文章目录
- 1.程序填空
- 1.1函数调用
- 1.2前置和后置“++”、“--”运算符重载
- 1.3异常处理
- 1.4文本文件读取
- 2.程序阅读
- 2.1C++编程基础
- 2.2继承与派生
- 2.3静态成员
- 2.4继承与派生
- 2.5 输入输出
- 2.6 模板
- 3.程序改错
- 3.1三种访问权限
- 3.2 友元
- 3.3抽象类不能实例化对象
- 3.4常数据成员初始化必须使用构造函数的初始化列表
- 3.5以引用传递的方式向函数传递对象
- 4.程序设计
- 4.1运算符重载
- 4.2多态的程序实现方法
1.程序填空
1.1函数调用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
public:
void set(char ch)
{
c = ch;
}
void show()
{
cout << "char in Test is:" << c << endl;
}
private:
char c;
};
int main()
{
Test test1,test2;
test1.set('a');
test2.set('b');
test1.show();
test2.show();
return 0;
}
1.2前置和后置“++”、“–”运算符重载
模板就是这样,具体根据题目要求
point& operator++(){
//前置运算符,需要引用返回,不需要参数。返回自增后的值
x++;
y++;
return *this;
}
point operator++(int){
//后置++,不需要引用返回,需要参数区分。返回自增前的值
point temp(x,y);
x++;
y++;
return temp;
}
1.3异常处理
void check(int score)
{
try
{
1.if (score > 100)throw"成绩超高!";
2.else if (score < 60)throw"成绩不及格!";
else cout << "the score is OK..." << score << endl;
}
3.catch (char* s)
{
cout << s << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
check(45);
check(90);
check(101);
return 0;
}
1.4文本文件读取
int main()
{
char s[100];
1.fstream infile("f2.dat", ios::in); //定义文件流对象,打开磁盘文件
2. if (!infile) //如果打开失败,infile 返回0值
{
cerr << "打开 f2.dat 文件失败!\n" << endl;
cerr << "f2.dat 可能不存在,或者文件已损坏,或者没有权限!\n" << endl;
cerr << "按任意键退出程序...\n" << endl;
getch();
exit(1);
}
3. while (!infile.eof())
{
infile.getline(s, sizeof(s));
cout << s << endl;
}
infile.close();//关闭磁盘文件“f2.dat”
return 0;
}
2.程序阅读
2.1C++编程基础
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void test1()
{
const int T = 5;//控制平方根和最大n值
int i, s = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= T; i++)
{
s += i * i;//实现平方和
cout << s << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
}
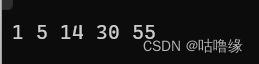
2.2继承与派生
class A
{
int a;
public:
A(int aa = 0) { a = aa; cout << "A():" << a << endl; }
};
class B :public A {
int b;
public:
B(int aa = 0, int bb = 0) : A(aa) { b = bb; cout << "B():" << b << endl; }
};
int main()
{
B x(5), y(6, 7);
return 0;
}

2.3静态成员
class CTest {
public:
CTest(int iVar) :m_iVar(iVar) { m_iCount++; }
~CTest() { }
void Print()const;
static int GetCount() { return m_iCount; }
private:
int m_iVar;
static int m_iCount;
};
int CTest::m_iCount = 0;
void CTest::Print()const
{
cout << this->m_iVar << " " << this->m_iCount << " ";
}
int main() {
CTest oTest1(6);
oTest1.Print();
CTest oTest2(8);
oTest2.Print();
cout << CTest::GetCount();
return 0;
}
定义了一个名为CTest的类,该类具有一个整数成员变量m_iVar和一个静态整数成员变量m_iCount。它还定义了一个构造函数,该构造函数使用初始化列表初始化成员变量,并将静态成员变量递增1。它还定义了一个析构函数和一个名为Print()的公共成员函数,该函数打印对象的成员变量值和静态成员变量值
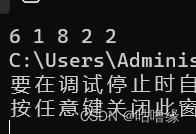
2.4继承与派生
class Base {
private: int Y;
public:
Base(int y = 0) { Y = y; cout << "Base(" << y << ")\n"; }
~Base() { cout << "~Base()\n"; }
void print() { cout << Y << " "; }
};
class Derived :public Base {
private: int Z;
public:
Derived(int y, int z) :Base(y)
{
Z = z; cout << "Derived(" << y << "," << z << ")\n";
}
~Derived() { cout << "~Derived()\n"; }
void print() { Base::print(); cout << Z << endl; }
};
int main() {
Derived d(10, 20); d.print();
return 0;
}

2.5 输入输出
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout.flags(ios::oct);
cout << "OCT:161=" << 161 << endl;
cout.flags(ios::dec);
cout << "DEC:161=" << 161 << endl;
cout.flags(ios::hex);
cout << "Hex:161=" << 161 << endl;
cout.flags(ios::uppercase|ios::hex);
cout << "UPPERCASE:161=" << 161 << endl;
return 0;
}
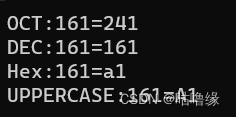
输入输出知识点
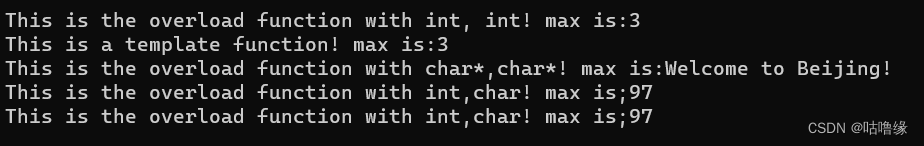
2.6 模板
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
//声明函数模板
T myMax(T x, T y) {
cout << "This is a template function! max is:";
return x > y ? x : y;
}
const char* myMax(const char* x, const char* y) { //重载的普通函数
cout << "This is the overload function with char*,char*! max is:";
return strcmp(x, y) > 0 ? x : y;
}
//重载的普通函数
int myMax(int x, int y) {
cout << "This is the overload function with int, int! max is:";
return x > y ? x : y;
}
int myMax(int x, char y) { //重载的普通函数
cout << "This is the overload function with int,char! max is;";
return x > y ? x : y;
}
int main()
{
const char* s1 = "Beijing 2008", * s2 = "Welcome to Beijing!";
cout << myMax(2, 3) << endl;//调用重载的普通函数:int myMax(int x;int y)
cout << myMax(2.0, 3.0) << endl;//调用函数模板,此时T被 double 取代
cout << myMax(s1, s2) << endl; //调用重载的普通函数 :char* myMax(char * x,char* y)
cout << myMax(2, 'a') << endl;//调用重载的普通函数:int myMax(int x,char y)
cout << myMax(2.3, 'a') << endl; //调用重载的普通函数:int myMax(int x,char y)
return 0;
}
3.程序改错
3.1三种访问权限
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class T {
protected: //protected 改为 public 类和对象
int p;
public:
T(int m) { p = m; }
};
int main() {
T a(10);
cout << a.p << endl;
}
3.2 友元
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date;
class Time {
public:
Time(int h, int m, int s) { hour = h; minute = m; sec = s; }
void show(Date& d);
private:
int hour, minute, sec;
};
class Date {
public:
Date(int m, int d, int y) { month = m, day = d, year = y; }
void Time::show(Date&);//应当改为友元函数在前面加friend,
否则show函数将无法访问Date类的私有变量
private:
int month, day, year;
};
void Time::show(Date& d) {
cout << d.month << "-" << d.day << "-" << d.year << endl;
cout << hour << ":" << minute << ":" << sec << endl;
}
int main() {
Time t1(9, 23, 50);
Date d1(5, 1, 2023);
t1.show(d1);
return 0;
}
3.3抽象类不能实例化对象
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class CBase {
public:
CBase(int iBase = 0) :m_iBase(iBase) {}
virtual void Show() = 0;
int Get() const { return m_iBase; }
private:
int m_iBase;
};
class CDerive :public CBase {
public:
CDerive(int iBase = 0, int iDerive = 0) :CBase(iBase)
{
m_iDerive = iDerive;
}
void Show()
{
cout << CBase::Get() << "," << m_iDerive << endl;
}
private:
int m_iDerive;
};
int main() {
CBase obj(10);//虚函数不能初始化成员变量
因此应当改为CDerive(10)
obj.Show();
return 0;
}
3.4常数据成员初始化必须使用构造函数的初始化列表
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class CTest {
public:
CTest(int iVar = 0) { m_iVar = iVar; }
//初始化const修饰的成员变量
//CTest(int iVar = 0):m_iVar(iVar)
{};
void Print()const { cout << m_iVar << endl; }
private:
const int m_iVar;
};
int main() {
const CTest oTest(13);
oTest.Print();
return 0;
}
3.5以引用传递的方式向函数传递对象
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int& a, int& b)
{
int tmp; tmp = a; a = b; b = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int a = 19, b = 15;
cout << "a=" << a << "," << "b=" << b << endl;
swap(&a, &b); //swap(a,b)引用传递
cout << "a=" << a << "," << "b=" << b << endl;
return 0;
}
4.程序设计
4.1运算符重载
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point {
private:
int x;
int y;
public:
Point(int x1 = 0, int y1 = 0) : x(x1), y(y1) {}
void show();
friend Point operator+(const Point &, const Point & );
friend Point operator-(const Point &, const Point & );
};
/*!!!三个成员函数的定义!!!*/
void Point::show() {
cout << "(x,y) = " << "(" << x << "," << y << ")" << endl;
}
Point operator+(const Point &a1, const Point &a2) {
return Point(a1.x + a2.x, a1.y + a2.y);
}
Point operator-(const Point &a1, const Point &a2) {
return Point(a1.x - a2.x, a1.y - a2.y);
}
int main()
{
Point a1(1, 2);
Point a2(4, 5);
Point a;
a = a1 + a2;
cout << "a: ";
a.show();
a = a1 - a2;
cout << "a: ";
a.show();
return 0;
}
4.2多态的程序实现方法
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape {
public:
virtual double getArea () = 0;
};
/*!!!! Rectangle类的定义 !!!!!*/
class Rectangle: public Shape {
public :
Rectangle(double x, double y): length(x), width(y) {
}
double getArea() {
return length * width;
}
private:
double length, width;
};
/*!!!! Circle类的定义 !!!!!!*/
class Circle: public Shape {
public :
Circle(double r): R(r) {
}
double getArea() {
return 3.14 * R * R;
}
private:
double R;
};
int main() {
Shape *rect = new Rectangle(2, 3);
cout << rect->getArea() << endl;
Shape *circle = new Circle(2);
cout << circle->getArea() << endl;
delete rect;
delete circle;
return 0;
}