概述:
在做提交订单功能时,我们需要处理的事务很多,如:修改库存、计算优惠促销信息、会员积分加减、线上支付、金额计算、生成产品订单、生成财务信息、删除购物车等等。如果这些功能全部串行化处理,会发费很长的时间,特别是在大量数据并发的时候,有可能导致服务器崩溃等各种异常。
CompletableFuture 异步编排的出现,完全解决了上面的情况,这些功能基本可以并行处理。那么什么是CompletableFuture 异步编排?
-
CompletableFuture 异步编排是一个 Java 8 引入的异步编程工具,它提供了一种方便的方式来处理异步任务。
-
异步编排是指将多个异步任务按照一定的顺序或依赖关系组合起来执行,以实现更复杂的业务逻辑。
-
CompletableFuture 类实现了 Future 接口,所以你还是可以像以前一样通过
get方法阻塞或
者轮询的方式获得结果,但是这种方式不推荐使用。 -
CompletableFuture 和 FutureTask 同属于 Future 接口的实现类,都可以获取线程的执行结果。
如图:
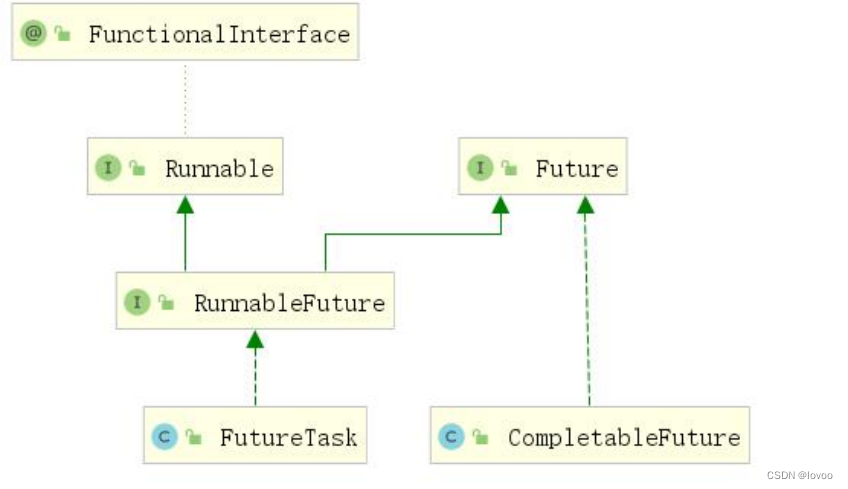
在编排异步操作时,CompletableFuture 提供了一些方法,例如 thenApply、thenAccept、thenRun 等,这些方法允许您在异步操作完成后执行一些操作。下面重点讲述这些方法。
一、创建异步对象
1 基本方法
CompletableFuture 提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作。
static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executorexecutor)
1、runXxxx 都是没有返回结果的,supplyXxx 都是可以获取返回结果的
2、可以传入自定义的线程池,否则就用默认的线程池;
2 示例:
public static void runAsync() {
System.out.println("runAsync....start....");
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果:" + i);
}, executorService);
System.out.println("runAsync....end....");
}
二、计算完成时回调方法
1 基本方法
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action):
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable>action);
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable>action, Executor executor):
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn);
- whenComplete 可以处理正常和异常的计算结果,exceptionally 处理异常情况。
- whenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 的区别:
whenComplete:是执行当前任务的线程执行继续执行 whenComplete 的任务。
whenCompleteAsync:是执行把 whenCompleteAsync 这个任务继续提交给线程池来进行执行
方法不以 Async 结尾,意味着 Action 使用相同的线程执行,而 Async 可能会使用其他线程
执行(如果是使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)
2 示例
public static void suplyAsync() {
try {
System.out.println("suplyAsync....start....");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 0;
System.out.println("计算结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService).whenComplete((res, err) -> {
System.out.println("异步任务完成了..结果.." + res);
System.out.println("异步任务完成了..异常.." + err);
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
System.out.println("发生了异常.返回默认值....");
return 10;
});
System.out.println("最终结果:" + future.get());
System.out.println("suplyAsync....end....");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
三、handle 方法
1 基本方法
public <U> Completionstage<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable,? extends U> fn);
public <U> Completionstage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U>fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U>
fn,Executor executor);
和 complete 一样,可对结果做最后的处理(可处理异常),可改变返回值。
2 示例
//完成后的处理
public static void suplyAsyncHandler() {
try {
System.out.println("suplyAsyncHandler....start....");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService).handle((res, err) -> {
if(res != null){
System.out.println("res:" + res);
return res * 2;
}
if (err != null){
System.out.println("err:" + err);
return 0;
}
return res;
});
System.out.println("最终结果====" + future.get());
System.out.println("suplyAsyncHandler....end....");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
四、线程串行化方法
1 基本方法
public <U> CompletableFuture<u> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<u> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn,Executor executor)
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executorexecutor);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public Completionstage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor);
- thenApply 方法:当一个线程依赖另一个线程时,获取上一个任务返回的结果,并返回当前
任务的返回值。 - thenAccept 方法:消费处理结果。接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果。
- thenRun 方法:只要上面的任务执行完成,就开始执行 thenRun,只是处理完任务后,执行
thenRun 的后续操作 - 带有 Async 默认是异步执行的。同之前。
以上都要前置任务成功完成。
Function<? super T,? extends U>
T:上一个任务返回结果的类型
U:当前任务的返回值类型
2 示例
//---多个任务串行执行-----------------------------------------------------
//ThenApplyAsync 可以获取上次的结果,有返回值
public static void suplyAsyncThenApplyAsync() {
try {
System.out.println("suplyAsyncThenRun....start....");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService).thenApplyAsync((res) -> {
System.out.println("任务1的结果是...." + res);
System.out.println("启动任务2..........");
return res;
}, executorService);
System.out.println("最终结果是:" + future);
System.out.println("suplyAsyncThenRun....end....");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//thenAcceptAsync 可以获取上次的结果,没返回值
public static void suplyAsyncThenAcceptAsync() {
try {
System.out.println("suplyAsyncThenRun....start....");
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService).thenAcceptAsync((res) -> {
System.out.println("任务1的结果是...." + res);
System.out.println("启动任务2..........");
}, executorService);
System.out.println("suplyAsyncThenRun....end....");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//thenRunAsync 不能获取上次任务的结果,没返回值
public static void suplyAsyncThenRun() {
try {
System.out.println("suplyAsyncThenRun....start....");
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService).thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("启动任务2..........");
}, executorService);
System.out.println("suplyAsyncThenRun....end....");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
五、两任务组合 - 都要完成
1 基本介绍
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other ,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<v> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> otherBiFunction<? super T,? super u,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other ,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor);
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(Completionstage<? extends U> other .BiConsumer<? super T,? super U> action);
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other .BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action) ;
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other ,BiConsumer<? super t. ? super Us action. Executor executor):
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other.Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other .Runnable action):
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> otherRunnable action,
Executor executor ;
两个任务必须都完成,触发该任务。
- thenCombine:组合两个 future,获取两个 future 的返回结果,并返回当前任务的返回值
- thenAcceptBoth:组合两个 future,获取两个 future 任务的返回结果,然后处理任务,没有
返回值。 - runAfterBoth:组合两个 future,不需要获取 future 的结果,只需两个 future 处理完任务后,
处理该任务。
2 示例
//---任务组合-----------------------------------------------------
public static void thenCombineAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程1:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果1:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程2:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("计算结果2:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = future1.thenCombineAsync(future2, (res1, res2) -> {
System.out.println("线程1结果....." + res1);
System.out.println("线程2结果....." + res2);
System.out.println("线程3开始.....");
return res1 + res2;
}, executorService);
System.out.println("线程3的结果是...." + future3.get());
}
public static void thenAcceptBothAsync() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程1:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果1:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程2:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("计算结果2:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
future1.thenAcceptBothAsync(future2, (res1, res2)-> {
System.out.println("线程1结果....." + res1);
System.out.println("线程2结果....." + res2);
System.out.println("线程3开始.....");
}, executorService);
}
public static void runAfterBothAsync() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程1:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果1:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程2:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("计算结果2:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
future1.runAfterBothAsync(future2, ()-> {
System.out.println("线程3开始.....");
}, executorService);
}
六、两任务组合 - 一个完成
1 函数介绍
public <U> CompletableFuture<u> applyToEither(
CompletionStage<? extends T> other , Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(
CompletionStage<? extends T> other , Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other , Function<? super T, U> fn,Executor executor):
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other , Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync
CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletableFuture<void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor ;
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEither (CompletionStage<?> other ,Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other ,Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other ,Runnable action,
Executor executor);
当两个任务中,任意一个 future 任务完成的时候,执行任务。
- applyToEither:两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务并有新的返回值。
- acceptEither:两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务,没有新的返回值。
- runAfterEither:两个任务有一个执行完成,不需要获取 future 的结果,处理任务,也没有返
回值。
2 示例
//---任务组合--一个都完成---------------------------------------------------
public static void applyToEitherAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程1:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果1:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程2:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("计算结果2:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = future1.applyToEitherAsync(future2, (res1) -> {
System.out.println("线程1结果....." + res1);
System.out.println("线程3开始.....");
return res1;
}, executorService);
System.out.println("线程3的结果是...." + future3.get());
}
public static void acceptEitherAsync() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程1:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果1:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程2:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("计算结果2:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
future1.acceptEitherAsync(future2, (res1)-> {
System.out.println("线程1结果....." + res1);
System.out.println("线程3开始.....");
}, executorService);
}
public static void runAfterEitherAsync() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程1:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("计算结果1:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程2:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("计算结果2:" + i);
return i;
}, executorService);
future1.runAfterEitherAsync(future2, ()-> {
System.out.println("线程3开始.....");
}, executorService);
}
七、多任务组合
1 函数介绍
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allof(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs);
public static CompletableFuture<0bject> anyof(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs);
- allof: 等待所有任务完成
- anyof: 只要有一个任务完成
2 示例
public static void allOf() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1执行");
return 10 / 2;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2执行");
return "hello";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> future03 = future01.thenCombineAsync(future02,
(result1, result2) -> {
System.out.println("任务3执行");
System.out.println("任务1返回值:" + result1);
System.out.println("任务2返回值:" + result2);
return "任务3返回值";
}, executor);
System.out.println(future03.get());
CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(future01, future02, future03);
allOf.get();// 阻塞等待所有任务完成
}
public static void anyOf() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1执行");
return 10 / 2;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2执行");
return "hello";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> future03 = future01.thenCombineAsync(future02,
(result1, result2) -> {
System.out.println("任务3执行");
System.out.println("任务1返回值:" + result1);
System.out.println("任务2返回值:" + result2);
return "任务3返回值";
}, executor);
System.out.println(future03.get());
CompletableFuture<Void> anyOf= CompletableFuture.allOf(future01, future02, future03);
anyOf.get();// 阻塞等待任一任务完成,返回值是执行成功的任务返回值
}
八、源码下载
https://gitee.com/charlinchenlin/koo-erp