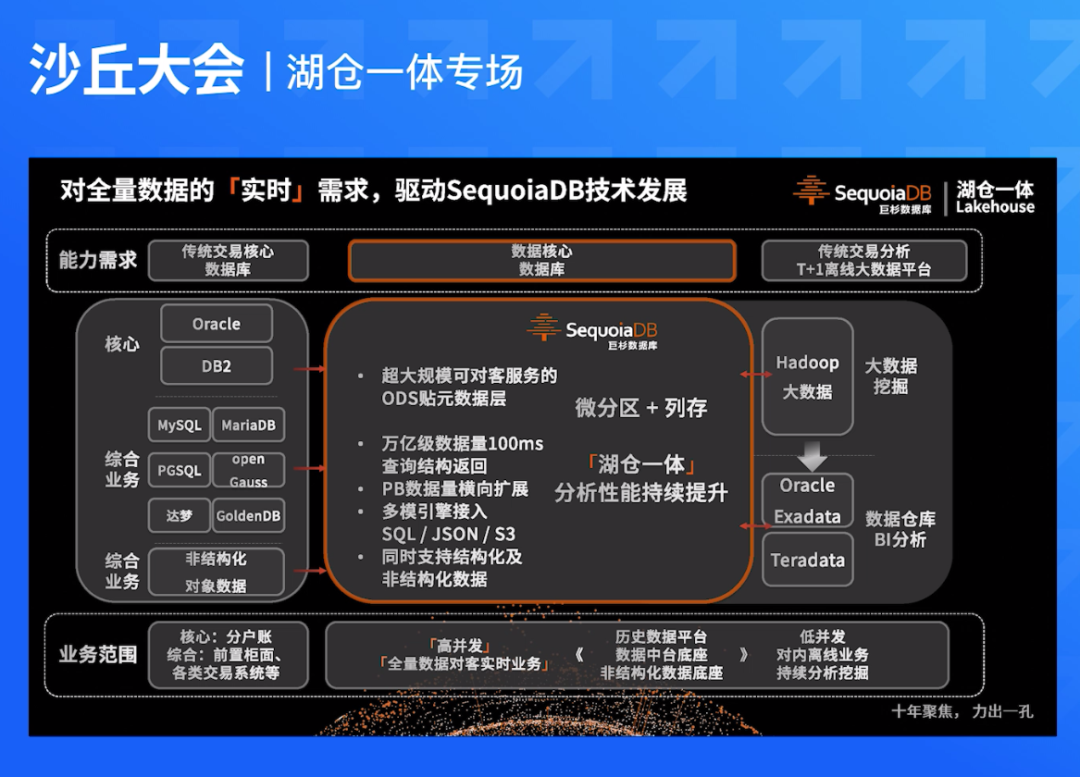
最近,看到很多轻量化工作是基于RepVGG改进而来,决定重新回顾一下RepVGG,并在此记录一些理解与心得。
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.03697
Introduction
RepVGG通过结构重参数化思想,让训练网络的多路结构(多分支模型训练时的优势——性能高)转换为推理网络的单路结构(模型推理时的好处——速度快、省内存),从而达到推理速度快与模型性能高兼备的效果。
Method
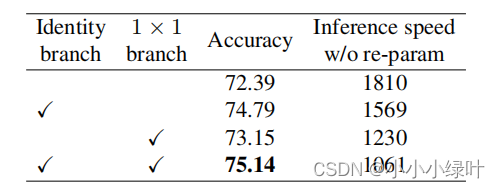
根据Resnet与Inception等论文论证,与单路直筒结构相比,增加shortcut与muti-branch可以提高模型的性能,RepVGG在VGG的基础上做了相关实验,从下表中可以发现,Identity branch与1x1 branch能够提高准确率,但同时推理时间也延长了许多。
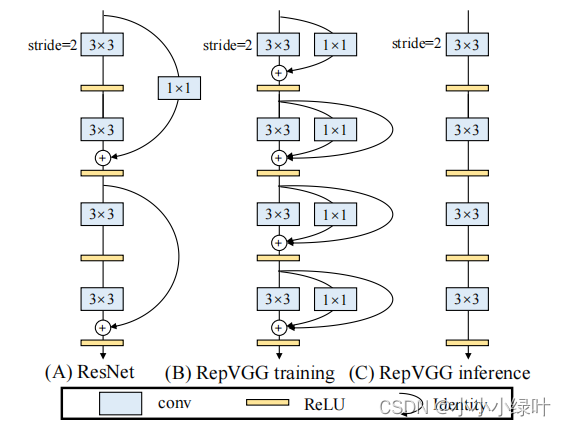
为了在保证模型精度的基础上,降低模型推理时间,RepVGG采用了结构重构的方法,即在训练时使用复杂结构,而测试时将复杂模型重构成单路直筒型模型,如下图所示。图B中,RepVGG在training时加入了shortcut和1x1 branch,而在test时,RepVGG重构成直筒型VGG模型,如图c。
Re-param for Plain Inference-time Model
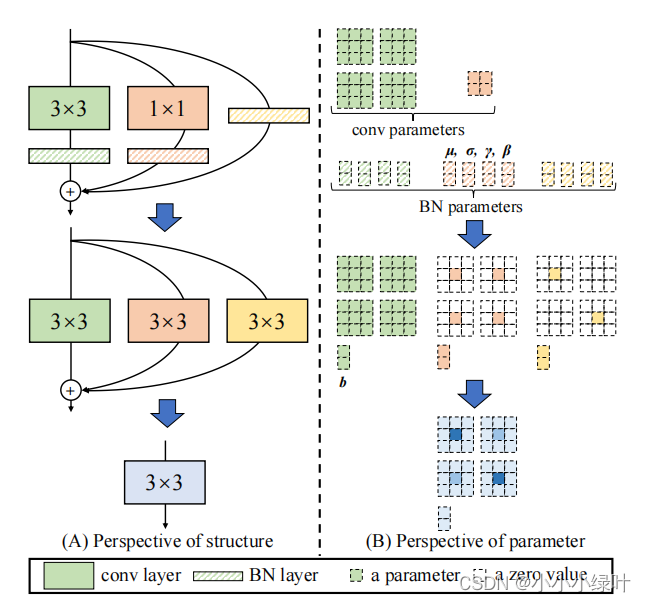
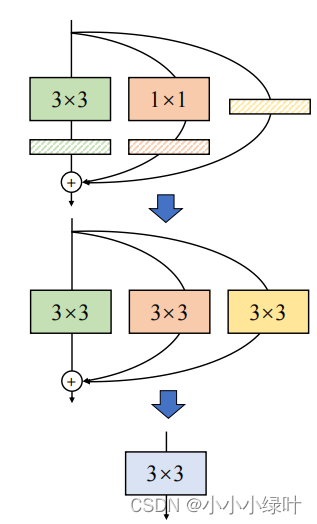
如下图所示,我们的目的是将带有BN层的3x3卷积与1x1卷积以及Identity mapping融合成一个3x3卷积,如何融合呢?操作分为两部:1.融合conv与bn;2.合并卷积。
1.Merge BN and Conv together

2. Fuse 3x3conv 1x1conv and identity
假设输入特征尺寸为(1x2x3x3),输出特征尺寸为输入相同,stride=1,那么conv3x3的卷积过程如下图所示,conv的特征尺寸为(2x2x3x3),首先对输入扩边,padding=kernel_size // 2,然后从左上角开始滑动窗口,最后获得右边的输出特征。
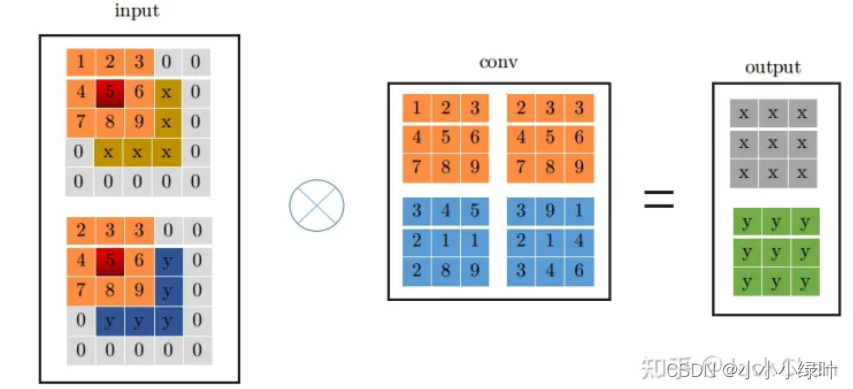
conv_1x1的卷积相较于3x3卷积更为简单,只需要将卷积参数与对应的单个输入参数相乘再相加。
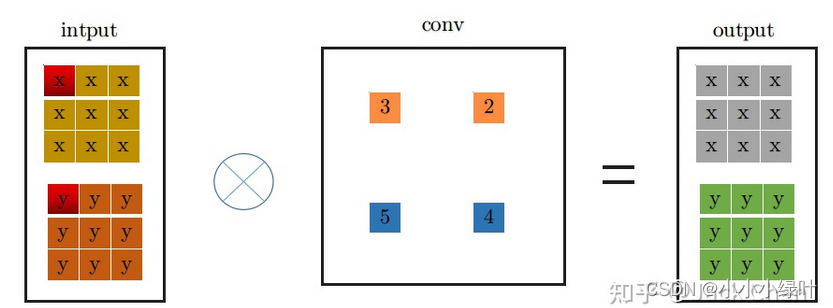
为了使conv_1x1可以与conv_3x3线性相加,我们可以将conv_1x1的1x1卷积核扩边成3x3的卷积核,这样形式上就可以变成conv_3x3,同时,结果与conv_1x1一致。
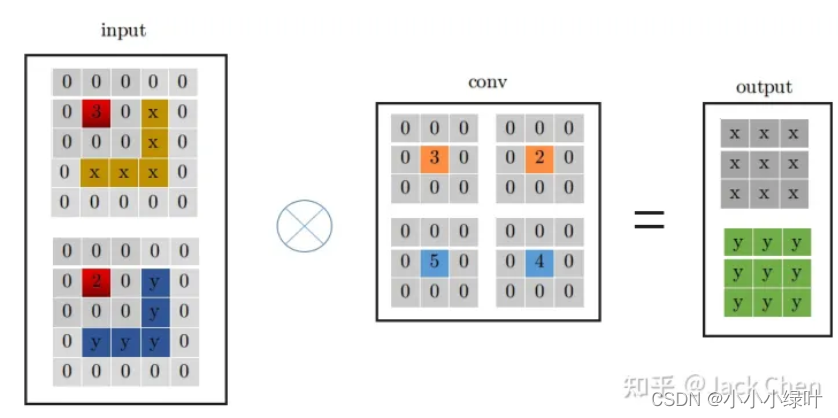
同样,Identity mapping可以看作特殊的conv_1x1,参数是固定的,即输入特征的某一层对应的卷积参数为1,其余均为0。我们可以按照上面介绍的conv_1x1与conv_3x3转化方式,将Identity mapping转化成conv_3x3的形式,如下图所示。
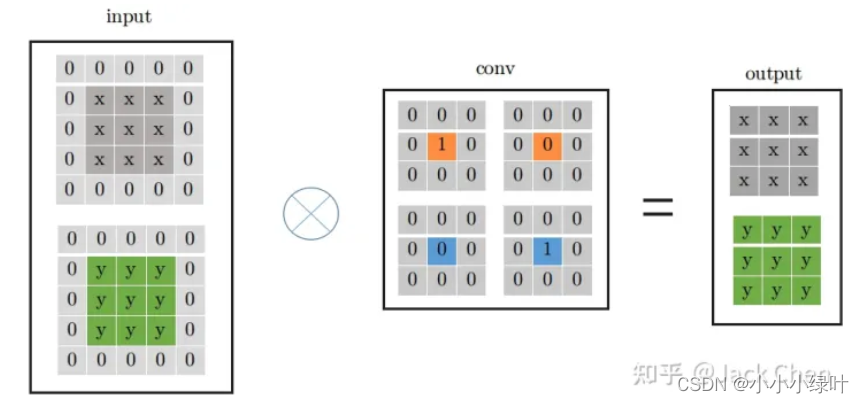
如此,我们就可以将带有BN层的3x3卷积与1x1卷积以及Identity mapping融合成一个3x3卷积。
code
我们看一下代码如何实现RepVGG,首先,我们看到deploy的控制Flag,当depoly为False时,模型处于training状态,结构没有重参化,当deploy为True时,模型处于test状态,需要对结构重参。
结构重参时,需要调用switch_to_deploy(),该函数的作用是调用self.get_equivalent_kernel_bias()获得重构后的kernel, bias, 对重构卷积赋值–self.rbr_reparam = nn.Conv2d,其中Conv2d的参数是kernel,偏移是bias,将参数detach脱离计算图,并删除其余卷积操作内存(否则无法正常运行)。
get_equivalent_kernel_bias(self):逻辑很简单,分为两部:1.调用self._fuse_bn_tensor()将conv与bn融合。需要注意的是,identity没有conv,只有BN操作,所以在self._fuse_bn_tensor()函数中需要构造卷积kernel,kernel_value[i, i % input_dim, 1, 1] = 1,需要注意分组卷积的形式。函数的返回值 return kernel3x3 + self._pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(kernel1x1) + kernelid, bias3x3 + bias1x1 + biasid
class RepVGGBlock(nn.Module):
'''RepVGGBlock is a basic rep-style block, including training and deploy status
This code is based on https://github.com/DingXiaoH/RepVGG/blob/main/repvgg.py
'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1, padding_mode='zeros', deploy=False, use_se=False):
super(RepVGGBlock, self).__init__()
""" Initialization of the class.
Args:
in_channels (int): Number of channels in the input image
out_channels (int): Number of channels produced by the convolution
kernel_size (int or tuple): Size of the convolving kernel
stride (int or tuple, optional): Stride of the convolution. Default: 1
padding (int or tuple, optional): Zero-padding added to both sides of
the input. Default: 1
dilation (int or tuple, optional): Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
groups (int, optional): Number of blocked connections from input
channels to output channels. Default: 1
padding_mode (string, optional): Default: 'zeros'
deploy: Whether to be deploy status or training status. Default: False
use_se: Whether to use se. Default: False
"""
self.deploy = deploy
self.groups = groups
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
assert kernel_size == 3
assert padding == 1
padding_11 = padding - kernel_size // 2
self.nonlinearity = nn.ReLU()
if use_se:
raise NotImplementedError("se block not supported yet")
else:
self.se = nn.Identity()
if deploy:
self.rbr_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=True, padding_mode=padding_mode)
else:
self.rbr_identity = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=in_channels) if out_channels == in_channels and stride == 1 else None
self.rbr_dense = conv_bn(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=groups)
self.rbr_1x1 = conv_bn(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, padding=padding_11, groups=groups)
def forward(self, inputs):
'''Forward process'''
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_reparam'):
return self.nonlinearity(self.se(self.rbr_reparam(inputs)))
if self.rbr_identity is None:
id_out = 0
else:
id_out = self.rbr_identity(inputs)
return self.nonlinearity(self.se(self.rbr_dense(inputs) + self.rbr_1x1(inputs) + id_out))
def get_equivalent_kernel_bias(self):
kernel3x3, bias3x3 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_dense)
kernel1x1, bias1x1 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_1x1)
kernelid, biasid = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_identity)
return kernel3x3 + self._pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(kernel1x1) + kernelid, bias3x3 + bias1x1 + biasid
def _pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(self, kernel1x1):
if kernel1x1 is None:
return 0
else:
return torch.nn.functional.pad(kernel1x1, [1, 1, 1, 1])
def _fuse_bn_tensor(self, branch):
if branch is None:
return 0, 0
if isinstance(branch, nn.Sequential):
kernel = branch.conv.weight
running_mean = branch.bn.running_mean
running_var = branch.bn.running_var
gamma = branch.bn.weight
beta = branch.bn.bias
eps = branch.bn.eps
else:
assert isinstance(branch, nn.BatchNorm2d)
if not hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
input_dim = self.in_channels // self.groups
kernel_value = np.zeros((self.in_channels, input_dim, 3, 3), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(self.in_channels):
kernel_value[i, i % input_dim, 1, 1] = 1
self.id_tensor = torch.from_numpy(kernel_value).to(branch.weight.device)
kernel = self.id_tensor
running_mean = branch.running_mean
running_var = branch.running_var
gamma = branch.weight
beta = branch.bias
eps = branch.eps
std = (running_var + eps).sqrt()
t = (gamma / std).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1)
return kernel * t, beta - running_mean * gamma / std
def switch_to_deploy(self):
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_reparam'):
return
kernel, bias = self.get_equivalent_kernel_bias()
self.rbr_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.rbr_dense.conv.in_channels, out_channels=self.rbr_dense.conv.out_channels,
kernel_size=self.rbr_dense.conv.kernel_size, stride=self.rbr_dense.conv.stride,
padding=self.rbr_dense.conv.padding, dilation=self.rbr_dense.conv.dilation, groups=self.rbr_dense.conv.groups, bias=True)
self.rbr_reparam.weight.data = kernel
self.rbr_reparam.bias.data = bias
for para in self.parameters():
para.detach_()
self.__delattr__('rbr_dense')
self.__delattr__('rbr_1x1')
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_identity'):
self.__delattr__('rbr_identity')
if hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
self.__delattr__('id_tensor')
self.deploy = True
Drawback
在RepVGG中存在一个致命的缺点,我们知道RepVGG是为了轻量化而生,但是结构重参导致模型参数方差较大,从而引起量化误差,实验证明,RepVGG通过训练后量化会将准确率降低20%,与此同时,由于特殊的training与test结构差异,RepVGG很难进行感知量化训练。为了对量化友好,Repopt提出了很好的思路解决这个问题,我们下篇继续介绍Repopt。
![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计-高中辅助教学系统-(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/357aeed419f44f4b82182fc63c14c2b0.png)
![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django电商小程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7b33af2b994d4196938bf1f0e9188993.png)