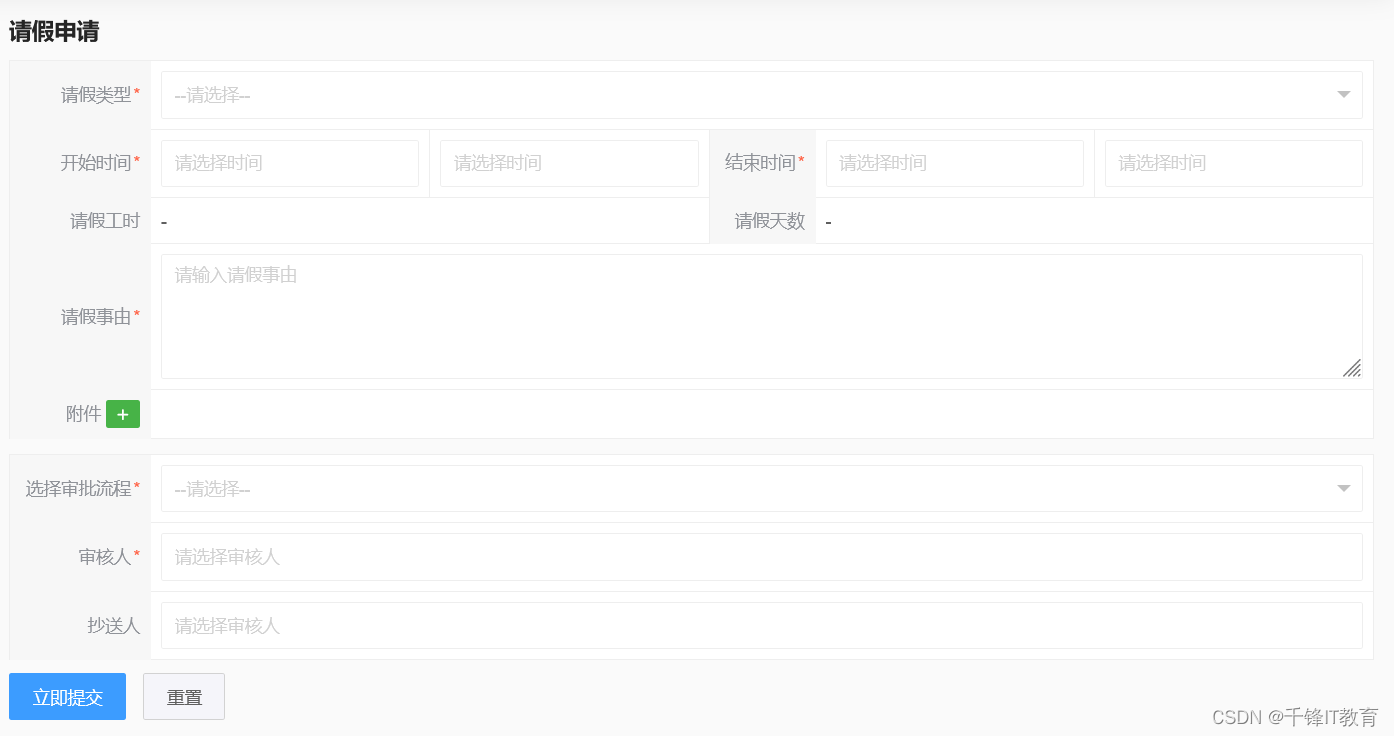
1、python的数据类型

可以使用type()函数获取任何对象的数据类型
x = 10
print(type(x)) # 打印<class 'int'>2、python 数字
Int 或整数是完整的数字,正数或负数,没有小数,长度不限。
浮动或“浮点数”是包含小数的正数或负数。
浮点数也可以是带有“e”的科学数字,表示 10 的幂。
x = 27e4
y = 15E2
z = -49.8e100
print(type(x)) # <class 'float'>
print(type(y)) # <class 'float'>
print(type(z)) # <class 'float'>复数用 "j" 作为虚部编写。
x = 2+3j
y = 7j
z = -7j
print(type(x)) # <class 'complex'>
print(type(y)) # <class 'complex'>
print(type(z)) # <class 'complex'>2、使用casting完成数据类型转换
有点像C/C++中的强制类型转换,不过在python中是使用类的构造函数完成强制类型转化。比如在python中int()就是一个类,只需要使用构造函数传递参数进去即可完成数据类型转换。
#—————————————————转化为 int 类型————————————————————————
x = int(1) # x是1
y = int(2.5) # y是2
z = int("3") # z是3
x = float(1) # x 将是 1.0
#—————————————————转化为 float 类型——————————————————————
y = float(2.5) # y 将是 2.5
z = float("3") # z 将是 3.0
w = float("4.6") # w 将是 4.6
#—————————————————转化为 str 类型————————————————————————
x = str("S2") # x 将是 'S2'
y = str(3) # y 将是 '3'
z = str(4.0) # z 将是 '4.0'3、字符串
在字符串中可以使用三个引号(双引号或者单引号)将多个字符串赋值给变量。
a = """Python is a widely used general-purpose, high level programming language.
It was initially designed by Guido van Rossum in 1991
and developed by Python Software Foundation.
It was mainly developed for emphasis on code readability,
and its syntax allows programmers to express concepts in fewer lines of code."""
print(a)和C/C++一样,python中的字符串实际上也是一个字符数组,所以可以通过[]索引的方式取字符串中相应位置的字符。
a = "Hello, World!"
print(a[1]) # 打印e使用索引完成对字符串数组切片操作
b = "Hello, World!"
# 获取从位置 2 到位置 5(不包括)的字符,打印 llo
print(b[2:5])
# 获取从位置 5 到位置 1 的字符,从字符串末尾开始计数,打印 orl
print(b[-5:-2])