目录
一.简单查找
①find(first, last, val);
②find_if & find_if_not
③count & count_if
④all_of & any_of & none_of
二.重复值的查找
①adjacent_find(first, end);
②search_n(first, end, count, val);
三.查找子序列
①search(first1, end1, first2, end2);
②find_first_of(first1, end1, first2, end2);
③find_end(first1, end1, first2, end2);
页数:P771(A.2.1查找对象的算法)
算法头文件:<algorithm>
参数注释:
first:序列的起始迭代器
last:序列的结尾迭代器
val:特定的一个值
unaryPred:自定义一元函数,用于自定义查找方式
binaryPred:自定义二元函数,用于自定义查找方式
一.简单查找
①find(first, last, val);
在first与last之间查找值为val的元素。如果有就返回该元素位置(迭代器),无就返回end迭代器。
使用示例:
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 2, 4, 1 , 3, 5, 2, 4, 6 };
vector<int>::iterator it = find(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 2);
if (it == arr.end()) cout << "无";
else cout << "有";
return 0;
}
②find_if & find_if_not
find_if(first, last, unaryPred);
find_if_not(first, last, unaryPred);
在first与last之间按指定方式查找元素。如果有就返回该元素位置(迭代器),无就返回end迭代器。
使用示例:
bool func(int n)
{
if (n == 3) return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 2, 4, 1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6 };
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(arr.begin(), arr.end(), func);
if (it == arr.end()) cout << "无";
else cout << "有";
return 0;
}
③count & count_if
count(first, last, val);
count_if(first, last, unaryPred);
在first与last之间,统计val值共出现多少次,返回一个记录出现次数的计数器(本质是int类型)。
count_if目的与count一致,区别是统计方式不再是具体val值,而是自定义统计方式。
使用示例:
bool func(int n)
{
if (n == 3 || n == 1 || n == 6) return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 2, 4, 1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6 };
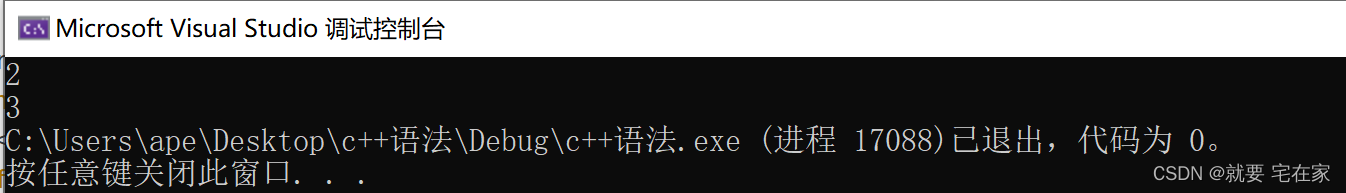
int sum = count(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 4);
cout << sum << endl;
sum = count_if(arr.begin(), arr.end(), func);
cout << sum;
return 0;
}
④all_of & any_of & none_of
all_of(first, last, unaryPred);
any_of(first, last, unaryPred);
none_of(first, last, unaryPred);
在first与last之间,上述三个函数目的分别是:按自定义函数(的方式)查找各元素都成功、对任意一个元素查找成功、所有元素查找都失败。
返回值为bool类型,成功返回true,失败返回false。
bool func(int n)
{
if (n == 3) return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 2, 4, 1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6 };
if (all_of(arr.begin(), arr.end(), func)) cout << "TRUE";
else cout << "FALSE";
cout << endl;
if (any_of(arr.begin(), arr.end(), func)) cout << "TRUE";
else cout << "FALSE";
cout << endl;
if (none_of(arr.begin(), arr.end(), func)) cout << "TRUE";
else cout << "FALSE";
return 0;
}
二.重复值的查找
①adjacent_find(first, end);
要求支持前向迭代器。
查找相邻元素是否重复。如果有重复,返回第一对重复元素迭代器;没有则返回end迭代器。
同时该函数有重载类型,第三个参数为自定义函数,用于自定义查找方式:
adjacent_find(first, end, binaryPred);
使用示例:
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 2, 4, 1, 3, 3, 2, 4, 6 };
vector<int>::iterator it = adjacent_find(arr.begin(), arr.end());
//vector<int> arr = { 2, 4, 1, 3, 3, 2, 4, 6 };
// ^
// it
if (it == arr.end()) cout << "无";
else cout << *it;
return 0;
}
②search_n(first, end, count, val);
查找在first到end之间,是否存在count个相邻的值为val的元素。若存在,返回重复的起始位置迭代器;否则返回end迭代器。
使用示例:
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 2, 4, 1, 3, 0, 3, 2, 0, 4, 6, 0 };
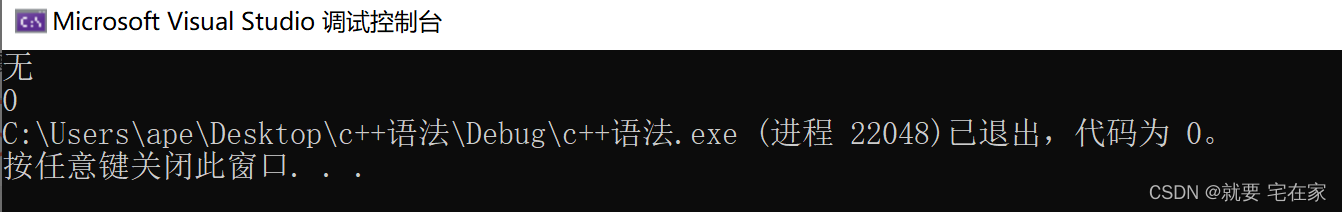
vector<int>::iterator it = search_n(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 3, 0);
if (it == arr.end()) cout << "无";
else cout << *it;
cout << endl;
arr = { 2, 4, 1, 3, 0, 0, 0, 3, 2, 0, 4, 6, 0 };
it = search_n(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 3, 0);
//arr = { 2, 4, 1, 3, 0, 0, 0, 3, 2, 0, 4, 6, 0 };
// ^
// it
if (it == arr.end()) cout << "无";
else cout << *it;
return 0;
}
三.查找子序列
①search(first1, end1, first2, end2);
在first1到end1之间,查找有无特定子序列,子序列起始为first2,结尾为end2。
如果有,返回在范围first1到end1之间,第一次出现的位置迭代器;否则返回end1迭代器。
使用示例:
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 2, 4, 1, 3, 0, 3, 2, 0, 4, 6, 0, 0, 3, 2 };
vector<int> tmp = { 0, 3, 2 };
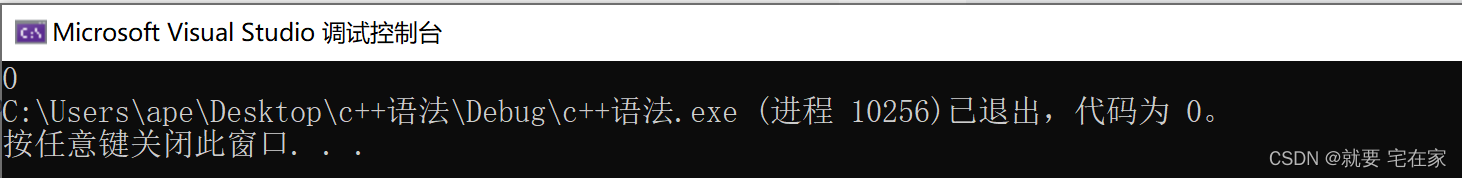
vector<int>::iterator it = search(arr.begin(), arr.end(), tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
if (it == arr.end()) cout << "无";
else cout << *it;
return 0;
}
②find_first_of(first1, end1, first2, end2);
该函数是在first1到end1范围中,查找第一个与first2到end2中任意元素匹配的元素,并返回该位置迭代器;如果没有匹配的,返回end1迭代器。
举个例子,范围1是{3, 2, 3, 4, 5};范围2是{7, 4};那么在查找时,范围1从左到右第一个与范围2中匹配的元素是4。因此,返回4所在的迭代器。
使用示例:
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 3, 2, 4, 1, 3, 0, 3, 2, 0, 4, 6, 0, 0, 3, 2 };
vector<int> tmp = { 7, 1, 0, 4};
vector<int>::iterator it = find_first_of(arr.begin(), arr.end(), tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
//vector<int> arr = { 3, 2, 4, 1, 3, 0, 3, 2, 0, 4, 6, 0, 0, 3, 2 };
// ^
// it
if (it == arr.end()) cout << "无";
else cout << *it;
return 0;
}
③find_end(first1, end1, first2, end2);
该函数作用与search类似,不同是匹配的是子序列最后一次出现的位置,返回值与search类似。
使用示例:
int main()
{
vector<int> arr = { 3, 2, 4, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 0, 4, 6, 1, 2, 3, 2 };
vector<int> tmp = { 1, 2, 3};
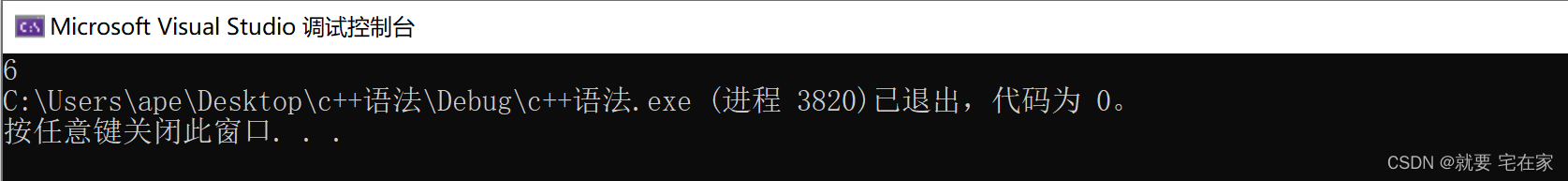
vector<int>::iterator it = find_end(arr.begin(), arr.end(), tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
//vector<int> arr = { 3, 2, 4, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 0, 4, 6, 1, 2, 3, 2 };
// ^
// it
if (it == arr.end()) cout << "无";
else cout << *(--it);
return 0;
} 
如有错误,敬请斧正