资源文件分类
1.android资源文件分为两类:
第一类是res目录下存放的可编译资源文件,编译时,系统会自动在R.java中生成资源文件的十六进制值,如下所示:
public final class R {
public static final class id {
public static final int action0 = 0x7f0b006d;
...
}
}
访问这种资源比较假单,使用Context的getResources方法得到Resorce对象,进而通过Resources的getXXX方法得到各种资源:
Resources resources = getResources();
String appName = resources.getString(R.string.app_name);
第二类是assets目录下存放的原始资源文件,apk在编译时不会编译assets下的资源文件,我们通过AssetManager对象来访问,AssetManager又来源于Resources类的getAssets方法:
Resources resources = getResources();
AssetManager am = getResources().getAssets();
InputStream is = getResources().getAssets().open("filename");
Resources是加载资源的重点。Resources内部各种方法其实都是间接调用AssetManager的内部方法,AssetManager负责向系统要资源。
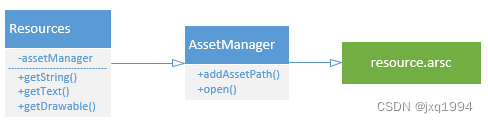
访问外部资源原理
加载资源的原理推荐查看Android 换肤之资源(Resources)加载源码分析
和Android资源动态加载以及相关原理分析
这里只是简单的说一下
context.getResources().getText()
##Resources
@NonNull public CharSequence getText(@StringRes int id) throws NotFoundException {
CharSequence res = mResourcesImpl.getAssets().getResourceText(id);
if (res != null) {
return res;
}
throw new NotFoundException("String resource ID #0x"
+ Integer.toHexString(id));
}
##ResourcesImpl
public AssetManager getAssets() {
return mAssets;
}
内部是调用了mResourcesImpl去访问的,这个对象是ResourcesImpl类型,最后是通过AssetManager去访问资源的。现在可以得出一个结论,AssetManager是真正加载资源的对象,而Resources是app层面API调用的类。
AssetManager
/**
* Provides access to an application's raw asset files; see {@link Resources}
* for the way most applications will want to retrieve their resource data.
* This class presents a lower-level API that allows you to open and read raw
* files that have been bundled with the application as a simple stream of
* bytes.
*/
public final class AssetManager implements AutoCloseable {
/**
* Add an additional set of assets to the asset manager. This can be
* either a directory or ZIP file. Not for use by applications. Returns
* the cookie of the added asset, or 0 on failure.
* @hide
*/
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public int addAssetPath(String path) {
return addAssetPathInternal(path, false /*overlay*/, false /*appAsLib*/);
}
}
这里非常的关键,需要解释一下,首先AssetManager是资源管理器,专门负责加载资源的,它内部有个隐藏方法addAssetPath,是用于加载指定路径下的资源文件,也就是说你把apk/jar的路径传给它,它就能把资源数据读到AssetManager,然后就可以访问了。
但是有个问题,虽然实际加载资源的是AssetManager,但是我们通过API访问的确是Resources对象,所以看下Resources对象的构造方法
ResourcesImpl的创建
/**
* Create a new Resources object on top of an existing set of assets in an
* AssetManager.
*
* @param assets Previously created AssetManager.
* @param metrics Current display metrics to consider when
* selecting/computing resource values.
* @param config Desired device configuration to consider when
* selecting/computing resource values (optional).
*/
public Resources(AssetManager assets, DisplayMetrics metrics, Configuration config) {
this(null);
mResourcesImpl = new ResourcesImpl(assets, metrics, config, new DisplayAdjustments());
}
看到这个构造方法,有点感觉了吧。可以通过AssetManager对象去构造mResourcesImpl对象,之前也分析过资源访问是通过mResourcesImpl.getAssets().getXXX()方法来完成的,那现在就有办法解决加载外部apk资源的问题了。
创建ResourcesImpl需要4个参数:
-
参数一: AssetManager 具体资源管理(重要)
-
参数二: DisplayMetrics 屏幕的一些封装
通过getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density 获取过屏幕的密度
通过getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels 获取过屏幕的宽度等 -
参数三: Configuration 一些配置信息
-
参数四: DisplayAdjustments 资源的兼容性等
加载外部apk资源的解决思路
首先,我们需要有3个工程:一个是宿主工程,用来加载外部资源;另一个是插件工程,用来提供外部资源。还有一个是公共库,定义了获取资源的接口方法。宿主工程和插件工程都引入该公共库。引入的方法:
File => Project Structure =>
插件工程
- 字符串资源定义
<string name="hello_message">Hello</string>
- 图片资源定义
在drawable文件夹里放一个名为ic_baseline_train_24.png的图片
创建读取资源的类:
public class UIUtils implements IDynamic {
public String getTextString(Context context){
return context.getResources().getString(R.string.hello_message);
}
public Drawable getImageDrawable(Context ctx){
return ctx.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.ic_baseline_train_24);
}
public View getLayout(Context ctx){
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = LayoutInflater.from(ctx);
View view = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.activity_main,null);
return view;
}
}
编译好该插件工程后,我们将生成的apk文件命名为plugin1.apk,将该apk文件复制到宿主文件的assets目录下:
#build.gradle
assemble.doLast {
android.applicationVariants.all { variant ->
// Copy Release artifact to HostApp's assets and rename
if (variant.name == "release") {
variant.outputs.each { output ->
File originFile = output.outputFile
println originFile.absolutePath
copy {
from originFile
into "$rootDir/app/src/main/assets"
rename(originFile.name, "plugin1.apk")
}
}
}
}
}
宿主工程
我们创建一个宿主工程,并在应用启动的时候将assets下的插件apk复制到sd卡下 /data/data/包名/files的路径下面,然后加载插件工程生成的apk文件,并显示出插件里的资源。
public class BaseActivity extends Activity {
private AssetManager mAssetManager;
public Resources mResources;
private Resources.Theme mTheme;
protected HashMap<String, PluginInfo> plugins = new HashMap<String, PluginInfo>();
private String dexPath1,dexPath2; //apk文件地址
private String fullReleaseFilePath; //释放目录
private String plugin1name = "plugin1.apk";
private String plugin2name = "plugin2.apk";
public ClassLoader classLoader1,classLoader2;
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {
super.attachBaseContext(newBase);
Utils.extractAssets(newBase,plugin1name);
Utils.extractAssets(newBase,plugin2name);
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
genegatePluginInfo(plugin1name);
genegatePluginInfo(plugin2name);
fullReleaseFilePath = getDir("dex",0).getAbsolutePath();
dexPath1 = this.getFileStreamPath(plugin1name).getPath();
dexPath2 = this.getFileStreamPath(plugin2name).getPath();
classLoader1 = new DexClassLoader(dexPath1,
fullReleaseFilePath,null,getClassLoader());
classLoader2 = new DexClassLoader(dexPath2,
fullReleaseFilePath,null,getClassLoader());
}
/**
* 加载外部的插件,生成插件对应的ClassLoader
* @param pluginName
*/
protected void genegatePluginInfo(String pluginName) {
File extractFile = this.getFileStreamPath(pluginName);
File fileRelease = getDir("dex", 0);
String dexpath = extractFile.getPath();
DexClassLoader classLoader = new DexClassLoader(dexpath, fileRelease.getAbsolutePath(), null, getClassLoader());
plugins.put(pluginName, new PluginInfo(dexpath, classLoader));
}
/**
* 重要
* 通过反射,创建AssetManager对象,调用addAssetPath方法,把插件Plugin的路径添加到这个AssetManager对象中
* @param dexPath
*/
protected void loadResources(String dexPath) {
try {
AssetManager assetManager = AssetManager.class.newInstance();
Method addAssetPath = assetManager.getClass().getMethod("addAssetPath", String.class);
addAssetPath.invoke(assetManager, dexPath);
mAssetManager = assetManager;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Resources superRes = super.getResources();
mResources = new Resources(mAssetManager, superRes.getDisplayMetrics(), superRes.getConfiguration());
mTheme = mResources.newTheme();
mTheme.setTo(super.getTheme());
}
}
/**
* 重要
* 重写Acitivity的getAsset,getResources和getTheme方法
* mAssetManager是指向插件的,如果这个对象为空,就调用父类ContextImpl的getAssets方法,
* 这个时候得到的AssetManager对象就指向宿主HostApp,读取的资源也就是HostApp中的资源
* @return
*/
@Override
public AssetManager getAssets() {
if(mAssetManager == null){
return super.getAssets();
}
return mAssetManager;
}
@Override
public Resources getResources() {
if(mResources == null){
return super.getResources();
}
return mResources;
}
@Override
public Resources.Theme getTheme() {
if(mTheme == null){
return super.getTheme();
}
return mTheme;
}
这里创建了一个基类BaseActivity来做 加载APK资源之前的准备工作。真正的加载APK资源是在MainActivity中:
public class MainActivity extends BaseActivity {
private TextView textView;
private ImageView imageView;
private LinearLayout layout;
private Button btn1,btn2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = findViewById(R.id.text);
imageView = findViewById(R.id.imageview);
layout = findViewById(R.id.layout);
btn1 = findViewById(R.id.btn1);
btn2 = findViewById(R.id.btn2);
btn1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
PluginInfo pluginInfo = plugins.get("plugin1.apk");
loadResources(pluginInfo.getDexPath());
// doSomething(pluginInfo.getClassLoader(),"com.chinatsp.plugin1");
doSomethingOther(pluginInfo.getClassLoader(),"com.chinatsp.plugin1");
// doSomethingAnother(pluginInfo.getClassLoader(),"com.chinatsp.plugin1");
}
});
btn2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
PluginInfo pluginInfo = plugins.get("plugin2.apk");
loadResources(pluginInfo.getDexPath());
// doSomething(pluginInfo.getClassLoader(),"com.chinatsp.plugin2");
// doSomethingOther(pluginInfo.getClassLoader(),"com.chinatsp.plugin2");
doSomethingAnother(pluginInfo.getClassLoader(),"com.chinatsp.plugin2");
}
});
System.out.println(getString(R.string.hello));
}
/**
* 通过反射,获取插件中的类,构造出插件类的对象uiUtils,再反射调用插件类对象UIUtils中的方法
* @param cl
* @param uiUtilsPkgName
*/
private void doSomething(ClassLoader cl,String uiUtilsPkgName) {
try {
Class clazz = cl.loadClass(uiUtilsPkgName + ".UIUtils");
Object uiUtils = RefInvoke.createObject(clazz);
String str = (String) RefInvoke.invokeInstanceMethod(uiUtils, "getTextString", Context.class, this);
textView.setText(str);
Drawable drawable = (Drawable) RefInvoke.invokeInstanceMethod(uiUtils, "getImageDrawable", Context.class, this);
imageView.setBackground(drawable);
layout.removeAllViews();
View view = (View) RefInvoke.invokeInstanceMethod(uiUtils, "getLayout",Context.class,this);
layout.addView(view);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("DEMO", "msg:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 直接反射获取插件类中的R文件R.java的内部类,获取内部类中资源文件对应生成的16进制的值,也就R.string.xxx
* R.drawable.xxx对应的值,通过getResources方法的getxxx方法来获取资源文件
* @param cl
* @param uiUtilsPkgName
*/
private void doSomethingOther(ClassLoader cl,String uiUtilsPkgName) {
try {
Class stringClass = cl.loadClass(uiUtilsPkgName + ".R$string");
int resId1 = (int) RefInvoke.getStaticFieldObject(stringClass,"hello_message");
textView.setText(getResources().getString(resId1));
Class drawableClass = cl.loadClass(uiUtilsPkgName + ".R$drawable");
int resId2 = (int) RefInvoke.getStaticFieldObject(drawableClass,"ic_baseline_train_24");
imageView.setBackground(getResources().getDrawable(resId2));
Class layoutClass = cl.loadClass(uiUtilsPkgName + ".R$layout");
int resId3 = (int) RefInvoke.getStaticFieldObject(layoutClass,"activity_main");
View view = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(resId3,null);
layout.removeAllViews();
layout.addView(view);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("DEMO", "msg:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 通过反射,获取插件中的类,构造出插件类的对象dynamicObject,再直接调用插件类对象UIUtils中的方法
* @param cl
* @param uiUtilsPkgName
*/
private void doSomethingAnother(ClassLoader cl,String uiUtilsPkgName) {
Class mLoadClassDynamic = null;
try {
mLoadClassDynamic = cl.loadClass(uiUtilsPkgName + ".UIUtils");
Object dynamicObject = mLoadClassDynamic.newInstance();
IDynamic dynamic = (IDynamic) dynamicObject;
String str = dynamic.getTextString(this);
textView.setText(str);
Drawable drawable = dynamic.getImageDrawable(this);
imageView.setBackground(drawable);
layout.removeAllViews();
View view = dynamic.getLayout(this);
layout.addView(view);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("DEMO", "msg:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Source Code