文章目录
- 前言
- 基本认识
- 基本使用
- 一.构造函数
- 默认构造函数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 其它构造函数
- ①string(const char* s)
- ②string(size_t n, char c)
- ③string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
- 二.容量接口
- ①size与length
- ②max_size
- ③capacity
- ④empty
- ⑤clear
- ⑥reverse
- ⑦resize
- 三.修改接口
- ①+=
- ②[]
- ③push_back
- ④append
- ⑤c_str
- ⑥ find
- ⑦rfind
- 四.迭代器——iterator
- 基本概念
- ①begin与end
- ②rbegin和rend
前言
在C语言中是没有字符串类型的,但是我们会经常对字符串进行操作,因此到了C++就提出了string类,用于对字符串进行操作,下面我们来了解一下。
基本认识
- 字符串是表示字符序列的类
- 因为string类实现的比STL早,所以不在容器里。
- string类的使用跟容器,都基本是通过调用接口实现的。
- string类是basic_string模板的实例化,操作的数据类型为char。
string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名——
typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator>string;
- string类只能操作单个字符,不能对多个字符一块操作。
基本使用
库里面的类——那就要包含头文件
#include<string>
要使用库里的类:
- 展开命名空间
using namespace::std;
- 或者指定作用域
std::string A;
一.构造函数
默认构造函数
函数:
string()
功能:初始化为空字符串,后面跟上一定长度的0或者说为\0。
例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string A;
return 0;
}
打开监视窗口,看初始化后的结果:
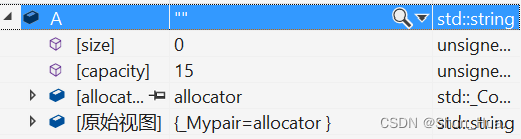
- 给我们显示的只是一个空字符串。
- 那实际上呢?
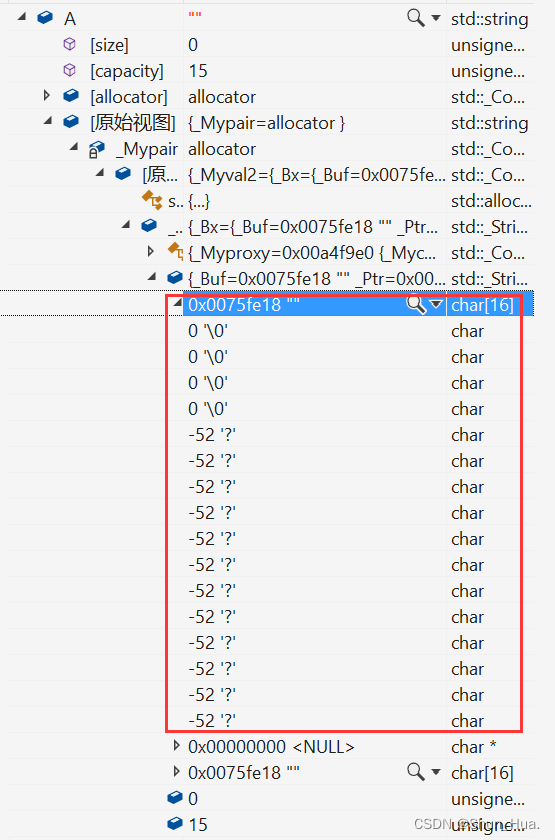
- 其实是一个数组,空间是16个字节,前4个元素初始化为0——\0。
拷贝构造函数
函数:
string(const string&s)
//这里的const将权限缩到最小,所以既可以传string又可以传const string
功能:拷贝构造。
举例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string A;
string B(A);
string C = A;
//这里也是拷贝构造,因为是用一个已经初始化的对象初始化另一个正在初始化的对象。
return 0;
}
其它构造函数
①string(const char* s)
函数:
string(const char* s)
功能:用一个字符串初始化一个string类。
例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string B("hello world");
return 0;
}
②string(size_t n, char c)
函数:
string(size_t n, char c)
功能:将string类初始化为n个c字符。
例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string B(6,'x');
cout << B << endl;
return 0;
}
执行结果:
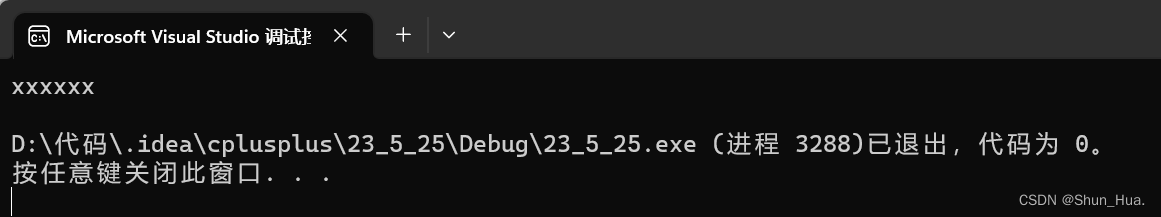
③string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
函数:
string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
static const size_t npos = -1;//-1就等于FFFFFFFF
功能:将一个string类的内容从第pos个位置开始,到npos位置的字符拷贝到另一个string类中。
例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string B("hello world");
string A(B, 0, 5);
//这里的0按照数组的下标进行计算的。
//5是包括从0位置开始的5个元素。
cout << A << endl;
return 0;
}
二.容量接口
①size与length
- 说明:size与length都是求string类的有效字符。
有效字符就是求除了\0的字符。
举例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string A("hello");
cout << A.size() << endl;
cout << A.length() << endl;
return 0;
}
补充:size的设计是为了迎合容器,因为只有字符串才叫长度,其它的都叫size。
②max_size
函数:
size_t max_size() const;
功能:字符串能够达到的最大长度。
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
string A;
cout<<A.max_size()<<endl;
return 0;
}

③capacity
- 功能:求字符类当前有效字符的最大容量。
举例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string A("hello");
cout << A.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
执行结果:
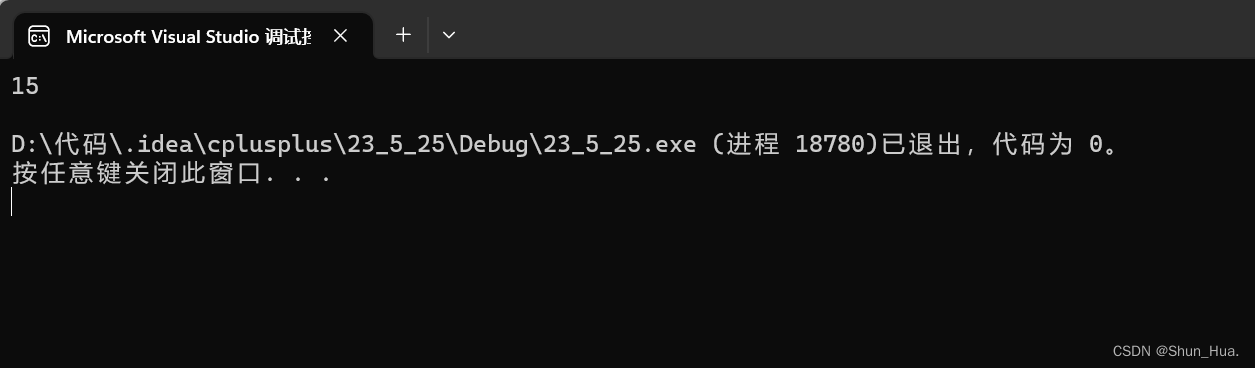
-
可我们明明开了16个字节,但是这里却说开辟了15个字节,为什么呢?
-
因为:我们并没有算\0的空间,只算了能够存储有效字符的空间。
那如果我们这样写呢?
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
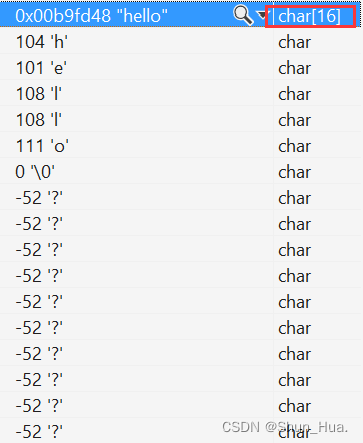
string A("hel\0lo\0");
cout << A.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:

识别出来的字符串是这样的:
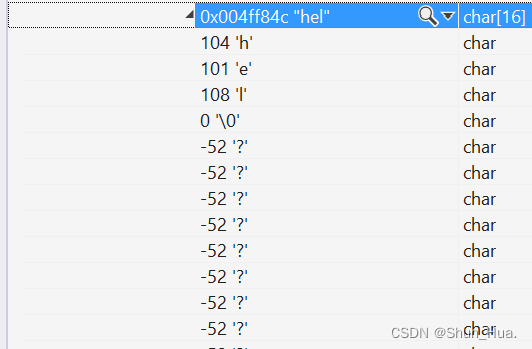
- 因此:string类只识别到第一个\0为止,之后的不做考虑。
那如果我们存20个字节,那么string类会对我们的空间进行扩容吗?
例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string A("hello");
int prev_capacity = A.capacity();
cout << prev_capacity << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
while (A.size() != prev_capacity)
{
A += 'x';
}
A += 'x';
cout << A.capacity() << endl;
prev_capacity = A.capacity();
}
return 0;
}
执行结果:
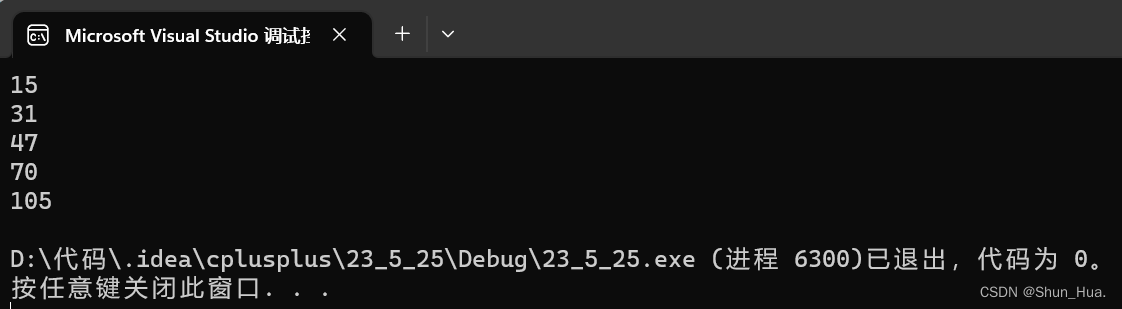
我们可以看出——这里是会扩容的,而且第一次扩容是2倍扩容(算上\0),之后的扩容接近1.5倍扩容。(VS2019)
我们再换到Linux平台上进行测试:
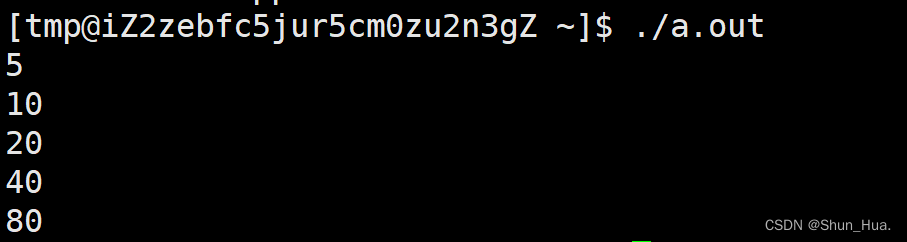
- 不难看出,这里的扩容是以两倍进行扩容的。
④empty
函数:
bool empty() const;
//说明:加了const,所以使用empty是不会对string类进行修改的。
功能:检测string是否为空,为空返回真,其余情况返回假。
例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string A("\0");
if (A.empty())
{
printf("YES\n");
}
else
{
printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}
结果:
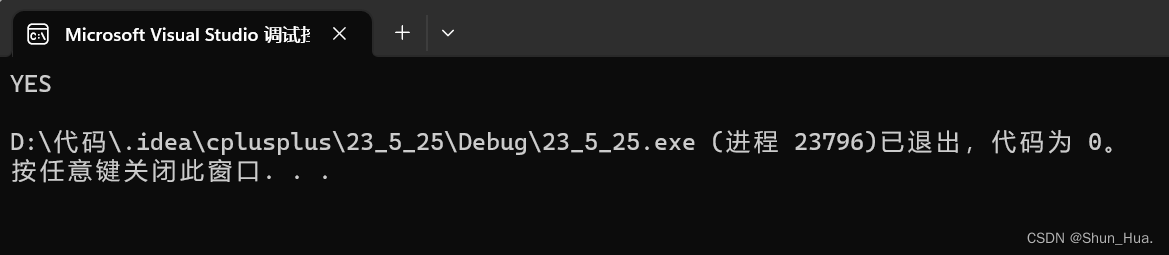
⑤clear
函数:
void clear();
功能:减少string中的字符,使之成为空字符串,也就是字符串的长度为0。
例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace::std;
int main()
{
string A("hello world");
A.clear();
if (A.empty())
{
printf("YES\n");
}
else
{
printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}
结果:
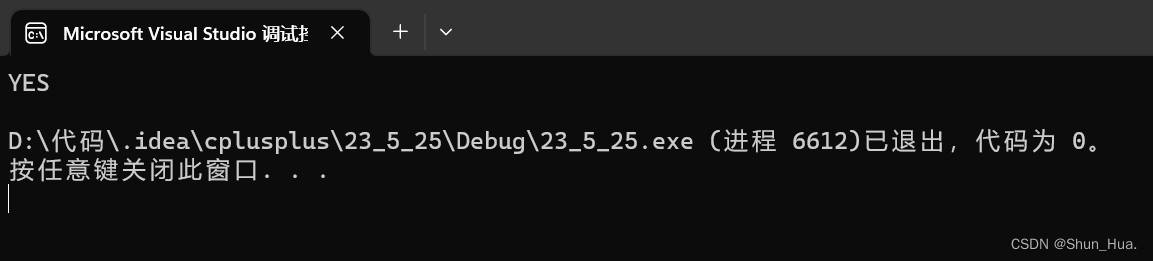
⑥reverse
函数:
void reserve (size_t n = 0);
功能:为字符串预留n空间,当n大于capacity时进行扩容,其余情况按照原先的capacity。
结果:使string的capacity大于等于原来的capacity。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
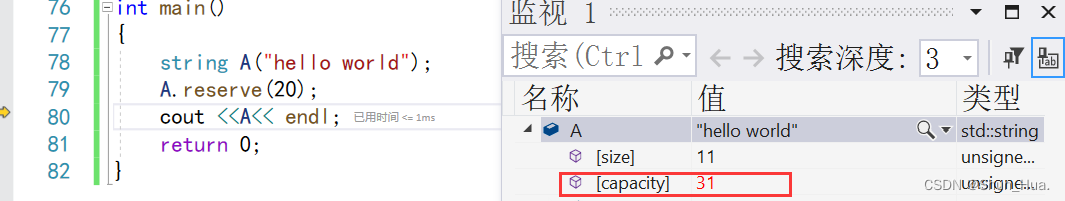
string A("hello world");
A.reserve(20);
cout <<A<< endl;
return 0;
}
执行前:capacity——15

执行后:capacity——31
⑦resize
函数:
void resize (size_t n);
void resize (size_t n, char c);
//这两个是函数重载
功能:
- 当n小于size时,会将多于n的字符全部删除,对于少的则不做处理。
- 当n大于size时,如果没有第二个参数,会将大于size的部分填充为\0,如果有第二个参数,则会将大于size的部分填充为第二个参数的值。
例1:小于size
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
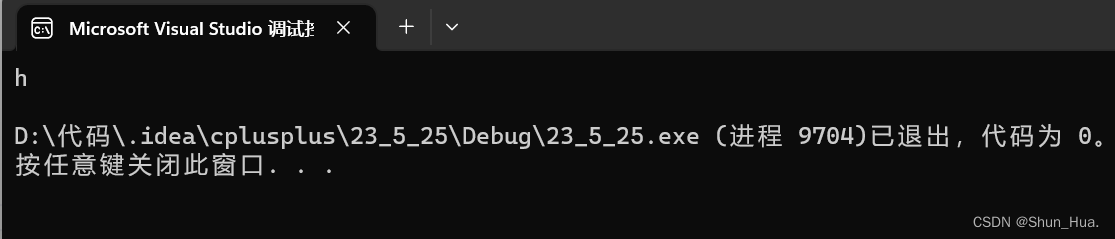
string A("hello world");
A.resize(1,'x');//这里的x其实没啥用
cout << A << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
例2:大于size
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
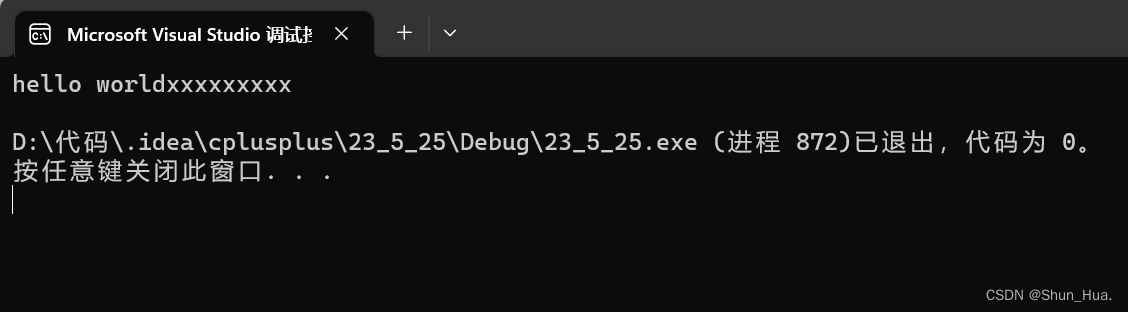
string A("hello world");
A.resize(20,'x');
cout << A << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
三.修改接口
①+=
函数:
string& operator+= (const string& str);
string& operator+= (const char* s);
string& operator+= (char c);
功能:+=一个字符串/字符/string类
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
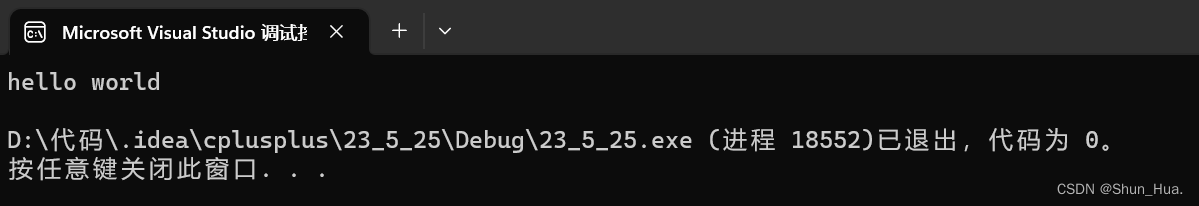
string A;
A += "hello";
A += ' ';
string B("world");
A += B;
cout << A << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
②[]
函数:
char& operator[] (size_t pos);
const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const;
功能:访问字符串下标位置的字符。
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
string A("hello");
char a = A[0];
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
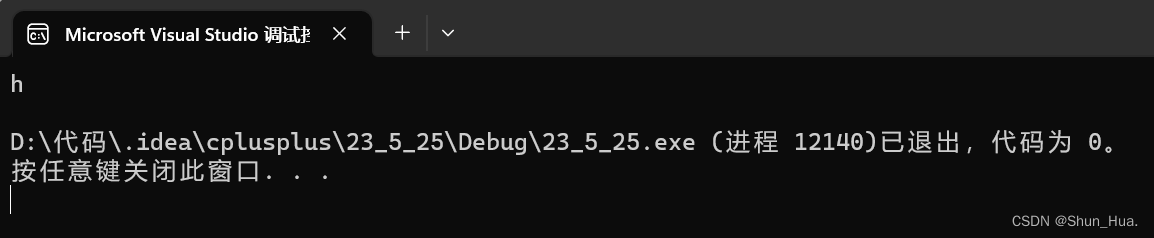
③push_back
函数
void push_back (char c);
功能:再string末尾后追加一个字符
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
string A("hello");
A.push_back('x');
cout << A << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
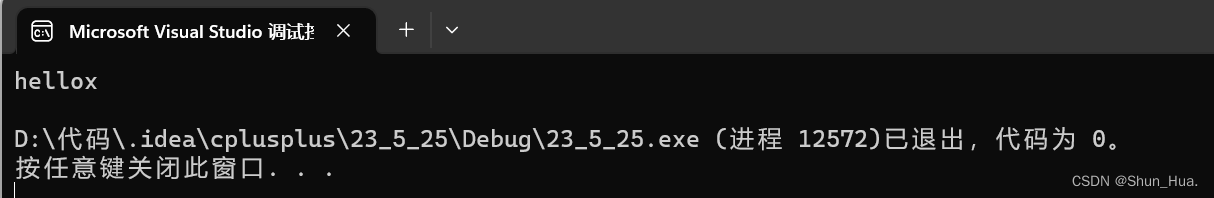
④append
函数:
string& append (const string& str);
string& append (const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen);
string& append (const char* s);
string& append (const char* s, size_t n);
string& append (size_t n, char c);
功能:在指定string后面追加 n个字符/(前n个字符的)字符串/string(从subpos位置到sublen位置)。
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
string A("hello world");
string B(" hello");
A.append(B,0,6);
cout << A << endl;
A.append(B);
cout << A << endl;
A.append(" hello", 0, 6);
cout << A << endl;
A.append(6, 'x');
cout << A << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
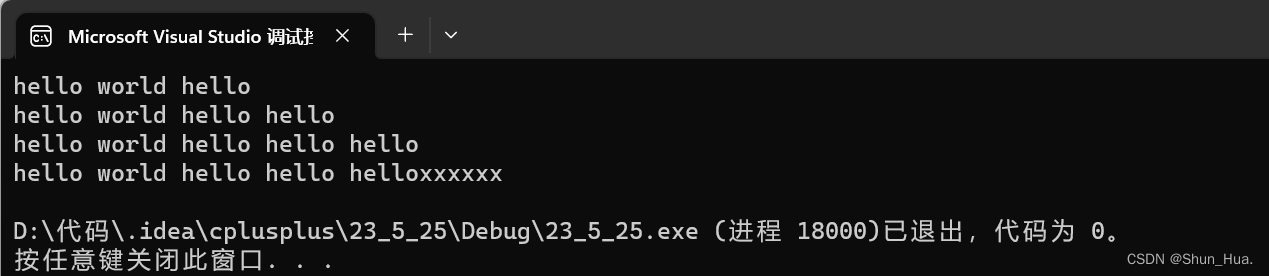
⑤c_str
函数:
const char* c_str() const;
功能:返回一个字符串,类型是const char *。
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
string A("hello");
const char* a = A.c_str();
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
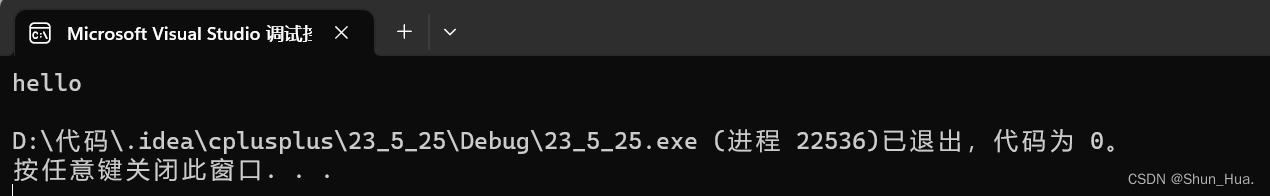
⑥ find
函数:
size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
//pos是要查找string的下标,n是要在指定字符串中查找的长度。
//size_t,如果成功返回一个匹配成功的下标,如果失败返回-1(转换为无符号整形)。
功能:在string类的指定pos下标位置开始,向后查找目标【string/字符串(指定查找前n个)/字符】——的字符c位置,并返回其位置。
注意:查找的是(字符串,string里面的)字符。
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
string A("hello world");
string B("world");
cout << A.find(B, 0)<<endl;
cout << A.find("world", 0) <<endl;
cout << A.find("world", 0, 5) <<endl;
cout << A.find('w', 0) <<endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
⑦rfind
函数:
size_t rfind (const string& str, size_t pos = npos) const;
size_t rfind (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
size_t rfind (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
size_t rfind (char c, size_t pos = npos) const;
原理:同find
功能:在string类的指定pos下标位置开始,向前查找目标【string/字符串(指定查找前n个)/字符】——的字符c位置,并返回其位置。
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
string A("hello world");
string B("world");
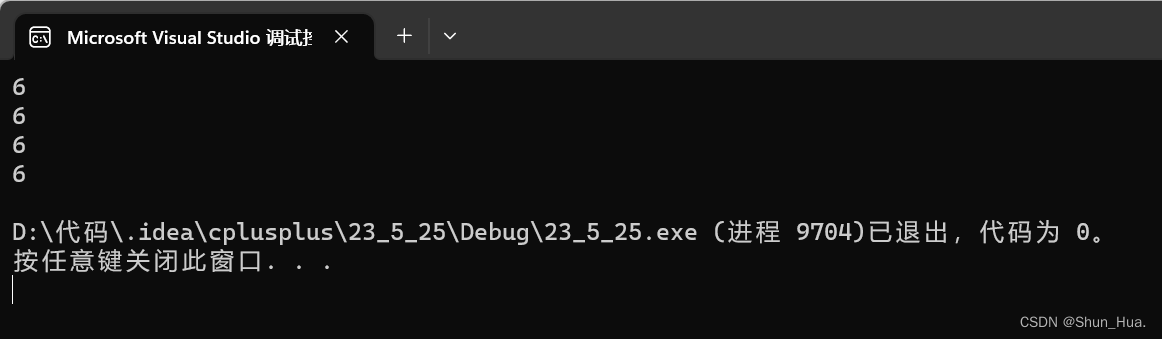
cout << A.rfind(B, 5)<<endl;
cout << A.rfind("world", 10) <<endl;
cout << A.rfind("world", 10, 5) <<endl;
cout << A.rfind('w', 10) <<endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
四.迭代器——iterator
基本概念
迭代器的作用是用来访问容器(用来保存元素的数据结构)中的元素,所以使用迭代器,我们就可以访问容器中里面的元素。
①begin与end
函数:
reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;
功能:获取string的开头位置。
函数:
iterator end();
const_iterator end() const;
功能:获取string最后一个有效字符的位置。
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
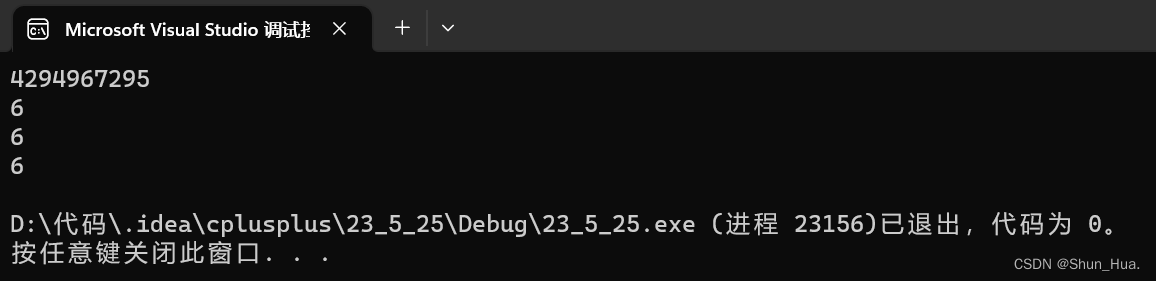
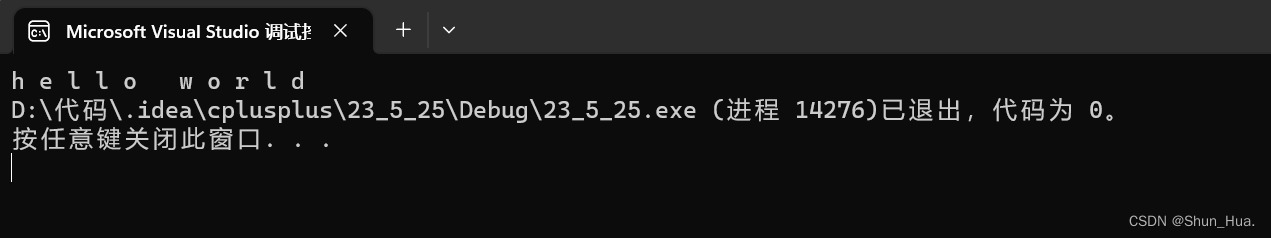
string A("hello world");
string::iterator it = A.begin();
//当A是const修饰的类时,我们就要用string::const_iterator迭代器
while (it != A.end())
{
cout << *it << " " ;
it++;
}
return 0;
}
结果:
②rbegin和rend
函数:
reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;
功能:获取最后一个有效字符的位置。
函数:
reverse_iterator rend();
const_reverse_iterator rend() const;
功能:获取第一个字符的位置。
例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
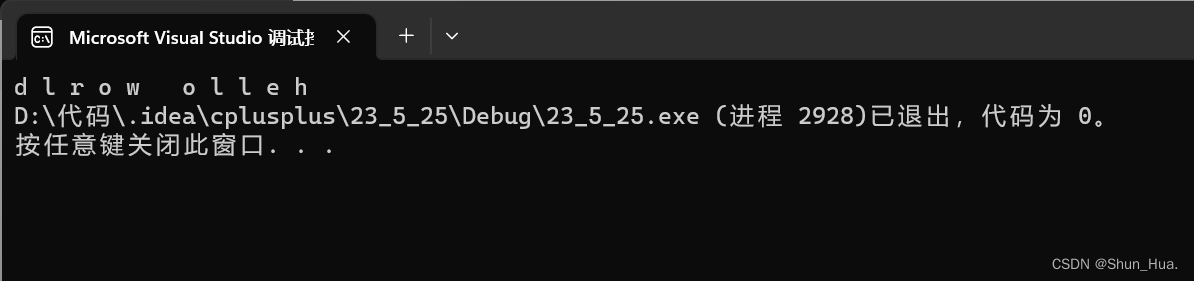
string A("hello world");
string::reverse_iterator it = A.rbegin();
while (it != A.rend())
{
cout << *it << " " ;
it++;
}
return 0;
}
说明:这里的rbegin + 1是倒着加1
结果:
其余内容请看文档