阅读目录
- 集成 Gorilla Mux
- 为什么不选择 HttpRouter?
- 安装 gorilla/mux
- 使用 gorilla/mux
- 迁移到 Gorilla Mux
- 1. 新增 homeHandler
- 2. 指定 Methods () 来区分请求方法
- 3. 请求路径参数和正则匹配
- 4. 命名路由与链接生成
集成 Gorilla Mux
我们将选用 gorilla/mux 来作为 goblog 的路由器。
https://github.com/gorilla/mux
为什么不选择 HttpRouter?
HttpRouter
https://github.com/julienschmidt/httprouter
Gin
https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin
HttpRouter 是目前来讲速度最快的路由器,且被知名框架 Gin 所采用。
不选择 HttpRouter 的原因是其功能略显单一,没有路由命名功能,不符合我们的要求。
HttpRouter 和 Gin 比较适合在要求高性能,且路由功能要求相对简单的项目中,如 API 或微服务。在全栈的 Web 开发中,gorilla/mux 在性能上虽然有所不及,但是功能强大,比较实用。
安装 gorilla/mux
这是我们第一次安装第三方依赖,goblog 项目将使用官方推荐的 Go Module 来管理第三方依赖。
Go Modules 相关知识下一节再来讲。本节专注于安装和使用 gorilla/mux。
下面使用 go get 命令安装 gorilla/mux :
go get -u github.com/gorilla/mux
安装成功后使用 git status 可以看到有两个文件变跟:
输出:
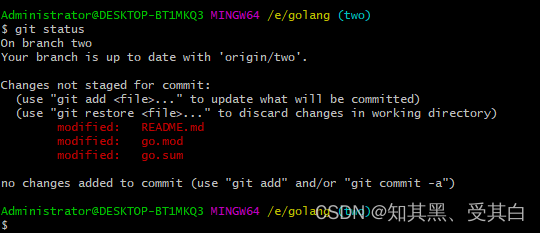
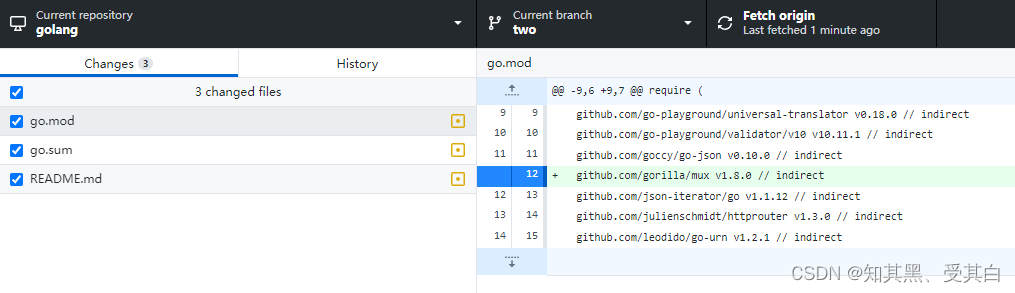
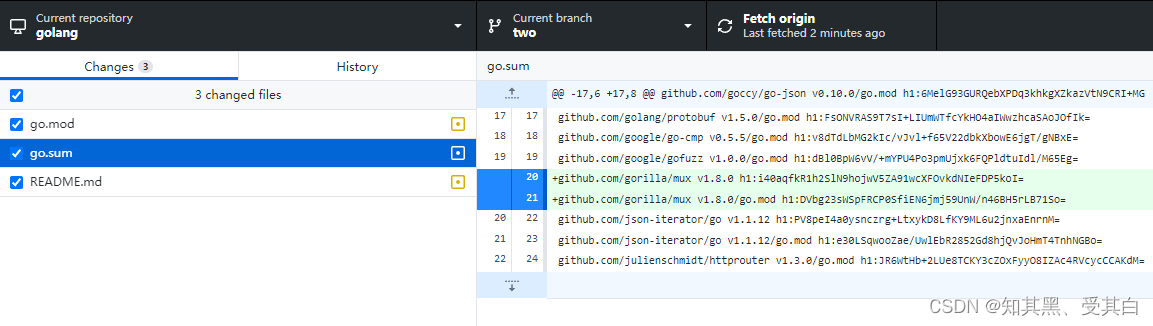
提示: 下一节,我们再来讲解这两个文件的作用。
使用 gorilla/mux
gorilla/mux 因实现了 net/http 包的 http.Handler 接口,故兼容 http.ServeMux ,也就是说,我们可以直接修改一行代码,即可将 gorilla/mux 集成到我们的项目中:
main.go
func main() {
router := mux.NewRouter()
}
注意: 修改以上代码后保存,因为安装了 Go for Visual Studio Code 插件,VSCode 会自动在文件顶部的 import 导入 mux 库,我们无需手动添加。
依次以下链接:
localhost:3000/
localhost:3000/about
localhost:3000/articles
localhost:3000/no-exists
localhost:3000/articles/2
localhost:3000/articles/
可以发现:
1、2 和 3 可以正常访问。
4 无法访问到自定义的 404 页面
5 文章详情页无法访问
6 可以访问到文章页面,但是 ID 为空
这是因为 gorilla/mux 的路由解析采用的是 精准匹配 规则,而 net/http 包使用的是 长度优先匹配 规则。
精准匹配 指路由只会匹配准确指定的规则,这个比较好理解,也是较常见的匹配方式。
长度优先匹配 一般用在静态路由上(不支持动态元素如正则和 URL 路径参数),优先匹配字符数较多的规则。
以我们的 goblog 为例:
router.HandleFunc("/", defaultHandler)
router.HandleFunc("/about", aboutHandler)
使用 长度优先匹配 规则的 http.ServeMux 会把除了 /about 这个匹配的以外的所有 URI 都使用 defaultHandler 来处理。
而使用 精准匹配 的 gorilla/mux 会把以上两个规则精准匹配到两个链接,/ 为首页,/about 为关于,除此之外都是 404 未找到。
知道这个规则后,配合上面几个测试链接的返回结果,会更好理解。
一般 长度优先匹配 规则用在静态内容处理上比较合适,动态内容,例如我们的 goblog 这种动态网站,使用 精准匹配 会比较方便。
迁移到 Gorilla Mux
基于以上规则,接下来改进代码:
main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
)
func homeHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/html; charset=utf-8")
fmt.Fprint(w, "<h1>Hello, 欢迎来到 goblog!</h1>")
}
func aboutHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/html; charset=utf-8")
fmt.Fprint(w, "此博客是用以记录编程笔记,如您有反馈或建议,请联系 "+
"<a href=\"mailto:1157818690@qq.com\">1157818690@qq.com</a>")
}
func notFoundHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/html; charset=utf-8")
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
fmt.Fprint(w, "<h1>请求页面未找到 :(</h1><p>如有疑惑,请联系我们。</p>")
}
func articlesShowHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
vars := mux.Vars(r)
id := vars["id"]
fmt.Fprint(w, "文章 ID:"+id)
}
func articlesIndexHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprint(w, "访问文章列表")
}
func articlesStoreHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprint(w, "创建新的文章")
}
func main() {
router := mux.NewRouter()
router.HandleFunc("/", homeHandler).Methods("GET").Name("home")
router.HandleFunc("/about", aboutHandler).Methods("GET").Name("about")
router.HandleFunc("/articles/{id:[0-9]+}", articlesShowHandler).Methods("GET").Name("articles.show")
router.HandleFunc("/articles", articlesIndexHandler).Methods("GET").Name("articles.index")
router.HandleFunc("/articles", articlesStoreHandler).Methods("POST").Name("articles.store")
// 自定义 404 页面
router.NotFoundHandler = http.HandlerFunc(notFoundHandler)
// 通过命名路由获取 URL 示例
homeURL, _ := router.Get("home").URL()
fmt.Println("homeURL: ", homeURL)
articleURL, _ := router.Get("articles.show").URL("id", "23")
fmt.Println("articleURL: ", articleURL)
http.ListenAndServe(":3000", router)
}
接下来我们一步步分解代码。
1. 新增 homeHandler
首先,因为使用的是精确匹配,我们将 defaultHandler 变更 homeHandler 且将处理 404 的代码移除。
2. 指定 Methods () 来区分请求方法
看下这两个路由:
router.HandleFunc("/articles", articlesIndexHandler).Methods("GET").Name("articles.index")
router.HandleFunc("/articles", articlesStoreHandler).Methods("POST").Name("articles.store")
命令行:
E:\golang\src>curl http://127.0.0.1:3000/articles
访问文章列表
E:\golang\src>curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:3000/articles
创建新的文章
E:\golang\src>
解析正确。
注意: 在 Gorilla Mux 中,如未指定请求方法,默认会匹配所有方法。
3. 请求路径参数和正则匹配
我们的文章详情页面的匹配:
router.HandleFunc("/articles/{id:[0-9]+}", articlesShowHandler).Methods("GET").Name("articles.show")
注意 ID 路径的设置:
{id:[0-9]+}
有以下规则:
- 使用 {name} 花括号来设置路径参数。
- 在有正则匹配的情况下,使用
:区分。第一部分是名称,第二部分是正则表达式。
[0-9]+
限定了 一个或者多个的数字。如果你访问非数字的 ID ,如 localhost:3000/articles/string 即会看到 404 页面。
再看下在 Handler 里面我们如何获取到这个参数:
func articlesShowHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
vars := mux.Vars(r)
id := vars["id"]
fmt.Fprint(w, "文章 ID:"+id)
}
Mux 提供的方法 mux.Vars® 会将 URL 路径参数解析为键值对应的 Map,使用以下方法即可读取:
vars["id"]
4. 命名路由与链接生成
router.HandleFunc("/", homeHandler).Methods("GET").Name("home")
router.HandleFunc("/articles/{id:[0-9]+}", articlesShowHandler).Methods("GET").Name("articles.show")
Name() 方法用来给路由命名,传参是路由的名称,接下来我们就可以靠这个名称来获取到 URI:
homeURL, _ := router.Get("home").URL()
fmt.Println("homeURL: ", homeURL)
articleURL, _ := router.Get("articles.show").URL("id", "1")
fmt.Println("articleURL: ", articleURL)
命令行切到我们的 air 窗口,即可看到 fmt.Println 打印出来的内容:


![[附源码]计算机毕业设计云南美食管理系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/198c5612d7da40c59fd7457bab70a6c3.png)




![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot学分制环境下本科生学业预警帮扶系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/62a6f64ad23d4eb0b3bb4881f51e5164.png)