目录
sort()方法
1.sort()方法的格式
2.使用sort()方法时要导入的类
3.作用
4.作用的对象
5.注意
6.代码及结果
(1)代码
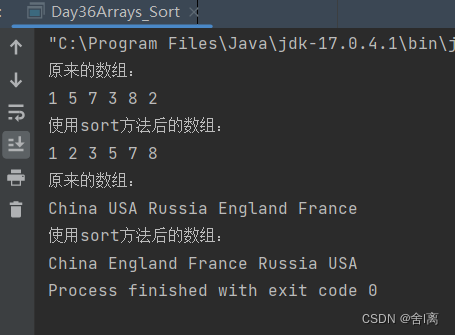
(2)结果
sort()方法
1.sort()方法的格式
数组对象及对象数组的排序方法格式:
(1)public static void sort(int[ ] a)
对数组a按自然顺序排序。
(2)public static void sort(int[ ] a,int fromIndex, int toIndex)
对数组a中的元素从起始下标fromIndex到终止下标toIndex之间的 元素排序。
(3)public static void sort(Object[ ] a)
对数组a按自然顺序排序。
(4)public static void sort(Object[ ] a,int fromIndex, int toIndex)
对数组a中的元素从起始下标fromIndex到终止下标toIndex之间的 元素排序。
(5)public static <T> void sort(T[ ] a,Comparator <?super T>c)
使用比较器对象c对数组a排序。
2.使用sort()方法时要导入的类
import java.util.Arrays;
3.作用
对数组进行(默认升序)排序。
4.作用的对象
(1)基本类型的数组
(2)对象数组(要使用Comparable接口)
5.注意
(1)使用sort()方法前要导入Arrays类。
(2)不能对布尔型数组排序。
(3)字符串排序是按字符的Unicode码排序的。
6.代码及结果
(1)代码
package csdn.every.day;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Day36Arrays_Sort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 5, 7, 3, 8, 2};
//sort()方法的使用
//基本类型排序
System.out.println("原来的数组:");
for (int n : a) {
System.out.print(n + " ");
}
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println("\n使用sort方法后的数组:");
for (int n : a) {
System.out.print(n + " ");
}
//字符串数组排序
String[] names = {"China", "USA", "Russia", "England", "France"};
System.out.println("\n原来的数组:");
for (String n : names) {
System.out.print(n + " ");
}
Arrays.sort(names);
System.out.println("\n使用sort方法后的数组:");
for (String n : names) {
System.out.print(n + " ");
}
}
}
(2)结果





![[C++]哈希表实现,unordered_map\set封装](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/00deabab0b6441a381c1cb2c44b4d60f.png)