1.创建Maven Module
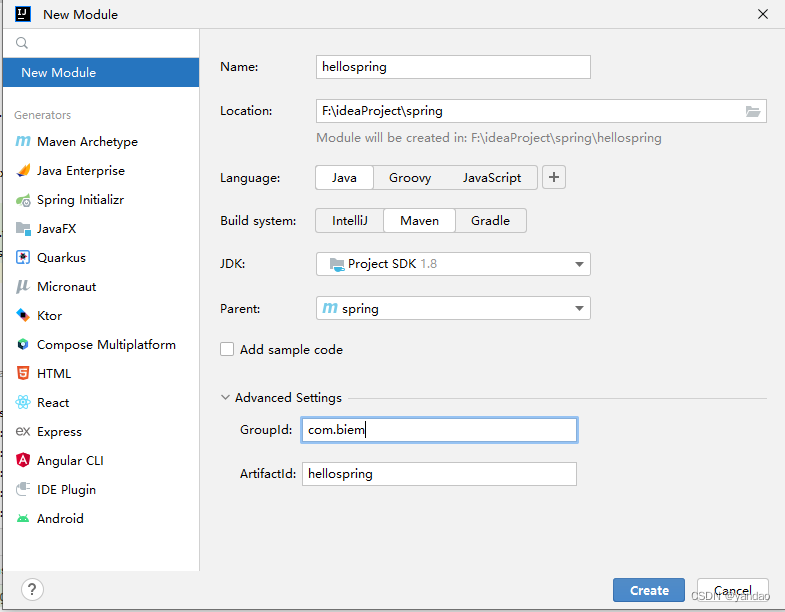
2.pom.xml引入依赖
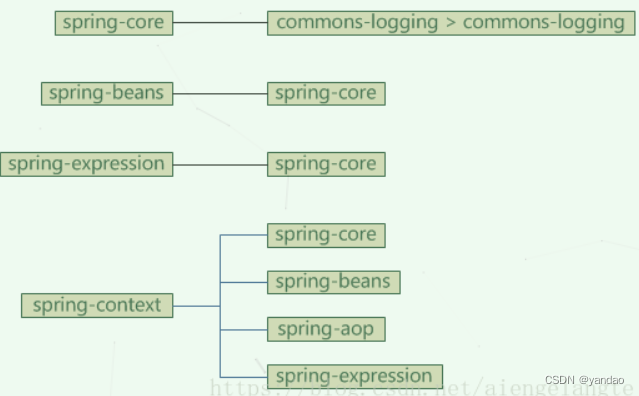
此图引用于https://www.cnblogs.com/Zz-maker/p/11199331.html
Maven种的依赖的传递性,spring-context依赖于core,beans,aop,expression等模块,但是在pom.xml中只引用spring-context即可:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<groupId>com.biem</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>hellospring</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
引入spring-context后,可以同maven查看spring-context的依赖关系
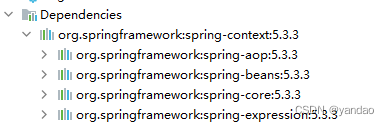
2.创建com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld
package com.biem.spring.pojo;
/**
* ClassName: HelloWorld
* Package: com.biem.spring.pojo
* Description:
*
* @Create 2023/5/25 16:42
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class HelloWorld {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("Hello Spring");
}
}
3.新建applicationContext.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
bean:配置一个bean对象,将对象给IOC容器管理
属性:
id:bean的唯一标识,不能重复
class:设置bean对象所对于的类型
-->
<bean id="helloworld" class="com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld"></bean>
</beans>
4.测试类com.biem.spring.text.HelloWorldTest.java
package com.biem.spring.test;
import com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* ClassName: HelloWorldTest
* Package: com.biem.spring.test
* Description:
*
* @Create 2023/5/25 16:47
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class HelloWorldTest {
@Test
public void test(){
//获取IOC容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取IOC容器中的Bean对象
HelloWorld helloworld = (HelloWorld)context.getBean("helloworld");
helloworld.sayHello();
}
}
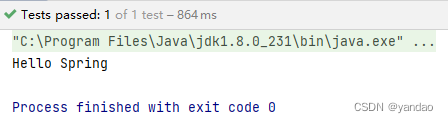
5.运行结果
知识点增强
5.1 IOC思想
Inversion of Control,翻译过来是反转控制。
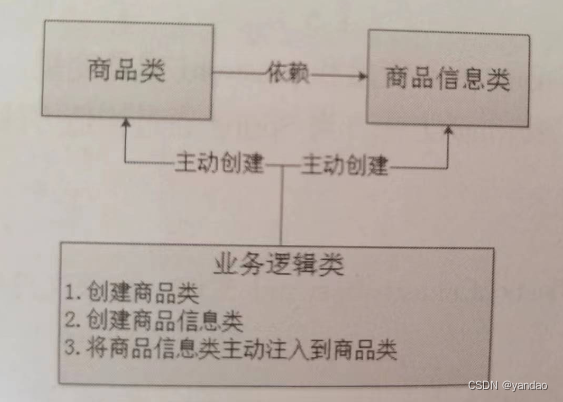
5.1.1 获取资源的传统方式
在应用程序中的组件需要获取资源时,传统的方式是组件主动的从容器中获取所需要的资源,在这样的模式下开发人员往往需要知道在具体容器中特定资源的获取方式,增加了学习成本,同时降低了开发效率。
5.1.2 反转控制方式获取资源
反转控制的思想完全颠覆了应用程序组件获取资源的传统方式:反转了资源的获取方向——改由容器主动的将资源推送给需要的组件,开发人员不需要知道容器是如何创建资源对象的,只需要提供接收资源的方式即可,极大的降低了学习成本,提高了开发的效率。这种行为也称为查找的被动形式。
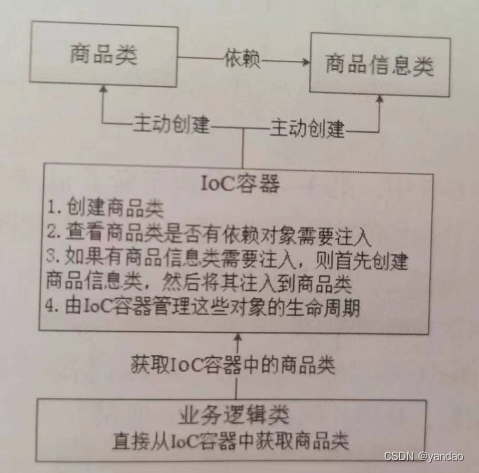
5.1.3 DI
DI:Dependency Injection,翻译过来是依赖注入。
DI 是 IOC 的另一种表述方式:即组件以一些预先定义好的方式(例如:setter 方法)接受来自于容器
的资源注入。相对于IOC而言,这种表述更直接。
所以结论是:IOC 就是一种反转控制的思想, 而 DI 是对 IOC 的一种具体实现。
5.2 IOC容器在Spring中的实现
Spring 的 IOC 容器就是 IOC 思想的一个落地的产品实现。IOC 容器中管理的组件也叫做 bean。在创建
bean 之前,首先需要创建 IOC 容器。Spring 提供了 IOC 容器的两种实现方式:
5.2.1 BeanFactory
这是 IOC 容器的基本实现,是 Spring 内部使用的接口。面向 Spring 本身,不提供给开发人员使用。
5.2.2 ApplicationContext
BeanFactory 的子接口,提供了更多高级特性。面向 Spring 的使用者,几乎所有场合都使用ApplicationContext 而不是底层的 BeanFactory。
5.3 ApplicationContext的主要实现类
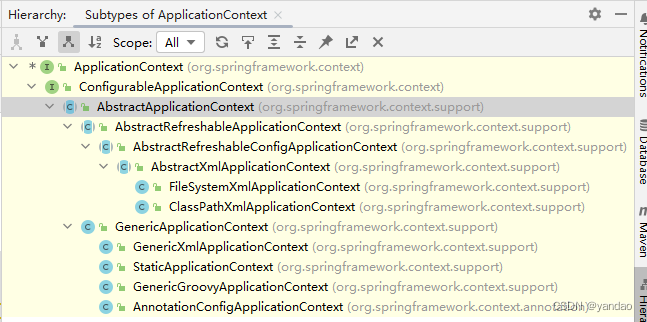
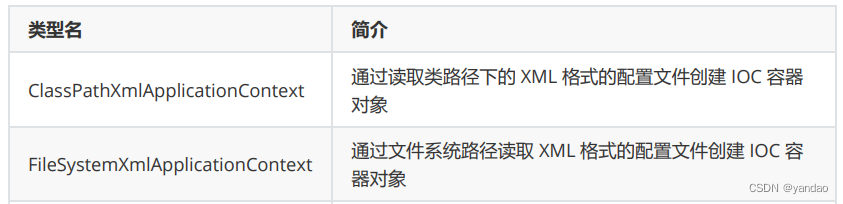
5.4 获取bean的方式
5.4.1 方式一:根据id获取
由于 id 属性指定了 bean 的唯一标识,所以根据 bean 标签的 id 属性可以精确获取到一个组件对象。
上个实验中我们使用的就是这种方式。
ApplicationContext.xml
<bean id="helloworld" class="com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld"></bean>
com.biem.spring.text.HelloWorldTest.java
@Test
public void getBeanById(){
//获取IOC容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取IOC容器中的Bean对象
HelloWorld helloworld = (HelloWorld)context.getBean("helloworld");
helloworld.sayHello();
}
5.4.2 方式二:根据类型获取
ApplicationContext.xml
<bean id="helloworld" class="com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld"></bean>
com.biem.spring.text.HelloWorldTest.java
@Test
public void getBeanByClassType(){
//获取IOC容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取IOC容器中的Bean对象
HelloWorld helloworld = context.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
helloworld.sayHello();
}
5.4.3 方式三:根据id和类型
ApplicationContext.xml
<bean id="helloworld" class="com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld"></bean>
com.biem.spring.text.HelloWorldTest.java
@Test
public void getBeanByIdAndClassType(){
//获取IOC容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取IOC容器中的Bean对象
HelloWorld helloworld = context.getBean("helloworld",HelloWorld.class);
helloworld.sayHello();
}
5.4.4 注意
5.4.4.1 根据类型获取bean时,要求IOC容器中指定类型的bean唯一
当IOC容器中一共配置了两个:
ApplicationContext.xml
<bean id="helloworld" class="com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld"></bean>
<bean id="helloworldOne" class="com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld"></bean>
<bean id="helloworldTwo" class="com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld"></bean>
根据类型获取时会抛出异常:
org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException:
No qualifying bean of type 'com.biem.spring.pojo.HelloWorld' available:
expected single matching bean but found 3: helloworld,helloworldOne,helloworldTwo
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveNamedBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1262)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:494)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:349)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:342)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBean(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1177)
at com.biem.spring.test.HelloWorldTest.getBeanByClassType(HelloWorldTest.java:40)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:50)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:47)
at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:17)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runLeaf(ParentRunner.java:325)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:78)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:57)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:288)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363)
at org.junit.runner.JUnitCore.run(JUnitCore.java:137)
at com.intellij.junit4.JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.startRunnerWithArgs(JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.java:69)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater$1.execute(IdeaTestRunner.java:38)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.TestsRepeater.repeat(TestsRepeater.java:11)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater.startRunnerWithArgs(IdeaTestRunner.java:35)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.JUnitStarter.prepareStreamsAndStart(JUnitStarter.java:235)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.JUnitStarter.main(JUnitStarter.java:54)
5.4.4.2 如果组件类实现了接口,根据接口类型可以获取 bean 吗?
可以,前提是bean唯一
5.4.4.3 如果一个接口有多个实现类,这些实现类都配置了 bean,根据接口类型可以获取 bean 吗?
不行,因为bean不唯一
5.4.4.4 根据类型来获取bean时,在满足bean唯一性的前提下,其实只是看:『对象 instanceof 指定的类
型』的返回结果,只要返回的是true就可以认定为和类型匹配,能够获取到。