目录
分类
代码
分析
一、类模板
一)代码
二)注意事项
三)运行结果
二、完全具体化的模板类
一)代码
二)注意事项
三)执行结果
三、部分具体化的模板类
一)代码
二)注意事项
三)执行结果
分类
函数模板没有部分具体化的说法,只有类模板才有,分为完全具体化和部分具体化
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//类模板
template<class T1,class T2>
class AA
{
public:
T1 m_x;
T2 m_y;
AA(const T1 x,const T2 y):m_x(x),m_y(y){cout<<"类模板:构造函数。\n";}
void show()const;
};
//成员函数类外实现
template<class T1,class T2>
void AA<T1,T2>::show()const{
cout<<"类模板:x="<<m_x<<",y="<<m_y<<endl;
}
//类模板完全具体化,为模板类的通用类型参数指定具体的数据类型
template<>//11111111空的尖括号
class AA<int,string>//2222222222AA<int,string>作为类名,
{
public:
int m_x;
string m_y;
//333333333
AA(const int x,const string y):m_x(x),m_y(y){cout<<"完全具体化:构造函数。\n";}
void show()const;
};
//成员函数类外实现
//没有不确定的参数,不需要写模板标签
void AA<int,string>::show()const{
cout<<"完全具体化:x="<<m_x<<",y="<<m_y<<endl;
}
//
//函数模板没有部分具体化的说法,只有类模板才有,
//部分具体化:为多个模板参数的部分参数指定具体数据类型
//类模板部分具体化
template<class T1>
class AA<T1,string>//第一个参数不确定,第二个时string
{
public:
T1 m_x;
string m_y;
AA(const T1 x,const string y):m_x(x),m_y(y){cout<<"部分具体化:构造函数。\n";}
void show()const;
};
//成员函数类外实现
template<class T1>//有不确定的参数需要写模板标签
void AA<T1,string>::show()const{
cout<<"部分具体化:x="<<m_x<<",y="<<m_y<<endl;
}
int main()
{
//具体化程度高的类优先于具体化程度低的类,具体化的类优先于没有具体化的类
AA<int,string>aa1(8,"我是一只小猫咪。");
aa1.show();
return 0;
}分析
具体化程度高的类优先于具体化程度低的类,具体化的类优先于没有具体化的类
一、类模板
一)代码
//类模板
template<class T1,class T2>
class AA
{
public:
T1 m_x;
T2 m_y;
AA(const T1 x,const T2 y):m_x(x),m_y(y){cout<<"类模板:构造函数。\n";}
void show()const;
};
//成员函数类外实现
template<class T1,class T2>
void AA<T1,T2>::show()const{
cout<<"类模板:x="<<m_x<<",y="<<m_y<<endl;
}
二)注意事项
①类的声明和成员函数的类外实现头部要加类标签template<class T1,class T2>
三)运行结果
只有当程序不存在完全具体化和部分具体化模板类的时候才执行此类代码
注释掉完全具体化和部分具体化模板类,结果如下

二、完全具体化的模板类
类模板完全具体化:为模板类的所有通用类型参数指定具体的数据类型
一)代码
template<>//11111111空的尖括号
class AA<int,string>//2222222222AA<int,string>作为类名,
{
public:
int m_x;
string m_y;
//333333333
AA(const int x,const string y):m_x(x),m_y(y){cout<<"完全具体化:构造函数。\n";}
void show()const;
};
//成员函数类外实现
//没有不确定的参数,不需要写模板标签
void AA<int,string>::show()const{
cout<<"完全具体化:x="<<m_x<<",y="<<m_y<<endl;
}
二)注意事项
①模板类的定义要加模板标签, template<>//空的尖括号
②类成员函数类外实现,//没有不确定的参数,不需要写模板标签
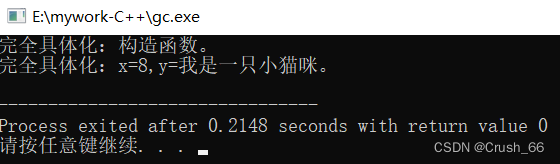
三)执行结果
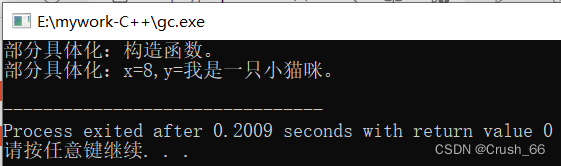
当三者同时存在时,执行此完全具体化模板类,结果如下
三、部分具体化的模板类
部分具体化:为多个模板参数的部分参数指定具体数据类型
一)代码
//类模板部分具体化
template<class T1>
class AA<T1,string>//第一个参数不确定,第二个时string
{
public:
T1 m_x;
string m_y;
AA(const T1 x,const string y):m_x(x),m_y(y){cout<<"部分具体化:构造函数。\n";}
void show()const;
};
//成员函数类外实现
template<class T1>//有不确定的参数需要写模板标签
void AA<T1,string>::show()const{
cout<<"部分具体化:x="<<m_x<<",y="<<m_y<<endl;
}
二)注意事项
①模板类的定义要加类模板的标签template<class T1> //第一个参数不确定,第二个时string
②成员函数类外实现,//有不确定的参数需要写模板标签template<class T1>
三)执行结果
当程序只存在没有具体化的类模板和此部分具体化的模板类时,执行此代码,结果如下