Using a lambda expression,we can make the code more compact and elegant。
在使用lambda表达式时,可以使代码更加简洁和优雅。
Lambda,希腊字母λ,在C#编程语言中,被引入为Lambda表达式,表示为匿名函数(匿名方法)。
编程时离不开函数,函数都有函数名和函数体,声明函数名是为了方便多次使用,可是很多时候函数只使用一次,那么函数名就变得多余,这样就产生了匿名函数(匿名方法)。
很多编程语言都有Lambde表达式,如Python、JavaScript、Java等等,这似乎是现代编程语言的标配了。
作为编程语言C#和编程环境Visual Stuidio的发展,总得不停地变幻出新花样,功能还是那个功能或者略有增强,得益于编译器的强大,C#3.0推出了Lambda表达式。
其实这些是非必要的,只是为C#编码增加一些色彩和亮点而已,但是别人总喜欢这么写,我们就得熟悉这些规则了。
举例1:计算两个整数的相加和相减。
① 一般写法
//声明变量
private delegate int calculate(int x, int y);//声明一个用于计算的委托类型
private calculate MyCalculate;//声明一个委托实例
//声明函数
private int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x+y;
}
private int Reduce(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}就可以直接使用了。
MyCalculate = new calculate(Add);
string StrResultAdd = MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString();
MyCalculate = new calculate(Reduce);
string StrResultReduce = MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString();
//
textBox1.Text = $"两数相加结果:{StrResultAdd}" + Environment.NewLine;
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text+ $"两数相减结果:{StrResultReduce}" + Environment.NewLine;② 使用自定义的委托
使用自定义的委托来使用Lamda可以让代码更简洁:
MyCalculate = delegate(int x,int y)
{
return x + y;
};
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text+"两数相加结果:" + MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString()+Environment.NewLine;
MyCalculate = delegate (int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
};
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "两数相减结果:" + MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString() + Environment.NewLine;上面得到的结果是一样的。
③ 使用Func委托
FUNC委托的重载:
Func<TResult>;
Func<T1,T2,TResult>;
Func<T1,...,T16,TResult>;
使用系统内置的FUNC命名的委托来写LambDa表达式:
Func<int,int,int> MyAdd = (int x, int y) => { return x + y; };
Func<int, int, int> MyReduce = (int x, int y) => { return x - y; };
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + $"两数相加结果:{MyAdd(7,2).ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + $"两数相减结果:{MyReduce(7, 2).ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;④ 使用规范的Lambda表达式
更简洁的写法:
MyCalculate = (int x, int y) => { return x + y; };
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text+$"两数相加结果:{MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;
MyCalculate = (int x, int y) => { return x - y; };
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text+$"两数相减结果:{MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;
完整代码:
namespace Lambda
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private delegate int calculate(int x, int y);//声明一个用于计算的委托类型
private calculate MyCalculate;//声明一个委托实例
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//1
MyCalculate = new calculate(Add);
string StrResultAdd = MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString();
MyCalculate = new calculate(Reduce);
string StrResultReduce = MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString();
textBox1.Text = $"两数相加结果:{StrResultAdd}" + Environment.NewLine;
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text+ $"两数相减结果:{StrResultReduce}" + Environment.NewLine;
//2
MyCalculate = delegate(int x,int y)
{
return x + y;
};
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text+"两数相加结果:" + MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString()+Environment.NewLine;
MyCalculate = delegate (int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
};
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "两数相减结果:" + MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString() + Environment.NewLine;
//3
Func<int,int,int> MyAdd = (int x, int y) => { return x + y; };
Func<int, int, int> MyReduce = (int x, int y) => { return x - y; };
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + $"两数相加结果:{MyAdd(7,2).ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + $"两数相减结果:{MyReduce(7, 2).ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;
//4
MyCalculate = (int x, int y) => { return x + y; };
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text+$"两数相加结果:{MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;
MyCalculate = (int x, int y) => { return x - y; };
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text+$"两数相减结果:{MyCalculate(7, 2).ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;
}
private int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x+y;
}
private int Reduce(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}结果显示:
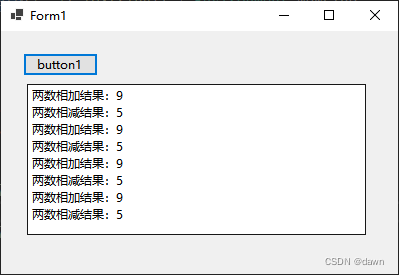
上面通过对比说明了Lambda表达式的应用,可以看出这样的写法相比传统的写法还是干净利落,的确简洁而优雅一些。
上面的可以改写:
private delegate int calculate1(int x, int y,string str);//声明一个用于计算的委托类型
private calculate1 MyCalculate1;//声明一个委托实例
MyCalculate1 = (int x, int y,string StrOP) => {
switch (StrOP)
{
case "+":
return x + y; break;
case "-": return x - y; break;
default: return 0; break;
}
};
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + $"两数相加结果:{MyCalculate1(7, 2,"+").ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + $"两数相减结果:{MyCalculate1(7, 2,"-").ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;或者:
Func<int, int, string,int> MyOperate = (int x, int y, string StrOP) => {
switch (StrOP)
{
case "+":
return x + y; break;
case "-": return x - y; break;
default: return 0;break;
}
};
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + $"两数相加结果:{MyOperate(7, 2,"+").ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + $"两数相减结果:{MyOperate(7, 2,"-").ToString()}" + Environment.NewLine;从上面的代码演示中可以看出,Lambda与委托是紧密相连的。
举例2:求几个数的最大值与最小值。
① 一般写法:
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text += "最大值:"+GetMax(new int[6]{7, 11,23,4,15,6}).ToString();
textBox1.Text += Environment.NewLine;
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + GetMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }).ToString();
}
private static int GetMax(int[] Arr)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach( int a in Arr)
{
if(a > ReturnValue) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
}
private static int GetMin(int[] Arr)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (a < ReturnValue) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
}② 使用委托来改写:
//声明委托
private delegate int GetMaxOrMin(int[] Arr);
private GetMaxOrMin MyGetMaxOrMin;
//定义函数
private static int GetMax(int[] Arr)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach( int a in Arr)
{
if(a > ReturnValue) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
}
private static int GetMin(int[] Arr)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (a < ReturnValue) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
}
//使用
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MyGetMaxOrMin = new GetMaxOrMin( GetMax);
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }).ToString();
textBox1.Text += Environment.NewLine;
MyGetMaxOrMin = new GetMaxOrMin(GetMin);
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }).ToString();
}
③ 使用自定义的委托
MyGetMaxOrMin=delegate(int[] Arr)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (a > ReturnValue) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
};
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }).ToString();
MyGetMaxOrMin = delegate (int[] Arr)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (a < ReturnValue) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
};
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + GetMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }).ToString();到这里,我们看到这两个方法只是判断位置的代码略有不同,其他的都相同,那么这个地方就可以使用委托来代替,就是把判断方法当做参数传进去。
private delegate Boolean Judge(int x,int y);//定义判断
private Judge MyJudge;//实例化委托
private delegate int GetMaxOrMin(int[] Arr,Judge j);//定义得到最大值或者最小值的计算方法
private GetMaxOrMin MyGetMaxOrMin;//实例化
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MyGetMaxOrMin=delegate(int[] Arr,Judge MyJude)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (MyJudge(a,ReturnValue)) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
};
MyJudge = delegate (int x, int y) { return x > y; };
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 },MyJudge).ToString();
MyJudge = delegate (int x, int y) { return x < y; };
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 },MyJudge).ToString();
}上面的写法的效果是一样的。
④ 使用Func委托
Func<int[],Judge,int> MyGetMax = (int[] Arr,Judge MyJudge) => {
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (MyJudge(a, ReturnValue)) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
};
MyJudge = delegate (int x, int y) { return x > y; };
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + MyGetMax(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 },MyJudge).ToString();
MyJudge = delegate (int x, int y) { return x < y; };
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + MyGetMax(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }, MyJudge).ToString();⑤ 使用更简洁的Lambda表达式
var MyGetMaxOrMin1 = (int[] Arr,Judge J1 ) =>
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (J1(a, ReturnValue)) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
};
Judge JudgeMax = (int x, int y) => { return x > y; };
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin1(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }, JudgeMax).ToString();
Judge JudgeMin = (int x, int y) => { return x < y; };
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin1(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }, JudgeMin).ToString();完整代码:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
namespace Lambda
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private delegate int calculate(int x, int y);//声明一个用于计算的委托类型
private calculate MyCalculate;//声明一个委托实例
private delegate int calculate1(int x, int y,string str);//声明一个用于计算的委托类型
private calculate1 MyCalculate1;//声明一个委托实例
private delegate Boolean Judge(int x,int y);
private Judge MyJudge;
private delegate int GetMaxOrMinA(int[] Arr);
private GetMaxOrMinA MyGetMaxOrMinA;
private delegate int GetMaxOrMin(int[] Arr,Judge j);
private GetMaxOrMin MyGetMaxOrMin;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + GetMax(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }).ToString();
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + GetMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }).ToString();
textBox1.Text += Environment.NewLine +"=====" + Environment.NewLine;
MyGetMaxOrMinA = new GetMaxOrMinA(GetMax);
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + MyGetMaxOrMinA(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }).ToString();
MyGetMaxOrMinA = new GetMaxOrMinA(GetMin);
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + MyGetMaxOrMinA(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }).ToString();
textBox1.Text += Environment.NewLine + "=====" + Environment.NewLine;
MyGetMaxOrMin = delegate (int[] Arr, Judge MyJude)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (MyJudge(a, ReturnValue)) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
};
MyJudge = delegate (int x, int y) { return x > y; };
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }, MyJudge).ToString();
MyJudge = delegate (int x, int y) { return x < y; };
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }, MyJudge).ToString();
textBox1.Text += Environment.NewLine +"=====" + Environment.NewLine;
Func<int[], Judge, int> MyGetMax = (int[] Arr, Judge MyJudge) =>
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (MyJudge(a, ReturnValue)) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
};
MyJudge = delegate (int x, int y) { return x > y; };
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + MyGetMax(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }, MyJudge).ToString();
MyJudge = delegate (int x, int y) { return x < y; };
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + MyGetMax(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }, MyJudge).ToString();
textBox1.Text += Environment.NewLine +"=====" + Environment.NewLine;
var MyGetMaxOrMin1 = (int[] Arr,Judge Judge1 ) =>
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (Judge1(a, ReturnValue)) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
};
Judge JudgeMax = (int x, int y) => { return x > y; };
textBox1.Text += "最大值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin1(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }, JudgeMax).ToString();
Judge JudgeMin = (int x, int y) => { return x < y; };
textBox1.Text += "最小值:" + MyGetMaxOrMin1(new int[6] { 7, 11, 23, 4, 15, 6 }, JudgeMin).ToString();
}
private static int GetMax(int[] Arr)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach( int a in Arr)
{
if(a > ReturnValue) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
}
private static int GetMin(int[] Arr)
{
int ReturnValue = Arr[0];
foreach (int a in Arr)
{
if (a < ReturnValue) ReturnValue = a;
}
return ReturnValue;
}
private static List<int> GetEven(List<int> list)
{
List<int> ReturnList =new List<int>();
foreach (var a in list)
{
if (a %2 == 0) ReturnList.Add(a);
}
return ReturnList;
}
private static List<int> GetOdd(List<int> list)
{
List<int> ReturnList = new List<int>();
foreach (var a in list)
{
if ( (a+1) % 2 == 0) ReturnList.Add(a);
}
return ReturnList;
}
}
}显示结果图:

![使用[阿里问题定位神器]Arthas入门](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/becf2d23ceb129eb2635d714998be106.png)