文章目录
- SpringBoot整合Thymeleaf
- 0x01_入门案例
- 0x02_Thymeleaf视图解析简介
- 0x03_Thymeleaf的表达式
- 0x04_Thymeleaf的标签
- th:text
- th:each
- th:object
- th:href
- th:action
- th:onclick
- th:if
- th:value
- 0x05_内置对象
- `#dates`
- `#Strings`
- `#Numbers`
- 域对象
- 0x0x_补充一些概念
- 国际化
- Thymeleaf缓存区
- 重定向和请求转发的区别(路径的书写问题)
- thymeleaf内置对象列表
- 模版引擎总结
- 网页静态化技术
SpringBoot整合Thymeleaf
SpringBoot官方推荐使用的引擎模版是Thymeleaf

0x01_入门案例
首先需要加入依赖:
官网有很多关于thymeleaf的配置说明,其中有几个现在需要关注:
spring.thymeleaf.prefix 默认 classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.suffix 默认 .html
spring.thymeleaf.mode 默认 HTML
第一个参数指定了前缀,或者说是解析thymeleaf模版的路径
第二个参数指定了后缀,是html格式的(这点和FreeMarker类似,但是freeMarker解析的是
ftlh)
除了这2个参数之外,个人觉得应该配置一下缓存:
spring:
thymeleaf:
cache: false # 开发时关闭缓存,不然看不到实时页面
可能在开发过程中,大家会觉得每次更改页面后,都要重新重启服务,很是麻烦与反人类,可以通过配置热启动来改善(即上面的写法:spring.thymeleaf.cache=false)
其他配置项采用默认就可以了,想要看有哪些默认项的话,可以全局打开 ThymeleafProperties.java 类。
就比如我上面说的
spring.thymeleaf.prefix和spring.thymeleaf.suffix这两个参数,默认值可以通过ThymeleafProperties.java查看。下面列出了这个类的所有属性:private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING; public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/"; public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; private boolean checkTemplate = true; private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true; private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/"; private String suffix = ".html"; private String mode = "HTML"; private Charset encoding; private boolean cache; private Integer templateResolverOrder; private String[] viewNames; private String[] excludedViewNames; private boolean enableSpringElCompiler; private boolean renderHiddenMarkersBeforeCheckboxes; private boolean enabled; private final Servlet servlet; private final Reactive reactive;
回到入门的这个项目:
Thymeleaf 模板引擎默认会读取 resources 目录下的templates目录,这个目录是用来存放 HTML 页面的。
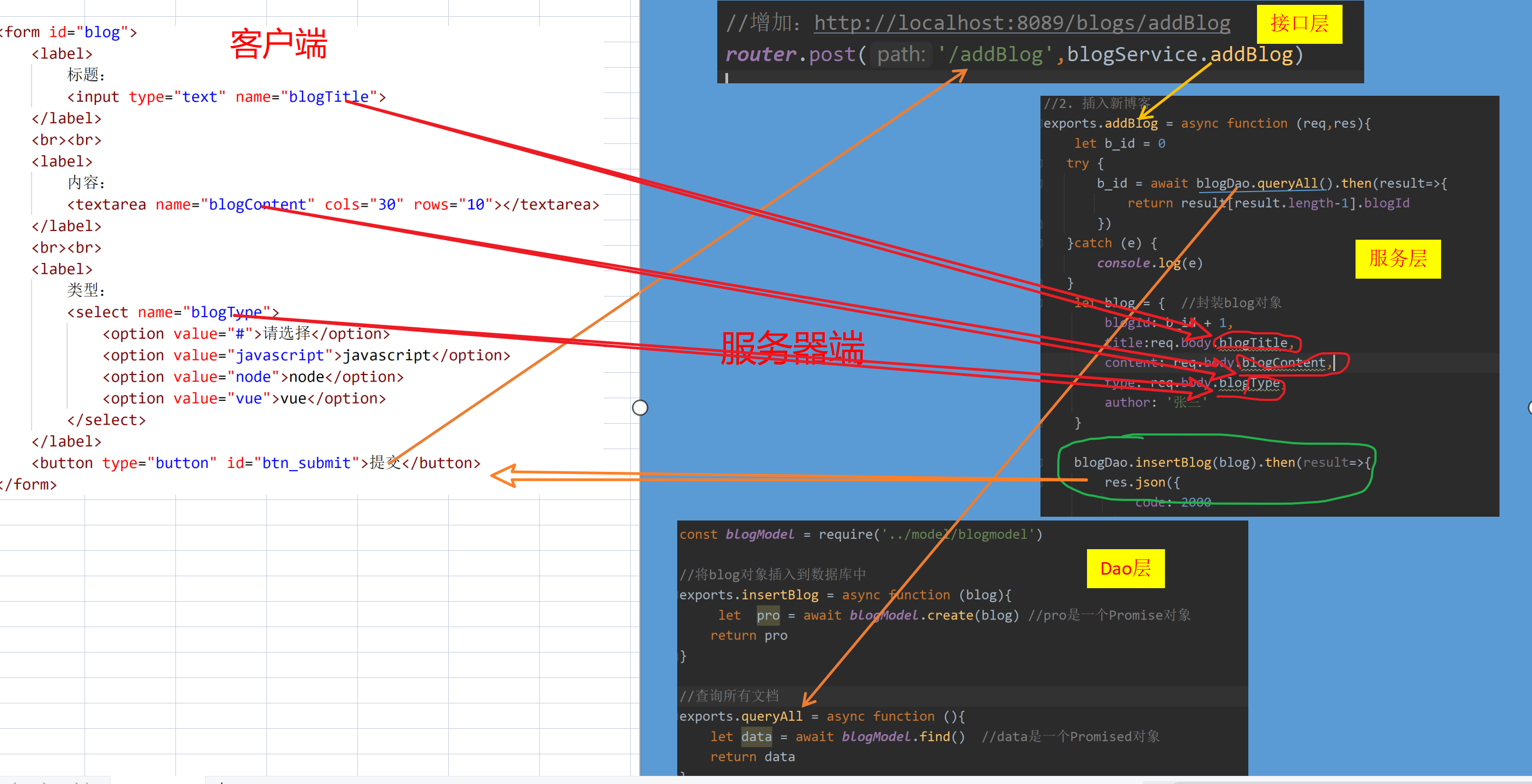
新建一个控制器,利用业务层来查询所有的员工:
package com.bones.controller;
import com.bones.bean.Emp;
import com.bones.service.EmpService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* <p>
* 前端控制器
* </p>
*
* @author bones
* @since 2022-11-29
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/emp")
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
@RequestMapping("findAll")
public String findAll(Map<String,Object> map){
// 调用业务层查询所有员工
List<Emp> empList = empService.findAll();
map.put("empList",empList);
return "all";
}
}
关于业务层和持久层,因为是比较“搬砖”的操作,所以我直接用mybatis-plus生成了。
上面的controller代码中:
@Controller:被@Controller标记的类实际上就是个SpringMVC Controller对象,它是一个控制器类@RequestMapping("/emp"),指明映射路径,要注意,上面的这个处理单元访问的URL是http://localhost:8080/emp/findAll@Autowired:用来注入一个EmpService对象Map<String,Object> map:用于传输给前端数据
templates/all.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Thymeleaf </h1>
<table>
<tr>
<th>索引</th>
<th>序号</th>
<th>总人数</th>
<th>偶数索引?</th>
<th>奇数索引?</th>
<th>第一?</th>
<th>最后?</th>
<th>工号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>职务</th>
<th>上级</th>
<th>入职日期</th>
<th>工资</th>
<th>补助</th>
<th>部门号</th>
</tr>
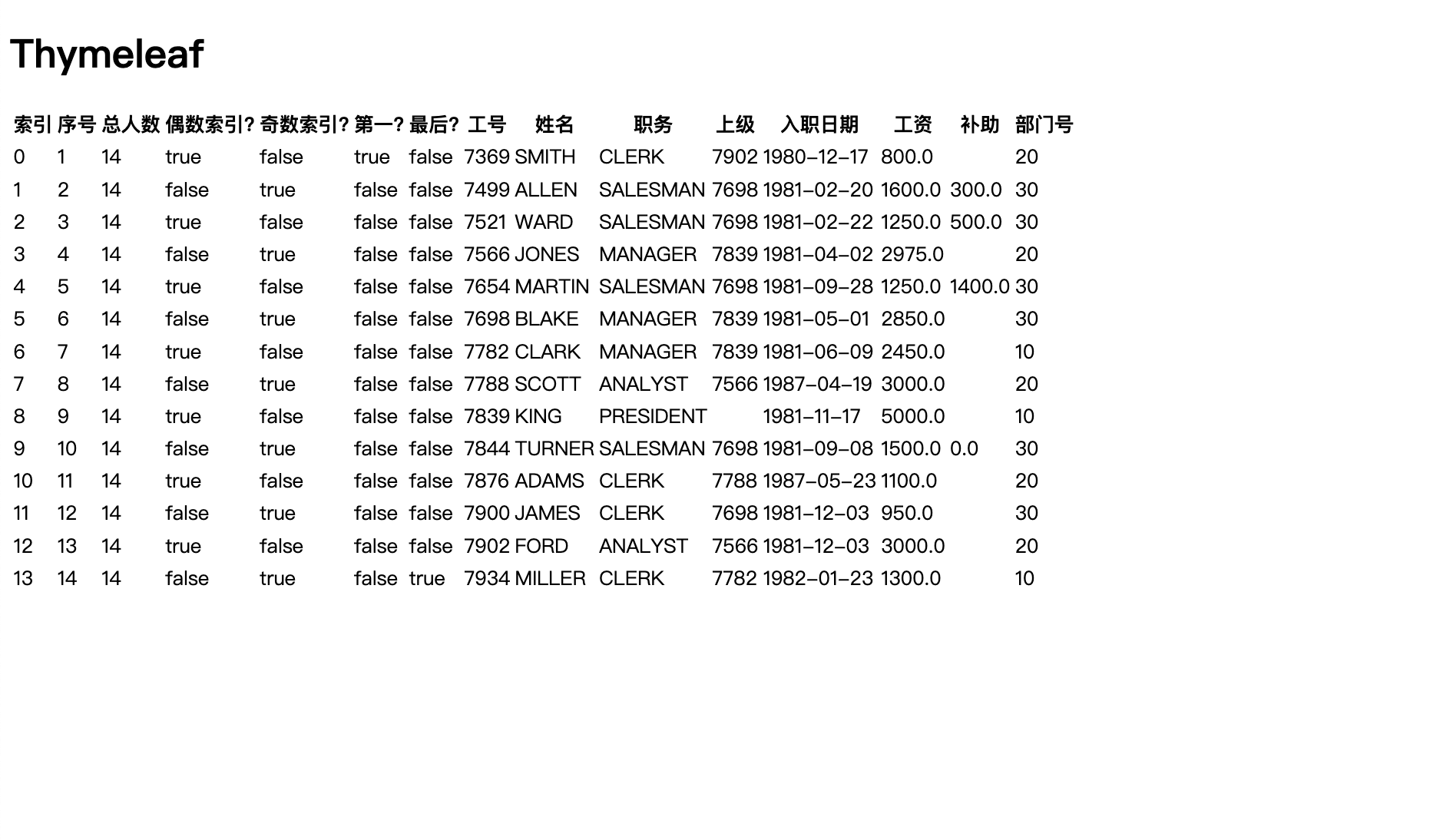
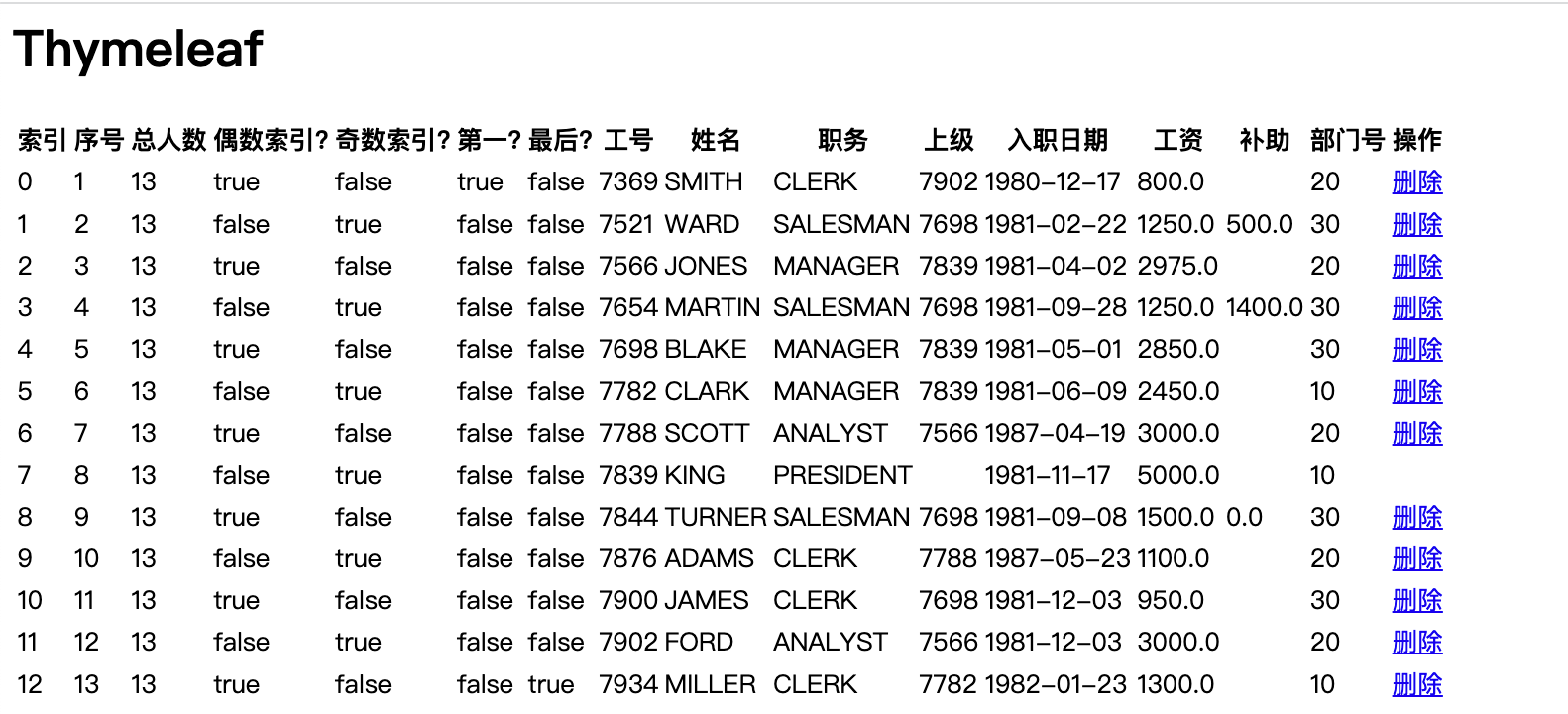
<tr th:each="emp,i:${empList}">
<td th:text="${i.index}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.count}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.size}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.odd}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.even}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.first}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.last}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.empno}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.ename}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.job}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.mgr}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.hiredate}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.sal}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.comm}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.deptno}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">:为 Thymeleaf 的命名空间,通过引入命名空间就可以在 HTML 文件中使用 Thymeleaf 标签语言,用关键字 “th”来标注。
其次,可以注意一下thymeleaf对于list的遍历的语法:
<tr th:each="emp,i:${empList}"> <td th:text="${i.index}"></td> <td th:text="${i.count}"></td> <td th:text="${i.size}"></td> <td th:text="${i.odd}"></td> <td th:text="${i.even}"></td> <td th:text="${i.first}"></td> <td th:text="${i.last}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.empno}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.ename}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.job}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.mgr}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.hiredate}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.sal}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.comm}"></td> <td th:text="${emp.deptno}"></td> </tr>
页面效果:
你可能好奇浏览器中是怎么解析上面的html文件的呢?
可以右键查看一下页面的元素:

数据就好像是纯文本塞进去的一样。
0x02_Thymeleaf视图解析简介
英文官方文档3.0 http://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
什么是Thymeleaf?
Thymeleaf 是一种适用于 Web 和独立环境的现代服务器端 Java 模板引擎,能够处理 HTML、XML、JavaScript、CSS 甚至纯文本。
Thymeleaf 的主要目标是提供一种优雅且高度可维护的模板创建方式。为实现这一点,它建立在自然模板Natural Templates的概念之上,以不影响模板用作设计原型的方式将其逻辑注入模板文件。这改善了设计的沟通并弥合了设计和开发团队之间的差距。
什么是自然模版
Natural Templates?用
Thymeleaf编写的HTML模板在外观和功能上仍然类似于HTML,从而使应用程序中运行的实际模板可以用作有用的设计工件。
Thymeleaf 的设计从一开始就考虑了 Web 标准——尤其是 HTML5——允许您在需要时创建完全验证的模板。
Thymeleaf 在有网和没网的环境下都可以正常工作,既能让美工在浏览器中查看页面的静态效果,也能让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。
这是因为Thymeleaf支持 HTML 原型,在 HTML 标签里增加额外的属性来达到模板+数据的展示方式。
浏览器在解释 HTML 的时候会忽略未定义的标签属性,所以 Thymeleaf 可以静态地运行;当有数据返回页面时,Thymeleaf 标签会动态地替换静态内容。
Thymeleaf的主要目标是将优雅的自然模板带到开发工作流程中,并将HTML在浏览器中正确显示,并且可以作为静态原型,让开发团队能更容易地协作。Thymeleaf能够处理HTML,XML,JavaScript,CSS甚至纯文本。
长期以来,jsp在视图领域有非常重要的地位,随着时间的变迁,出现了一位新的挑战者:Thymeleaf,Thymeleaf是原生的,不依赖于标签库.它能够在接受原始HTML的地方进行编辑和渲染.因为它没有与Servelet规范耦合,因此Thymeleaf模板能进入jsp所无法涉足的领域。
Thymeleaf在Spring Boot项目中放入到resources/templates中。这个文件夹中的内容是无法通过浏览器URL直接访问的(和WEB-INF效果一样),所有Thymeleaf页面必须先走控制器。
下面列出一些常用的表达式、标签、函数:
常用表达式:
${...}变量表达式*{...}选择表达式#{...}文字表达式@{...}URL 表达式#maps对象表达式
常用标签:
- th:action 定义服务器端控制器路径。
- th:each 循环语句
- th:field 表单字段
- th:href URL 链接
- th:id div 标签中的 ID
- th:if 条件判断
- th:include 引入文件
- th:fragment 定义代码片段
- th:object 替换对象
- th:src 图片地址
- th:text 文本
- th:value 属性值
常用函数:
#dates日期函数#lists列表函数#arrays数组函数#strings字符串函数#numbers数字函数#calendars日历函数#objects对象函数#bools布尔函数
0x03_Thymeleaf的表达式
Thymeleaf通过标准变量表达式完成数据的展示和处理
- 1 标准变量表达式必须依赖标签,不能独立使用
- 2 标准变量表达式一般在开始标签中,以 th开头
- 3 语法为:
<tag th:***="${key}" ></tag> - 4 表达式中可以通过
${}取出域中的值并放入标签的指定位置 - 5
${}在这里不能单独使用,必须在th:后面的双引号里使用
对于单个变量,可以通过${...}取值。
比如现在完成这样一个场景:
用户输入想要查询的工号,可以根据这个工号查询数据,并且回显出来:
EmpController中的处理单元:
@RequestMapping("/queryAllEmpno")
public String findEmpno(Map<String,Object> map){
List<Integer> empnoList = empService.findEmpnoList();
map.put("empnoList",empnoList);
return "queryEmp";
}
@RequestMapping("/queryEmpbyEmpno")
public ModelAndView queryEmpbyEmpno(Integer empno){
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
List<Integer> empnoList = empService.findEmpnoList();
if (empnoList.contains(empno)){
Emp emp = empService.findEmpByEmpno(empno);
mv.addObject("emp",emp);
mv.setViewName("showEmp");
return mv;
}else {
mv.setViewName("invalidate");
return mv;
}
}
queryAllEmpno用于查询所有员工的编号,将一个list返回给前端
queryEmpbyEmpno用于查询指定编号的员工
所以对应2个页面:
queryEmp.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>请选择你想要查询的员工编号</h1>
<ul th:each="empno:${empnoList}">
<li th:text="${empno}"></li>
</ul>
<form action="/emp/queryEmpbyEmpno" method="POST">
<h3>请填写你想要查询的员工编号:</h3>
<input type="text" name="empno">
<input type="submit" value="查询">
</form>
</body>
</html>
这里涉及遍历list集合的语法:
<ul th:each="empno:${empnoList}"> <li th:text="${empno}"></li> </ul>以及提交数据给后端:
<form action="/emp/queryEmpbyEmpno" method="POST"> <h3>请填写你想要查询的员工编号:</h3> <input type="text" name="empno"> <input type="submit" value="查询"> </form>
showEmp.html展示查询结果:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
table,th,td,th{
border: 1px solid forestgreen;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>
查询成功:
</h2>
<table>
<tr>
<th>员工编号</th>
<th>员工姓名</th>
<th>员工入职日期</th>
<th>员工上级</th>
<th>员工职位</th>
<th>员工薪资</th>
<th>员工补助</th>
<th>员工所属部门编号</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td th:text="${emp.empno}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.ename}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.hiredate}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.mgr}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.job}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.sal}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.comm}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.deptno}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
<a th:href="@{/emp/queryAllEmpno}">
返回
</a>
</body>
</html>
并且有一个链接
<a th:href="@{/emp/queryAllEmpno}">返回</a>可以回到刚才的页面。
除此之外,还有一个提示用户输入信息有攻击性行为,提示用户回到首页的html页面:
invalidate.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>您的行为存在攻击行为,建议您回到首页!</h1>
<a th:href="@{/index}">回到首页</a>
</body>
</html>
这个页面也有
th:href="@{}"表达式:th:href="@{/index}请求的是后台这个处理单元:
MainController:(这个controller的命名是我随便取的,可能不是很符合规范)package com.bones.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller public class MainController { @RequestMapping("/index") public String index(){ return "index"; } }
以上总结了2个表达式的使用:
${}:用于访问容器上下文环境中的变量,功能同jstl中${}。@{}:超链接url表达式。
另外还有几个表达式:
#{}:消息表达式(井号表达式,资源表达式)。通常与th:text属性一起使用,指明声明了th:text的标签的文本是#{}中的key所对应的value,而标签内的文本将不会显示。(消息表达式#{…}主要用于Thymeleaf模板页面国际化内容的动态替换和展示。)*{}:选择表达式(星号表达式)。选择表达式与变量表达式有一个重要的区别:选择表达式计算的是选定的对象,而不是整个环境变量映射。也就是:只要是没有选择的对象,选择表达式与变量表达式的语法是完全一样的。那什么是选择的对象呢?是一个:th:object对象属性绑定的对象。
下面练习这两个表达式,不过首先要注意:查看并修改idea的files encoding ,修改为UTF-8、勾选自动转为ascii码(防止修改完成后页面出现乱码)
除此之外,如果下面的例子还有乱码就要参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/sunp_csdn/article/details/122821197
以及关于国际化的知识来解决:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43437874/article/details/118840835
还要注意的是,在application.yaml中要正确配置:
spring:
# 模版引擎thymeleaf
thymeleaf:
prefix: classpath:/templates/
suffix: .html
# 数据源
datasource:
username: XXXX
password: XXXX
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
messages:
basename: i18n/msg
上面spring.messages.basename默认值为messages,根据properties的位置修改为:
i18n│ │ └── resources │ │ ├── application.yaml │ │ ├── i18n │ │ │ ├── msg.properties │ │ │ ├── msg_en_US.properties │ │ │ └── msg_zh_CN.properties这里附上一张图:

express.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>i18n</h1>
<h1 th:text="#{name}"></h1>
<a th:href="@{/msg(lang='zh_CN')}">中文</a>
<a th:href="@{/msg(lang='en_US')}">English</a>
</body>
</html>
关于*{}表达式的使用,这里再举一个例子:(下面再实体类上面的注解是Lombok)
首先是2个实体类:Role
package com.bones.bean;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@Builder
public class Role {
private Long roleId;
private String roleName;
}
User
package com.bones.bean;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@Builder
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
private String email;
private Double money;
private Role role;
}
然后是控制层UserController的请求单元:
package com.bones.controller;
import com.bones.bean.Role;
import com.bones.bean.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.util.Date;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public String getUser(Model model){
//添加User信息(包括Role信息)
Role role = Role.builder().roleId(1L).roleName("admin").build();
User user = User.builder().role(role).username("张三").password("123456").age(23).birthday(new Date()).build();
model.addAttribute("user",user);
return "showUser";
}
}
页面:showUser.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Thymeleaf 表达式*{}的用法 </h1>
<div th:object="${user.role}">
<p th:text="*{roleName}"></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
页面效果:

*{}:选择表达式,是选定的对象,不是整个环境的映射。如果没对象,和变量表达式${} 基本上没区别
0x04_Thymeleaf的标签
上面的多个例子中涉及了多个标签,比如:
th:text
上面练了很多次了,不多说
补充一下三目运算符:
th:text="${emp.ename eq 'KING'}?大boss:删除"
th:each
数据迭代,取出域中的数据(数组/集合)去进行循环,通常配合**th:text="${x1.x3}"**使用
th:object
(和*{}一起使用)
th:href
比如th:href="@{x1(x2=${x3.x4})}"
x1为超链接指向的路径;x2为自己命名的名称;x3,x4为上边数据迭代中的**th:text=“${x1.x3}”**x1和x3.
<a th:href="@{/goods/doDeleteById(id=${g.id})}">
delete
</a>
关于超链接指向地址,还提供了restful风格的写法,
平时我们所写代码地址上带请求数据一般为:a/b/c?id=x
而restful这种风格为:a/b/c/{id}
<a th:href="@{/goods/doFindById/{id}(id=${g.id})}">
update
</a>
在这种语法中,{id}为一个变量表达式,由后面()内的内容补充,如果我们希望在后端的Controller类的方法参数中获得传递的参数,就需要加@PathVariable描述参数.
除此以外,还有以下标签,依次举例说明:
th:action
提交表单,语法:th:action="@{x1}",x1为表单所要提交至的地址.
比如随便写个登录框:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> 登录 </h1>
<form th:action="@{/loginUser}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" >
密码:<input type="password" name="password" >
<p>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
后台处理单元:
@PostMapping("/loginUser")
public String loginUser(String username, String password, Model model){
model.addAttribute("username",username);
return "success";
}
success页面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
欢迎您
<span th:text="${username}"></span>
</h1>
</body>
</html>
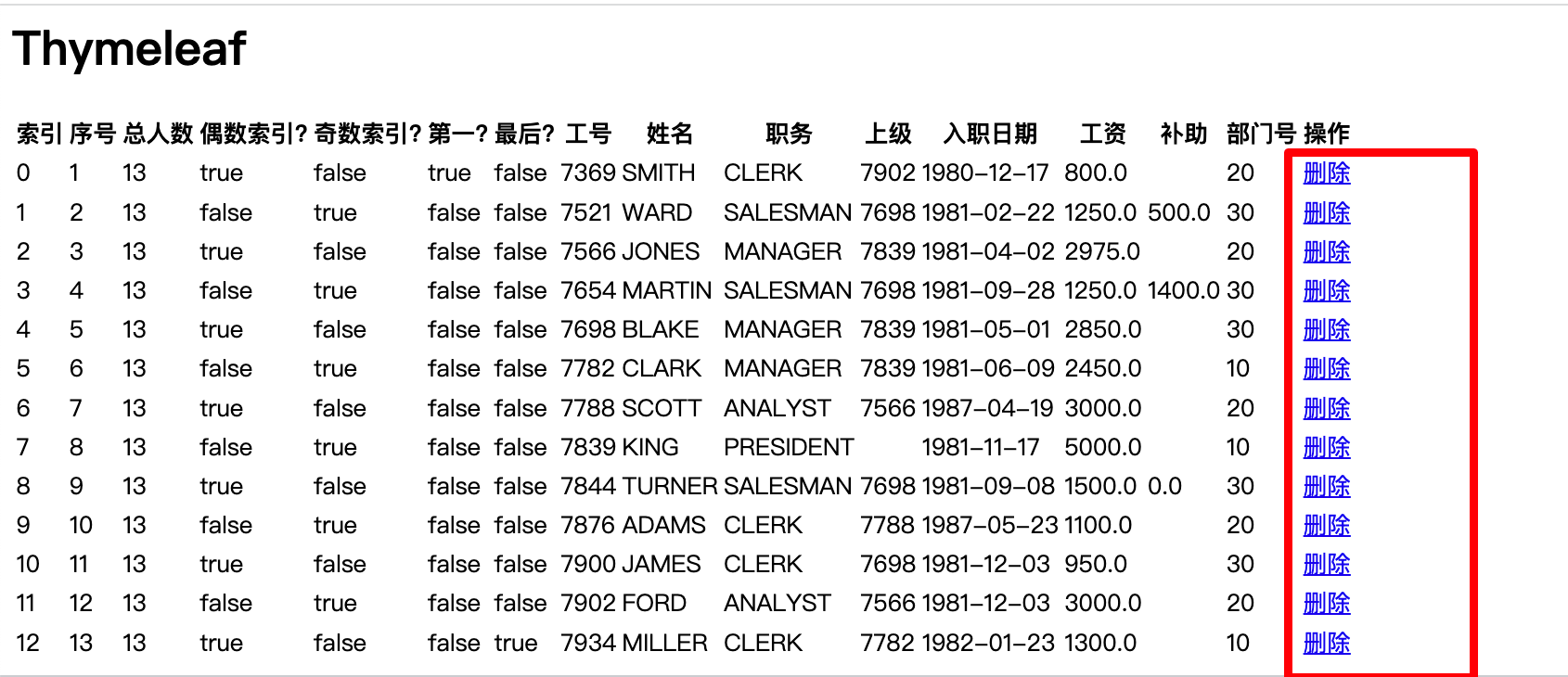
th:onclick
点击事件
举例:点击“删除”,会删除数据库中的数据:
前端all.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Thymeleaf </h1>
<table>
<tr>
<th>索引</th>
<th>序号</th>
<th>总人数</th>
<th>偶数索引?</th>
<th>奇数索引?</th>
<th>第一?</th>
<th>最后?</th>
<th>工号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>职务</th>
<th>上级</th>
<th>入职日期</th>
<th>工资</th>
<th>补助</th>
<th>部门号</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="emp,i:${empList}">
<td th:text="${i.index}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.count}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.size}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.odd}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.even}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.first}"></td>
<td th:text="${i.last}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.empno}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.ename}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.job}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.mgr}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.hiredate}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.sal}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.comm}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.deptno}"></td>
<td>
<a href="javascript:void(0)" th:onclick="removeEmp([[${emp.empno}]])">删除</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
<script>
function removeEmp(empno){
var conf = confirm("请问是否删除员工编号为"+empno+"的信息?")
if (conf){
window.location.href = "removeEmp?empno="+empno;
}
}
</script>
后台处理单元:
@RequestMapping("/removeEmp")
public String removeEmp(Integer empno){
System.out.println(empno);
empService.removeEmpByEmpno(empno);
return "forward:/emp/findAll";
}
其他JS的事件也类似,onblur,onfocus等等方法。
th:if
现在完成一个功能,名为KING的员工是大老板,不能删除。
在上面的例子中只需要这么修改即可:
<a th:if="${!(emp.ename eq 'KING')}" href="javascript:void(0)" th:onclick="removeEmp([[${emp.empno}]])">删除</a>
加了:
th:if="${!(emp.ename eq 'KING')}",此时,只要满足条件,就会显示a标签。
页面效果:(可以看到KING的删除a标签没了)
th:value
表单元素,设置HTML标签中表单元素value属性时使用。
常用的标签基本展示完毕,其实还有很多,用到了还可以再另外学。
0x05_内置对象
Thymeleaf提供了一些内置对象,内置对象可直接在模板中使用。这些对象是以#引用的。
使用内置对象的语法
1引用内置对象需要使用#
2大部分内置对象的名称都以s结尾。如:strings、numbers、dates
3常见内置对象如下
#arrays:数组操作的工具;
#aggregates:操作数组或集合的工具;
#bools:判断boolean类型的工具;
#calendars:类似于
#dates,但是是java.util.Calendar类的方法;
#ctx:上下文对象,可以从中获取所有的thymeleaf内置对象;
#dates:日期格式化内置对象,具体方法可以参照java.util.Date;
#numbers: 数字格式化;#strings:字符串格式化,具体方法可以参照String,如startsWith、contains等;
#objects:参照java.lang.Object;
#lists:列表操作的工具,参照java.util.List;
#sets:Set操作工具,参照java.util.Set;
#maps:Map操作工具,参照java.util.Map;
#messages:操作消息的工具。
更多的内置对象,可以通过package org.thymeleaf.expression包下都有对应的类查看:

这里主要来看域对象,Strings,Numbers,Dates
#dates
常用方法有
${#dates.format(date)}
${#dates.format(date, 'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm')}
举例:
<td th:text="${#dates.format(emp.hiredate,'YYYY-MM-dd')}"></td>
#Strings
常用方法有:
${#strings.isEmpty(name)}
${#strings.contains(name,'ez')}
${#strings.containsIgnoreCase(name,'ez')}
${#strings.startsWith(name,'Don')}
${#strings.endsWith(name,endingFragment)}
${#strings.indexOf(name,frag)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.substring(name,3,5)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.substringAfter(name,prefix)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.substringBefore(name,suffix)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.replace(name,'las','ler')} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.prepend(str,prefix)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.append(str,suffix)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.toUpperCase(name)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.toLowerCase(name)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.trim(str)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.length(str)} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.equals(first, second)}
${#strings.equalsIgnoreCase(first, second)}
${#strings.concat(values...)}
${#strings.concatReplaceNulls(nullValue, values...)}
举例:查询名字中包含“E”的员工
<tr th:each="e:${empList}" th:if="${#strings.contains(e.ename,'E')}" >
<td th:text="${e.empno}"></td>
<td th:text="${e.ename}"></td>
<td th:text="${e.job}"></td>
<td th:text="${e.mgr}"></td>
<td th:text="${e.hiredate}"></td>
<td th:text="${e.sal}"></td>
<td th:text="${e.comm}"></td>
<td th:text="${e.deptno}"></td>
</tr>
#Numbers
常用方法:
${#numbers.formatInteger(num,3)}
${#numbers.formatInteger(num,3,'POINT')}
${#numbers.formatDecimal(num,3,2)}
${#numbers.formatDecimal(num,3,2,'COMMA')}
${#numbers.sequence(from,to)}
${#numbers.sequence(from,to,step)}
举例:
#numbers.formatDecimal(numbwe,整数位,整数位千分位标识符,小数位,小数位表示符)
${#numbers.formatDecimal(num,1,'COMMA',2,'POINT')}
显示:99,999,999.99
${#numbers.formatDecimal(num,0,'COMMA',2,'POINT')}则显示 .00
${#numbers.formatDecimal(num,1,'COMMA',2,'POINT')}则显示 0.00
COMMA:','(逗号)
POINT:‘.’(点)
域对象
三个域:request,session,application(servletContext)
用法:
request:<br/>
<span th:text="${#httpServletRequest.getAttribute('msg')}"></span><br/>
<span th:text="${#request.getAttribute('msg')}"></span><br/>
<span th:text="${msg}"></span><br/>
session:<br/>
<span th:text="${#httpSession.getAttribute('msg')}"></span><br/>
<span th:text="${#session.getAttribute('msg')}"></span><br/>
<span th:text="${session.msg}"></span><br/>
application:<br/>
<span th:text="${#servletContext.getAttribute('msg')}"></span><br/>
<span th:text="${application.msg}"></span><br/>
0x0x_补充一些概念
国际化
国际化,也叫 i18n,为啥叫这个名字呢?因为国际化英文是 internationalization ,在 i 和 n 之间有 18 个字母,所以叫 i18n。我们的应用如果做了国际化就可以在不同的语言环境下,方便的进行切换,最常见的就是中文和英文之间的切换,国际化这个功能也是相当的常见。
在 Spring 中,就通过 AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver 对国际化提供了支持,开发者通过简单配置,就可以在项目中直接使用国际化功能了。
这一支持,在 Spring Boot 中得到进一步的简化,在 Spring Boot 中,我们也可以通过寥寥数行代码就能方便的实现国际化功能,接下来松哥就来和大家说一说 Spring Boot 中的国际化。
项目中的国际化我们往往需要多方面的支持,例如后端做国际化、前端页面也要做国际化,共同搭配,才能真正实现国际化的功能。
Thymeleaf缓存区
还记得之前提到的在application.yaml中提到的配置吗?
spring:
# 模版引擎thymeleaf
thymeleaf:
cache: false
cache是thymeleaf带有的一个缓存区,我们将它设置为false即可不需要每次重启服务,直接刷新界面就可以(但要注意服务端的代码修改的话还是需要重启服务器)
但也不要一味的认为cache的设置就是麻烦的,它主要的作用是要在项目上线时设置为true(不设置默认为true),这样它会提供一个缓存区,不用每次都向服务器请求数据,可以有效的提高响应速度.
重定向和请求转发的区别(路径的书写问题)
其实这个在学习JSP/Servlet的时候一定会接触:
1)当我们的url地址没有以"/“开头时,默认这个内容要替换到现在地址栏url最后一个”/"后的内容进行拼接.
2)请求转发:return “forward:doGoodsUI”;
重定向:return “redirect:/goods/doGoodsUI”;
请求转发由于是服务端内部转发所以可以不写"/“,直接跳转;
而重定向由于是二次请求二次响应,且可以跳转至别的资源甚至是别的服务器,所以需要写绝对地址,必须以”/"开头!
thymeleaf内置对象列表
见链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a1a677c2599b
模版引擎总结
3种模版引擎:JSP,FreeMarker,Thymeleaf
jsp
优点:
1、功能强大,可以写java代码
2、支持jsp标签(jsp tag)
3、支持表达式语言(el)
4、官方标准,用户群广,丰富的第三方jsp标签库
缺点:
性能问题。不支持前后端分离
freemarker
FreeMarker是一个用Java语言编写的模板引擎,它基于模板来生成文本输出。FreeMarker与Web容器无关,即在Web运行时,它并不知道Servlet或HTTP。它不仅可以用作表现层的实现技术,而且还可以用于生成XML,JSP或Java 等。
目前企业中:主要用Freemarker做静态页面或是页面展示
优点:
1、不能编写java代码,可以实现严格的mvc分离
2、性能非常不错
3、对jsp标签支持良好
4、内置大量常用功能,使用非常方便
5、宏定义(类似jsp标签)非常方便
6、使用表达式语言
缺点:
1、不是官方标准
2、用户群体和第三方标签库没有jsp多
Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf是个XML/XHTML/HTML5模板引擎,可以用于Web与非Web应用。
Thymeleaf的主要目标在于提供一种可被浏览器正确显示的、格式良好的模板创建方式,因此也可以用作静态建模。你可以使用它创建经过验证的XML与HTML模板。相对于编写逻辑或代码,开发者只需将标签属性添加到模板中即可。接下来,这些标签属性就会在DOM(文档对象模型)上执行预先制定好的逻辑。Thymeleaf的可扩展性也非常棒。你可以使用它定义自己的模板属性集合,这样就可以计算自定义表达式并使用自定义逻辑。这意味着Thymeleaf还可以作为模板引擎框架。
优点:静态html嵌入标签属性,浏览器可以直接打开模板文件,便于前后端联调。springboot官方推荐方案。
缺点:模板必须符合xml规范
除此以外,现在的趋势是前后端分离,比如前端用VUE。
网页静态化技术
FreeMarker用于网页静态化技术最多。
使用方法将页面转换成静态页面的过程(本文主要介绍了其中的一种:模板技术(FreeMarker))
页面静态化是以空间换时间的方式,在添加和修改对象时就生成静态页面,访问时实际访问的是一个静态页面
优点
- (1)降低查询数据库的次数,减轻数据库的压力,从而提高查询效率
- (2)响应速度快,可以提高用户的体验
页面静态化的编程步骤
(1)导入FreeMarker.jar
(2)获取模板(Template)对象
(3)准备数据
(4)template.process() 生成静态资源
(5)创建xxx.ftl静态化页面模板
(6)测试运行