个人主页:平行线也会相交💪
欢迎 点赞👍 收藏✨ 留言✉ 加关注💓本文由 平行线也会相交 原创
收录于专栏【C++之路】💌
本专栏旨在记录C++的学习路线,望对大家有所帮助🙇
希望我们一起努力、成长,共同进步。🍓
目录
- 日期类(Date.cpp)成员函数的实现
- 构造函数
- bool类型的运算符重载
- 得到该月有几天GetMonthDay
- 运算符重载+=和+
- 运算符重载-=和-
- 运算符重载前置++和后置++
- 运算符重载前置--后置--
- 两个日期相差几天
- 日期类(Date.h)
- 日期测试
- TestDate1()
- TestDate2()
- TestDate3()
- TestDate4()
- TestDate5()
- TestDate6()
日期类(Date.cpp)成员函数的实现
//构造函数,声明和定义分析不能同时给缺省参数,一般是声明给缺省参数
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (month > 0 && month < 13 && day>0 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
}
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& x)
{
if (_year < x._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month < x._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day < x._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& x)
{
return _year == x._year
&& _month == x._month
&& _day == x._day;
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& x)
{
return *this < x || *this == x;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& x)
{
return !(*this <= x);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& x)
{
return !(*this < x);
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& x)
{
return !(*this == x);
}
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
//由于要频繁调用daysArr,所以我们把daysArr放到静态区
static int daysArr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
//if ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0) && month == 2)
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
return 29;
}
else
{
return daysArr[month];
}
return daysArr[month];
}
//+=复用+
//Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
//{
// *this = *this + day;
// return *this;
//}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
//+复用+=
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
/*tmp._day += day;
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{
tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
tmp._month++;
if (tmp._month == 13)
{
tmp._year++;
tmp._month = 1;
}
}
return tmp;*/
//出了作用域后tmp销毁,所以不能用引用返回
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator -=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month = 13;
--_year;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date:: operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;//这里是拷贝构造
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
//前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
//后置++
//增加int参数并不是为了接收具体的值,这里仅仅是占位,为了就是跟前置++构成重载
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
//前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
//后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
//两个日期相差几天
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
//默认认为第一个日期大,第二个小
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
构造函数
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (month > 0 && month < 13 && day>0 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
}
}
bool类型的运算符重载
bool Date::operator<(const Date& x)
{
if (_year < x._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month < x._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day < x._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& x)
{
return _year == x._year
&& _month == x._month
&& _day == x._day;
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& x)
{
return *this < x || *this == x;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& x)
{
return !(*this <= x);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& x)
{
return !(*this < x);
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& x)
{
return !(*this == x);
}
得到该月有几天GetMonthDay
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
//由于要频繁调用daysArr,所以我们把daysArr放到静态区
static int daysArr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
//if ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0) && month == 2)
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
return 29;
}
else
{
return daysArr[month];
}
return daysArr[month];
}
运算符重载+=和+
这里有两种方式来写+=和+的赋值运算符重载。
先来看第一种:+=复用+的方式,请看:
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
//+复用+=
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
/*tmp._day += day;
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{
tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
tmp._month++;
if (tmp._month == 13)
{
tmp._year++;
tmp._month = 1;
}
}
return tmp;*/
//出了作用域后tmp销毁,所以不能用引用返回
return tmp;
}
现在来看第二种写法,+=复用+
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp._day += day;
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{
tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
tmp._month++;
if (tmp._month == 13)
{
tmp._year++;
tmp._month = 1;
}
}
//出了作用域后tmp销毁,所以不能用引用返回
return tmp;
}
//+=复用+
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
*this = *this + day;
return *this;
}
现在这两种写法哪一种好呢?对于每种方式的+的赋值运算符重载没啥太大的区别(都要都要创建两个对象,一个是Date tmp(*this);,另外一个就是return tmp);但是对于+=的赋值运算符重载,第一种方式并没有创建对象,而第二种方式的+=的符重运算符重载由于又调用了一次+的赋值运算符重载函数(即多创建了两个对象)。所以最终第一种方式(+复用+=)显然更好一些,第二种方式差就差再+=复用+的时候多创建了两个对象。
运算符重载-=和-
Date& Date::operator -=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month = 13;
--_year;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date:: operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;//这里是拷贝构造
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
运算符重载前置++和后置++
//前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
//后置++
//增加int参数并不是为了接收具体的值,这里仅仅是占位,为了就是跟前置++构成重载,方便区分
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
运算符重载前置–后置–
//前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
//后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
两个日期相差几天
//两个日期相差几天
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
//默认认为第一个日期大,第二个小
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
日期类(Date.h)
class Date
{
public:
//构造函数
Date(int year = 22, int month = 5, int day = 20);
//不需要写拷贝构造函数,所以下面可以选择直接注释掉
Date (const Date& d)
{
cout << "Date(const Date& d)" << endl;
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
bool operator<(const Date& x);
bool operator==(const Date& x);
bool operator<=(const Date& x);
bool operator>(const Date& x);
bool operator>=(const Date& x);
bool operator!=(const Date& x);
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date operator+(int day);
Date& operator -=(int day);
Date operator-(int day);
Date& operator++();//前置++
Date operator++(int);//后置++
Date& operator--();//前置--
Date operator--(int);//后置++
//计算两个日期相差多少天
int operator-(const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
日期测试
TestDate1()
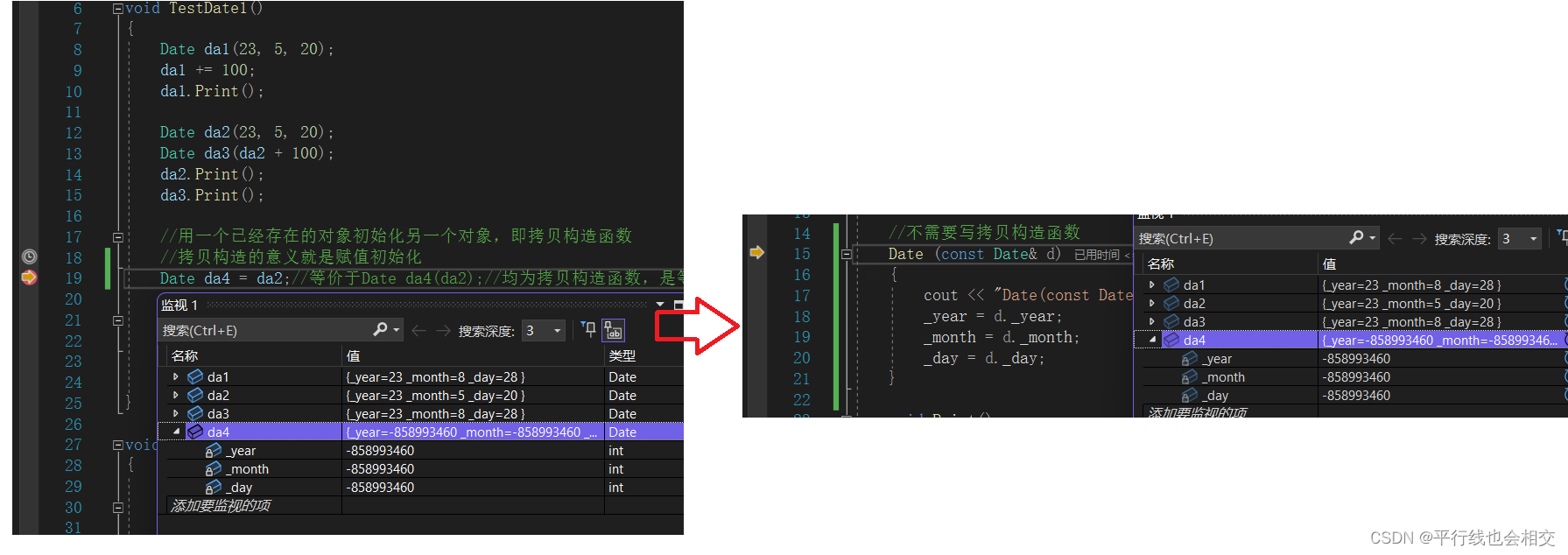
void TestDate1()
{
Date da1(23, 5, 20);
da1 += 100;
da1.Print();
Date da2(23, 5, 20);
Date da3(da2 + 100);
da2.Print();
da3.Print();
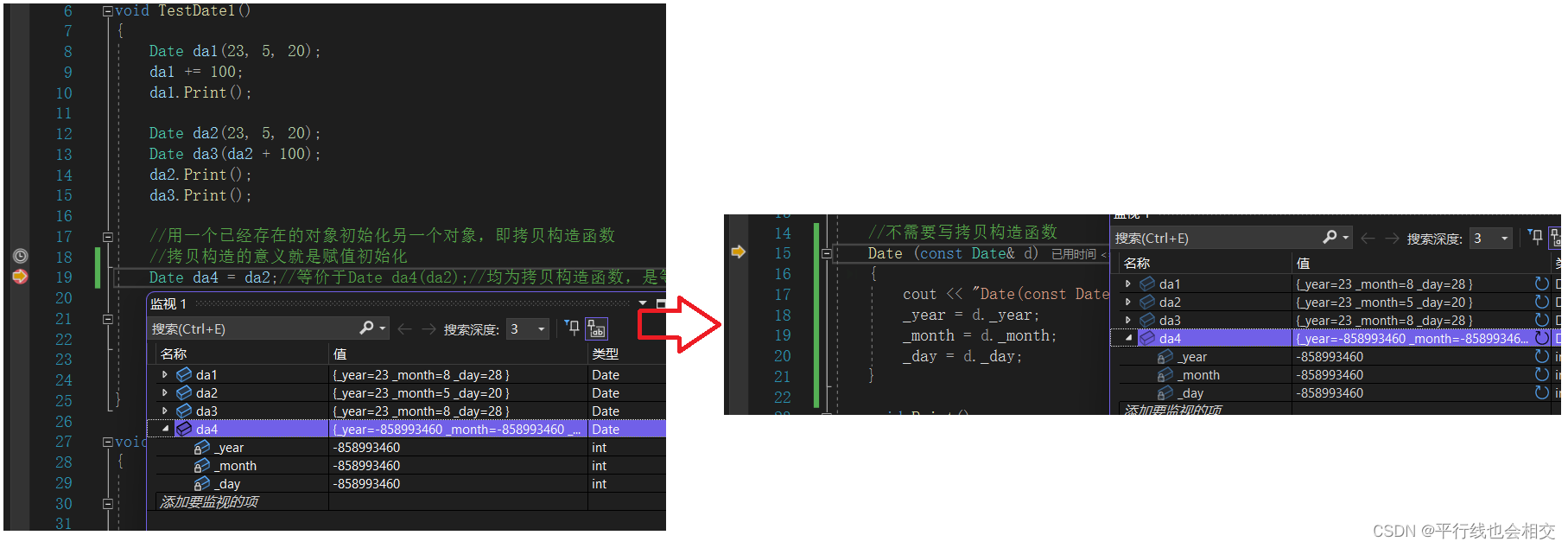
//用一个已经存在的对象初始化另一个对象,即拷贝构造函数
//拷贝构造的意义就是赋值初始化
Date da4 = da2;//等价于Date da4(da2);//均为拷贝构造函数,是等价的
//而赋值重载的意义纯粹的就是拷贝
//已经存在的两个对象之间进行复制拷贝,即运算符重载函数
da4 = da1;
}
这里指的注意的是Date da4 = da2;是等价于Date da4(da2);,因为这里实在用一个已经存在的对象初始化另外一个对象,所以这里调用的是拷贝构造函数,而不是调用=的赋值运算符重载。
如下如:

TestDate2()
{
Date da1(2021, 5, 21);
//无论前置还是后置++都需要++
//前置++就返回++以后的对象,后置++就返回++之前的对象
//编译器这里成全一个同时委屈一个,为了区分这里的重载
++da1;//da1.operator++()
da1++;//da1.operator++(0)
Date da2(2024, 5, 20);
Date da3(2023, 3, 14);
bool ret1 = da2 < da3;//自定义类型转换为对应的函数
int i = 0, j = 2;
bool ret2 = i < j;//内置类型编译器知道怎么比较,故编译器会自动处理内置类型的重载
}
TestDate3()
//测试日期类的-=
void TestDate3()
{
Date da1(2023, 5, 20);
da1 -= 50;
da1.Print();
Date da2(2023, 5, 21);
da2 -= 88;
da2.Print();
Date da3(2023, 5, 25);
da3 -= 100;
da3.Print();
Date da4(2024, 5, 20);
da4 -= 10000;
da4.Print();
}
TestDate4()
void TestDate4()
{
Date d1(2020, 5, 20);
d1 += 100;
d1.Print();
Date da2(2023, 5, 21);
da2 += -100;
da2.Print();
Date da3(2023, 5, 5);
da3 -= -100;
da3.Print();
}
TestDate5()
void TestDate5()
{
Date da1(2023, 5, 5);
Date ret1 = da1--;//调用da1.operator(&da1,0);
ret1.Print();
da1.Print();
Date da2(2023, 5, 5);
Date ret2 = --da2;//调用da1.operator++(&da1);
ret2.Print();
da2.Print();
}
TestDate6()
void TestDate6()
{
Date da1(2023, 5, 20);
Date da2(2022, 5, 21);
Date da3(1949, 10, 1);
Date da4(2023, 5, 20);
cout << da1 - da2 << endl;
cout << da2 - da1 << endl;
cout << da3 - da4 << endl;
cout << da4 - da3 << endl;
}
好了,以上就是用C++来实现日期类。
就到这里,再见啦各位!!!