常数整数乘法优化

文章目录
- 常数整数乘法优化
- 基于正则有符号数的常数整数乘法优化
- Example 1: 20 x 20x 20x
- Example 2: 153 x 153x 153x
- Example 3: 15 x 15x 15x
- 正则有符号数编码 CSD
- 二进制序列转CSD编码算法流程
- 代码实现
- 欢迎关注公众号【三戒纪元】
嵌入式机器学习或深度学习算法中很大一部分运算涉及常数乘法:
- 神经网络的卷积层和全连接层将来自前一层的数据和固定的权重矩阵相乘计算输出,SVM算法中通过固定的矩阵和向量乘法计算判决函数;
- 图像处理中各种滤波器算法也需要计算图像数据和固定的滤波器核的二维卷积。
基于正则有符号数的常数整数乘法优化
就是通过移位和加减法实现常数乘法的优化。
常数乘法分为:
- 单常数乘法 SCM —— Single Contant Multipilication
- 多常数乘法 MCM —— Multiple Constants Multiplication
Example 1: 20 x 20x 20x
20 = ( 10100 ) 2 = ( 10000 ) 2 + ( 100 ) 2 = 2 4 + 2 2 20=(1 0100)_2=(10000)_2+(100)_2=2^4+2^2 20=(10100)2=(10000)2+(100)2=24+22
因此
20
x
20x
20x乘积可表示为
20
x
=
(
2
4
+
2
2
)
x
=
2
4
x
+
2
2
x
20x=(2^4+2^2)x=2^4x+2^2x
20x=(24+22)x=24x+22x
对于整数 x ,上述运算进一步表示为
20
x
=
(
x
≪
4
)
+
(
x
≪
2
)
20x = (x≪4)+(x≪2)
20x=(x≪4)+(x≪2)
不难发现:加法次数和二进制形式中的1的个数有关
Example 2: 153 x 153x 153x
153 x = ( 10011001 ) 2 x 153x = (1001 1001)_2 x 153x=(10011001)2x
153 x = ( x ≪ 7 ) + ( x ≪ 4 ) + ( x ≪ 3 ) + x 153x=(x≪7)+(x≪4)+(x≪3)+x 153x=(x≪7)+(x≪4)+(x≪3)+x
需要进行3次加法,还能简化吗?
可以的。
153
=
(
10011001
)
2
153=(1001 1001)_2
153=(10011001)2
= > 153 x = 10010000 x + 1001 x => 153x = 10010000x + 1001x =>153x=10010000x+1001x
令 y = x × ( 1001 ) 2 令 y=x×(1001)_2 令y=x×(1001)2
153
x
=
y
+
y
≪
4
153x = y + y ≪ 4
153x=y+y≪4
仅需要2次加法
Example 3: 15 x 15x 15x
15 = ( 1111 ) 2 15=(1111)_2 15=(1111)2
15 x = x ≪ 3 + x ≪ 2 + x ≪ 1 + x 15x=x≪3+x≪2+x≪1+x 15x=x≪3+x≪2+x≪1+x
这还不是最优的,重新分解15
15
=
(
10000
)
2
−
(
1
)
2
15=(10000)_2−(1)_2
15=(10000)2−(1)2
15
x
=
x
≪
4
−
x
15x=x≪4−x
15x=x≪4−x
因此,定义新的“有符号二进制形式”:
15
=
(
1000
1
ˉ
)
2
=
2
4
−
2
0
15=(1 000\bar{1})_2=2^4−2^0
15=(10001ˉ)2=24−20
正则有符号数编码 CSD
将有符号整数转换为非0位最少的“有符号二进制序列”,这一序列成为 CSD:Canonical Signed Digit
为了尽可能降低常数乘法的运算量,我们希望找出非 0 位尽可能少的有符号二进制序列表示给定的常数。
对于无符号整数的二进制形式,从低位开始扫描,把所有长度大于2的连续1位串替换成 100 ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ 0 1 ˉ 100···0\bar{1} 100⋅⋅⋅01ˉ
例如 十进制 15 599,二进制为11 1100 1110 1111,可以转换为 $ 1000\bar{1}01000\bar{1}000\bar{1}$
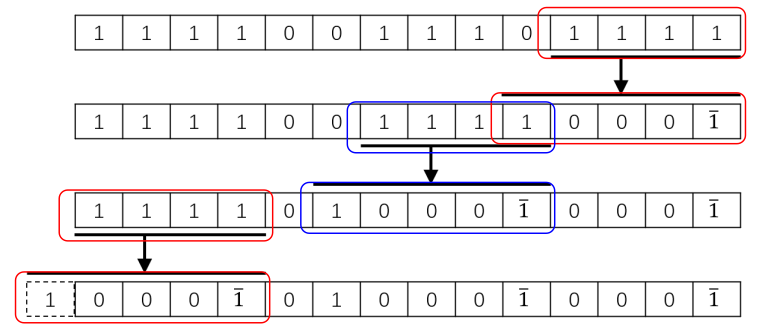
因此,可以实现乘法优化:
x
×
(
11110011101111
)
2
=
x
×
(
1000
1
ˉ
01000
1
ˉ
000
1
ˉ
)
2
x×(11110011101111)_2=x×(1000\bar{1}01000\bar{1}000\bar{1})_2
x×(11110011101111)2=x×(10001ˉ010001ˉ0001ˉ)2
= x ≪ ( 14 − x ) ≪ ( 10 + x ) ≪ ( 8 − x ) ≪ ( 4 − x ) =x≪(14−x)≪(10+x)≪(8−x)≪(4−x) =x≪(14−x)≪(10+x)≪(8−x)≪(4−x)
二进制序列转CSD编码算法流程
- 设置
{ b − 1 = 0 b N = b N − 1 γ − 1 = 0 \begin{cases} b_{-1} = 0 \\ b_N = b_{N-1} \\ \gamma_{-1} = 0 \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧b−1=0bN=bN−1γ−1=0
执行下面的循环 伪代码
f
o
r
(
i
=
1
t
o
N
−
1
)
for (i =1 \ to \ N-1)
for(i=1 to N−1)
{
\{
{
θ i = b i ⨁ b i − 1 \theta_i = b_i \ \bigoplus b_{i-1} θi=bi ⨁bi−1
$$
\gamma_i = (1 - \gamma_{i-1})\theta_{i}
$$
a i = ( 1 − 2 b i + 1 ) γ i a_i = (1-2b_{i+1})\gamma_i ai=(1−2bi+1)γi
} \} }
代码实现
import numpy as np
####################
# 生成二进制数的CSD表示
####################
## 将二进制字串(整数,无'0b'前缀)转成字典
# 代码清单 4-20
def bin_str_to_dict(bv): return {n:int(v=='1') for n,v in enumerate(bv[::-1])}
## 将二进制字串(整数)转成CSD表示
def bin_str_to_csd(bv):
w=len(bv)
b=bin_str_to_dict(bv)
b[-1]=0
b[w]=b[w-1]
gamma={-1:0}
a={}
theta={}
for i in range(w):
theta[i]=b[i]^b[i-1]
gamma[i]=(1-gamma[i-1])*theta[i]
a[i]=(1-2*b[i+1])*gamma[i]
return a
## 将16-bit整数表示为二进制字串,用补码表示负数
def int16_to_bin_str(v):
if v<0: v+=65536
bv=bin(v)[2:]
return '0'*(16-len(bv))+bv
## 将16-bit有符号整数转成CSD表示
def int16_to_csd(v):
bv=int16_to_bin_str(v)
csd=bin_str_to_csd(bv)
return csd
## 将字典转回16-bit整数
def dict_to_int16(d):
v=sum([(2**k)*v for k,v in d.items()])
if v>32767: v-=65536
return v
## 将字典内容打印成二进制字串
def dict_to_str(d):
s=''
for n in range(max(d.keys())+1):
if n in d:
s={-1:'n',0:'0',1:'1'}[d[n]]+s
else:
s='x'+x
return s[::-1]
## 将CSD内容转成移位运算指令字符串
# 代码清单 4-21
def csd_to_code(csd):
s=''
for n,v in csd.items():
if v==0:
continue
elif n==0:
s+='+x' if v>0 else '-x'
else:
s+='+(x<<%d)'%n if v>0 else '-(x<<%d)'%n
return s[1:] if s[0]=='+' else s
## 将16-bit有符号整数转成移位运算指令字符串
def int16_to_code(v):
return csd_to_code(bin_str_to_csd(int16_to_bin_str(v)))
####################
# 单元测试
####################
if __name__=='__main__':
print('\n[Randy] ---- test 1 ----')
bv=int16_to_bin_str(-141)
print('[Randy] bv:\n ',bv)
d=bin_str_to_dict(bv)
print('[Randy] d=bin_str_to_dict(bv):\n ',d)
v=dict_to_int16(d)
print('[Randy] v=dict_to_int16(d):\n ',v)
csd=bin_str_to_csd(bv)
print('[Randy] csd :\n ',csd )
print('[Randy] dict_to_str(csd) :\n ',dict_to_str(csd) )
print('[Randy] dict_to_int16(csd) :\n ',dict_to_int16(csd) )
print('[Randy] csd_to_code(csd) :\n ',csd_to_code(csd) )
print('[Randy] int16_to_code(-141):\n ',int16_to_code(-141))
# test2
print('\n[Randy] ---- test 2 ----')
bv=int16_to_bin_str(141)
print('[Randy] bv:\n ',bv)
d=bin_str_to_dict(bv)
print('[Randy] d=bin_str_to_dict(bv):\n ',d)
v=dict_to_int16(d)
print('[Randy] v=dict_to_int16(d):\n ',v)
csd=bin_str_to_csd(bv)
print('[Randy] csd :\n ',csd )
print('[Randy] dict_to_str(csd) :\n ',dict_to_str(csd) )
print('[Randy] dict_to_int16(csd):\n ',dict_to_int16(csd))
print('[Randy] csd_to_code(csd) :\n ',csd_to_code(csd) )
print('[Randy] int16_to_code(141):\n ',int16_to_code(141))
# test3
print('\n[Randy] ---- test 3 ----')
for v in range(-32768,32768):
csd=int16_to_csd(v)
v1=dict_to_int16(csd)
if v%10000==0:
print('[Randy] %d'%v)
if v!=v1:
print('[ERR] %d,%d'%(v,v1))
print('[ERR] ',bv)
print('[ERR] ',dict_to_str(csd))
结果:
[Randy] ---- test 1 ----
[Randy] bv:
1111111101110011
[Randy] d=bin_str_to_dict(bv):
{0: 1, 1: 1, 2: 0, 3: 0, 4: 1, 5: 1, 6: 1, 7: 0, 8: 1, 9: 1, 10: 1, 11: 1, 12: 1, 13: 1, 14: 1, 15: 1}
[Randy] v=dict_to_int16(d):
-141
[Randy] csd :
{0: -1, 1: 0, 2: 1, 3: 0, 4: -1, 5: 0, 6: 0, 7: -1, 8: 0, 9: 0, 10: 0, 11: 0, 12: 0, 13: 0, 14: 0, 15: 0}
[Randy] dict_to_str(csd) :
n010n00n00000000
[Randy] dict_to_int16(csd) :
-141
[Randy] csd_to_code(csd) :
-x+(x<<2)-(x<<4)-(x<<7)
[Randy] int16_to_code(-141):
-x+(x<<2)-(x<<4)-(x<<7)
[Randy] ---- test 2 ----
[Randy] bv:
0000000010001101
[Randy] d=bin_str_to_dict(bv):
{0: 1, 1: 0, 2: 1, 3: 1, 4: 0, 5: 0, 6: 0, 7: 1, 8: 0, 9: 0, 10: 0, 11: 0, 12: 0, 13: 0, 14: 0, 15: 0}
[Randy] v=dict_to_int16(d):
141
[Randy] csd :
{0: 1, 1: 0, 2: -1, 3: 0, 4: 1, 5: 0, 6: 0, 7: 1, 8: 0, 9: 0, 10: 0, 11: 0, 12: 0, 13: 0, 14: 0, 15: 0}
[Randy] dict_to_str(csd) :
10n0100100000000
[Randy] dict_to_int16(csd):
141
[Randy] csd_to_code(csd) :
x-(x<<2)+(x<<4)+(x<<7)
[Randy] int16_to_code(141):
x-(x<<2)+(x<<4)+(x<<7)
[Randy] ---- test 3 ----
[Randy] -30000
[Randy] -20000
[Randy] -10000
[Randy] 0
[Randy] 10000
[Randy] 20000
[Randy] 30000








![[golang gin框架] 36.Gin 商城项目-RESTful API 设计指南,允许Cros跨域 ,提供api接口实现前后端分离,以及JWT的使用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/d457a449cac6ec586a795213d09d5fa6.png)
