环境配置:
ubuntu20.04 LTS
ROS noetic
编程工具:vs code,远程通过ssh访问
扫描仪:YDLidar-G4
YDLidar驱动:
YDLidar SDK
YDLidar ROS 功能包
1 . YDLidar-SDK通信协议
雷达扫描输出的数据以十六进制格式输出到通信接口。
无强度字节偏移的数据包格式:(12字节)
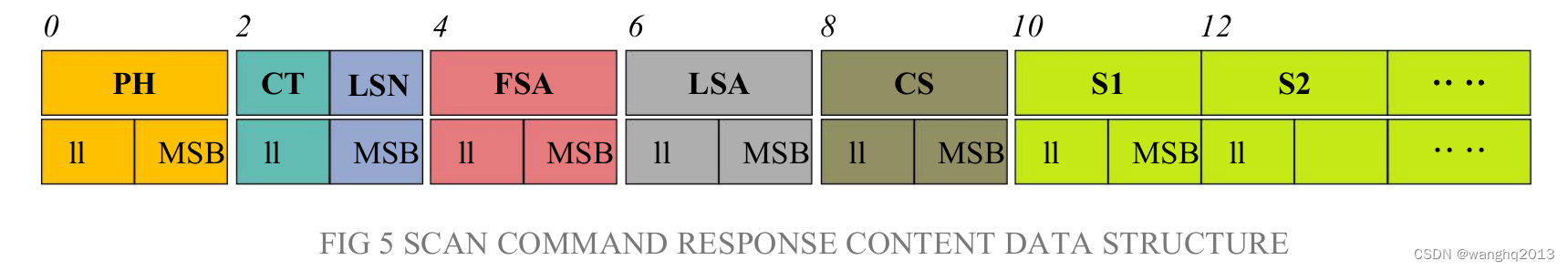
有强度字节偏移的数据包格式:(13字节)
 雷达扫描输出数据格式表:
雷达扫描输出数据格式表:
| 内容 | 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| H(2B) | Packet header | 2 Byte in length, Fixed at 0x55AA, low is front, high in back. |
| CT(1B) | Package type | Indicates the current packet type. (0x00 = CT & 0x01): Normal Point cloud packet. (0x01 = CT & 0x01): Zero packet. |
| LSN(1B) | Sample Data Number | ndicates the number of sampling points contained in the current packet. There is only once zero point of data in thre zero packet. the value is 1. |
| FSA(2B) | Starting angle | The angle data corresponding to the first sample point in the smapled data. |
| LSA(2B) | End angle | The angle data corresponding to the last sample point in the sampled data. |
| CS(2B) | Check code | The check code of the current data packet uses a two-byte exclusive OR to check the current data packet. |
| Si(2B/3B) | Sampling data | The system test sampling data is the distance data of the sampling point. Note: If the LiDAR has intensity, Si is 3 Byte. otherwise is 2 Byte. Si(3B)–>I(1B)(D(2B)): first Byte is Inentsity, The last two bytes are the Distance. |
Zero resolution
Start data packet: (CT & 0x01) = 0x01, LSN = 1, Si = 1.
scan frequency: When it was a zero packet, The Lidar Scan frequency: SF = (CT >> 1) / 10.f; The Calculated frequency is the Lidar real-time frequency of the previous frame. If SF is non-zero, the protocol has real-time frequency.
Distance analysis:
Distance solution formula:
Triangle LiDAR: Distance(i) = Si / 4;
TOF LiDAR: Distance(i) = Si;
Intensity analysis:
Si(3B) split into three bytes : S(0) S(1) S(2)
Inensity solution formula:
Triangle LiDAR:
Intensity(i) = uint16_t((S(1) & 0x03)<< 8 | S(0));
Distance(i) = uint16_t(S(2) << 8 | S(1)) >> 2;
Angle analysis:(4字节)
First level analysis:
Starting angle solution formula:
A
n
g
l
e
F
S
A
=
R
s
h
i
f
t
b
i
t
(
F
S
A
,
1
)
64
Angle_{FSA}=\frac{Rshiftbit(FSA, 1)}{64}
AngleFSA=64Rshiftbit(FSA,1)
End angle solution formula:
A
n
g
l
e
L
S
A
=
R
s
h
i
f
t
b
i
t
(
L
S
A
,
1
)
64
Angle_{LSA}=\frac{Rshiftbit(LSA, 1)}{64}
AngleLSA=64Rshiftbit(LSA,1)
Intermediate angle solution formula:
A
n
g
l
e
i
=
d
i
f
f
(
A
n
g
l
e
)
L
S
N
−
1
∗
i
+
A
n
g
l
e
F
S
A
(
0
,
1
,
…
,
L
S
N
−
1
)
Angle_{i}=\frac{diff(Angle)}{LSN - 1}*i + Angle_{FSA} (0,1,\ldots,LSN-1)
Anglei=LSN−1diff(Angle)∗i+AngleFSA(0,1,…,LSN−1)
A
n
g
l
e
0
:
A
n
g
l
e
F
S
A
Angle_{0} : Angle_{FSA}
Angle0:AngleFSA;
A
n
g
l
e
L
S
N
−
1
:
A
n
g
l
e
L
S
A
Angle_{LSN-1} : Angle_{LSA}
AngleLSN−1:AngleLSA;
Rshiftbit(data,1) means shifting the data to the right by one bit.
diff Angle means the clockwise angle difference from the starting angle (uncorrected value) to the ending angle (uncorrected value),and LSN represents the number of packet samples in this frame.
diff(Angle):
(
A
n
g
l
e
(
L
S
A
)
−
A
n
g
l
e
(
F
S
A
)
)
(Angle(LSA) - Angle(FSA))
(Angle(LSA)−Angle(FSA));
If less than zero,
d
i
f
f
(
A
n
g
l
e
)
=
(
A
n
g
l
e
(
L
S
A
)
−
A
n
g
l
e
(
F
S
A
)
)
+
360
diff(Angle) = (Angle(LSA)- Angle(FSA)) + 360
diff(Angle)=(Angle(LSA)−Angle(FSA))+360 ,
otherwise
d
i
f
f
(
A
n
g
l
e
)
=
(
A
n
g
l
e
(
L
S
A
)
−
A
n
g
l
e
(
F
S
A
)
)
diff(Angle) = (Angle(LSA)- Angle(FSA))
diff(Angle)=(Angle(LSA)−Angle(FSA)).
double Angle_FSA = (FSA >> 1) / 64;
double Angle_LSA = (LSA >> 1) / 64;
double angle_diff = Angle_LSA - Angle_FSA;
if(angle_diff < 0) {
angle_diff += 360;
}
double Angle[LSN];
for(int i = 0; i < LSN; i++) {
if(LSN > 1) {
Angle[i] = i* angle_diff / (LSN - 1) + Angle_FSA;
} else {
Angle[i] = Angle_FSA;
}
}
Second-level analysis:
Triangle Lidar only has current Second-level analysis, TOF Lidar does not need.
Angle correction formula:
A
n
g
l
e
i
=
A
n
g
l
e
i
+
A
n
g
C
o
r
r
e
c
t
i
Angle_{i} = Angle_{i} + AngCorrect_{i}
Anglei=Anglei+AngCorrecti; (
1
,
2
,
…
,
L
S
N
1,2,\ldots,LSN
1,2,…,LSN)
AngCorrect is the angle correction value, and its calculation formula is as follows,
t
a
n
−
1
tan^{-1}
tan−1 is an inverse trigonometric function. and the return angle value is:
if(
D
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
i
Distance_{i}
Distancei == 0)
{
A
n
g
C
o
r
r
e
c
t
i
AngCorrect_{i}
AngCorrecti = 0;
}
else
{
A
n
g
C
o
r
r
e
c
t
i
=
a
t
a
n
(
21.8
∗
155.3
−
D
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
i
155.3
∗
D
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
i
)
∗
(
180
/
3.1415926
)
AngCorrect_{i} = atan(21.8 * \frac{155.3 - Distance_{i}}{155.3*Distance_{i}}) * (180/3.1415926)
AngCorrecti=atan(21.8∗155.3∗Distancei155.3−Distancei)∗(180/3.1415926);
}
For example, In the data packet, the 4th to 8th bytes are 28 E5 6F BD 79, so LSN = 0x28 = 40(dec), FSA = 0x6FE5, LSA = 0x79BD, and bring in the first-level solution formula, and get:
A
n
g
l
e
F
S
A
=
223.7
8
°
Angle_{FSA} = 223.78^{°}
AngleFSA=223.78°
A
n
g
l
e
L
S
A
=
243.4
7
°
Angle_{LSA} = 243.47^{°}
AngleLSA=243.47°
d
i
f
f
(
A
n
g
l
e
)
=
A
n
g
l
e
L
S
A
−
A
n
g
l
e
F
S
A
=
243.4
7
°
−
223.7
8
°
=
19.6
9
°
diff(Angle) = Angle_{LSA} - Angle_{FSA} = 243.47^{°} - 223.78^{°} = 19.69^{°}
diff(Angle)=AngleLSA−AngleFSA=243.47°−223.78°=19.69°
A
n
g
l
e
i
=
19.6
9
°
39
∗
(
i
−
1
)
+
223.7
8
°
Angle_{i} = \frac{19.69^{°}}{39}*(i -1) + 223.78^{°}
Anglei=3919.69°∗(i−1)+223.78° (
1
,
2
,
…
,
L
S
N
1,2,\ldots,LSN
1,2,…,LSN)
Assume that in the frame data:
D
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
1
=
1000
Distance_{1} = 1000
Distance1=1000
D
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
L
S
N
=
8000
Distance_{LSN} = 8000
DistanceLSN=8000
bring in the second-level solution formula, you get:
A
n
g
C
o
r
r
e
c
t
1
=
−
6.762
2
°
AngCorrect_{1} = -6.7622^{°}
AngCorrect1=−6.7622°
A
n
g
C
o
r
r
e
c
t
L
S
N
=
−
7.837
4
°
AngCorrect_{LSN} = -7.8374^{°}
AngCorrectLSN=−7.8374°
A
n
g
l
e
F
S
A
=
A
n
g
l
e
1
+
A
n
g
C
o
r
r
e
c
t
1
=
217.017
8
°
Angle_{FSA} = Angle_{1} + AngCorrect_{1} = 217.0178^{°}
AngleFSA=Angle1+AngCorrect1=217.0178°
A
n
g
l
e
L
S
A
=
A
n
g
l
e
L
S
A
+
A
n
g
C
o
r
r
e
c
t
L
S
A
=
235.632
6
°
Angle_{LSA} = Angle_{LSA} + AngCorrect_{LSA} = 235.6326^{°}
AngleLSA=AngleLSA+AngCorrectLSA=235.6326°
Similarly,
A
n
g
l
e
i
(
2
,
3
,
…
,
L
S
N
−
1
)
Angle_{i}(2,3, \ldots,LSN-1)
Anglei(2,3,…,LSN−1), can be obtained sequentially.
for(int i = 0; i < LSN; i++) {
if(Distance[i] > 0) {
double AngCorrect = atan(21.8 * (155.3 - Distance[i]) / (155.3 * Distance[i]));
Angle[i] += AngCorrect * 180 / M_PI;//degree
}
if(Angle[i] >= 360) {
Angle[i] -= 360;
}
}
Note: TOF LiDAR does not neeed second-level analysis.
Check code parsing:
The check code uses a two-byte exclusive OR to verify the
current data packet. The check code itself does not participate in
XOR operations, and the XOR order is not strictly in byte order.
Therefore, the check code solution formula is:
C
S
=
X
O
R
∑
i
=
1
n
(
C
i
)
CS = XOR \sum_{i=1}^{n}(C^i)
CS=XORi=1∑n(Ci)
No intensity Si(2B):
uint16_t checksumcal = PH;
checksumcal ^= FSA;
for(int i = 0; i < 2 * LSN; i = i +2 ) {
checksumcal ^= uint16_t(data[i+1] <<8 | data[i]);
}
checksumcal ^= uint16_t(LSN << 8 | CT);
checksumcal ^= LSA;
## uint16_t : unsigned short
Intensity Si(3B):
uint16_t checksumcal = PH;
checksumcal ^= FSA;
for(int i = 0; i < 3 * LSN; i = i + 3) {
checksumcal ^= data[i];
checksumcal ^= uint16_t(data[i+2] <<8 | data[i + 1]);
}
checksumcal ^= uint16_t(LSN << 8 | CT);
checksumcal ^= LSA;
## uint16_t : unsigned short
example
No Intensity:

uint8_t Buffer[12];
Buffer[0] = 0xAA;
Buffer[1] = 0x55;
Buffer[2] = 0x01;
Buffer[3] = 0x01;
Buffer[4] = 0x53;
Buffer[5] = 0xAE;
Buffer[6] = 0x53;
Buffer[7] = 0xAE;
Buffer[8] = 0xAB;
Buffer[9] = 0x54;
Buffer[10] = 0x00;
Buffer[11] = 0x00;
uint16_t check_code = 0x55AA;
uint8_t CT = Buffer[2] & 0x01;
uin8_t LSN = Buffer[3];
uint16_t FSA = uint16_t(Buffer[5] << 8 | Buffer[4]);
check_code ^= FSA;
uint16_t LSA = uint16_t(Buffer[7] << 8 | Buffer[6]);
uint16_t CS = uint16_t(Buffer[9] << 8 | Buffer[8]);
double Distance[LSN];
for(int i = 0; i < 2 * LSN; i = i + 2) {
uint16_t data = uint16_t(Buffer[10 + i + 1] << 8 | Buffer[10 + i]);
check_code ^= data;
Distance[i / 2 ] = data / 4;
}
check_code ^= uint16_t(LSN << 8 | CT);
check_code ^= LSA;
double Angle[LSN];
if(check_code == CS) {
double Angle_FSA = (FSA >> 1) / 64;
double Angle_LSA = (LSA >> 1) / 64;
double Angle_Diff = (Angle_LSA - Angle_FSA);
if(Angle_Diff < 0) {
Angle_Diff = Angle_Diff + 360;
}
for(int i = 0; i < LSN; i++) {
if(LSN > 1) {
Angle[i] = i * Angle_Diff/ (LSN- 1) + Angle_FSA;
} else {
Angle[i] = Angle_FSA;
}
if(Distance[i] > 0) {
double AngCorrect = atan(21.8 * (155.3 - Distance[i]) / (155.3 * Distance[i]));
Angle[i] = Angle[i] + AngCorrect * 180 / M_PI;
}
if(Angle[i] >= 360) {
Angle[i] -= 360;
}
}
}
Intensity:

uint8_t Buffer[13];
Buffer[0] = 0xAA;
Buffer[1] = 0x55;
Buffer[2] = 0x01;
Buffer[3] = 0x01;
Buffer[4] = 0x53;
Buffer[5] = 0xAE;
Buffer[6] = 0x53;
Buffer[7] = 0xAE;
Buffer[8] = 0xAB;
Buffer[9] = 0x54;
Buffer[10] = 0x00;
Buffer[11] = 0x00;
Buffer[12] = 0x00;
uint16_t check_code = 0x55AA;
uint8_t CT = Buffer[2] & 0x01;
uin8_t LSN = Buffer[3];
uint16_t FSA = uint16_t(Buffer[5] << 8 | Buffer[4]);
check_code ^= FSA;
uint16_t LSA = uint16_t(Buffer[7] << 8 | Buffer[6]);
uint16_t CS = uint16_t(Buffer[9] << 8 | Buffer[8]);
double Distance[LSN];
uin16_t Itensity[LSN];
for(int i = 0; i < 3 * LSN; i = i + 3) {
check_code ^= Buffer[10 + i];
uint16_t data = uint16_t(Buffer[10 + i + 2] << 8 | Buffer[10 + i + 1]);
check_code ^= data;
Itensity[i / 3] = uint16_t((Buffer[10 + i + 1] & 0x03) <<8 | Buffer[10 + i]);
Distance[i / 3] = data >> 2;
}
check_code ^= uint16_t(LSN << 8 | CT);
check_code ^= LSA;
double Angle[LSN];
if(check_code == CS) {
double Angle_FSA = (FSA >> 1) / 64;
double Angle_LSA = (LSA >> 1) / 64;
double Angle_Diff = (Angle_LSA - Angle_FSA);
if(Angle_Diff < 0) {
Angle_Diff = Angle_Diff + 360;
}
for(int i = 0; i < LSN; i++) {
if(LSN > 1) {
Angle[i] = i * Angle_Diff/ (LSN- 1) + Angle_FSA;
} else {
Angle[i] = Angle_FSA;
}
if(Distance[i] > 0) {
double AngCorrect = atan(21.8 * (155.3 - Distance[i]) / (155.3 * Distance[i]));
Angle[i] = Angle[i] + AngCorrect * 180 / M_PI;
}
}
}
1 )编译过程
创建一个工作空间,把雷达SDK驱动和雷达ROS功能包下载到工作空间的src目录。然后catkin_make编译安装。
mkdir -p ydlidar_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/YDLIDAR/YDLidar-SDK.git
git clone https://github.com/YDLIDAR/ydlidar_ros_driver.git
cd ..
catkin_make
由于SDK驱动支持C++外,还支持PYTHON语言,所以,编译前可能需要先安装swig、python3-pip和python。
编译后,生成 ydlidar_ros_driver包中的ydlidar_ros_driver_node。
然后,环境变量设置:
echo "source ~/ydlidar_ws/devel/setup.bash">> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
运行(对于 YDLidar-G4):
roslaunch ydlidar_ros2_driver ydlidar_view.launch
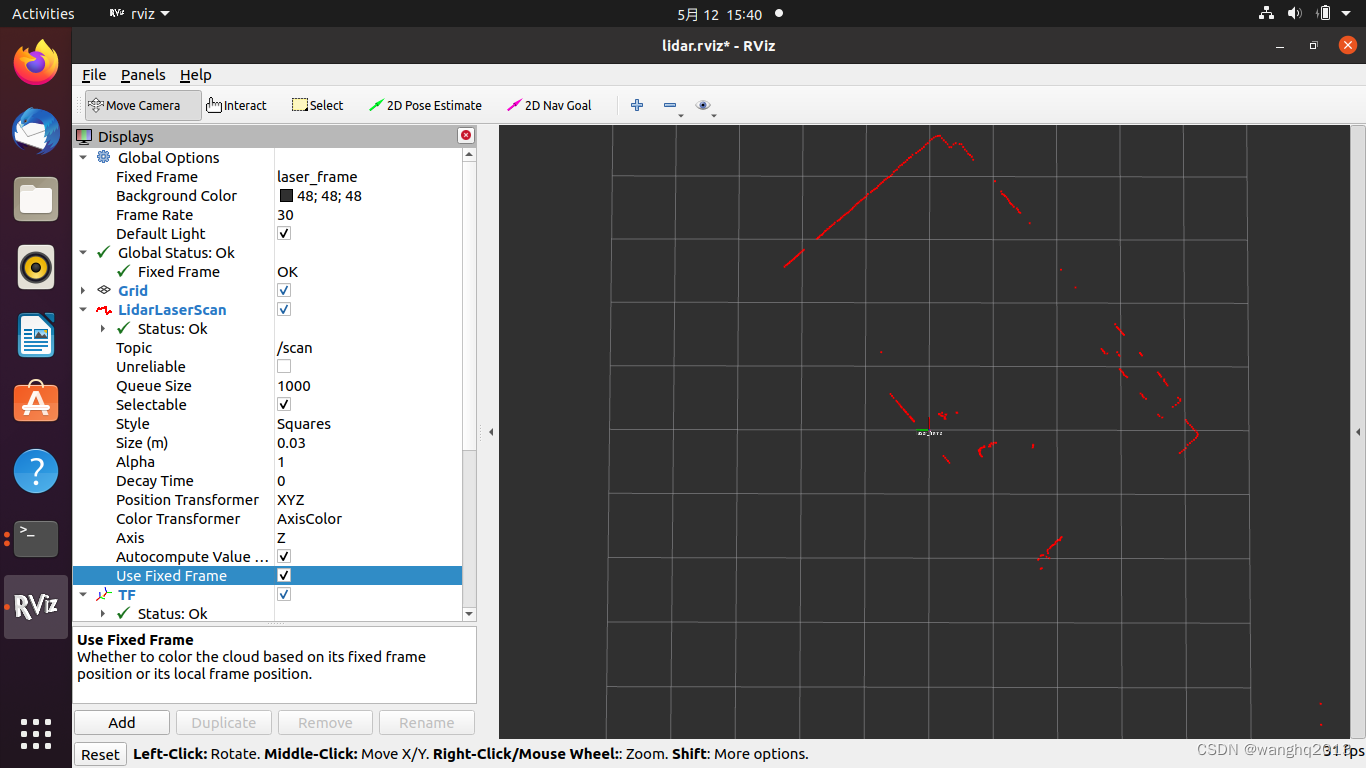 2) 源码分析
2) 源码分析
SDK的驱动源码由core/base|common|math|network|serial 几个部分组成:
core
│ ├── base
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── datatype.h
│ │ ├── locker.h
│ │ ├── thread.h
│ │ ├── timer.cpp
│ │ ├── timer.h
│ │ ├── typedef.h
│ │ ├── utils.h
│ │ ├── v8stdint.h
│ │ └── ydlidar.h
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── common
│ │ ├── ChannelDevice.h
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── DriverInterface.h
│ │ ├── ydlidar_datatype.h
│ │ ├── ydlidar_def.cpp
│ │ ├── ydlidar_def.h
│ │ ├── ydlidar_help.h
│ │ └── ydlidar_protocol.h
│ ├── math
│ │ ├── angles.h
│ │ └── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── network
│ │ ├── ActiveSocket.cpp
│ │ ├── ActiveSocket.h
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── PassiveSocket.cpp
│ │ ├── PassiveSocket.h
│ │ ├── SimpleSocket.cpp
│ │ ├── SimpleSocket.h
│ │ └── StatTimer.h
│ └── serial
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── common.h
│ ├── impl
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── unix
│ │ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ │ ├── list_ports_linux.cpp
│ │ │ ├── lock.c
│ │ │ ├── lock.h
│ │ │ ├── unix.h
│ │ │ ├── unix_serial.cpp
│ │ │ └── unix_serial.h
│ │ └── windows
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── list_ports_win.cpp
│ │ ├── win.h
│ │ ├── win_serial.cpp
│ │ └── win_serial.h
│ ├── serial.cpp
│ └── serial.h
SDK驱动编译安装后,按照CMakeLists.txt配置,将被安装在/usr/local/目录下,包括头文件,库文件,文档和测试程序等。
.
├── bin
│ ├── etlidar_test.py
│ ├── et_test
│ ├── gs_test
│ ├── lidar_c_api_test
│ ├── plot_tof_test.py
│ ├── plot_ydlidar_test.py
│ ├── rosdepc
│ ├── sdm_test
│ ├── test.py
│ ├── tmini_test
│ ├── tof_test
│ ├── tof_test.py
│ ├── tri_and_gs_test
│ ├── tri_restart
│ ├── tri_test
│ └── ydlidar_test.py
├── etc
├── games
├── include
│ ├── core
│ │ ├── base
│ │ │ ├── datatype.h
│ │ │ ├── locker.h
│ │ │ ├── thread.h
│ │ │ ├── timer.h
│ │ │ ├── typedef.h
│ │ │ ├── utils.h
│ │ │ ├── v8stdint.h
│ │ │ └── ydlidar.h
│ │ ├── common
│ │ │ ├── ChannelDevice.h
│ │ │ ├── DriverInterface.h
│ │ │ ├── ydlidar_datatype.h
│ │ │ ├── ydlidar_def.h
│ │ │ ├── ydlidar_help.h
│ │ │ └── ydlidar_protocol.h
│ │ ├── math
│ │ │ └── angles.h
│ │ ├── network
│ │ │ ├── ActiveSocket.h
│ │ │ ├── PassiveSocket.h
│ │ │ ├── SimpleSocket.h
│ │ │ └── StatTimer.h
│ │ └── serial
│ │ ├── common.h
│ │ ├── impl
│ │ │ └── unix
│ │ │ ├── lock.h
│ │ │ ├── unix.h
│ │ │ └── unix_serial.h
│ │ └── serial.h
│ ├── src
│ │ ├── CYdLidar.h
│ │ ├── ETLidarDriver.h
│ │ ├── filters
│ │ │ ├── FilterInterface.h
│ │ │ └── NoiseFilter.h
│ │ ├── GS1LidarDriver.h
│ │ ├── GS2LidarDriver.h
│ │ ├── SDMLidarDriver.h
│ │ ├── YDlidarDriver.h
│ │ └── ydlidar_sdk.h
│ └── ydlidar_config.h
├── lib
│ ├── cmake
│ │ └── ydlidar_sdk
│ │ ├── ydlidar_sdkConfig.cmake
│ │ ├── ydlidar_sdkConfigVersion.cmake
│ │ └── ydlidar_sdkTargets.cmake
│ ├── libydlidar_sdk.a
│ ├── pkgconfig
│ │ └── YDLIDAR_SDK.pc
│ ├── python2.7
│ │ ├── dist-packages
│ │ │ ├── ydlidar.py
│ │ │ └── _ydlidar.so
│ │ └── site-packages
│ └── python3.8
│ └── dist-packages
│ ├── rosdepc
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── __pycache__
│ │ │ ├── __init__.cpython-38.pyc
│ │ │ └── rosdepc.cpython-38.pyc
│ │ └── rosdepc.py
│ └── rosdepc-1.0.2.dist-info
│ ├── entry_points.txt
│ ├── INSTALLER
│ ├── LICENSE
│ ├── METADATA
│ ├── RECORD
│ ├── top_level.txt
│ └── WHEEL
其中,startup目录下的initenv.sh,涉及/dev/ttyUSB*的识别,出问题较多。
#!/bin/bash
echo 'KERNEL=="ttyUSB*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="10c4", ATTRS{idProduct}=="ea60", MODE:="0666", GROUP:="dialout", SYMLINK+="ydlidar"' >/etc/udev/rules.d/ydlidar.rules
echo 'KERNEL=="ttyACM*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0483", ATTRS{idProduct}=="5740", MODE:="0666", GROUP:="dialout", SYMLINK+="ydlidar"' >/etc/udev/rules.d/ydlidar-V2.rules
echo 'KERNEL=="ttyUSB*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="067b", ATTRS{idProduct}=="2303", MODE:="0666", GROUP:="dialout", SYMLINK+="ydlidar"' >/etc/udev/rules.d/ydlidar-2303.rules
service udev reload
sleep 2
service udev restart
编译安装后,对于G4雷达生成对应的文件 “/etc/udev/rules.d/ydlidar.rules”,一般的,/dev/ttyUSB0对应于雷达ROS功能包中串口通信中的“port”参数,即:“dev/ydlidar”
vscode 调试源码时,配置文件:
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Linux",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**", #功能包头文件路径
"/usr/local/include/**", #SDK头文件路径
"/opt/ros/noetic/include/**" #ROS系统及消息头文件路径
],
"defines": [],
"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/gcc",
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "gnu++14",
"intelliSenseMode": "linux-gcc-x64"
}
],
"version": 4
}
雷达数据类型(LaserFan.msg):
std_msgs/Header header
float32 angle_min
float32 angle_max
float32 time_increment
float32 scan_time
float32 range_min
float32 range_max
float32[] angles
float32[] ranges
float32[] intensities
节点源码:
//ydlidar_ros_driver.cpp
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include "sensor_msgs/LaserScan.h"
#include "sensor_msgs/PointCloud.h"
//#include "ydlidar_ros_driver/LaserFan.h"
#include "std_srvs/Empty.h"
#include "src/CYdLidar.h"
#include "ydlidar_config.h"
#include <limits> // std::numeric_limits
#define SDKROSVerision "1.0.2"
CYdLidar laser;
bool stop_scan(std_srvs::Empty::Request &req,
std_srvs::Empty::Response &res) {
ROS_DEBUG("Stop scan");
return laser.turnOff();
}
bool start_scan(std_srvs::Empty::Request &req,
std_srvs::Empty::Response &res) {
ROS_DEBUG("Start scan");
return laser.turnOn();
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
ros::init(argc, argv, "ydlidar_ros_driver"); //节点初始化
ROS_INFO("YDLIDAR ROS Driver Version: %s", SDKROSVerision);
ros::NodeHandle nh; //声明一个ROS句柄
ros::Publisher scan_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::LaserScan>("scan", 1); //注册一个/scan话题的消息发布者
ros::Publisher pc_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud>("point_cloud",1);//注册一个/point_cloud话题的消息发布者
ros::NodeHandle nh_private("~"); //利用函数模板进行ROS对象的雷达属性设置
std::string str_optvalue = "/dev/ydlidar";
nh_private.param<std::string>("port", str_optvalue,"/dev/ydlidar");
///lidar port //雷达属性设置,对应于lidar.launch(For G4)中的参数
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSerialPort, str_optvalue.c_str(),
str_optvalue.size());
///ignore array
nh_private.param<std::string>("ignore_array", str_optvalue, "");
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropIgnoreArray, str_optvalue.c_str(),
str_optvalue.size());
std::string frame_id = "laser_frame";
nh_private.param<std::string>("frame_id", frame_id, "laser_frame");
//int property/
/// lidar baudrate
int optval = 230400;
nh_private.param<int>("baudrate", optval, 230400);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSerialBaudrate, &optval, sizeof(int));
/// tof lidar
optval = TYPE_TRIANGLE;
nh_private.param<int>("lidar_type", optval, TYPE_TRIANGLE);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropLidarType, &optval, sizeof(int));
/// device type
optval = YDLIDAR_TYPE_SERIAL;
nh_private.param<int>("device_type", optval, YDLIDAR_TYPE_SERIAL);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropDeviceType, &optval, sizeof(int));
/// sample rate
optval = 9;
nh_private.param<int>("sample_rate", optval, 9);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSampleRate, &optval, sizeof(int));
/// abnormal count
optval = 4;
nh_private.param<int>("abnormal_check_count", optval, 4);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropAbnormalCheckCount, &optval, sizeof(int));
//intensity bit count
optval = 10;
nh_private.param<int>("intensity_bit", optval, 10);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropIntenstiyBit, &optval, sizeof(int));
//bool property/
/// fixed angle resolution
bool b_optvalue = false;
nh_private.param<bool>("resolution_fixed", b_optvalue, true);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropFixedResolution, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));
/// rotate 180
nh_private.param<bool>("reversion", b_optvalue, true);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropReversion, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));
/// Counterclockwise
nh_private.param<bool>("inverted", b_optvalue, true);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropInverted, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));
b_optvalue = true;
nh_private.param<bool>("auto_reconnect", b_optvalue, true);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropAutoReconnect, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));
/// one-way communication
b_optvalue = false;
nh_private.param<bool>("isSingleChannel", b_optvalue, false);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSingleChannel, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));
/// intensity
b_optvalue = false;
nh_private.param<bool>("intensity", b_optvalue, false);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropIntenstiy, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));
/// Motor DTR
b_optvalue = false;
nh_private.param<bool>("support_motor_dtr", b_optvalue, false);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSupportMotorDtrCtrl, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));
//float property/
/// unit: °
float f_optvalue = 180.0f;
nh_private.param<float>("angle_max", f_optvalue, 180.f);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropMaxAngle, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));
f_optvalue = -180.0f;
nh_private.param<float>("angle_min", f_optvalue, -180.f);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropMinAngle, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));
/// unit: m
f_optvalue = 16.f;
nh_private.param<float>("range_max", f_optvalue, 16.f);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropMaxRange, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));
f_optvalue = 0.1f;
nh_private.param<float>("range_min", f_optvalue, 0.1f);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropMinRange, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));
/// unit: Hz
f_optvalue = 10.f;
nh_private.param<float>("frequency", f_optvalue, 10.f);
laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropScanFrequency, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));
bool invalid_range_is_inf = false;
nh_private.param<bool>("invalid_range_is_inf", invalid_range_is_inf,invalid_range_is_inf);
bool point_cloud_preservative = false;
nh_private.param<bool>("point_cloud_preservative", point_cloud_preservative,point_cloud_preservative);
//注册启停服务,绑定雷达启停回调函数
ros::ServiceServer stop_scan_service = nh.advertiseService("stop_scan",stop_scan);
ros::ServiceServer start_scan_service = nh.advertiseService("start_scan",start_scan);
// initialize SDK and LiDAR
bool ret = laser.initialize();//雷达初始化
if (ret) {//success
//Start the device scanning routine which runs on a separate thread and enable motor.
ret = laser.turnOn();
} else {
ROS_ERROR("%s\n", laser.DescribeError());
}
ros::Rate r(30);
while (ret && ros::ok()) {
LaserScan scan;
//雷达扫描和点云消息数据处理
if (laser.doProcessSimple(scan)) {
sensor_msgs::LaserScan scan_msg;
sensor_msgs::PointCloud pc_msg;
// ydlidar_ros_driver::LaserFan fan;
ros::Time start_scan_time;
start_scan_time.sec = scan.stamp / 1000000000ul;
start_scan_time.nsec = scan.stamp % 1000000000ul;
scan_msg.header.stamp = start_scan_time;
scan_msg.header.frame_id = frame_id;
pc_msg.header = scan_msg.header;
// fan.header = scan_msg.header;
scan_msg.angle_min = (scan.config.min_angle);
scan_msg.angle_max = (scan.config.max_angle);
scan_msg.angle_increment = (scan.config.angle_increment);
scan_msg.scan_time = scan.config.scan_time;
scan_msg.time_increment = scan.config.time_increment;
scan_msg.range_min = (scan.config.min_range);
scan_msg.range_max = (scan.config.max_range);
int size = (scan.config.max_angle - scan.config.min_angle) /
scan.config.angle_increment + 1;
scan_msg.ranges.resize(size,invalid_range_is_inf ? std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity() : 0.0);
scan_msg.intensities.resize(size);
pc_msg.channels.resize(2);
int idx_intensity = 0;
pc_msg.channels[idx_intensity].name = "intensities";
int idx_timestamp = 1;
pc_msg.channels[idx_timestamp].name = "stamps";
for (size_t i = 0; i < scan.points.size(); i++) {
int index = std::ceil((scan.points[i].angle - scan.config.min_angle) /scan.config.angle_increment);
if (index >= 0 && index < size) {
if (scan.points[i].range >= scan.config.min_range) {
scan_msg.ranges[index] = scan.points[i].range;
scan_msg.intensities[index] = scan.points[i].intensity;
}
}
if (point_cloud_preservative ||
(scan.points[i].range >= scan.config.min_range &&
scan.points[i].range <= scan.config.max_range)) {
geometry_msgs::Point32 point;
point.x = scan.points[i].range * cos(scan.points[i].angle);
point.y = scan.points[i].range * sin(scan.points[i].angle);
point.z = 0.0;
pc_msg.points.push_back(point);
pc_msg.channels[idx_intensity].values.push_back(scan.points[i].intensity);
pc_msg.channels[idx_timestamp].values.push_back(i * scan.config.time_increment);
}
}
scan_pub.publish(scan_msg);
pc_pub.publish(pc_msg);
// laser_fan_pub.publish(fan);
} else {
ROS_ERROR("Failed to get Lidar Data");
}
r.sleep();
ros::spinOnce();
}
laser.turnOff();
ROS_INFO("[YDLIDAR INFO] Now YDLIDAR is stopping .......");
laser.disconnecting();
return 0;
}
- 问题及解决
在调试G4雷达功能包时,用“ls -l /dev/ttyUSB*”指令,一直显示找不到串口。后来,转而顺利调试了SLD-1雷达,返回来调试G4时,无论在ROS2版本的还是ROS版本的都出现同一个问题。后来在同事的帮助下,换了根C-USB数据线,再试,问题解决了,找到了串口/dev/ttyUSB0。
参考文献: 【1】YDLidar-SDK Communication Protocol
【2】ydlidar激光雷达的安装与驱动
【3】驱动EAI的激光雷达YDLIDAR-X4