这里给大家分享我在网上总结出来的一些知识,希望对大家有所帮助
Set是一种类似于数组的数据结构,但是它的值是唯一的,即Set中的每个值只会出现一次。Set对象的实例可以用于存储任何类型的唯一值,从而使它们非常适用于去重。
Map是一种键值对集合,其中每个键都是唯一的,可以是任何类型,而值则可以是任何类型。Map对象的实例可以用于存储复杂的对象,并且可以根据键进行快速的查找和访问。
以下是Set和Map的一些常用方法:
Set:
- new Set(): 创建一个新的Set对象
- add(value): 向Set对象中添加一个新的值
- delete(value): 从Set对象中删除一个值
- has(value): 检查Set对象中是否存在指定的值
- size: 获取Set对象中的值的数量
- clear(): 从Set对象中删除所有值
Map:
- new Map(): 创建一个新的Map对象
- set(key, value): 向Map对象中添加一个键值对
- get(key): 根据键获取Map对象中的值
- delete(key): 从Map对象中删除一个键值对
- has(key): 检查Map对象中是否存在指定的键
- size: 获取Map对象中的键值对数量
- clear(): 从Map对象中删除所有键值对
Set和Map是非常有用的数据结构,它们可以提高程序的性能和可读性,并且可以简化代码的编写。
Set
去重
使用 Set 可以轻松地进行数组去重操作,因为 Set 只能存储唯一的值。
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 5];
const uniqueArr = [...new Set(arr)];
console.log(uniqueArr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
数组转换
可以使用 Set 将数组转换为不包含重复元素的 Set 对象,再使用 Array.from() 将其转换回数组。
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 5];
const set = new Set(arr);
const uniqueArr = Array.from(set);
console.log(uniqueArr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
优化数据查找
使用 Set 存储数据时,查找操作的时间复杂度为 O(1),比数组的 O(n) 要快得多,因此可以使用 Set 来优化数据查找的效率。
const dataSet = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
if (dataSet.has(3)) {
console.log('数据已经存在');
} else {
console.log('数据不存在');
}
并集、交集、差集
Set数据结构可以用于计算两个集合的并集、交集和差集。以下是一些使用Set进行集合运算的示例代码:
const setA = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
const setB = new Set([2, 3, 4]);
// 并集
const union = new Set([...setA, ...setB]);
console.log(union); // Set {1, 2, 3, 4}
// 交集
const intersection = new Set([...setA].filter(x => setB.has(x)));
console.log(intersection); // Set {2, 3}
// 差集
const difference = new Set([...setA].filter(x => !setB.has(x)));
console.log(difference); // Set {1}
模糊搜索
Set 还可以通过正则表达式实现模糊搜索。可以将匹配结果保存到 Set 中,然后使用 Array.from() 方法将 Set 转换成数组。
const data = ['apple', 'banana', 'pear', 'orange'];
// 搜索以 "a" 开头的水果
const result = Array.from(new Set(data.filter(item => /^a/i.test(item))));
console.log(result); // ["apple"]
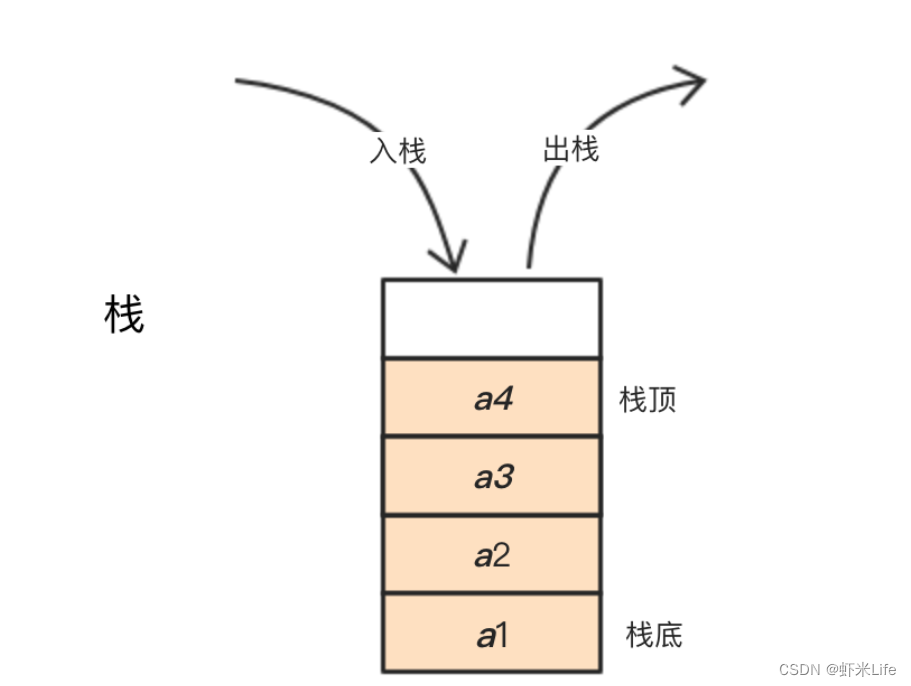
使用 Set 替代数组实现队列和栈
可以使用 Set 来模拟队列和栈的数据结构。
// 使用 Set 实现队列
const queue = new Set();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
queue.delete(queue.values().next().value); // 删除第一个元素
console.log(queue); // Set(2) { 2, 3 }
// 使用 Set 实现栈
const stack = new Set();
stack.add(1);
stack.add(2);
stack.add(3);
stack.delete([...stack][stack.size - 1]); // 删除最后一个元素
console.log(stack); // Set(2) { 1, 2 }
Map
将 Map 转换为对象
const map = new Map().set('key1', 'value1').set('key2', 'value2');
const obj = Object.fromEntries(map);
将 Map 转换为数组
const map = new Map().set('key1', 'value1').set('key2', 'value2');
const array = Array.from(map);
记录数据的顺序
如果你需要记录添加元素的顺序,那么可以使用Map来解决这个问题。当你需要按照添加顺序迭代元素时,可以使用Map来保持元素的顺序。
const map = new Map();
map.set('a', 1);
map.set('b', 2);
map.set('c', 3);
map.set('d', 4);
for (const [key, value] of map) {
console.log(key, value);
}
// Output: a 1, b 2, c 3, d 4
统计数组中元素出现次数
可以使用 Map 统计数组中每个元素出现的次数。
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 5];
const countMap = new Map();
arr.forEach(item => {
countMap.set(item, (countMap.get(item) || 0) + 1);
});
console.log(countMap.get(1)); // 2
console.log(countMap.get(2)); // 2
console.log(countMap.get(3)); // 1
统计字符出现次数
使用Map数据结构可以方便地统计字符串中每个字符出现的次数。
const str = 'hello world';
const charCountMap = new Map();
for (let char of str) {
charCountMap.set(char, (charCountMap.get(char) || 0) + 1);
}
console.log(charCountMap); // Map { 'h' => 1, 'e' => 1, 'l' => 3, 'o' => 2, ' ' => 1, 'w' => 1, 'r' => 1, 'd' => 1 }
缓存计算结果
在处理复杂的计算时,可能需要对中间结果进行缓存以提高性能。可以使用Map数据结构缓存计算结果,以避免重复计算。
const cache = new Map();
function fibonacci(n) {
if (n === 0 || n === 1) {
return n;
}
if (cache.has(n)) {
return cache.get(n);
}
const result = fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
cache.set(n, result);
return result;
}
console.log(fibonacci(10)); // 55
使用 Map 进行数据的分组
const students = [
{ name: "Tom", grade: "A" },
{ name: "Jerry", grade: "B" },
{ name: "Kate", grade: "A" },
{ name: "Mike", grade: "C" },
];
const gradeMap = new Map();
students.forEach((student) => {
const grade = student.grade;
if (!gradeMap.has(grade)) {
gradeMap.set(grade, [student]);
} else {
gradeMap.get(grade).push(student);
}
});
console.log(gradeMap.get("A")); // [{ name: "Tom", grade: "A" }, { name: "Kate", grade: "A" }]
使用 Map 过滤符合条件的对象
在实际开发中,我们常常需要在一个对象数组中查找符合某些条件的对象。此时,我们可以结合使用 Map 和 filter 方法来实现。比如:
const users = [
{ name: 'Alice', age: 22 },
{ name: 'Bob', age: 18 },
{ name: 'Charlie', age: 25 }
];
const userMap = new Map(users.map(user => [user.name, user]));
const result = users.filter(user => userMap.has(user.name) && user.age > 20);
console.log(result); // [{ name: 'Alice', age: 22 }, { name: 'Charlie', age: 25 }]