字符集/编码表
ex:ASCII码
字符char:单引号‘ ’引起来的单个字符
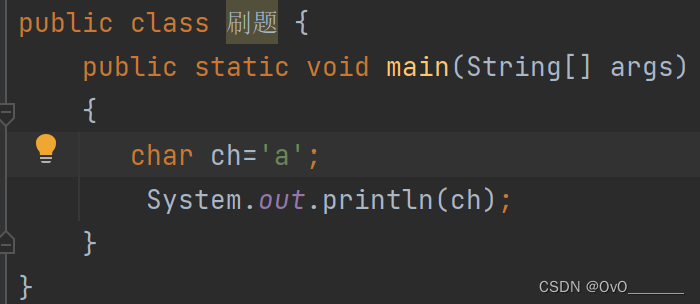
转义字符 ' \n '
作用:换行,单引号引用!!!
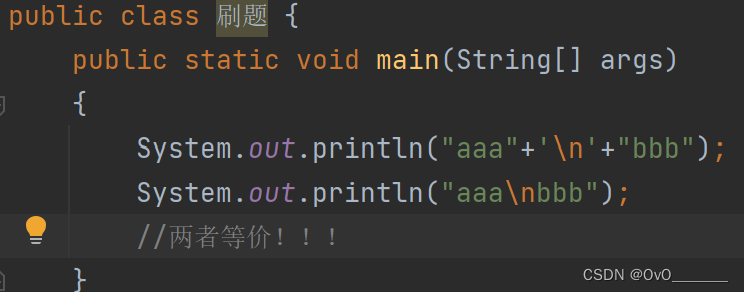
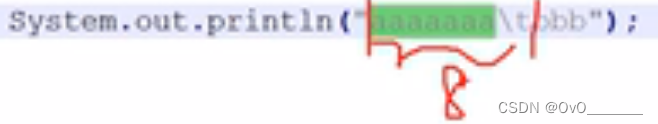
制表符 ' \t '
作用:加上 \t 前面一共空8个
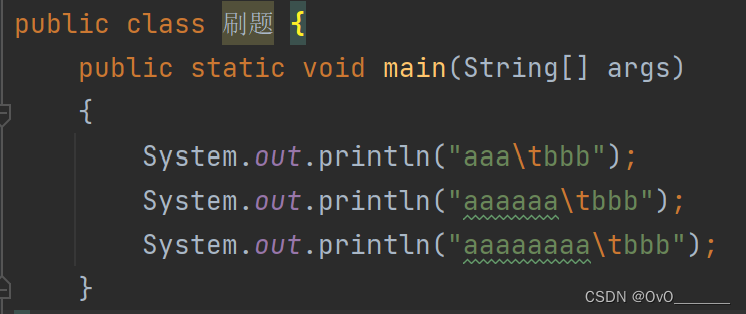
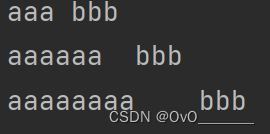
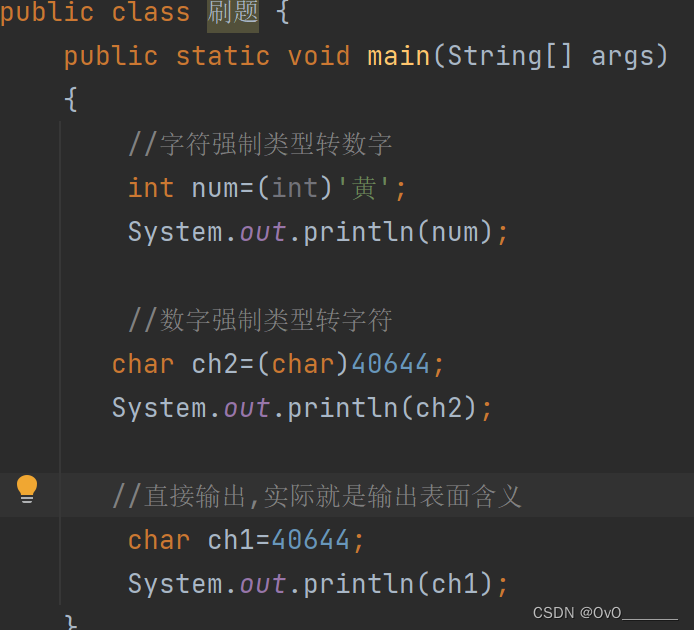
字符与编码的转换
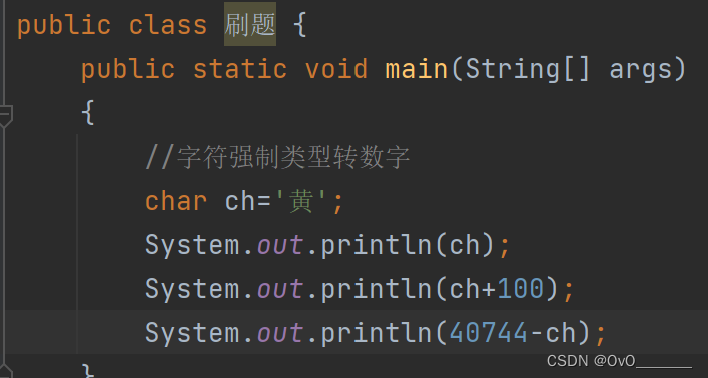
1.直接输出字符时,看到的char类型就是它本身的字面常量
2.直接参与运算时,实际是按照码进行计算的
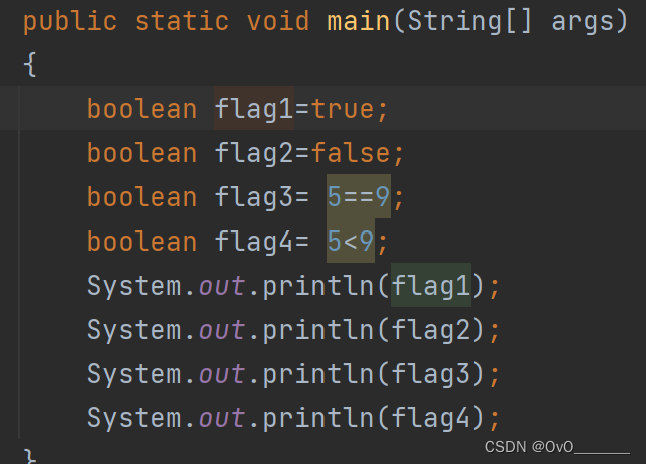
boolean布尔类型
类似标记数组,只有ture,false
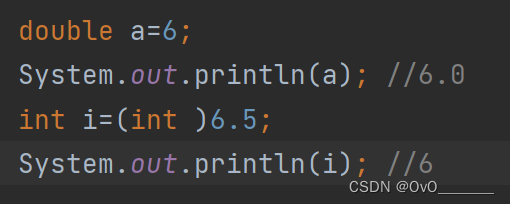
数据类型转化 &&数据类型级别
1.自动类型转换
2.强制类型转换
byte(<127) , short , char << int << long << float << double


final修饰
一个变量被final修饰,这个变量就变成了常量,该常量值则不可改变
类似:const int
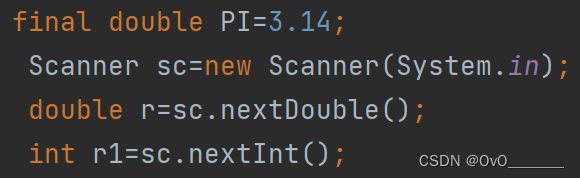
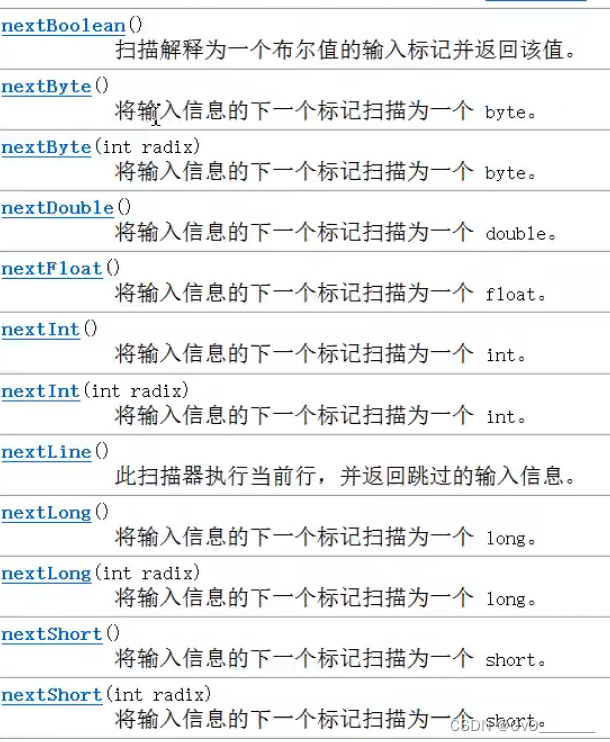
Scanner扫描器(输入)
头文件(import java.util.Scanner;)
多种类型输入,但没有nextChar();
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
sc.nextDouble();
sc.nextInt();
//年龄,身高,姓名,性别
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("亲输入年龄");
int age=sc.nextInt();
//System.out.println(age);
System.out.print("亲输入身高");
double height=sc.nextDouble();
//System.out.println(height);
System.out.print("亲输入姓名");
String name=sc.next(); //字符串string
//System.out.println(name);
//字符串格式输入性别
/*
System.out.print("亲输入性别");
String sex=sc.next();
System.out.println(sex);
*/
//字符格式输入性别
System.out.print("亲输入性别");
String sexStr=sc.next(); //输入一个字符串
char sex=sexStr.charAt(0); //代表读取该字符串的首位字符,charAt(0)
//System.out.println(sex);
//合并为:
//char sex=sc.next().charAt(0);
System.out.println("年龄为:"+age+"\n身高为:"+height+"\n姓名为:"+name+"\n性别为:"+sex);









![[笔记]C++并发编程实战 《二》线程管理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/53e6af3b3ce3478bbd390a6539e2e2ef.png)