一、背景:
今天一个小伙伴在开发中,常取不到数,像string转换int,int转换string 虽然好像只是倒过来了,但是实现的逻辑不一样,今天就是日期在计算过程中的转换做一个总结
二、步聚
1.JAVA中与日期时间相关的类
1.1java.util包中

1.2 java.time包中
JAVA8之后新增了java.time包,提供了一些与日期时间有关的新实现类:

具体每个类对应的含义说明梳理如下表:

2.时间间隔计算
2.1Period与Duration类
JAVA8开始新增的java.time包中有提供Duration和Period两个类,用于处理日期时间间隔相关的场景,两个类的区别点如下:

Duration与Period具体使用的时候还需要有一定的甄别,因为部分的方法很容易使用中被混淆,下面分别说明下。
-
Duration
Duration的最小计数单位为纳秒,其内部使用seconds和nanos两个字段来进行组合计数表示duration总长度。

Duration的常用API方法梳理如下:

关于Duration的主要API的使用,参见如下示意:
public void testDuration() { LocalTime target = LocalTime.parse("00:02:35.700"); // 获取当前日期,此处为了保证后续结果固定,注掉自动获取当前日期,指定固定日期 // LocalDate today = LocalDate.now(); LocalTime today = LocalTime.parse("12:12:25.600"); // 输出:12:12:25.600 System.out.println(today); // 输出:00:02:35.700 System.out.println(target); Duration duration = Duration.between(target, today); // 输出:PT12H9M49.9S System.out.println(duration); // 输出:43789 System.out.println(duration.getSeconds()); // 输出:900000000 System.out.println(duration.getNano()); // 输出:729 System.out.println(duration.toMinutes()); // 输出:PT42H9M49.9S System.out.println(duration.plusHours(30L)); // 输出:PT15.9S System.out.println(duration.withSeconds(15L));}
-
Period
Period相关接口与Duration类似,其计数的最小单位是天,看下Period内部时间段记录采用了年、月、日三个field来记录:

常用的API方法列举如下:

关于Period的主要API的使用,参见如下示意:
public void calculateDurationDays() {
LocalDate target = LocalDate.parse("2021-07-11");
// 获取当前日期,此处为了保证后续结果固定,注掉自动获取当前日期,指定固定日期 // LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate today = LocalDate.parse("2022-07-08"); // 输出:2022-07-08 System.out.println(today); // 输出:2021-07-11
System.out.println(target);
Period period = Period.between(target, today); // 输出:P11M27D, 表示11个月27天 System.out.println(period); // 输出:0, 因为period值为11月27天,即year字段为0 System.out.println(period.getYears()); // 输出:11, 因为period值为11月27天,即month字段为11
System.out.println(period.getMonths()); // 输出:27, 因为period值为11月27天,即days字段为27
System.out.println(period.getDays()); // 输出:P14M27D, 因为period为11月27天,加上3月,变成14月27天
System.out.println(period.plusMonths(3L)); // 输出:P11M15D,因为period为11月27天,仅将days值设置为15,则变为11月15天
System.out.println(period.withDays(15)); // 输出:P2Y3M44D System.out.println(Period.of(2, 3, 44));}
2.2.Duration与Period踩坑记
Duration与Period都是用于日期之间的计算操作。Duration主要用于秒、纳秒等维度的数据处理与计算。Period主要用于计算年、月、日等维度的数据处理与计算。
先看个例子,计算两个日期相差的天数,使用Duration的时候:
public void calculateDurationDays(String targetDate) { LocalDate target = LocalDate.parse(targetDate); LocalDate today = LocalDate.now(); System.out.println("today : " + today); System.out.println("target: " + target); long days = Duration.between(target, today).abs().toDays(); System.out.println("相差:" + days + "天");}
运行后会报错:
today : 2022-07-07target: 2022-07-11Exception in thread "main" java.time.temporal.UnsupportedTemporalTypeException: Unsupported unit: Seconds at java.time.LocalDate.until(LocalDate.java:1614) at java.time.Duration.between(Duration.java:475) at com.veezean.demo5.DateService.calculateDurationDays(DateService.java:24)
点击看下Duration.between源码,可以看到注释上明确有标注着,这个方法是用于秒级的时间段间隔计算,而我们这里传入的是两个天级别的数据,所以就不支持此类型运算,然后抛异常了。

再看下使用Period的实现:
public void calculateDurationDays(String targetDate) {
LocalDate target = LocalDate.parse(targetDate);
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("today : " + today);
System.out.println("target: " + target); // 注意,此处写法错误!这里容易踩坑: long days = Math.abs(Period.between(target, today).getDays()); System.out.println("相差:" + days + "天")
;}
执行结果:
today : 2022-07-07target: 2021-07-07相差:0天
执行是不报错,但是结果明显是错误的。这是因为getDays()并不会将Period值换算为天数,而是单独计算年、月、日,此处只是返回天数这个单独的值。
再看下面的写法:
public void calculateDurationDays(String targetDate) { LocalDate target = LocalDate.parse(targetDate); LocalDate today = LocalDate.now(); System.out.println("today : " + today); System.out.println("target: " + target); Period between = Period.between(target, today); System.out.println("相差:" + Math.abs(between.getYears()) + "年" + Math.abs(between.getMonths()) + "月" + Math.abs(between.getDays()) + "天");}
结果为:
today : 2022-07-07target: 2021-07-11相差:0年11月26天
所以说,如果想要计算两个日期之间相差的绝对天数,用Period不是一个好的思路。
3.计算日期差
-
通过LocalDate来计算
LocalDate中的toEpocDay可返回当前时间距离原点时间之间的天数,可以基于这一点,来实现计算两个日期之间相差的天数:

代码如下:
public void calculateDurationDays(String targetDate) {
LocalDate target = LocalDate.parse(targetDate);
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("today : " + today);
System.out.println("target: " + target);
long days = Math.abs(target.toEpochDay() - today.toEpochDay()); System.out.println("相差:" + days + "天");}
结果为:
today : 2022-07-07target: 2021-07-11相差:361天
-
通过时间戳来计算
如果是使用的Date对象,则可以通过将Date日期转换为毫秒时间戳的方式相减然后将毫秒数转为天数的方式来得到结果。需要注意的是通过毫秒数计算日期天数的差值时,需要屏蔽掉时分秒带来的误差影响。
public void calculateDaysGap(Date start, Date end) {
final long ONE_DAY_MILLIS = 1000L * 60 * 60 * 24; // 此处要注意,去掉时分秒的差值影响,此处采用先换算为天再相减的方式
long gapDays = Math.abs(end.getTime()/ONE_DAY_MILLIS - start.getTime()/ONE_DAY_MILLIS);
System.out.println(gapDays);
}
输出结果:
today : 2022-07-08target: 2021-07-11相差:362天
-
数学逻辑计算
分别算出年、月、日差值,然后根据是否闰年、每月是30还是31天等计数逻辑,纯数学硬怼方式计算。
不推荐、代码略...
4.计算接口处理耗时
在一些性能优化的场景中,我们需要获取到方法处理的执行耗时,很多人都是这么写的:
public void doSomething() { // 记录开始时间戳
long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); // do something ... // 计算结束时间戳
long endMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 计算相差的毫秒数 System.out.println(endMillis - startMillis);}
当然啦,如果你使用的是JDK8+的版本,你还可以这么写:
public void doSomething() {
// 记录开始时间戳
Instant start = Instant.now();
// do something ...
// 计算结束时间戳
Instant end = Instant.now();
// 计算相差的毫秒数
System.out.println(Duration.between(start, end).toMillis());
}
5.时间格式转换
项目中,时间格式转换是一个非常典型的日期处理操作,可能会涉及到将一个字符串日期转换为JAVA对象,或者是将一个JAVA日期对象转换为指定格式的字符串日期时间。
SimpleDataFormat实现
在JAVA8之前,通常会使用SimpleDateFormat类来处理日期与字符串之间的相互转换:
public void testDateFormatter() { SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); // 日期转字符串
String format = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date());
System.out.println("当前时间:" + format);
try {
// 字符串转日期
Date parseDate = simpleDateFormat.parse("2022-07-08 06:19:27"); System.out.println("转换后Date对象: " + parseDate);
// 按照指定的时区进行转换,可以对比下前面转换后的结果,会发现不一样 simpleDateFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT+5:00"));
parseDate = simpleDateFormat.parse("2022-07-08 06:19:27"); System.out.println("指定时区转换后Date对象: " + parseDate);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }}
输出结果如下:
当前时间:2022-07-08 06:25:31转换后Date对象: Fri Jul 08 06:19:27 CST 2022指定时区转换后Date对象: Fri Jul 08 09:19:27 CST 2022
补充说明:
SimpleDateFormat对象是非线程安全的,所以项目中在封装为工具方法使用的时候需要特别留意,最好结合ThreadLocal来适应在多线程场景的正确使用。
JAVA8之后,推荐使用DateTimeFormat替代SimpleDateFormat。
6.DataTimeFormatter实现
JAVA8开始提供的新的用于日期与字符串之间转换的类,它很好的解决了SimpleDateFormat多线程的弊端,也可以更方便的与java.time中心的日期时间相关类的集成调用。
public void testDateFormatter() {
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
// 格式化为字符串
String format = localDateTime.format(dateTimeFormatter); System.out.println("当前时间:" + format);
// 字符串转Date
LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse("2022-07-08 06:19:27", dateTimeFormatter);
Date date = Date.from(parse.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()); System.out.println("转换后Date对象: " + date);
}
输出结果:
当前时间:2022-07-08 18:37:46转换后Date对象: Fri Jul 08 06:19:27 CST 2022
7.日期时间格式模板
对于计算机而言,时间处理的时候按照基于时间原点的数字进行处理即可,但是转为人类方便识别的场景显示时,经常会需要转换为不同的日期时间显示格式,比如:
2022-07-08 12:02:342022/07/08 12:02:34.2382022年07月08日 12点03分48秒
在JAVA中,为了方便各种格式转换,提供了基于时间模板进行转换的实现能力:

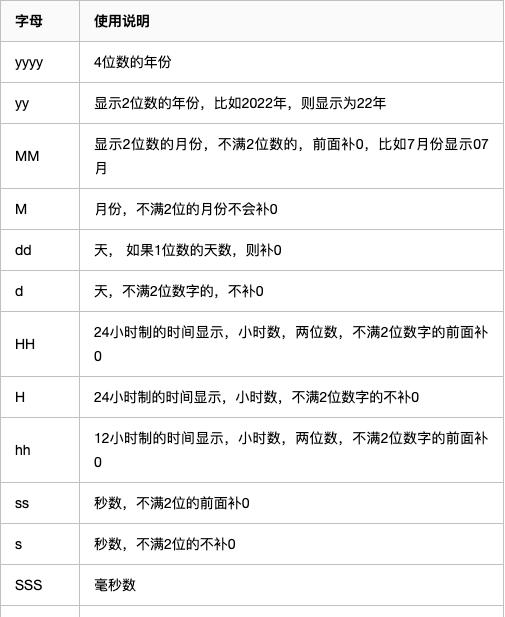
时间格式模板中的字幕含义说明如下:
8.消失的8小时问题
日期字符串存入DB后差8小时
在后端与数据库交互的时候,可能会遇到一个问题,就是往DB中存储了一个时间字段之后,后面再查询的时候,就会发现时间数值差了8个小时,这个需要在DB的连接信息中指定下时区信息:
spring.datasource.druid.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
界面时间与后台时间差8小时
在有一些前后端交互的项目中,可能会遇到一个问题,就是前端选择并保存了一个时间信息,再查询的时候就会发现与设置的时间差了8个小时,这个其实就是后端时区转换设置的问题。
SpringBoot的配置文件中,需要指定时间字符串转换的时区信息:
spring.jackson.time-zone=GMT+8
这样从接口json中传递过来的时间信息,jackson框架可以根据对应时区转换为正确的Date数据进行处理。





![[RSA议题分析] Aikido Turning EDRs to malicious wipers using 0-day exploits](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6eb9a127c2894aa391e88252bd0cc4a3.png#pic_center)