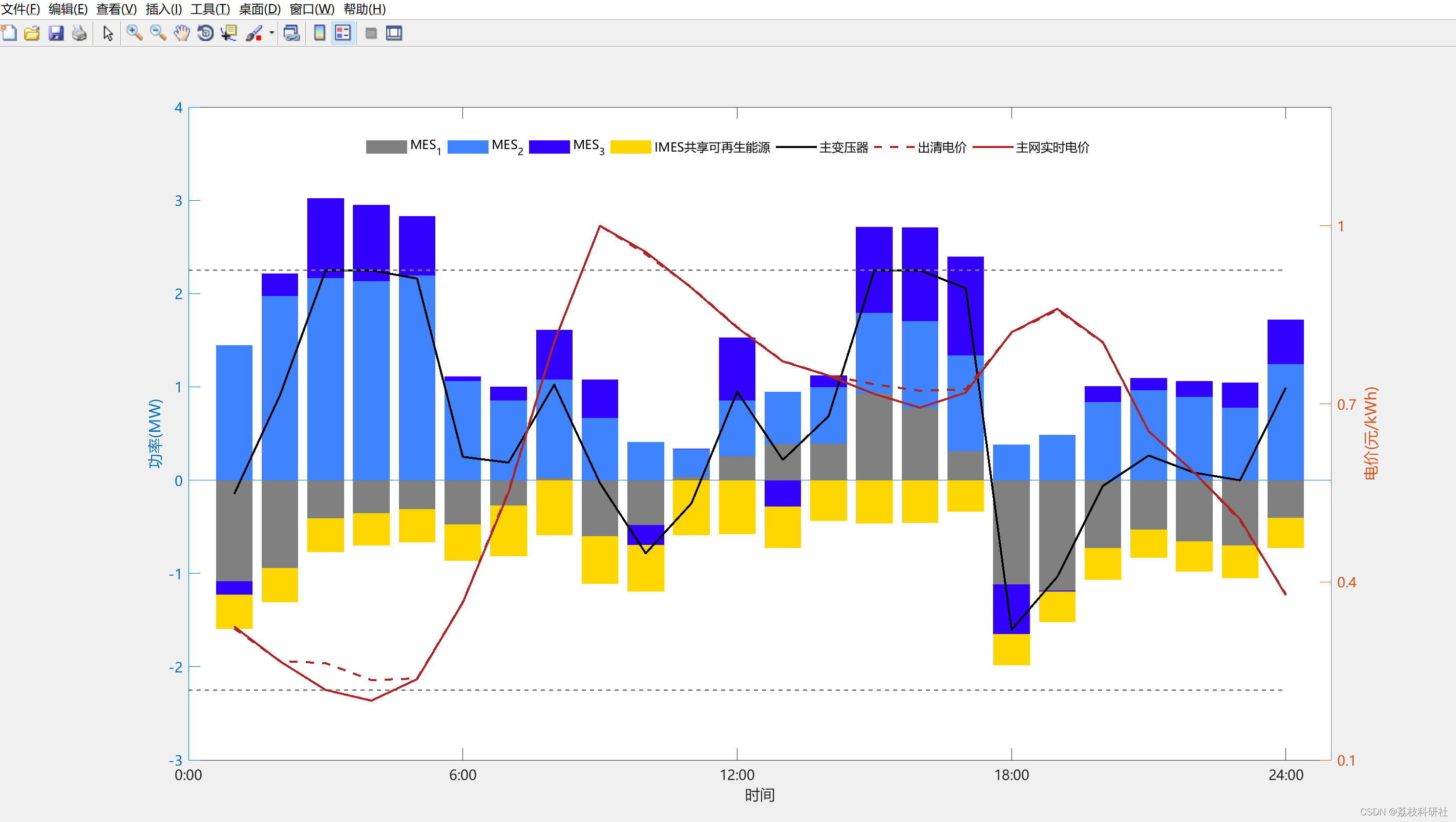
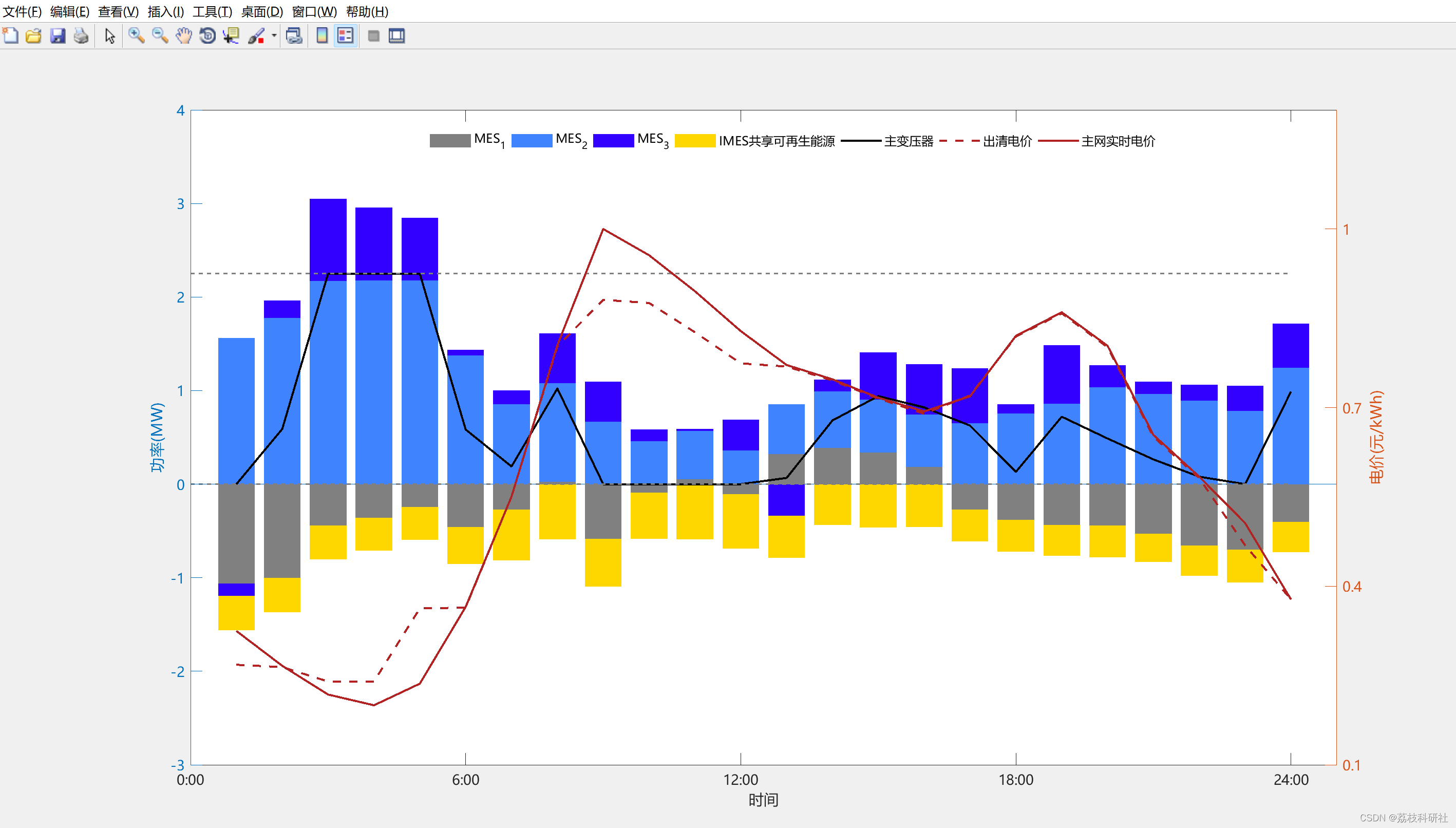
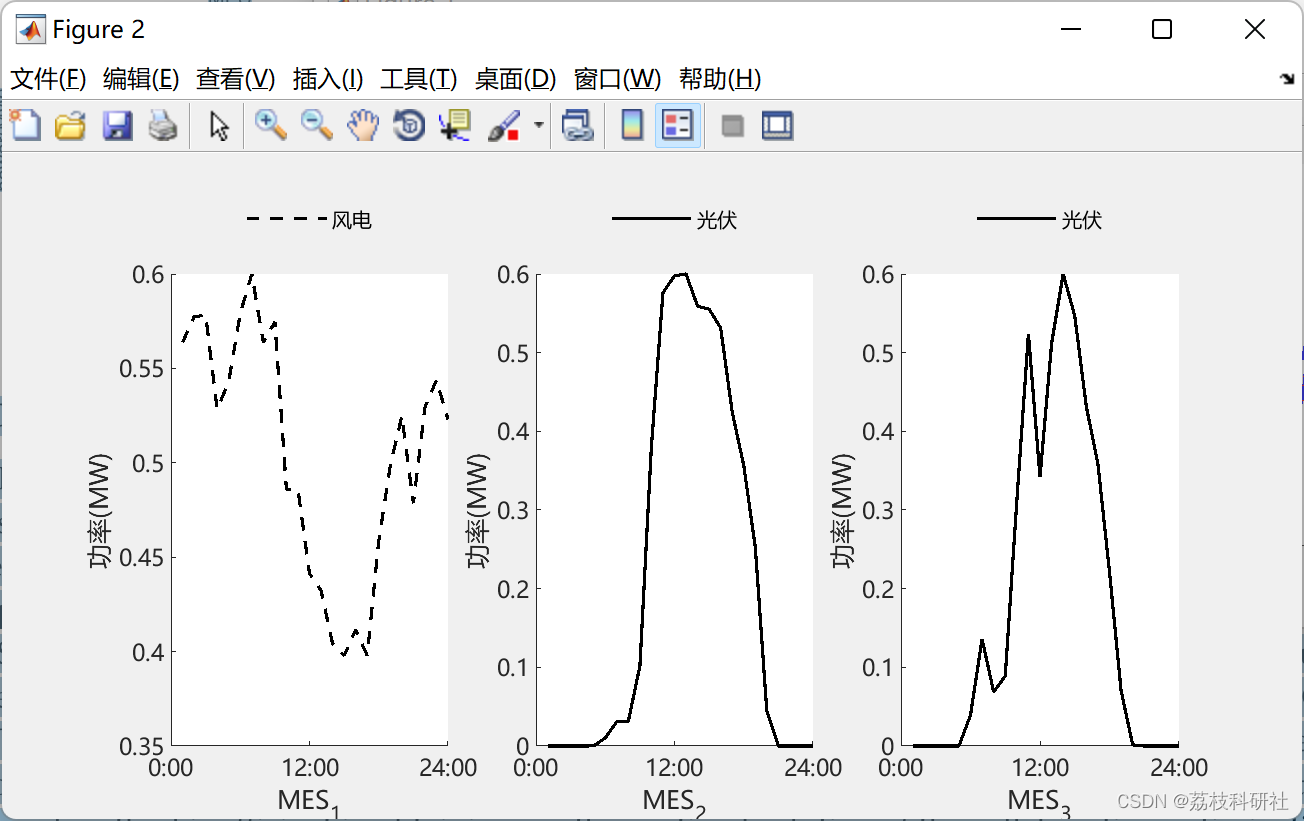
2.2 每个MES中的本地负荷和可再生能源(RES)曲线
原文图:
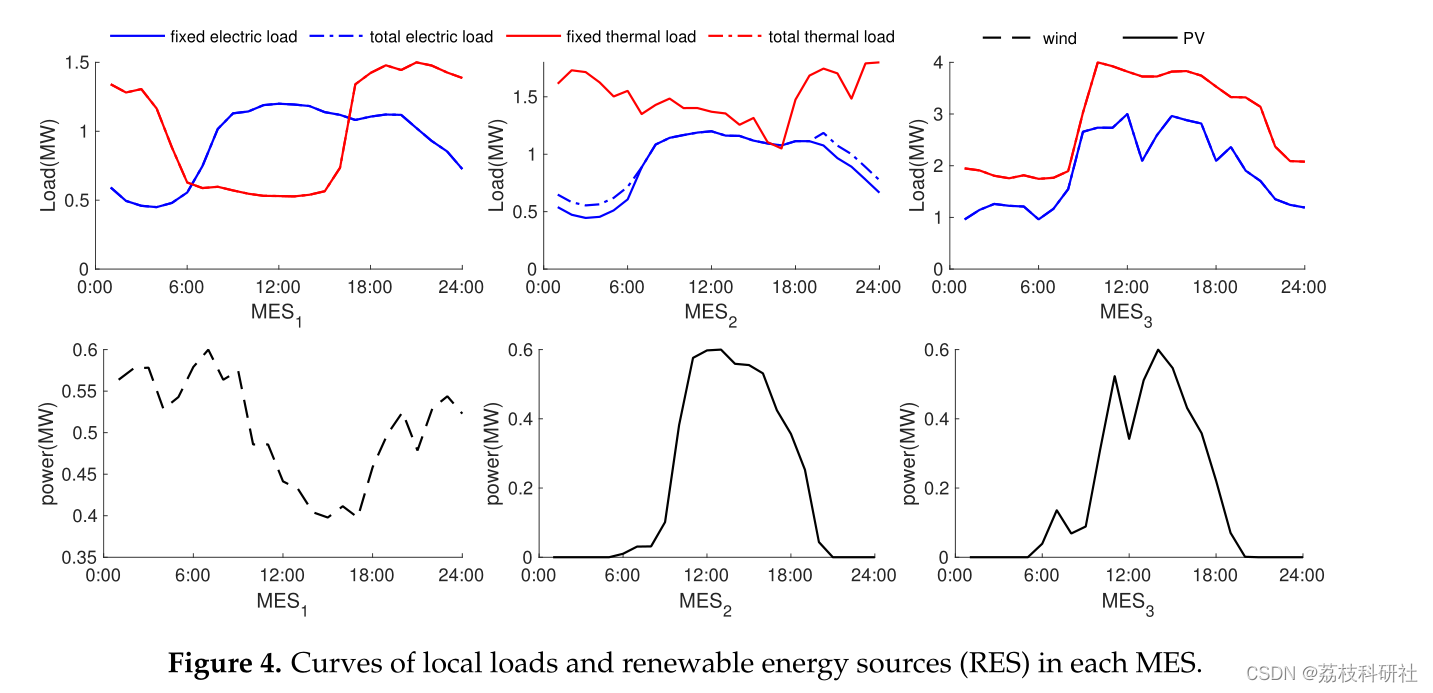
复现效果图
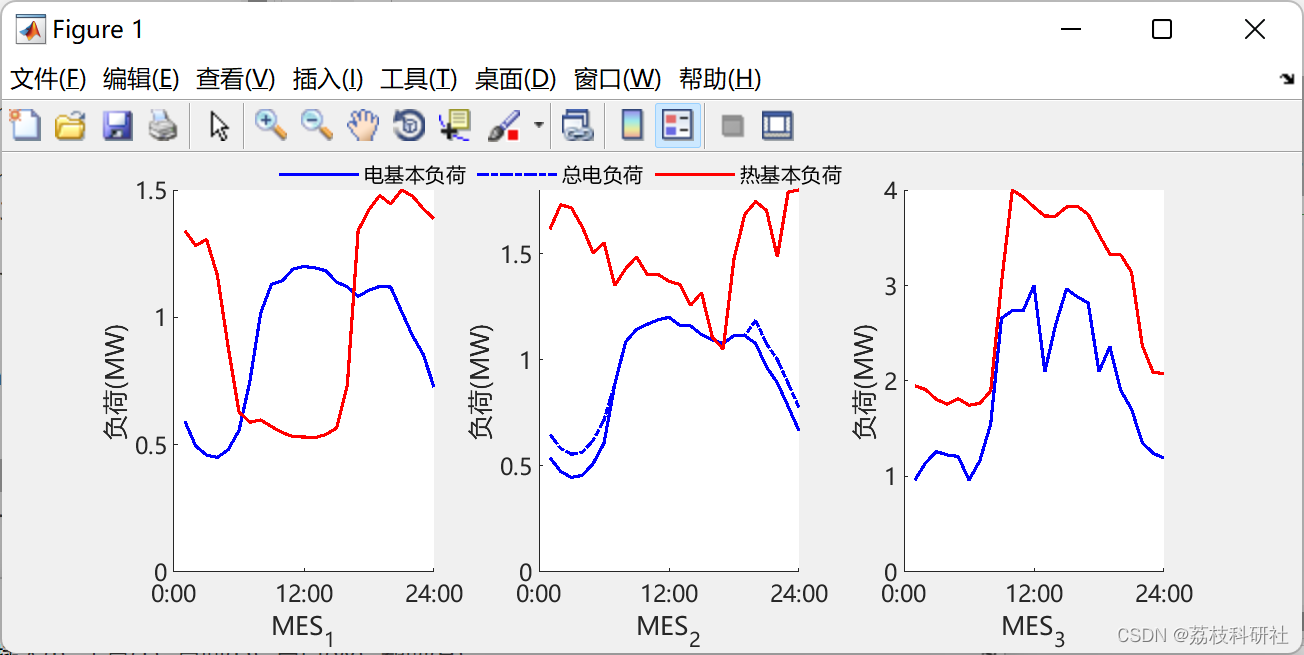
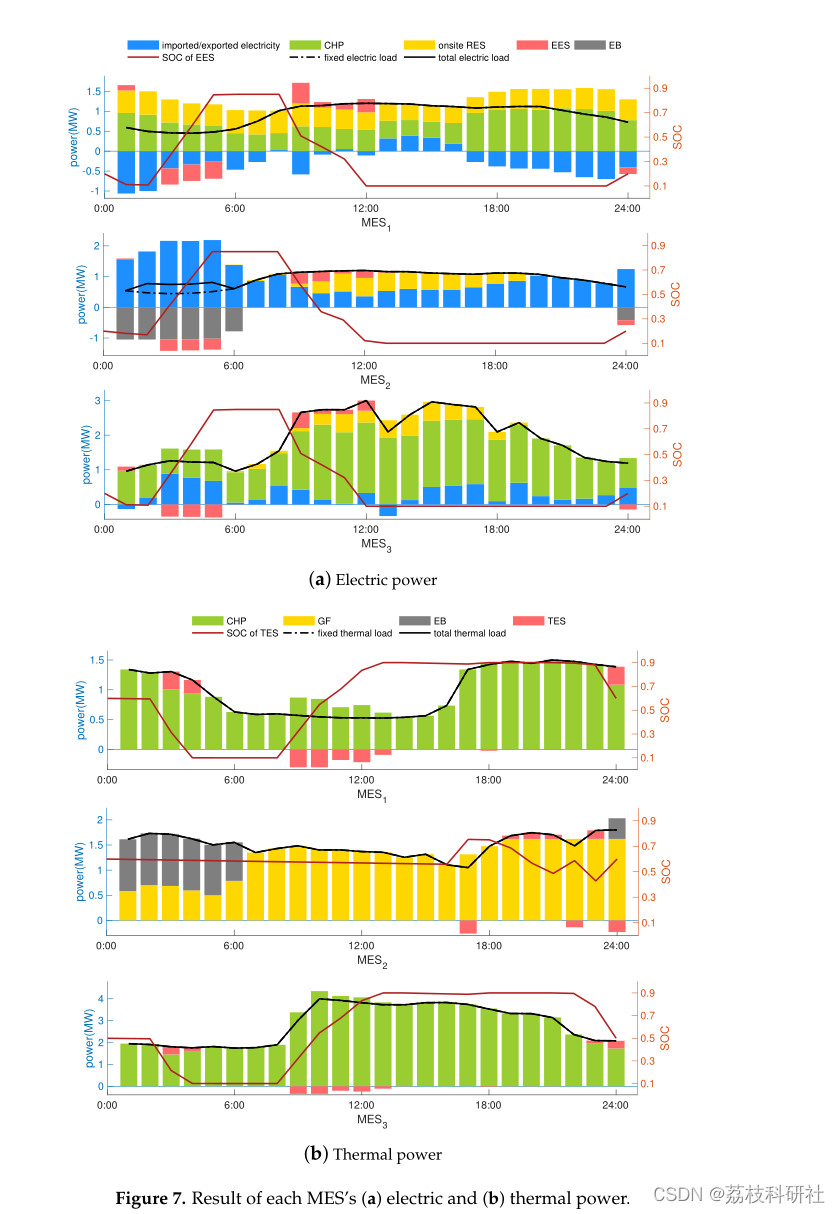
2.3 案例研究II:每个Mes ( a )电功率和( b )热功率的结果
原文图
复现效果图
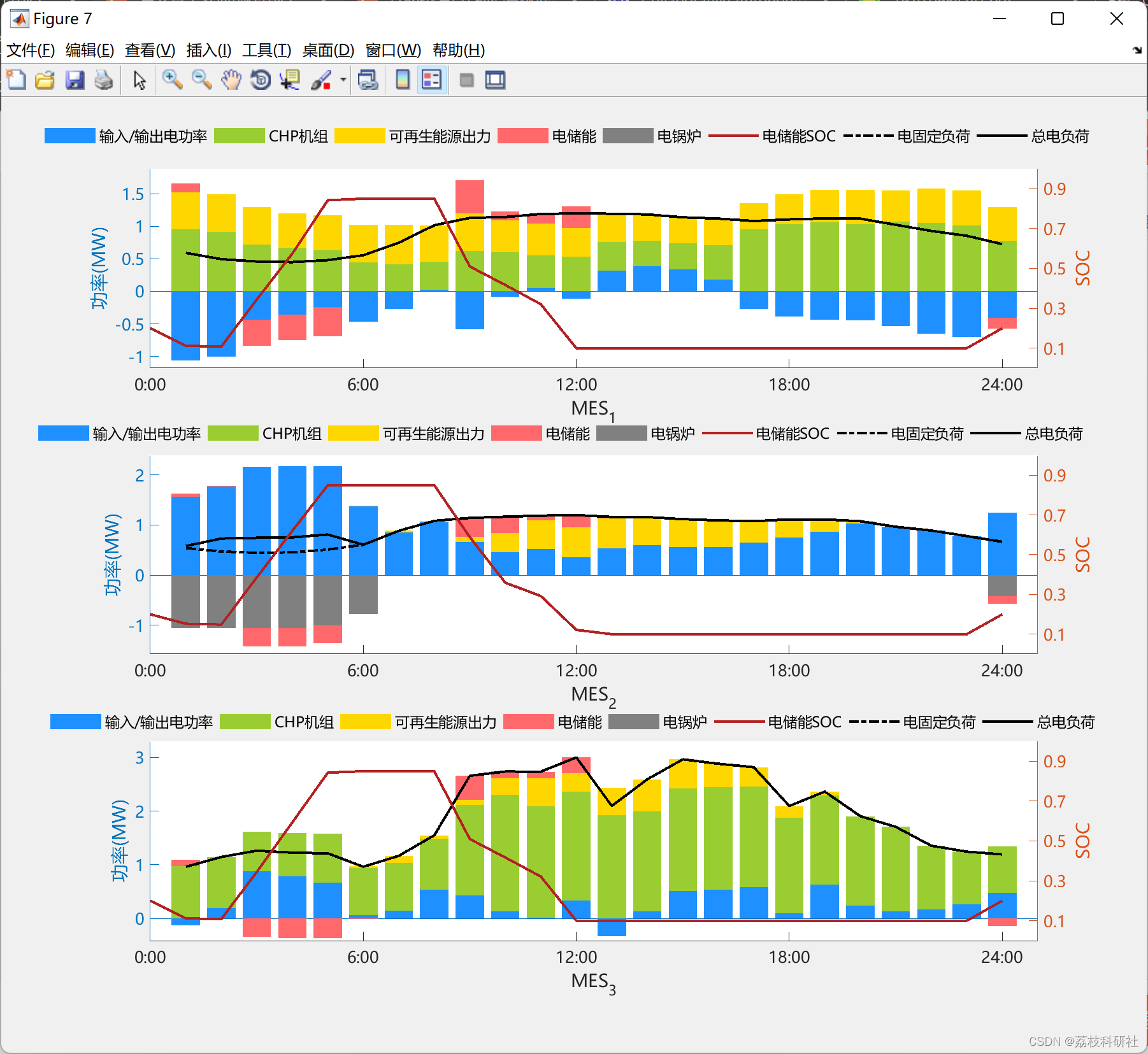
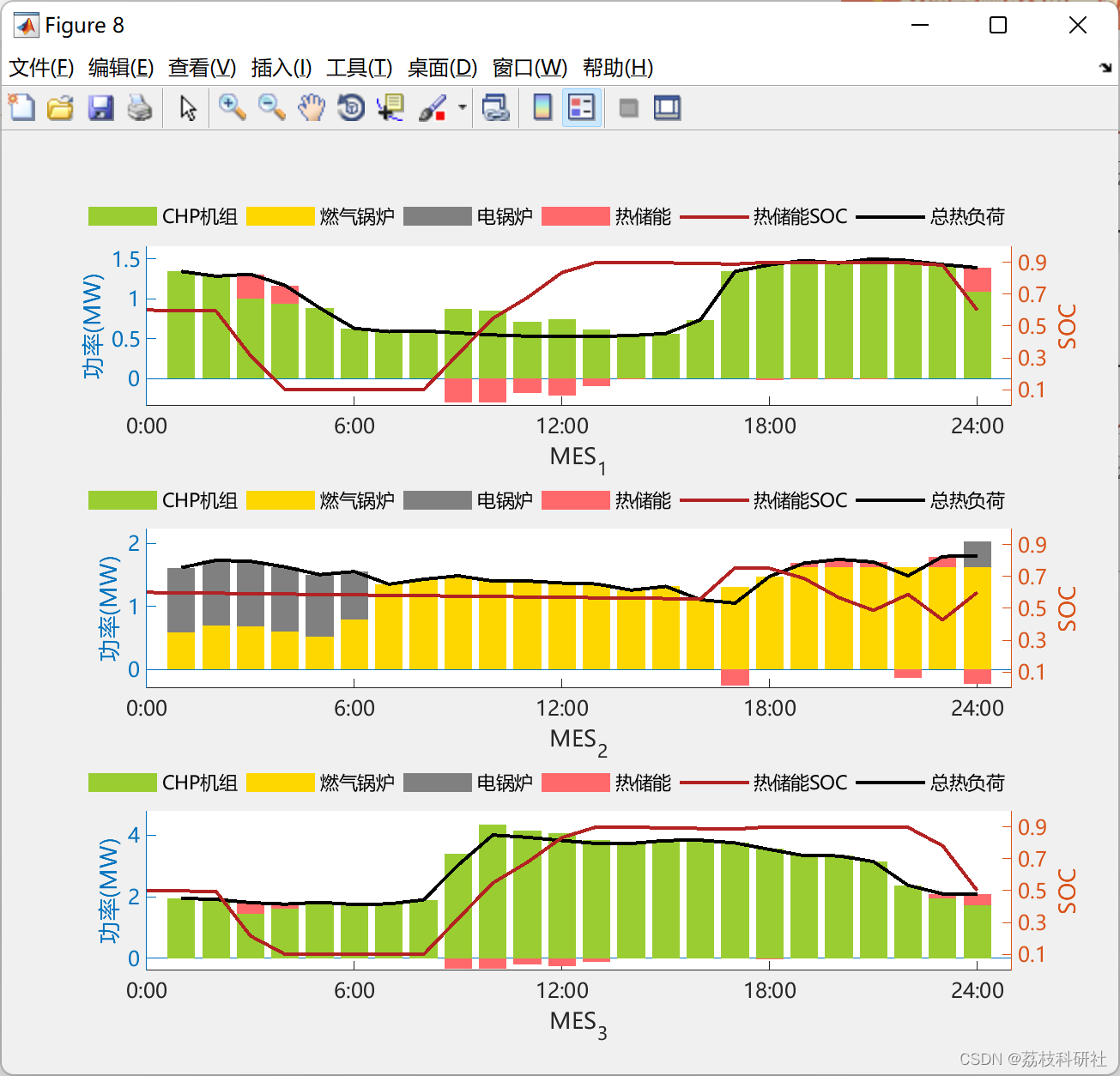
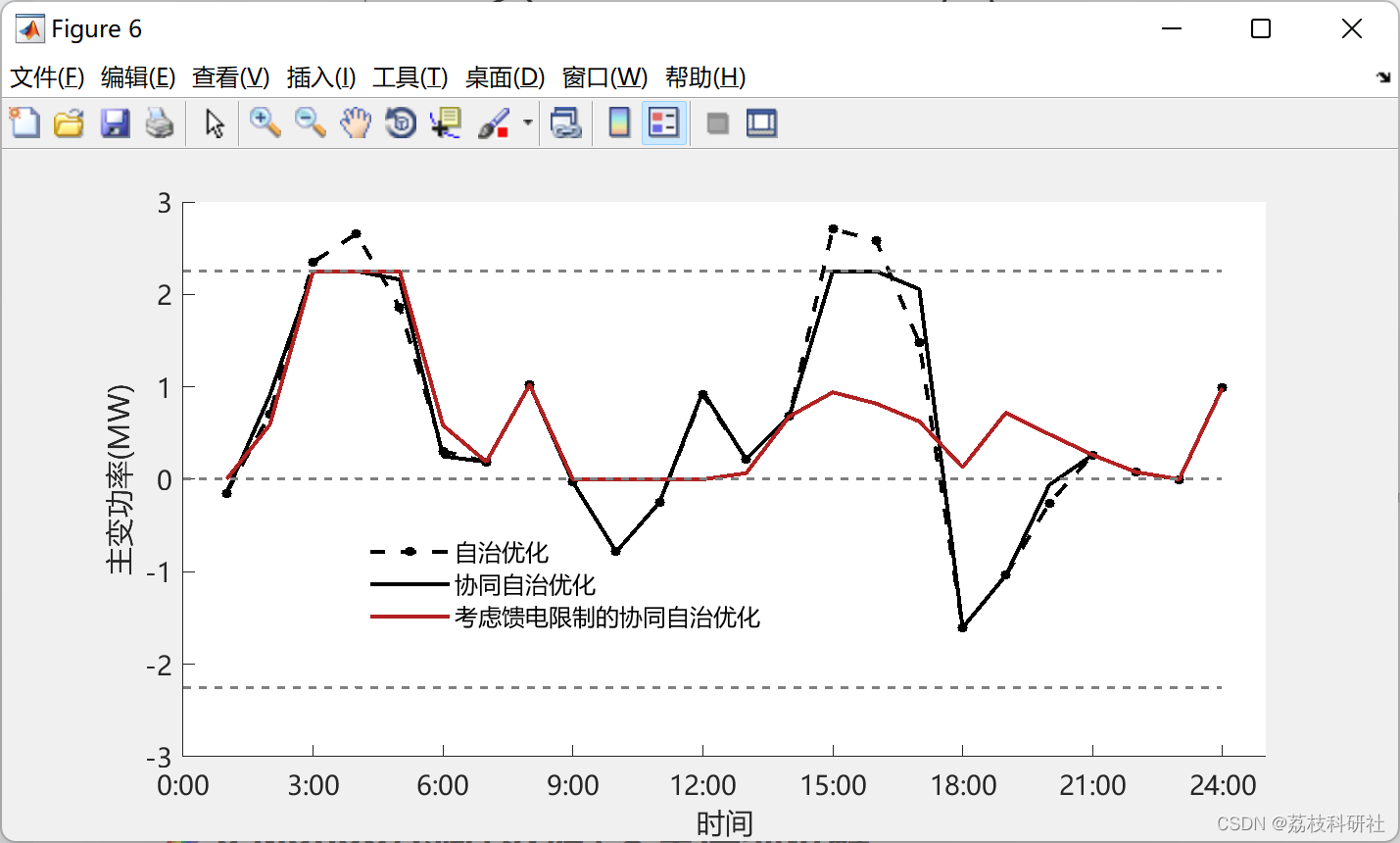
2.4 案例研究II:3种模式下的变压器功率
原文图:

复现效果图:
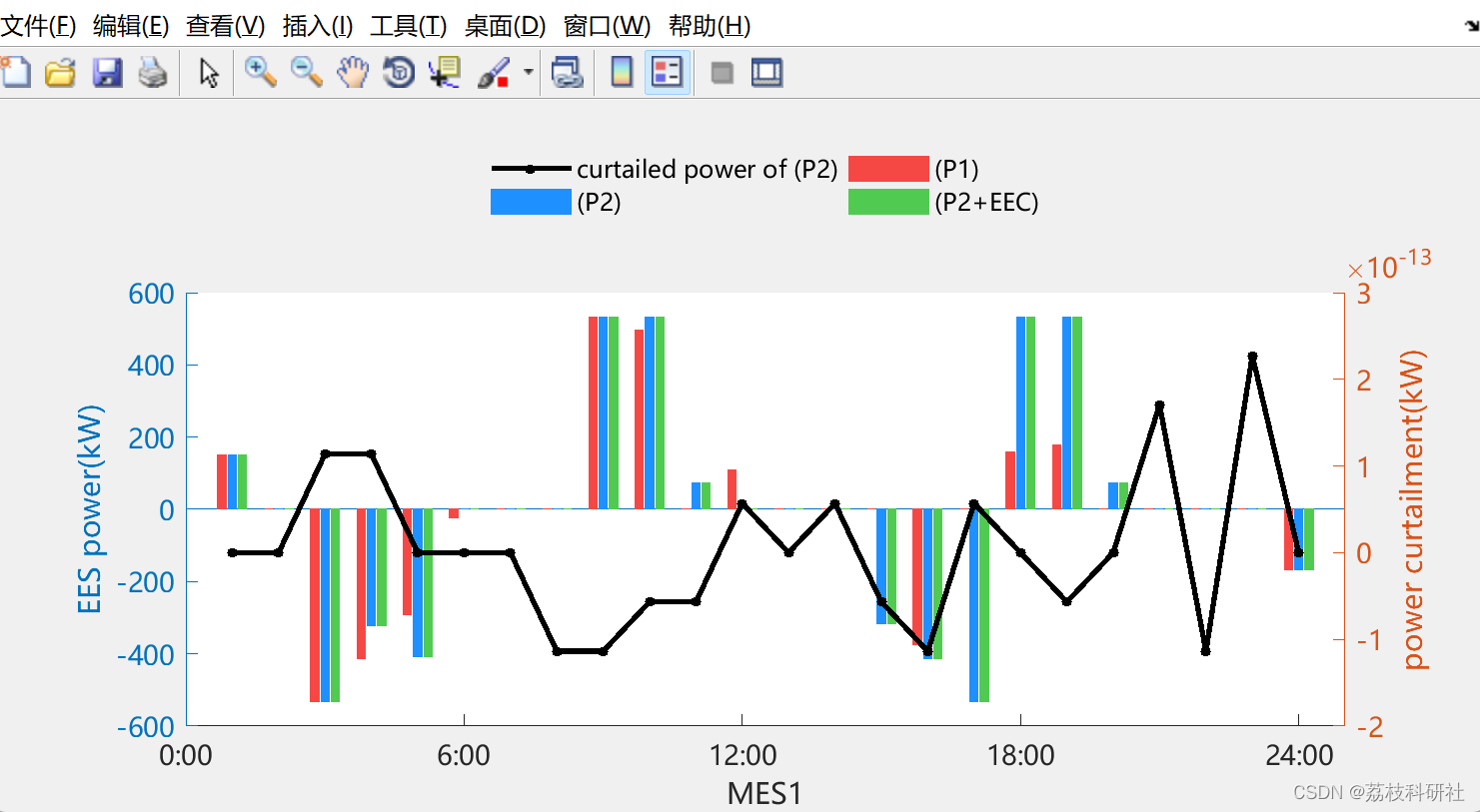
2.5 风力资源丰富的MES中RES限功率和EES的功率
Two issues will be discussed in this section. First, the impact of power losses on the simulationoutcomes. Second, the possibility of real-time coordination of the IMESs with the proposed 2S-TC framework.
In this paper, power losses that include the loss in the connecting line and the transformer are not considered for simplicity , which may have impacts on the local accommodation of RES. As for the collaborative autonomous mode with feed-in limitation, the loss actually has no impact on the RES accommodation, since a 100% accommodation is already guaranteed. Nevertheless, in the collaborative autonomous mode, when the transformer’s export power is within the feed-in limit, the incorporation of power loss would incentivize the local electricity usage and increase the RES accommodation. However, compared with TC that lowers local price to incentivize electricity usage when the exportation congestion occurs, the impact of power loss on accommodation rate is limited and not the focus of this benchmark.
2.5 结论
This paper proposes a two-stage TC framework for coordinating multiple interconnected MESs. Due to the nonlinearity of the storage’s complementarity constraint, a convexification technique is proposed along with two sufficient conditions to relax the constraint so that the convex problem applies to the distributed TC framework. In the proposed framework, each MES conducts rolling optimization autonomously at the lower level to minimize the operation cost under the given electricity price. At the same time, the upper-level system coordinator is responsible for updating the broadcasted price to solve the collaborative optimization iteratively . Considering the communication overhead and latency ,
a two-stage TC is established so that it even applies to real-time optimization with a short control interval, e.g., 5 min.
Compared with SG-RTC, the simulation shows that the proposed 2S-TC obtains results with an error of less than 1% within ten times fewer iterations. It is also verified that the collaborative optimization helps to achieve a 100% local accommodation of RES, compared to the autonomous case.
Furthermore, the benefits of different components in the MES and the effectiveness of the proposed convexification technique are also discussed in the simulation results.
Future work will include the analysis of establishing a competitive gas market. Another possible research direction is to consider price-responsive loads in our model to exploit the flexibility of end-customers.
🌈3 Matlab代码+数据+文章详细讲解
博客主页:电气辅导帮
🎉4 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。




![计算机系统基础实验——数据的机器级表示(计算浮点数 f 的绝对值[f])](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/301f8f3d414a4b5195bbeed611cbb3ce.png)