北邮22信通一枚~
跟随课程进度每周更新数据结构与算法的代码和文章
持续关注作者 解锁更多邮苑信通专属代码~
获取更多文章 请访问专栏~
北邮22信通_青山如墨雨如画的博客-CSDN博客
一.讲解
要想实现二叉树的路径显示,我们要按照先后顺序做这样几件事:
1.判断是否能够找到路径;
2.如果能找到路径,则将路径存储起来,如果不能找到路径,则返回查询失败的信息;
3.将路径按照一定的方法打印出来;
1.递归详解:是否能够找到路径并将找到的可行路径存储起来的实现函数
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r,
stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)
return true;
else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))
return true;
else if (stl_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))
return true;
stk.pop();
return false;
}首先我们向这个函数中传入3个参数,分别是待查找的目标,二叉树的根节点,一个空栈(用来存储路径);实现的具体过程运用了递归思想:对整个查找过程中的某次查找如果父节点数据域就是要查找的目标,返回真值;如果沿着他的左孩子找下去能找到目标,返回真值,如果沿着他的右孩子找下去能找到目标,返回真值。如果父节点不是目标并且沿着左孩子右孩子都找不到目标的话,弹出父节点返回假值。
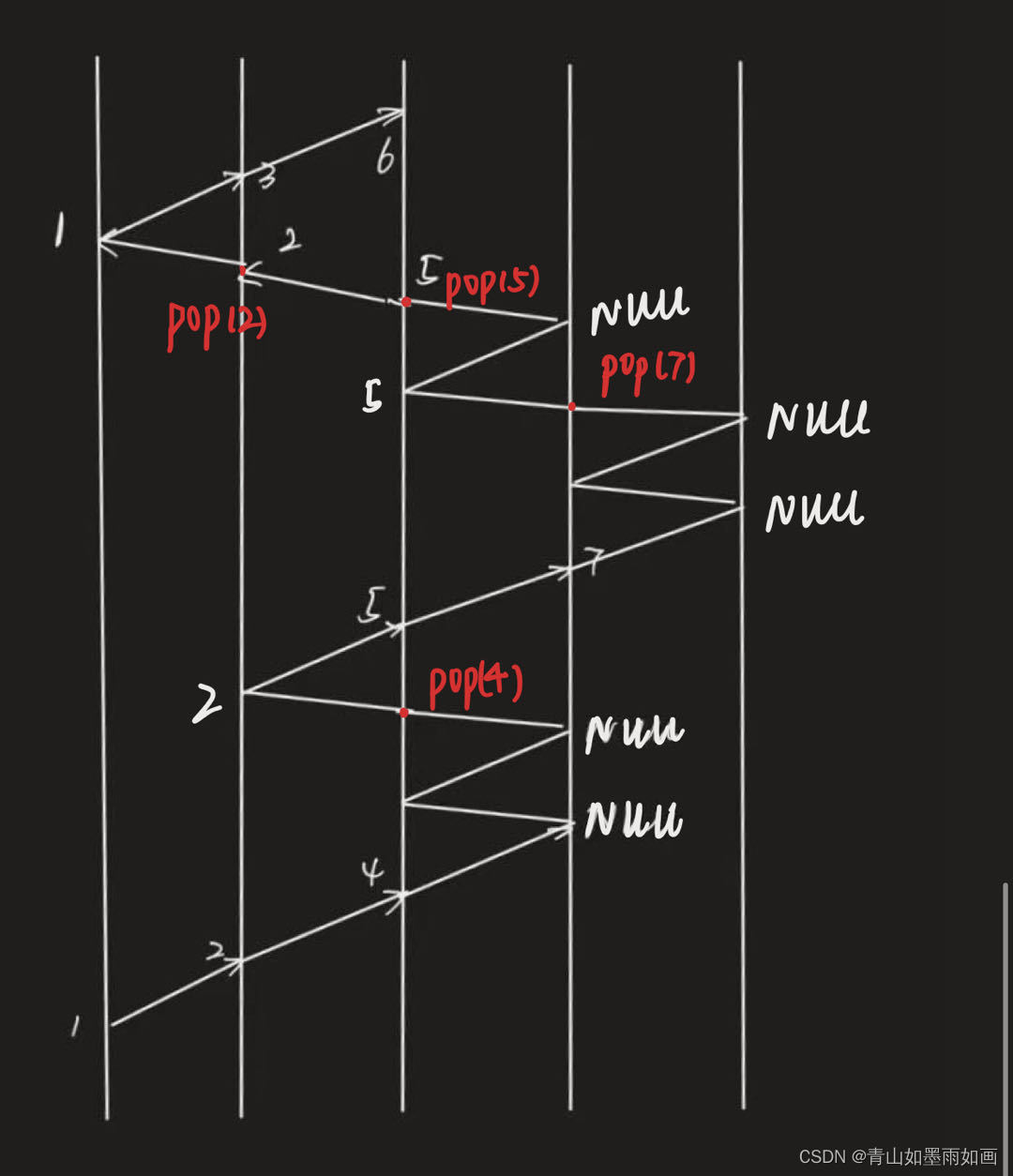
这里用例子重新讲解递归函数保存现场返回现场的运行过程:

如上图,我们要查找到结点6的路径:
按照函数编写顺序:
1首先入栈,判断1不是6(函数第5、6行),继续执行;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r,
stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)//现在是1,不是9
return true;//执行完毕,继续向下执行;
}执行到第7行,需要判断沿着1的左孩子2能不能找到合适路径,保存现场;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r,
stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)
return true;
else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))
return true;
/*
执行到这一步,需要重新判断stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk)
是否为真值;
函数保存现场不继续向下执行,将r->leftchild==2作为参数替代r==1,重新开始执行函数;
*/
}重新从第一行开始执行函数,2入栈,2不是6,向下执行;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r,
stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)
return true;//r==2不是9,继续向下执行;
}执行到第7行,需要判断沿着2的左孩子4能不能找到合适路径,保存现场;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r,
stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)
return true;
else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))
return true;
/*
执行到这一步,需要重新判断stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk)
是否为真值;
函数保存现场不继续向下执行,将r->leftchild->leftchild==4作为参数
替代r->leftchild==2,重新开始执行函数;
*/
}重新从第一行开始执行函数,4入栈,4不是6,向下执行;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r,
stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)
return true;
else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))
return true;
/*
执行到这一步,需要重新判断stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk)
是否为真值;
函数保存现场不继续向下执行,
将r->leftchild->leftchild->leftchild==NULL作为参数
替代r->leftchild->leftchild==4,重新开始执行函数;
*/
}发现4的左孩子是空,返回假值;
返回上一级现场,执行函数第8、9行,需要判断沿着4的右孩子能不能找到合适路径,保存现场;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r,
stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)
return true;
else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))
return true;
else if (stl_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))
return true;
/*
执行到这一步,需要重新判断stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk)
是否为真值;
函数保存现场不继续向下执行,
将r->leftchild->leftchild->rightchild==NULL作为参数
替代r->leftchild->leftchild==4,重新开始执行函数;
*/
}右孩子为空;
返回上一级现场,判断沿着2的右孩子5能不能找到可行的路径,保存现场,以此类推……
示意图如下:
2.打印路径的函数
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::stl_node_root_path(temp target)
{
stack<binnode<temp>>stk;
stl_search_path(target, this->root, stk);
if (stk.empty())
cout << target << "未能找到目标" << endl;
else
{
cout << target << "结点到根节点的路径为:" << endl;
binnode<temp>out;
while (!stk.empty())
{
out = stk.top();
if (stk.size() == 1)
cout << out.data;
else
cout << out.data << "->";
stk.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}对于给定的二叉树,首先调用上面讲解过的函数,如果有可行路径就将可行路径通过函数存储到本函数的栈空间中,然后通过控制条件输出,最终可以实现打印的效果。
3.另一种存储方式
使用模板类定义的栈存储也未尝不可。
代码如下:
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::linkstack_node_root_path(temp target)
{
linkstack<binnode<temp>>stk;
linkstack_search_path(target, this->root, stk);
if (stk.empty())
cout << target << "未能找到目标" << endl;
else
{
cout << target << "结点到根节点的路径为:" << endl;
binnode<temp>out;
while (!stk.empty())
{
out = stk.gettop();
if (stk.getsize() == 1)
cout << out.data;
else
cout << out.data << "->";
stk.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::linkstack_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, linkstack<binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)
return true;
else if (linkstack_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))
return true;
else if (linkstack_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))
return true;
stk.pop();
return false;
}二.完整代码:
2.1使用STL栈实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class student
{
private:
int ID;
string name;
public:
int existence;
student()
{
this->ID = 0;
this->name = "unknown name";
this->existence = 0;
}
student(int ID, string name)
{
this->ID = ID;
this->name = name;
this->existence = 1;
}
bool operator == (student& s)
{
return ((this->ID == s.ID) && (this->name == s.name)) ? true : false;
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, student& s)
{
output << "\"" << s.ID << " " << s.name << "\"";
return output;
}
};
template<class temp>
struct binnode
{
temp data;
binnode* leftchild;
binnode* rightchild;
};
template<class temp>
class bintree
{
private:
void create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n);
void release(binnode<temp>* r);
public:
binnode<temp>* root;
bintree(temp data[], int n);
void stl_node_root_path(temp target);
bool stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk);
~bintree();
};
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n)
{
if (i <= n && data[i - 1].existence != 0)
{
r = new binnode<temp>;
r->data = data[i - 1];
r->leftchild = NULL;
r->rightchild = NULL;
create(r->leftchild, data, 2 * i, n);
create(r->rightchild, data, 2 * i + 1, n);
}
}
template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::bintree(temp data[], int n)
{
create(this->root, data, 1, n);
}
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::release(binnode<temp>* r)
{
if (r != NULL)
{
release(r->leftchild);
release(r->rightchild);
delete r;
}
}
template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::~bintree()
{
release(this->root);
}
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::stl_node_root_path(temp target)
{
stack<binnode<temp>>stk;
stl_search_path(target, this->root, stk);
if (stk.empty())
cout << target << "未能找到目标" << endl;
else
{
cout << target << "结点到根节点的路径为:" << endl;
binnode<temp>out;
while (!stk.empty())
{
out = stk.top();
if (stk.size() == 1)
cout << out.data;
else
cout << out.data << "->";
stk.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)
return true;
else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))
return true;
else if (stl_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))
return true;
stk.pop();
return false;
}
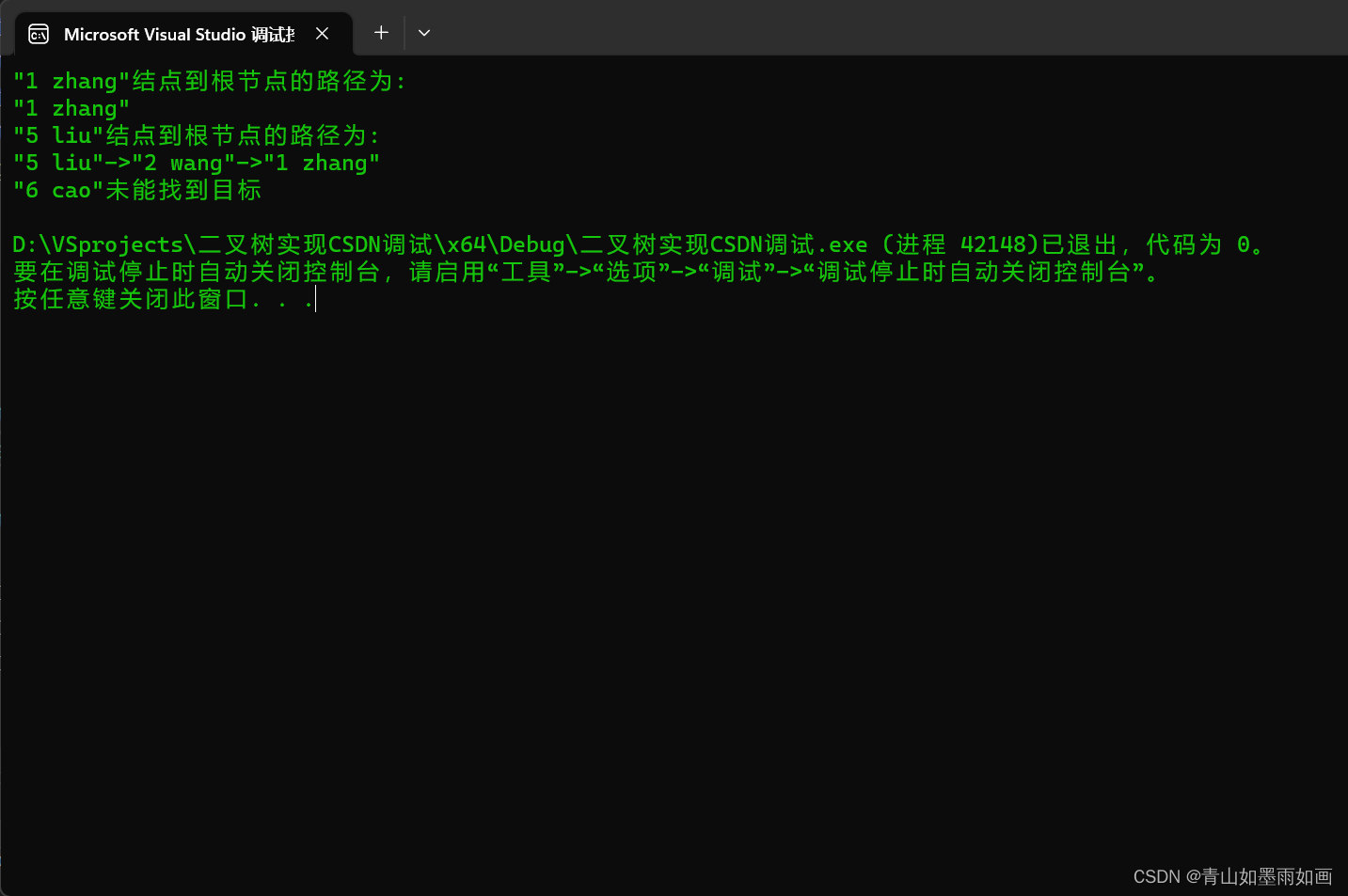
int main()
{
system("color 0A");
student stu[5] = { {1,"zhang"},{2,"wang"},{3,"li"},{4,"zhao"},{5,"liu"} };
bintree<student>tree(stu, 5);
student stu1(1, "zhang"), stu2(5, "liu"), stu3(6, "cao");
tree.stl_node_root_path(stu1);
tree.stl_node_root_path(stu2);
tree.stl_node_root_path(stu3);
return 0;
}2.2使用模板类定义的栈实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class student
{
private:
int ID;
string name;
public:
int existence;
student()
{
this->ID = 0;
this->name = "unknown name";
this->existence = 0;
}
student(int ID, string name)
{
this->ID = ID;
this->name = name;
this->existence = 1;
}
bool operator == (student& s)
{
return ((this->ID == s.ID) && (this->name == s.name)) ? true : false;
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, student& s)
{
output << "\"" << s.ID << " " << s.name << "\"";
return output;
}
};
//二叉树声明部分
template<class temp>
struct binnode;
//栈
template <class temp>
struct node
{
temp data;
node<temp>* next;
};
template <class temp>
class linkstack
{
public:
binnode<temp>* r;
int tag;
linkstack() { top = NULL; }
~linkstack();
void push(temp x);
temp pop();
temp gettop();
int getsize();
bool empty()
{
return top == NULL ? true : false;
}
private:
node<temp>* top;
};
template <class temp>
void linkstack<temp>::push(temp x)
{
node<temp>* p = new node<temp>;
p->data = x;
p->next = this->top;
this->top = p;
}
template<class temp>
temp linkstack<temp>::pop()
{
if (empty())throw "下溢";
temp x = this->top->data;
node<temp>* p = this->top;
this->top = this->top->next;
delete p;
return x;
}
template<class temp>
linkstack<temp>::~linkstack()
{
while (this->top != NULL)
{
node<temp>* p = this->top;
this->top = this->top->next;
delete p;
}
}
template<class temp>
temp linkstack<temp>::gettop()
{
if (empty())throw"下溢";
return this->top->data;
}
template<class temp>
int linkstack<temp>::getsize()
{
int num = 0;
node<temp>* p = this->top;
while (p != NULL)
{
num++;
p = p->next;
}
return num;
}
template<class temp>
struct binnode
{
temp data;
binnode* leftchild;
binnode* rightchild;
};
template<class temp>
class bintree
{
private:
void create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n);
void release(binnode<temp>* r);
public:
binnode<temp>* root;
bintree(temp data[], int n);
void linkstack_node_root_path(temp target);
bool linkstack_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, linkstack<binnode<temp>>& stk);
~bintree();
};
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n)
{
if (i <= n && data[i - 1].existence != 0)
{
r = new binnode<temp>;
r->data = data[i - 1];
r->leftchild = NULL;
r->rightchild = NULL;
create(r->leftchild, data, 2 * i, n);
create(r->rightchild, data, 2 * i + 1, n);
}
}
template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::bintree(temp data[], int n)
{
create(this->root, data, 1, n);
}
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::release(binnode<temp>* r)
{
if (r != NULL)
{
release(r->leftchild);
release(r->rightchild);
delete r;
}
}
template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::~bintree()
{
release(this->root);
}
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::linkstack_node_root_path(temp target)
{
linkstack<binnode<temp>>stk;
linkstack_search_path(target, this->root, stk);
if (stk.empty())
cout << target << "未能找到目标" << endl;
else
{
cout << target << "结点到根节点的路径为:" << endl;
binnode<temp>out;
while (!stk.empty())
{
out = stk.gettop();
if (stk.getsize() == 1)
cout << out.data;
else
cout << out.data << "->";
stk.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::linkstack_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, linkstack<binnode<temp>>& stk)
{
if (r == NULL)
return false;
stk.push(*r);
if (r->data == target)
return true;
else if (linkstack_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))
return true;
else if (linkstack_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))
return true;
stk.pop();
return false;
}
int main()
{
system("color 0A");
student stu[5] = { {1,"zhang"},{2,"wang"},{3,"li"},{4,"zhao"},{5,"liu"} };
bintree<student>tree(stu, 5);
student stu1(1, "zhang"), stu2(5, "liu"), stu3(6, "cao");
tree.linkstack_node_root_path(stu1);
tree.linkstack_node_root_path(stu2);
tree.linkstack_node_root_path(stu3);
return 0;
}2.3运行效果: