各位CSDN的uu们你们好呀,好久没有更新本专栏啦,甚是想念!!!今天,小雅兰的学习内容是用队列实现栈,下面,让我们进入Leetcode的世界吧!!!

这是小雅兰写过的栈和队列的文章,有兴趣的可以看看:
栈——“数据结构与算法”_认真学习的小雅兰.的博客-CSDN博客
队列——“数据结构与算法”_认真学习的小雅兰.的博客-CSDN博客
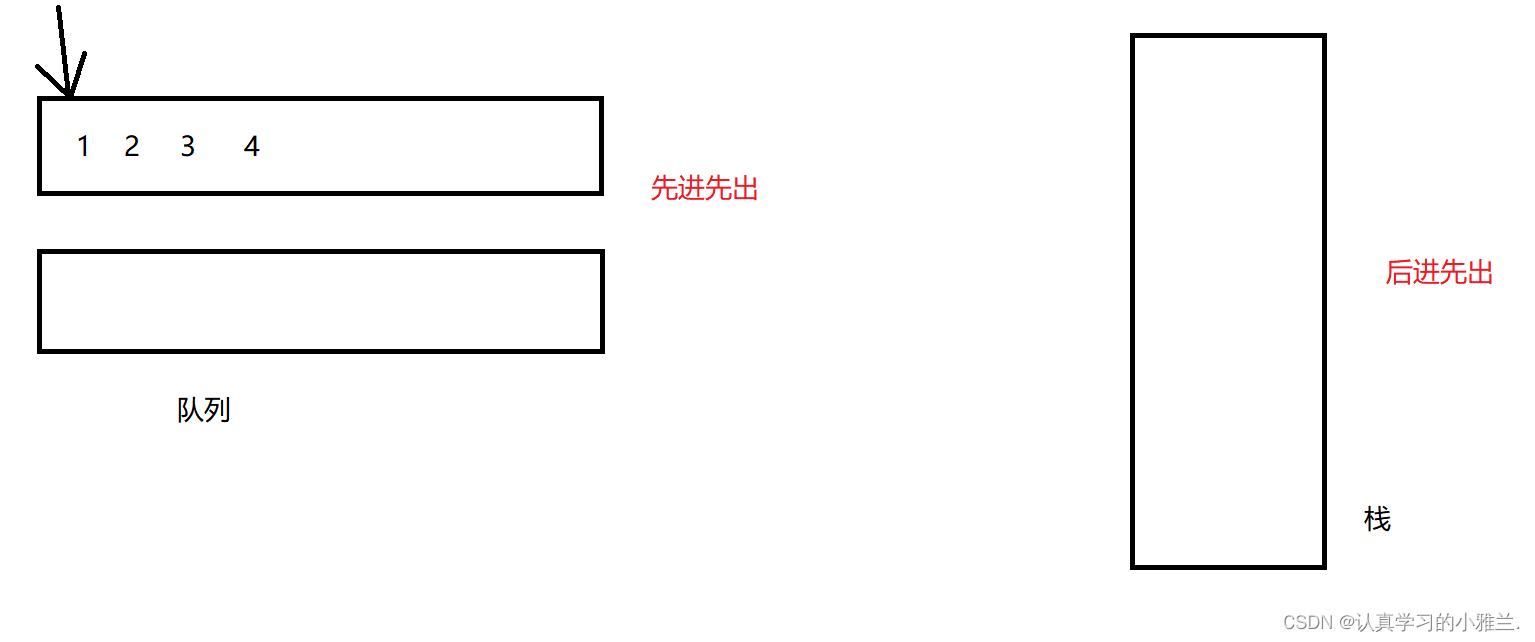
如图所示:
这里相当于 栈中的Push1 2 3 4这四个数据
 可以使用两个队列进行导数据
可以使用两个队列进行导数据
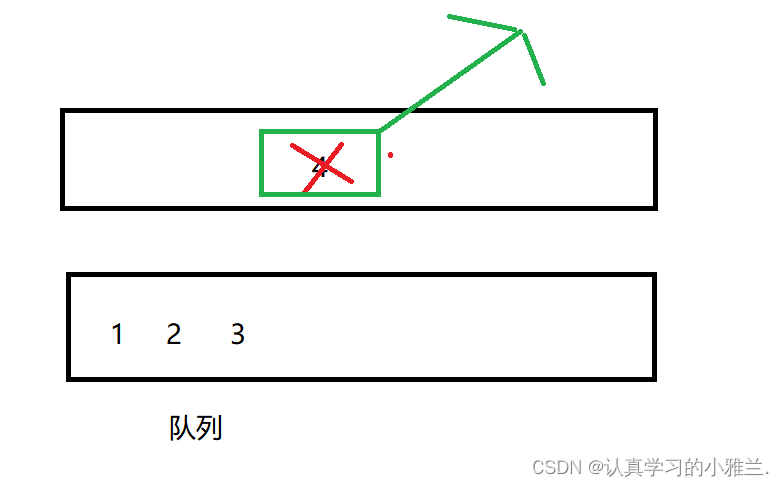
如果还想再导出一个数据,那么还是同样的方法:
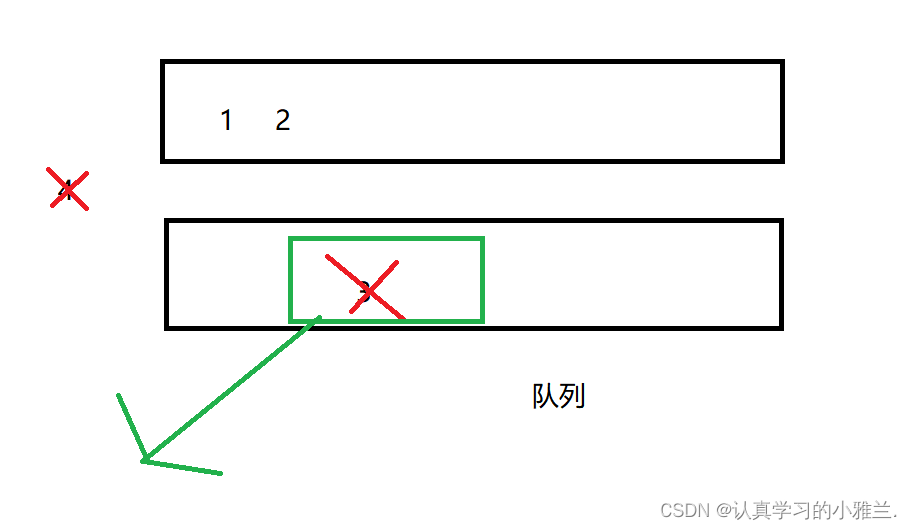
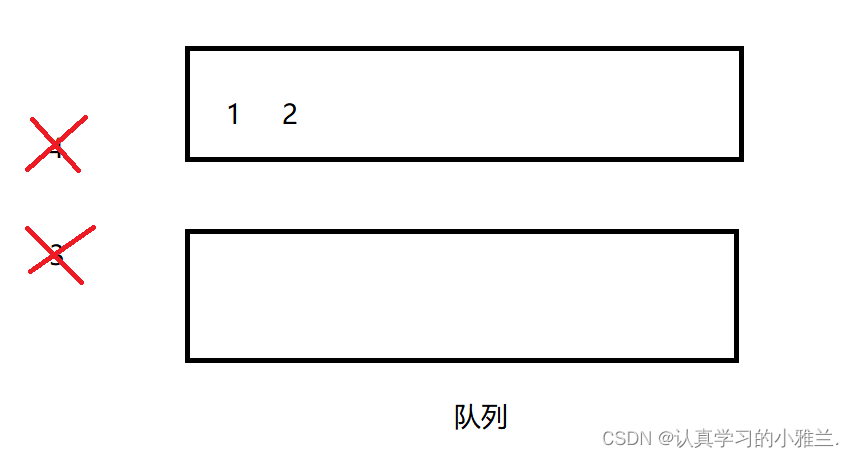
这里相当于栈中两次连续的Pop
如果还想Push5 6这两个数据,那么:
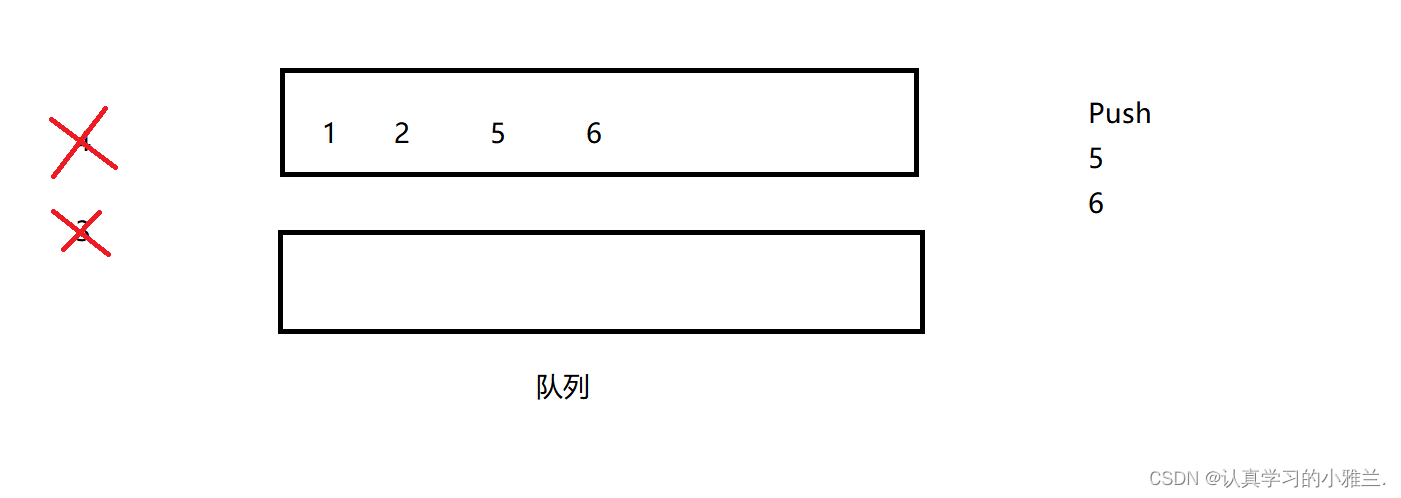
然后再Pop,还是一样的,这次Pop一次,Pop出的就是6啦
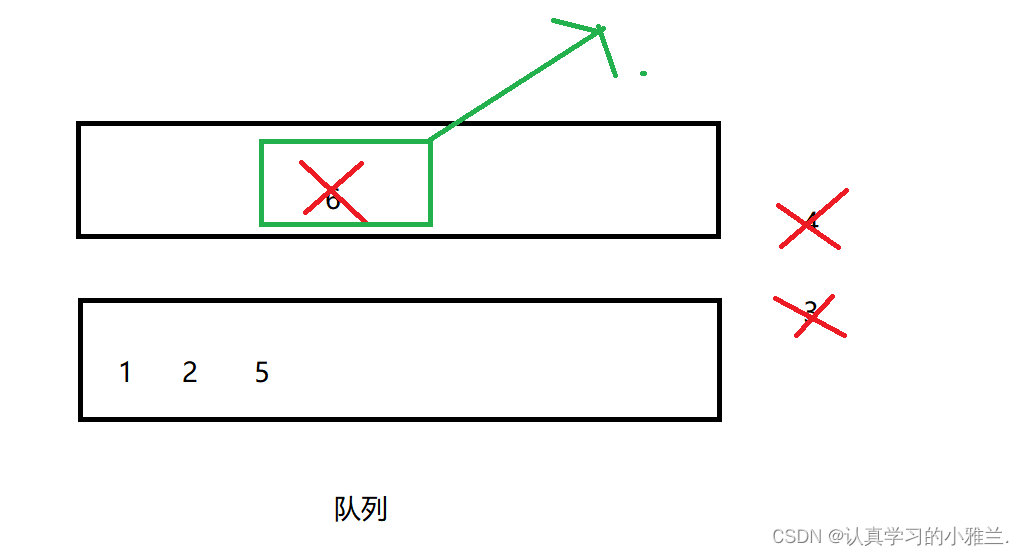
好的,那么我们的基本思路就是这样的啦,下面,我们开始用代码实现它吧
首先,我们用的是C语言的话,还要自己实现一个队列,直接上代码:
typedef int QDataType;
// 链式结构:表示队列
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QueueNode;
// 队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode* phead;//头指针
QueueNode* ptail;//尾指针
int size;
}Queue;
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
// 检测队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//是空队列的情况
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
// 检测队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL && pq->ptail == NULL;
}
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//1.一个结点
//2.多个结点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
//相当于头删
QueueNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
剩余的功能就按照Leetcode上面给定的来:
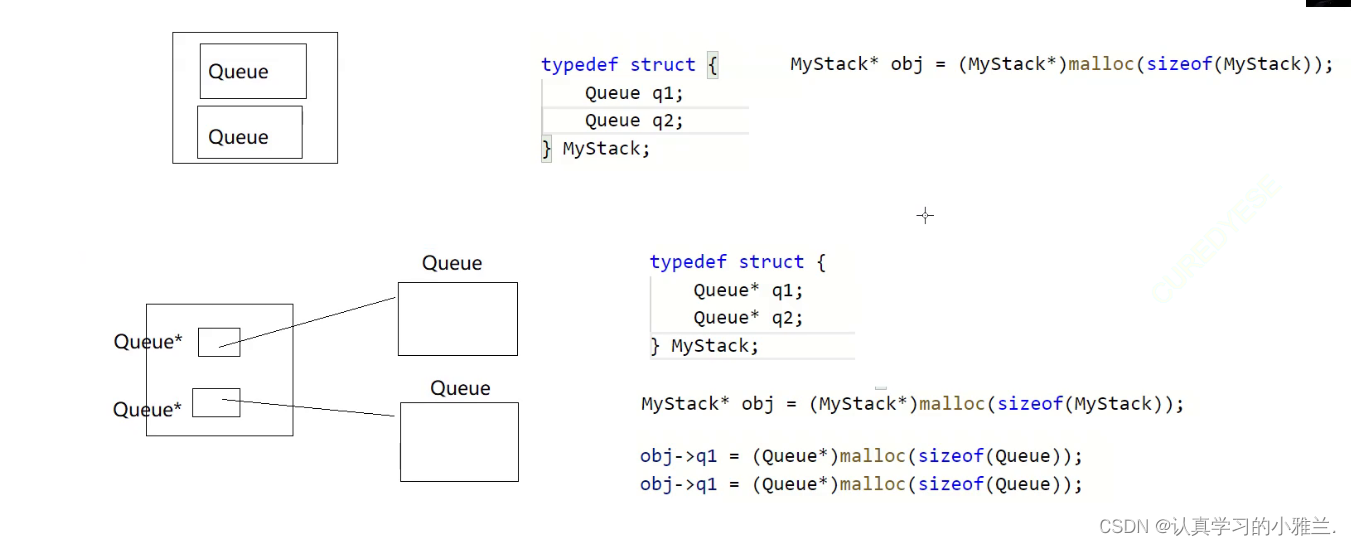
typedef struct { Queue q1; Queue q2; } MyStack;这是一个匿名结构体,把这个匿名结构体typedef成MyStack
MyStack* myStackCreate() { MyStack obj; return &obj; }这个程序能不能这样写呢?
答案当然是否定的。
MyStack是一个局部结构体变量,出了作用域,它就销毁了
它是存在栈帧里面的,栈帧已经销毁了
所以这就是一个野指针
正确的写法:
MyStack* myStackCreate() { MyStack* obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack)); if(obj==NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return NULL; } //这里->的优先级更高,取地址是对obj->q1和obj->q2取地址 QueueInit(&obj->q1); QueueInit(&obj->q2); return obj; }这里->的优先级更高,取地址是对obj->q1和obj->q2取地址
有的人可能会觉得在QueueInit里面取地址比较麻烦,那么,就衍生出了另外一种写法:
typedef struct { Queue* q1; Queue* q2; } MyStack; MyStack* myStackCreate() { MyStack* obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack)); if(obj==NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return NULL; } //两种写法 obj->q1=(Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue)); obj->q2=(Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue)); QueueInit(obj->q1); QueueInit(obj->q2); return obj; }
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) { //q1不为空 if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { QueuePush(&obj->q1,x); } else { QueuePush(&obj->q2,x); } }
删除数据:
由于不知道数据在q1还是在q2
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) { //由于不知道数据是在q1还是在q2 //q1为空 q2不为空 //这是一种假设 假设有可能错误 Queue* pEmptyQ=&obj->q1; Queue* pNonEmptyQ=&obj->q2; //q1不为空 if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { //q2为空 q1不为空 pEmptyQ=&obj->q2; pNonEmptyQ=&obj->q1; } //导数据 while(QueueSize(pNonEmptyQ)>1) { //非空里面的数据插入空 QueuePush(pEmptyQ,QueueFront(pNonEmptyQ)); //每区一个数据就把它Pop一下 QueuePop(pNonEmptyQ); } int top=QueueFront(pNonEmptyQ); QueuePop(pNonEmptyQ); return top; }
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) { if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { return QueueBack(&obj->q1); } else { return QueueBack(&obj->q2); } }
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) { return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2); }
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) { QueueDestroy(&obj->q1); QueueDestroy(&obj->q2); free(obj); }如果不Destroy,可能会内存泄漏
这个题目完整代码如下:
typedef int QDataType;
// 链式结构:表示队列
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QueueNode;
// 队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode* phead;//头指针
QueueNode* ptail;//尾指针
int size;
}Queue;
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
// 检测队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
// 检测队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL && pq->ptail == NULL;
}
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//1.一个结点
//2.多个节点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
//相当于头删
QueueNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
//这里->的优先级更高,取地址是对obj->q1和obj->q2取地址
QueueInit(&obj->q1);
QueueInit(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
//q1不为空
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
//由于不知道数据是在q1还是在q2
//q1为空 q2不为空
//这是一种假设 假设有可能错误
Queue* pEmptyQ=&obj->q1;
Queue* pNonEmptyQ=&obj->q2;
//q1不为空
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
//q2为空 q1不为空
pEmptyQ=&obj->q2;
pNonEmptyQ=&obj->q1;
}
//导数据
while(QueueSize(pNonEmptyQ)>1)
{
//非空里面的数据插入空
QueuePush(pEmptyQ,QueueFront(pNonEmptyQ));
//每区一个数据就把它Pop一下
QueuePop(pNonEmptyQ);
}
int top=QueueFront(pNonEmptyQ);
QueuePop(pNonEmptyQ);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
好啦,小雅兰今天的用队列实现栈的内容就到这里啦,还要继续加油刷题噢!!!