目录
增量式或位置式
目录
增量式或位置式
PID控制周期
T1 时间
T2 约4ms
PID C代码
最近有小伙伴向我提问关于PID的问题:通过比例阀控制水流速度(流量),
- 使用增量式还是位置式 PID?
- 他的比例法驱动频率是500Hz那么PID的控制周期应该选多少?
增量式或位置式
借用知乎网友的一个回答:
通过带有调节阀的管路向水箱注水,控制输出u为阀门开度,如果控制目标是注水速度(流量),则采用增量控制,达到目标流量后阀门会保持;如果控制目标是水位,则采用位置式,达到目标水位后阀门会基本处于零位(积分作用下会保持一定开度)。
可以看出,当控制输出u,和控制目标是一一对应关系(一定阀门开度对应一定流量)时,采用增量式;当控制输出u,影响的是控制目标的速度(水位变化的速度,即流量)时,采用位置控制。
又比如,通过油门控制车速,也是增量控制,根据期望速度加减油门,速度到了保持住。
我们这里控制水恒流量,应该选用增量式。
PID控制周期
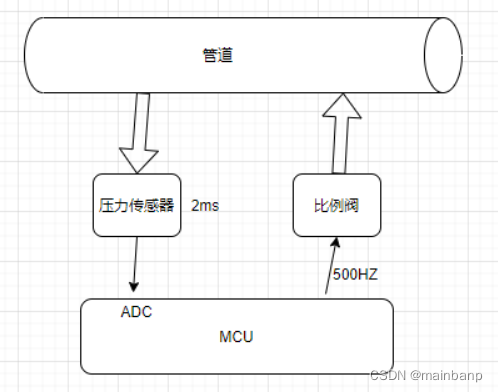
周期 = T1(比例阀变化 -> 物理压力变化量) + T2(压力电压变化量 -> ADC量化时间 )
T1 时间
这样具体要根据实际情况改变了,可以先按照100ms去调试。
T2 约4ms
可以查阅数据手册
压力传感器:
估算为2ms

MCU
算上软件滤波,ADC量化时间估算为2ms
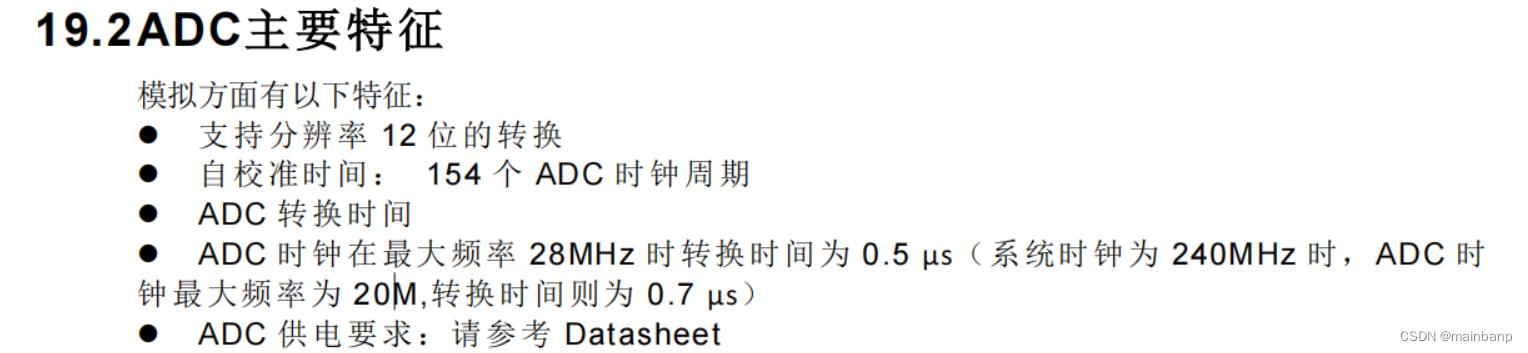

咱们这里先采用100ms~200ms的PID控制周期去调PID参数。
PID C代码
/*This file has been prepared for Doxygen automatic documentation generation.*/
/*! \file *********************************************************************
*
* \brief Header file for pid.c.
*
* - File: pid.h
* - Compiler: IAR EWAAVR 4.11A
* - Supported devices: All AVR devices can be used.
* - AppNote: AVR221 - Discrete PID controller
*
* \author Atmel Corporation: http://www.atmel.com \n
* Support email: avr@atmel.com
*
* $Name$
* $Revision: 456 $
* $RCSfile$
* $Date: 2006-02-16 12:46:13 +0100 (to, 16 feb 2006) $
*****************************************************************************/
#ifndef PID_H
#define PID_H
#include "stdint.h"
#define SCALING_FACTOR 128
/*! \brief PID Status
*
* Setpoints and data used by the PID control algorithm
*/
typedef struct PID_DATA{
//! Last process value, used to find derivative of process value.
int16_t lastProcessValue;
//! Summation of errors, used for integrate calculations
int32_t sumError;
//! The Proportional tuning constant, multiplied with SCALING_FACTOR
int16_t P_Factor;
//! The Integral tuning constant, multiplied with SCALING_FACTOR
int16_t I_Factor;
//! The Derivative tuning constant, multiplied with SCALING_FACTOR
int16_t D_Factor;
//! Maximum allowed error, avoid overflow
int16_t maxError;
//! Maximum allowed sumerror, avoid overflow
int32_t maxSumError;
} pidData_t;
/*! \brief Maximum values
*
* Needed to avoid sign/overflow problems
*/
// Maximum value of variables
#define MAX_INT INT16_MAX
#define MAX_LONG INT32_MAX
#define MAX_I_TERM (MAX_LONG / 2)
// Boolean values
#define FALSE 0
#define TRUE 1
void pid_Init(int16_t p_factor, int16_t i_factor, int16_t d_factor, struct PID_DATA *pid);
int16_t pid_Controller(int16_t setPoint, int16_t processValue, struct PID_DATA *pid_st);
void pid_Reset_Integrator(pidData_t *pid_st);
#endif
/*This file has been prepared for Doxygen automatic documentation generation.*/
/*! \file *********************************************************************
*
* \brief General PID implementation for AVR.
*
* Discrete PID controller implementation. Set up by giving P/I/D terms
* to Init_PID(), and uses a struct PID_DATA to store internal values.
*
* - File: pid.c
* - Compiler: IAR EWAAVR 4.11A
* - Supported devices: All AVR devices can be used.
* - AppNote: AVR221 - Discrete PID controller
*
* \author Atmel Corporation: http://www.atmel.com \n
* Support email: avr@atmel.com
*
* $Name$
* $Revision: 456 $
* $RCSfile$
* $Date: 2006-02-16 12:46:13 +0100 (to, 16 feb 2006) $
*****************************************************************************/
#include "pid.h"
#include "stdint.h"
/*! \brief Initialisation of PID controller parameters.
*
* Initialise the variables used by the PID algorithm.
*
* \param p_factor Proportional term.
* \param i_factor Integral term.
* \param d_factor Derivate term.
* \param pid Struct with PID status.
*/
void pid_Init(int16_t p_factor, int16_t i_factor, int16_t d_factor, struct PID_DATA *pid)
// Set up PID controller parameters
{
// Start values for PID controller
pid->sumError = 0;
pid->lastProcessValue = 0;
// Tuning constants for PID loop
pid->P_Factor = p_factor;
pid->I_Factor = i_factor;
pid->D_Factor = d_factor;
// Limits to avoid overflow
pid->maxError = MAX_INT / (pid->P_Factor + 1);
pid->maxSumError = MAX_I_TERM / (pid->I_Factor + 1);
}
/*! \brief PID control algorithm.
*
* Calculates output from setpoint, process value and PID status.
*
* \param setPoint Desired value.
* \param processValue Measured value.
* \param pid_st PID status struct.
*/
int16_t pid_Controller(int16_t setPoint, int16_t processValue, struct PID_DATA *pid_st)
{
int16_t error, p_term, d_term;
int32_t i_term, ret, temp;
error = setPoint - processValue;
// Calculate Pterm and limit error overflow
if (error > pid_st->maxError){
p_term = MAX_INT;
}
else if (error < -pid_st->maxError){
p_term = -MAX_INT;
}
else{
p_term = pid_st->P_Factor * error;
}
// Calculate Iterm and limit integral runaway
temp = pid_st->sumError + error;
if(temp > pid_st->maxSumError){
i_term = MAX_I_TERM;
pid_st->sumError = pid_st->maxSumError;
}
else if(temp < -pid_st->maxSumError){
i_term = -MAX_I_TERM;
pid_st->sumError = -pid_st->maxSumError;
}
else{
pid_st->sumError = temp;
i_term = pid_st->I_Factor * pid_st->sumError;
}
// Calculate Dterm
d_term = pid_st->D_Factor * (pid_st->lastProcessValue - processValue);
pid_st->lastProcessValue = processValue;
ret = (p_term + i_term + d_term) / SCALING_FACTOR;
if(ret > MAX_INT){
ret = MAX_INT;
}
else if(ret < -MAX_INT){
ret = -MAX_INT;
}
return((int16_t)ret);
}
/*! \brief Resets the integrator.
*
* Calling this function will reset the integrator in the PID regulator.
*/
void pid_Reset_Integrator(pidData_t *pid_st)
{
pid_st->sumError = 0;
}
/*This file has been prepared for Doxygen automatic documentation generation.*/
/*! \file *********************************************************************
*
* \brief Example of use of general PID implementation for AVR.
*
* Example of how to setup and use the general PID implementation in pid.c.
*
* - File: main.c
* - Compiler: IAR EWAAVR 4.11A
* - Supported devices: All AVR devices can be used.
* - AppNote: AVR221 - Discrete PID controller
*
* \author Atmel Corporation: http://www.atmel.com \n
* Support email: avr@atmel.com
*
* $Name$
* $Revision: 456 $
* $RCSfile$
* $Date: 2006-02-16 12:46:13 +0100 (to, 16 feb 2006) $
*****************************************************************************/
#include <inavr.h>
#include <ioavr.h>
#include "stdint.h"
#include "pid.h"
/*! \brief P, I and D parameter values
*
* The K_P, K_I and K_D values (P, I and D gains)
* need to be modified to adapt to the application at hand
*/
//! \xrefitem todo "Todo" "Todo list"
#define K_P 1.00
//! \xrefitem todo "Todo" "Todo list"
#define K_I 0.00
//! \xrefitem todo "Todo" "Todo list"
#define K_D 0.00
/*! \brief Flags for status information
*/
struct GLOBAL_FLAGS {
//! True when PID control loop should run one time
uint8_t pidTimer:1;
uint8_t dummy:7;
} gFlags = {0, 0};
//! Parameters for regulator
struct PID_DATA pidData;
/*! \brief Sampling Time Interval
*
* Specify the desired PID sample time interval
* With a 8-bit counter (255 cylces to overflow), the time interval value is calculated as follows:
* TIME_INTERVAL = ( desired interval [sec] ) * ( frequency [Hz] ) / 255
*/
//! \xrefitem todo "Todo" "Todo list"
#define TIME_INTERVAL 157
/*! \brief Timer interrupt to control the sampling interval
*/
#pragma vector = TIMER0_OVF_vect
__interrupt void TIMER0_OVF_ISR( void )
{
static uint16_t i = 0;
if(i < TIME_INTERVAL)
i++;
else{
gFlags.pidTimer = TRUE;
i = 0;
}
}
/*! \brief Init of PID controller demo
*/
void Init(void)
{
pid_Init(K_P * SCALING_FACTOR, K_I * SCALING_FACTOR , K_D * SCALING_FACTOR , &pidData);
// Set up timer, enable timer/counte 0 overflow interrupt
TCCR0A = (1<<CS00);
TIMSK0 = (1<<TOIE0);
TCNT0 = 0;
}
/*! \brief Read reference value.
*
* This function must return the reference value.
* May be constant or varying
*/
int16_t Get_Reference(void)
{
return 8;
}
/*! \brief Read system process value
*
* This function must return the measured data
*/
int16_t Get_Measurement(void)
{
return 4;
}
/*! \brief Set control input to system
*
* Set the output from the controller as input
* to system.
*/
void Set_Input(int16_t inputValue)
{
;
}
/*! \brief Demo of PID controller
*/
void main(void)
{
int16_t referenceValue, measurementValue, inputValue;
Init();
__enable_interrupt();
while(1){
// Run PID calculations once every PID timer timeout
if(gFlags.pidTimer)
{
referenceValue = Get_Reference();
measurementValue = Get_Measurement();
inputValue = pid_Controller(referenceValue, measurementValue, &pidData);
Set_Input(inputValue);
gFlags.pidTimer = FALSE;
}
}
}
/*! \mainpage
* \section Intro Introduction
* This documents data structures, functions, variables, defines, enums, and
* typedefs in the software for application note AVR221.
*
* \section CI Compilation Info
* This software was written for the IAR Embedded Workbench 4.11A.
*
* To make project:
* <ol>
* <li> Add the file main.c and pid.c to project.
* <li> Under processor configuration, select desired Atmel AVR device.
* <li> Enable bit definitions in I/O include files
* <li> High optimization on speed is recommended for best performance
* </ol>
*
* \section DI Device Info
* The included source code is written for all Atmel AVR devices.
*
* \section TDL ToDo List
* \todo Put in own code in:
* \ref Get_Reference(void), \ref Get_Measurement(void) and \ref Set_Input(int16_t inputValue)
*
* \todo Modify the \ref K_P (P), \ref K_I (I) and \ref K_D (D) gain to adapt to your application
* \todo Specify the sampling interval time \ref TIME_INTERVAL
*/
这是一份AVR的官方增量式代码,也很容易移植到不同的MCU,这份代码我也有实际产品使用过,非常好。