JSON Web Token(JWT)是目前都在用的前后分离跨域验证规则。
JWT由3部分组成
- Header——头部一般Base64URL编码,作用:声明token类型,声明token使用的加密算法。一般都是使用HMAC-SHA256或者RSA支持很多种算法(HS256、HS384、HS512、RS256、RS384、RS512、ES256、ES384、ES512、PS256、PS384)
- PayLoad——载荷(自定义数据)也叫消息体(payload)是一个JSON对象。一般Base64URL编码。存储用户信息,过期时间等等。。。因为载荷里面包含可以包含许多用户自定义信息,所以后端不用再频繁的与数据库进行交互,可以直接获取信息。但是这也导致载荷里不建议储存敏感信息,因为可以直接Base64URL解密就能看到了,当然你也可以额外再加密。 这些有效信息包含三个部分:标准中注册的声明、公共的声明和私有的声明
- Signature(签名其实是由Header+PayLoad+自定义密钥再由加密算法(HS256)或者其他算法生成。这也是jwt安全的真正原因)
1、引入依赖pom.xml
<!--jwt-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.auth0</groupId>
<artifactId>java-jwt</artifactId>
<version>3.8.2</version>
</dependency>2、编写jwt工具类JwtUtil.java
package com.muchuantong.util;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWT;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWTVerifier;
import com.auth0.jwt.algorithms.Algorithm;
import com.auth0.jwt.interfaces.Claim;
import com.auth0.jwt.interfaces.DecodedJWT;
/**
* @Author: Zou Tiancong
* @Date: 2021/12/1 0001 10:37
* @Annotation:jwtToken
*/
public class JwtUtil {
// 设置过期时间
private static final long EXPIRE_DATE = 60*1000;
// token秘钥
private static final String TOKEN_SECRET = "TEST-AUTH-TOKEN";
// 实现签名方法
public static String token(String id, String openId, String nickName) {
String token = "";
try {
// 这里将用户存入了Token,在下面的解析中,也会有解析的方法可以获取到Token里面的数据
// Token过期的时间
Date expireDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + EXPIRE_DATE);
// 秘钥及加密算法
Algorithm algorithm = Algorithm.HMAC256(TOKEN_SECRET);
// 设置头部信息,类型以及签名所用的算法
Map<String, Object> header = new HashMap<>();
header.put("typ", "JWT");
header.put("alg", "HS256");
// 携带用户信息,存入token,生成签名
token = JWT.create()
.withHeader(header) //设置头部信息Header
.withIssuer("TEST") //设置签名是由谁生成
.withSubject("AUTH-TOKEN") //设置签名的主题
.withAudience(nickName) //设置签名的观众
.withIssuedAt(new Date()) //设置生成签名的时间
.withExpiresAt(expireDate) //设置签名过期的时间
.withClaim("id", id) //自定义信息
.withClaim("openId", openId)//自定义信息
.withClaim("nickName", nickName)//自定义信息
.withJWTId(id) //jwt的id,主要用来作为一次性token,从而回避重放攻击
.sign(algorithm);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
return token;
}
// 验证token
public static boolean verify(String token) {
/**
* @desc 验证token,通过返回true
* @params [token]需要校验的串
**/
try {
Algorithm algorithm = Algorithm.HMAC256(TOKEN_SECRET);
JWTVerifier verifier = JWT.require(algorithm).build();
DecodedJWT jwt = verifier.verify(token);
String subject = jwt.getSubject();
List<String> audience = jwt.getAudience();
Map<String, Claim> claims = jwt.getClaims();
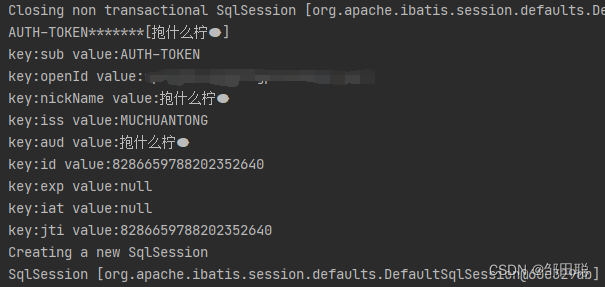
System.out.println(subject+"*******"+audience);
for (Map.Entry<String, Claim> entry : claims.entrySet()){
String key = entry.getKey();
Claim claim = entry.getValue();
String value = claim.asString();
System.out.println("key:"+key+" value:"+value);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Token已过期,需要重新登录");
}
return false;
}
// 生成token
public static String setToken(String id, String openId, String nickName) {
String token = token(id, openId, nickName);
return token;
}
}
2、自定义注解接口Auth.java
package com.muchuantong.util;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @Auther: ZouTiancong
* @Date: 2022/05/23/22:37
* @Description:
*/
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Auth {
boolean token() default true;
}
3、自定义注解APO实现类AuthAspect.java
package com.muchuantong.util;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @Auther: ZouTiancong
* @Date: 2022/05/23/22:39
* @Description:
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class AuthAspect {
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest request;
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.muchuantong.util.Auth)")
private void authPointcut() {
}
@Around("authPointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 获取方法签名信息从而获取方法名和参数类型
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
// 获取目标方法对象上注解中的属性值
Auth auth = methodSignature.getMethod().getAnnotation(Auth.class);
// 校验签名
if (auth.token()) {
boolean token = JwtUtil.verify(request.getHeader("token"));
// 如果token校验失败返回
if (!token) {
return new Result<>("401", "token已过期,请重新登录!");
}
}
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
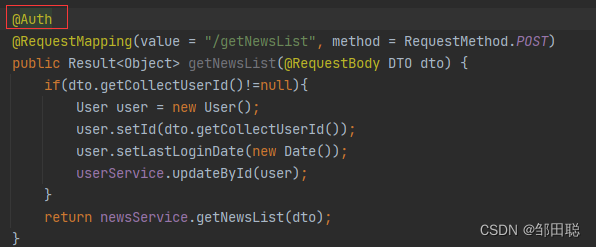
4、在需要token验证的地方加入注解@Auth
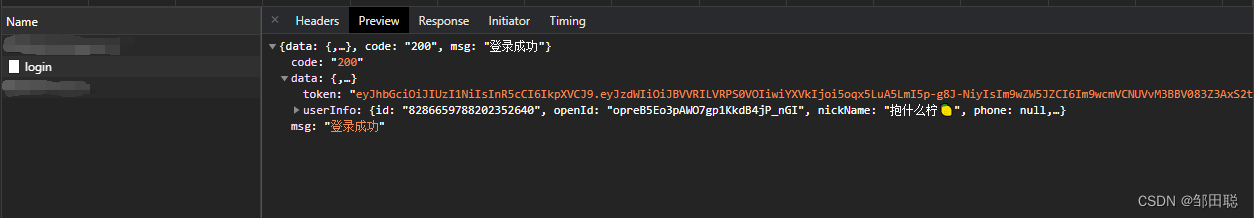
5、前端调用查看效果,token生成返回成功,后端也能成功读取数据







![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django基于Vue的社区拼购商城](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/525699b6392b455e9675adeeafb328bd.png)