目录结构
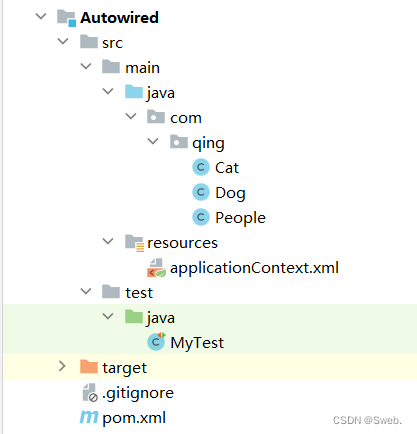
导入pom.xml依赖包
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- aop-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.19</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/junit/junit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>People类,人可以有多个宠物
package com.qing;
public class People {
private Cat cat;
private Dog dog;
private String name;
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"cat=" + cat +
", dog=" + dog +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Cat类
package com.qing;
public class Cat {
public void shout(){
System.out.println("喵");
}
}
Dog类
package com.qing;
public class Dog {
public void shout(){
System.out.println("汪");
}
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="cat" class="com.qing.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.qing.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="people" class="com.qing.People">
<property name="name" value="你好呀"></property>
<property name="cat" ref="cat"></property>
<property name="dog" ref="dog"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试代码
import com.qing.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
People people = context.getBean("people", People.class);
people.getDog().shout();
people.getCat().shout();
}
}
byName自动装配
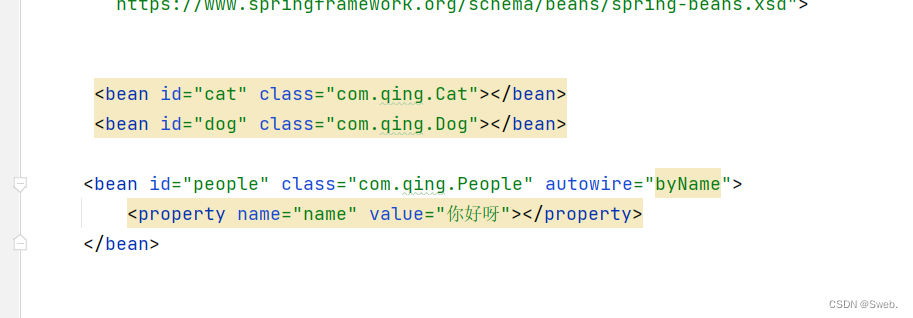
byName:会自动在容器上下文查找,和自己这个对象的set方法后面值对应的bean中的id
![]()
如果id不满足对象的名字,则会报错;例如:dog222不满足对象的id名字
byType自动装配
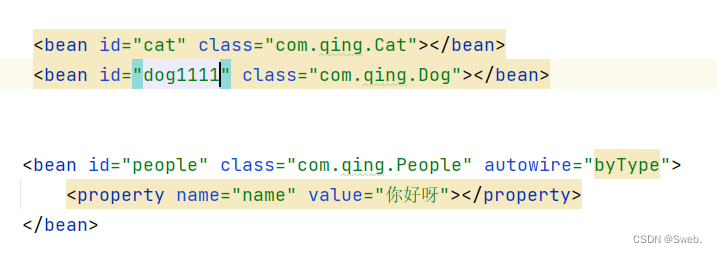
byType:会自动在容器上下文中查找,和自己对象属性相同的bean,可以省略id
不能有两个一样的id,属性名可以不同
注解实现自动装配
导入约束,并开启注解的支持
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="cat" class="com.qing.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog" class="com.qing.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="people" class="com.qing.People"></bean>
<!-- 开启注解的支持-->
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>在属性上配置注解
@Autowired
private Cat cat;
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
private String name;如果@Autowired自动装配的环境比较复杂,自动装配无法通过一个注解@Autowired完成的时候,我们可以使用@Qualifier(value="xxx")去配置@Autowired的使用,指定一个唯一的bean对象注入
总结:
- byname需要保证所有的bean的id唯一,并且这个bean需要和自动注入的属性的set方法的值一致
- bytype需要保证所有bean的class唯一,并且这个bean需要和自动注入的属性类型一致





![Linux系统编程——多线程[下]:生产消费模型信号量线程池](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/8d0f85dbc77ef825aeeffe7f6dafc360.png)