目录
1. 概念
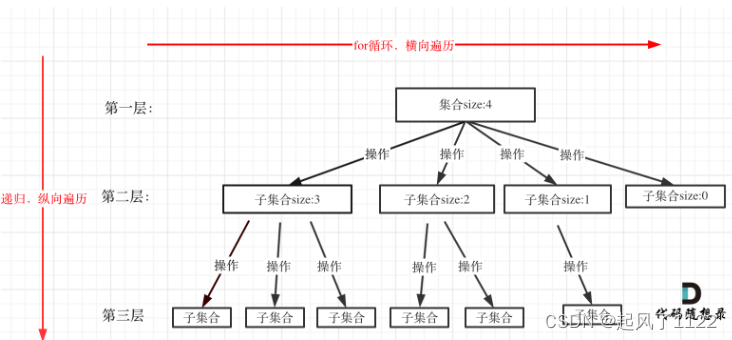
2. ArrayList集合框架图
3.ArrayList常见的方法
4. 自己实现ArrayList(Integer)
4.1 ArrayList构造
4.2 ArrayList容量的扩容
4.3 判断空满
4.4 pos坐标是否合法(含有)
4.5 ArrayList的增删元素
4.6 包含元素
4.7 get 和 set
4.8 获得第一个元素坐标
4.9 打印ArrayList
4.10 清空ArrayList
1. 概念
ArrayList实现了List接口,它是在一个连续的储存块中储存元素,与数组不同的是,通过在序列尾部添加新的元素,ArrayList能进行动态的增长。顺序表一般情况下采用数组存储,在数组上完成数据的增删查改,并且访问其元素可以直接通过元素的索引直接访问和更新。
注意:
- ArrayList是一种动态数组。
- ArrayList类是一种元素为Object引用的泛型集合。
2. ArrayList集合框架图

则:
- ArrayList是泛型实现的,使用时必须进行实例化;
- ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,则ArrayList支持随机访问;
- ArrayList实现了Cloneabel接口,则ArrayList支持clone;
- ArrayList实现了Serialzable接口,则ArrayList支持序列化;
- 和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList
3.ArrayList常见的方法
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | 尾插一个元素e |
| add(int index,E e) | 在index位置插入e |
| remove(int index) | 删除index位置的元素 |
| remove(Object o) | 删除第一个遇到的o |
| get(int index) | 获得index位置的元素 |
| set(int index,E e) | 将index位置的元素更新为e |
| clear() | 清空ArrayList |
| indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个的o的下标 |
| lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个o的下标 |
| subList(int fromIndex,int toIndex) | 截取[fromIndex,toIndex)的元素 |
| contains(Object o) | 判断是否包含o |
4. 自己实现ArrayList(Integer)
4.1 ArrayList构造
public class MyArrayList {
int[] elem;//储存元素
public int usedSize = 0;//元素个数,ArrayList集合大小默认为0
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;//ArrayList集合容量默认为10
//构造方法
public MyArrayList(){
this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];
}
...
}
4.2 ArrayList容量的扩容
当ArrayList中的元素个数不小于容量时,要对容量进行扩容,就是将ArrayList中的元素克隆到更大的数组中。
private void ensureCapacity() {
//将原数组克隆在更大的数组中
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);
}4.3 判断空满
空:元素为0,即usedSize为0;
满:元素个数等于容量
//空
private boolean isEmpty() {
return usedSize == 0;
}
//满
public boolean isFull() {
return usedSize == this.elem.length;
}4.4 pos坐标是否合法(含有)
即pos>=0 && pos < usedSize;
//是否合法
public boolean checkPosInAdd(int pos) {
return pos >= 0 && pos < usedSize;//合法
}4.5 ArrayList的增删元素
在尾插元素的时候,要判断是否具有足够的容量,如果不具有,要进行扩容,即调用4.2中ensureCapacity()方法。
在具体位置插入元素的时候,要判断坐标是否合法,不能大于数组大小,若大于,抛出异常。
在删除元素的时候,要判断坐标是否合法,不能大于数组大小,若大于,抛出异常,也要判断是否存在这个元素,若不存在,返回 -1。
// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
public void add(int data) {
if(isFull()){
ensureCapacity();
}
this.elem[usedSize] = data;
usedSize++;
}
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
if(!checkPosInAdd(pos)){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组越界");
}else{
this.elem[pos] = data;
usedSize++;
}
}
//删除第一次遇到的key
public void remove(int key) {
if(isEmpty()){
return;
}
int index = indexOf(key);
if(index == -1){
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < usedSize - 1; i++) {
elem[i] = elem[i + 1];
}
usedSize--;
}
//删除index坐标的元素
public void removeIndex(int index){
if(!checkPosInAdd(index)){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("不合法");
}else{
for (int i = index; i < usedSize; i++) {
elem[i] = elem[i + 1];
}
usedSize--;
}
}4.6 包含元素
即遍历整个数组,是否含有这个元素;
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i :
this.elem) {
if (i == toFind){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}4.7 get 和 set
可以根据索引直接返回和更新值,但是需要注意合法;不合法,抛出异常;
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int get(int pos) {
if(!checkPosInAdd(pos)){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组越界");
}else{
return elem[pos];
}
}
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为【更新为】 value
public void set(int pos, int value) {
if(!checkPosInAdd(pos)){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("越界");
}else {
elem[usedSize] = value;
usedSize++;
}
}4.8 获得第一个元素坐标
直接遍历数组,第一次碰到的这个元素,返回坐标,没有返回-1;
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for(int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++){
if(elem[i] == toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}4.9 打印ArrayList
可以直接遍历整个数组,进行打印;
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(elem[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}4.10 清空ArrayList
直接将usedSize大小变为0即可;
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
usedSize = 0;
}