要想全面快速学习Spring的内容,最好的方法肯定是先去Spring官网去查阅文档,在Spring官网中找到了适合新手了解的官网Guides,一共68篇,打算全部过一遍,能尽量全面的了解Spring框架的每个特性和功能。

接着上篇看过的guide25,接着往下看。
guide26、Building a Reactive RESTful Web Service
简单介绍了怎么构建一个简单的响应式的restful web服务。
1、构建实体类
public class Greeting {
private String message;
public Greeting() {
}
public Greeting(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return this.message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; }
}
2、创建响应式类,用来处理请求和响应,这个响应类返回一个"hello spring"的json对象。
@Component
public class GreetingHandler {
public Mono<ServerResponse> hello(ServerRequest request) {
return ServerResponse.ok().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.body(BodyInserters.fromValue(new Greeting("Hello, Spring!")));
}
}
3、创建路由器,路由器侦听路径/hello,并返回我们的反应式处理程序类提供的值。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class GreetingRouter {
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route(GreetingHandler greetingHandler) {
return RouterFunctions
.route(GET("/hello").and(accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)), greetingHandler::hello);
}
}
4、创建网络客户端,平常的spring restTemplate本质上是阻塞的,而对于响应式应用程序,webclinet是非阻塞的。webclient使用响应式特性,使用mono的形式保存方法返回的内容。
@Component
public class GreetingClient {
private final WebClient client;
public GreetingClient(WebClient.Builder builder) {
this.client = builder.baseUrl("http://localhost:8080").build();
}
public Mono<String> getMessage() {
return this.client.get().uri("/hello").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(Greeting.class)
.map(Greeting::getMessage);
}
}
5、测试
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
GreetingClient greetingClient = context.getBean(GreetingClient.class);
// We need to block for the content here or the JVM might exit before the message is logged
System.out.println(">> message = " + greetingClient.getMessage().block());
}
}
测试结果:
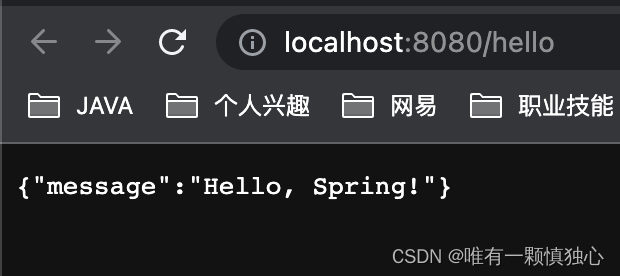
响应式编程概念理解:https://www.jianshu.com/p/035db36c5918
guide27、Building a Gateway
了解了gateway的一些基本功能,
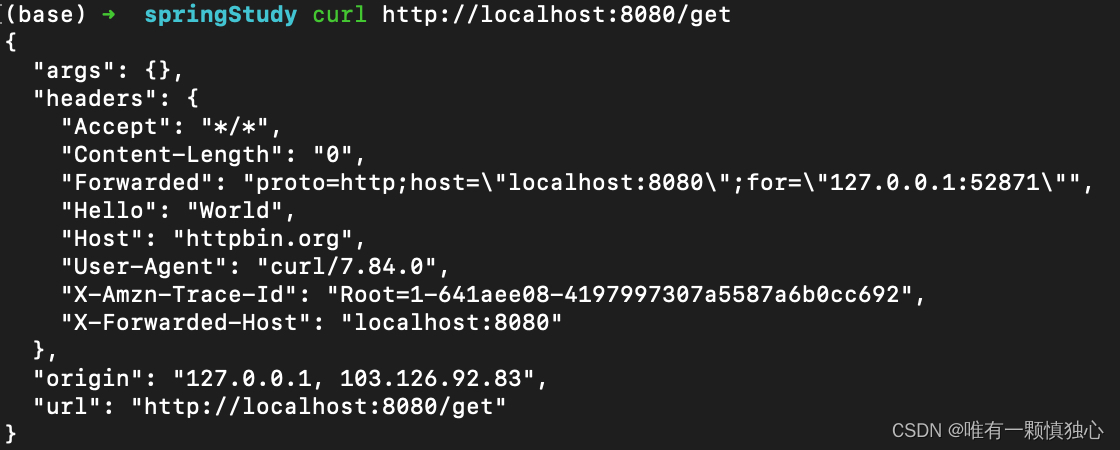
1、对路径包含/get的请求进行路由到https://httpbin.org/get,并且在路由配置中,增加了一个过滤器,过滤器在路由之前加上一个header到请求里。直接启动项目,就可以curl一下了。
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public RouteLocator myRoutes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route(p -> p
.path("/get")
.filters(f -> f.addRequestHeader("Hello", "World"))
.uri("http://httpbin.org:80"))
.build();
}
2、还可以再加一个路由。有时候由于网关背后的服务可能表现不佳,我们还可以将创建的路由包装在断路器中。并且新的路由中precidate变成了host,意思是host是*.circuitbreaker.com,才会被路由。
@Bean
public RouteLocator myRoutes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route(p -> p
.path("/get")
.filters(f -> f.addRequestHeader("Hello", "World"))
.uri("http://httpbin.org:80"))
.route(p -> p
.host("*.circuitbreaker.com")
.filters(f -> f.circuitBreaker(config -> config
.setName("mycmd")
.uri("http://httpbin.org:80"))
.build();
}
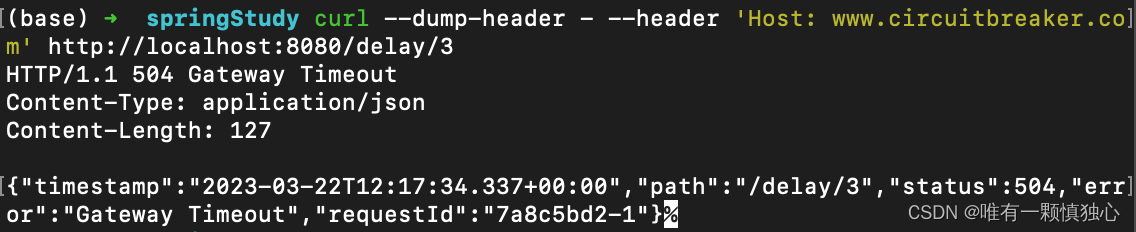
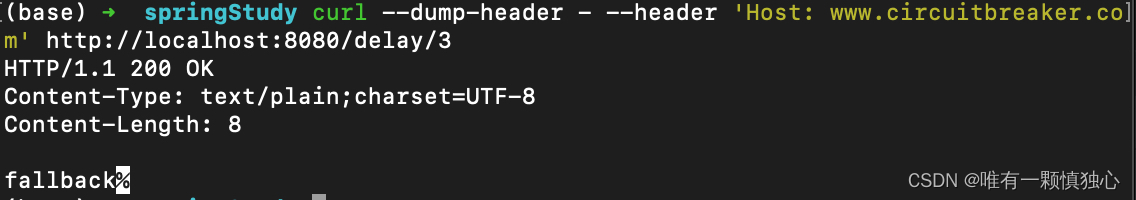
3、可以看到,断路器在等待 HTTPBin 的响应时超时。当断路器超时时,我们可以选择提供回退,以便客户端不会收到504而是其他更有意义的东西。例如,在生产场景中,我们可能会从缓存中返回一些数据,但在下述的简单示例中,我们会返回一个字符串response.
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@RequestMapping("/fallback")
public Mono<String> fallback() {
return Mono.just("fallback");
}
@Bean
public RouteLocator myRoutes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route(p -> p
.path("/get")
.filters(f -> f.addRequestHeader("Hello", "World"))
.uri("http://httpbin.org:80"))
.route(p -> p
.host("*.circuitbreaker.com")
.filters(f -> f.circuitBreaker(config -> config
.setName("mycmd")
.setFallbackUri("forward:/fallback")))
.uri("http://httpbin.org:80"))
.build();
}
}
涉及概念:
http://httpbin.org/ 这个网站能测试 HTTP 请求和响应的各种信息,比如 cookie、ip、headers
和登录验证等,且支持 GET、POST 等多种方法,对 web
开发和测试很有帮助。简单使用参考:https://blog.csdn.net/Hubz131/article/details/89157089
spring cloud
gateway官网文献:https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-gateway/reference/html/,核心的三个概念:
1、Route(路由) 这是Spring Cloud
Gateway的基本构建块,可简单理解成一条转发规则。包含:ID、目标URL、一组断言和一组过滤器 2、Predicate(断言) 这是一个
Java 8 的
Predicate,即java.util.function.Predicate这个接口,Gateway使用Predicate实现路由的匹配条件。断言,路径相匹配的进行路由。
3、Filter(过滤器) 一个标准的Spring WebFilter。Spring cloud
gateway中的filter分为两种类型的Filter,分别是Gateway Filter和Global
Filter。过滤器Filter将会对请求和响应进行修改处理。
guide28、Spring Cloud Stream
Spring Cloud Stream 是用来构建消息驱动的微服务程序的一个框架,它们通过 Apache Kafka 和 RabbitMQ 等消息中间件进行通信,涉及的概念主要包括source、processor、sink。
这块没有仔细深入。
guide29、Spring Cloud Task
Spring Cloud Task 是一个用于构建短期 Spring Boot微服务的框架,只需添加@EnableTask并将应用程序作为Spring Boot应用程序运行(单个应用程序上下文)。
Spring Cloud Task使用关系数据库存储已执行任务的结果。
写个demo, 首先是导入task、jdbc的依赖,application.yml配置文件连接好本地的mysql数据库。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableTask
public class SpringCloudTaskDemoApplication {
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner helloRunner() {
return new CommandLineRunner() {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("开始执行任务") ;
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1) ;
System.out.println("任务执行完成") ;
}
};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudTaskDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
直接执行,得出结果。run方法执行完以后我们的JVM进程也跟着结束了。这就是所谓的短期任务了,我们不需要任务一直执行,只需要在需要的时候执行即可。

注意:
@EnableTask: 该注解可以开启task功能。
任务执行完以后会在数据表中记录相关的执行结果信息:

guide30、Accessing data with R2DBC
Spring Data R2DBC项目是Spring提供的数据库响应式编程框架。
R2DBC是Reactive Relational Database Connectivity的首字母缩写词。 R2DBC是一个API规范倡议,它声明了一个响应式API,由驱动程序供应商实现,并以响应式编程的方式访问他们的关系数据库。
引入r2dbc相关的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>dev.miku</groupId>
<artifactId>r2dbc-mysql</artifactId>
<version>0.8.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
以及定义好实体类:
public class Customer {
@Idprivate Long id;
private final String firstName;
private final String lastName;
...
核心的是创建存储库接口,CustomerRepository扩展ReactiveCrudRepository接口。
public interface CustomerRepository extends ReactiveCrudRepository<Customer, Long> {
@Query("SELECT * FROM customer WHERE last_name = :lastname")
Flux<Customer> findByLastName(String lastName);
}
ReactiveCrudRepository继承了Repository,实现了基本的增删改查的模版方法。Spring Data R2DBC 还允许通过使用@Query注释来定义其他查询方法。
如果想要自定义操作,可以
1、按照方法名定义
findByName -> findBy<fieldName>
findByIdGreaterThan -> findBy<fieldName>GreaterThan
例如:
// 按名称查找
Flux<Customer> findByName(String name);
// 查找给定范围内的
Flux<Customer> findByIdGreaterThan(Long startId);
// 查找大于给定id的数据
Flux<Customer> findByIdGreaterThan(Long startId);
// 查询名称以给定字符串开头的数据
Flux<Customer> findByNameStartingWith(String start);
// 分页
Flux<Customer> findByIdGreaterThanEqual(Long startId, Pageable pageable);
2、手动编写SQL
例如上述的那种,用@Query注解。
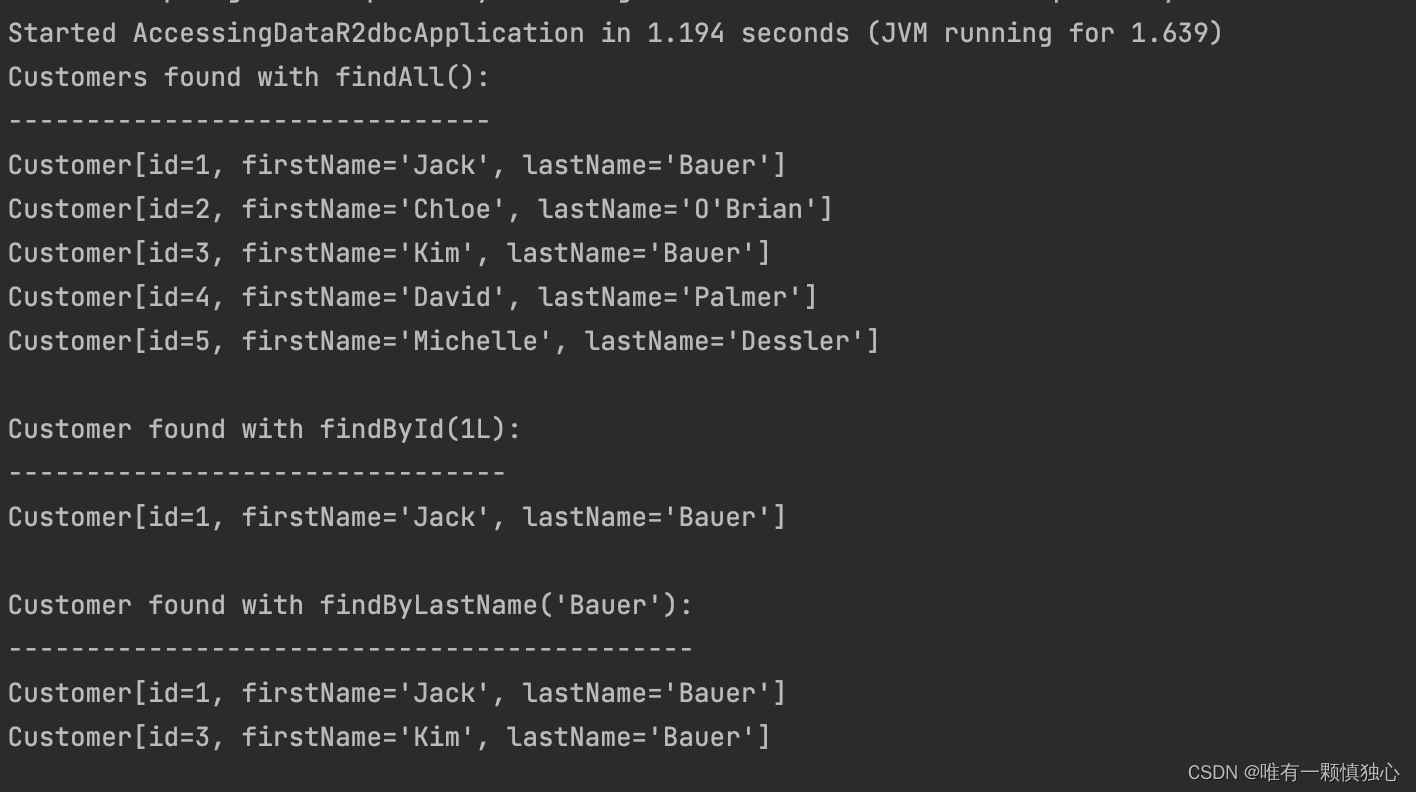
进行主类的编写,并且对R2DBC进行测试。
@SpringBootApplication
public class AccessingDataR2dbcApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AccessingDataR2dbcApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AccessingDataR2dbcApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
ConnectionFactoryInitializer initializer(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
ConnectionFactoryInitializer initializer = new ConnectionFactoryInitializer();
initializer.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
initializer.setDatabasePopulator(new ResourceDatabasePopulator(new ClassPathResource("schema.sql")));
return initializer;
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner demo(CustomerRepository repository) {
return (args) -> {
// save a few customers
repository.saveAll(Arrays.asList(new Customer("Jack", "Bauer"),
new Customer("Chloe", "O'Brian"),
new Customer("Kim", "Bauer"),
new Customer("David", "Palmer"),
new Customer("Michelle", "Dessler")))
.blockLast(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
// fetch all customers
log.info("Customers found with findAll():");
log.info("-------------------------------");
repository.findAll().doOnNext(customer -> {
log.info(customer.toString());
}).blockLast(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
log.info("");
// fetch an individual customer by ID
repository.findById(1L).doOnNext(customer -> {
log.info("Customer found with findById(1L):");
log.info("--------------------------------");
log.info(customer.toString());
log.info("");
}).block(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
// fetch customers by last name
log.info("Customer found with findByLastName('Bauer'):");
log.info("--------------------------------------------");
repository.findByLastName("Bauer").doOnNext(bauer -> {
log.info(bauer.toString());
}).blockLast(Duration.ofSeconds(10));;
log.info("");
};
}
}
输出结果: