目录
一、什么是线性表
二、顺序表
2.1什么是顺序表
2.2静态顺序表的代码实现
2.3动态顺序表的代码实现
三、链表
3.1什么是链表
3.2不带头单向不循环链表的代码实现
3.3带头双向循环链表的代码实现
四、顺序表和链表的区别
一、什么是线性表
线性表是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常的线性表有:链表、顺序表、栈、队列、字符串……
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不是一定连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
二、顺序表
2.1什么是顺序表
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
2.2静态顺序表的代码实现
//SeqList.h头文件
#pragma once
#define MAX_SIZE 10
typedef int SQDataType;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct SeqList
{
SQDataType a[MAX_SIZE];
int size;
}SL;
void SeqListInit(SL* ps);
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps, SQDataType x);
void SeqListPushFront(SL* ps, SQDataType x);
void SeqListPopBack(SL* ps);
void SeqListPopFront(SL* ps);
void SeqListPrint(SL* ps);//SeqList.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqList.h"
//顺序表的初始化
void SeqListInit(SL* ps)
{
memset(ps->a, 0, sizeof(SQDataType) * MAX_SIZE);
ps->size = 0;
}
//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps, SQDataType x)
{
if (ps->size >= MAX_SIZE)
{
printf("SeqList is Full\n");
}
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//打印
void SeqListPrint(SL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//……
//其他的接口函数可以自己实现2.3动态顺序表的代码实现
//SeqList.h文件
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int DatatType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
DatatType* data;
int size;
int capacity;
}SeqList;
// 对数据的管理:增删查改
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps);
void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps);
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps);
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, DatatType x);
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, DatatType x);
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps);
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps);
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, DatatType x);
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, DatatType x);
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos);//SeqList.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqList.h"
//初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->data = (DatatType*)malloc(sizeof(DatatType) * 4);
if (NULL == ps->data)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 4;
}
//销毁
void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->data);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
//打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void CheckCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
DatatType* tmp = (DatatType*)realloc(ps->data, sizeof(DatatType) * 2 * ps->capacity);
if (NULL == tmp)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->data = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
}
//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, DatatType x)
{
/*CheckCapacity(ps);
ps->data[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;*/
SeqListInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}
//头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, DatatType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, 0, x);
}
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps, 0);
}
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps, ps->size - 1);
}
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, DatatType x)
{
assert(ps);
//找到返回下标,没有找到返回-1
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->data[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, DatatType x)
{
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
CheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size - 1;
//往后移元素
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->data[end + 1] = ps->data[end];
end--;
}
//插入
ps->data[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos)
{
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
int start = pos;
while (start < ps->size - 1)
{
ps->data[start] = ps->data[start + 1];
start++;
}
ps->size--;
}三、链表
3.1什么是链表
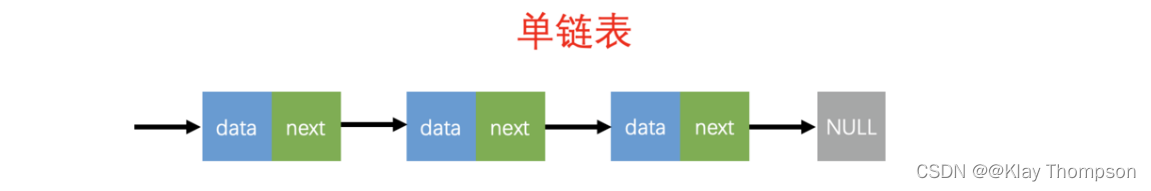
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。
3.2不带头单向不循环链表的代码实现
//SList.h文件
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
DataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
//头插、尾插、头删、尾删
void SLPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x);
void SLPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x);
void SLPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
void SLPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
//查找
SLTNode* SLFind(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x);
//修改
void SLModify(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x, int pos);
//打印
void SLPrint(SLTNode** pphead);
//销毁
void SLDestory(SLTNode** pphead);
// 在pos之前插入
void SLInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, DataType x);
// 在pos之后插入
void SLInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, DataType x);
// 删除pos位置的值
void SLErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
//删除pos位置后面的值
void SLEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);//SList.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SList.h"
SLTNode* BuyNode(DataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if (NULL == newnode)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
else
{
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
//头插、尾插、头删、尾删
void SLPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
}
void SLPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
void SLPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
//没有节点
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
//有一个节点
//if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
//{
// free(*pphead);
// *pphead = NULL;
//}
有多个节点
//else
//{
// SLTNode* del = *pphead;
// *pphead = del->next;
// free(del);
// del = NULL;
//}
SLTNode* del = *pphead;
*pphead = del->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
void SLPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
//没有节点
assert(*pphead);
//有一个节点
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
//有多个节点
else
{
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
SLTNode* prev = NULL;
while (tail->next)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
prev->next = NULL;
free(tail);
}
}
//查找
SLTNode* SLFind(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x)
{
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("没有此节点\n");
return NULL;
}
//修改
void SLModify(SLTNode** pphead, DataType x, int pos)
{
assert(*pphead);
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur && pos > 0)
{
cur = cur->next;
pos--;
}
cur->data = x;
}
//打印
void SLPrint(SLTNode** pphead)
{
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
//销毁
void SLDestory(SLTNode** pphead)
{
SLTNode* next = ( * pphead)->next;
while (*pphead)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = next;
if(next)
next = next->next;
}
*pphead = NULL;
next = NULL;
}
// 在pos之前插入
void SLInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, DataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);
SLTNode* cur = *pphead;
if (*pphead == pos)
{
newnode->next = pos;
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}
// 在pos之后插入
void SLInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, DataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);
SLTNode* next = pos->next;
newnode->next = next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
// 删除pos位置的值
void SLErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
if (pos == *pphead)
{
SLPopFront(pphead);
/**pphead = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;*/
}
else
{
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
}
//删除pos位置后面的值
void SLEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos->next);
assert(pos);
SLTNode* next = pos->next;
pos->next = next->next;
free(next);
next = NULL;
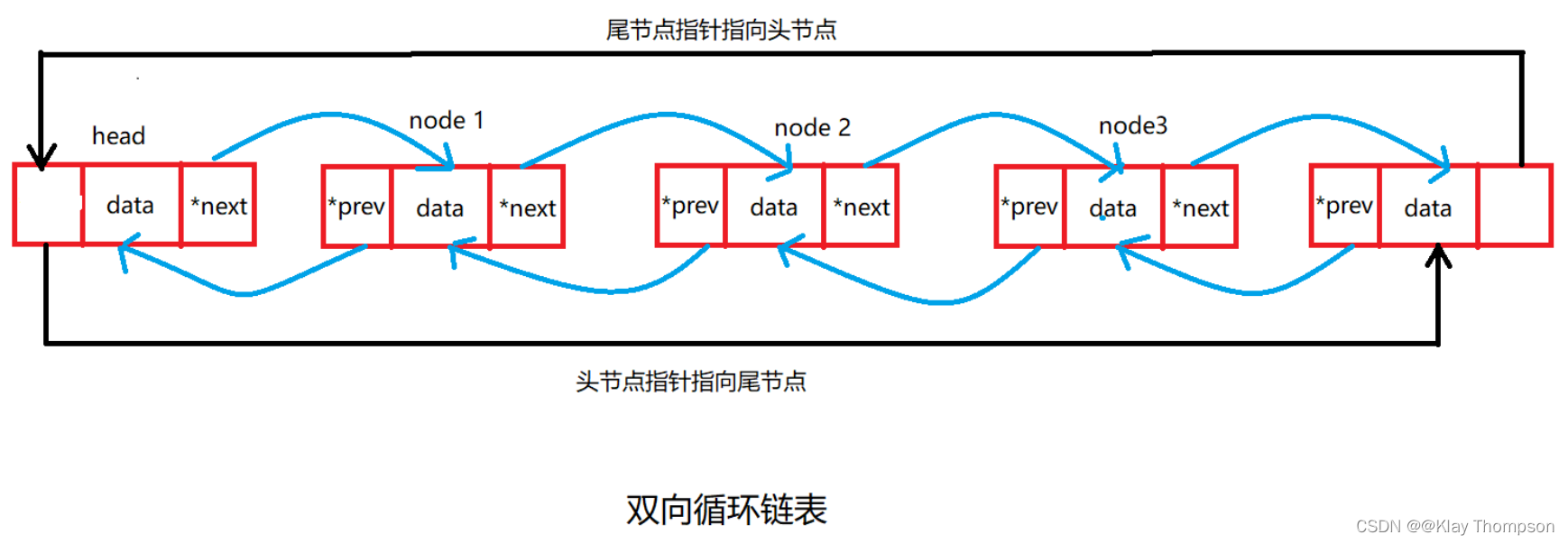
}3.3带头双向循环链表的代码实现
//List.h文件
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{
DataType data;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev;
}ListNode;
//初始化链表
void ListInit(ListNode* phead);
//尾插、尾删
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, DataType x);
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead);
//头插、头删
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, DataType x);
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead);
//打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead);
//查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, DataType x);
//判空
bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead);
//pos位置之前插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, DataType x);
//删除pos节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);
//销毁
void ListDestroy(ListNode* phead);//List.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "List.h"
//初始化
void ListInit(ListNode* phead)
{
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
phead->data = -1;
}
//malloc一个节点
ListNode* BuyNode(DataType x)
{
ListNode* newNode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail!\n");
return NULL;
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->prev = NULL;
return newNode;
}
//尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, DataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
ListNode* newNode = BuyNode(x);
tail->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = tail;
newNode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newNode;
}
//尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
ListNode* prev_tail = tail->prev;
prev_tail->next = phead;
phead->prev = prev_tail;
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
}
//头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, DataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);
ListNode* first = phead->next;
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = phead;
newnode->next = first;
first->prev = newnode;
}
//头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//判空
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListNode* del = phead->next;
phead->next = del->next;
del->next->prev = phead;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
//打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
printf("guard<==>");
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d<==>", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, DataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//判空
bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead)
{
return phead->next == phead;
}
//在POS位置前插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, DataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
ListNode* newnode = BuyNode(x);
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = prev;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
//删除POS位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
ListNode* posNext = pos->next;
posPrev->next = posNext;
posNext->prev = posPrev;
free(pos);
}
//销毁
void ListDestroy(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
}四、顺序表和链表的区别
| 不同点 | 顺序表 | 链表 |
| 存储空间上 | 物理上一定连续 | 逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持:O(1) | 不支持:O(N) |
| 任意位置插入或者删除元素 | 可能需要搬移元素,效率低O(N) | 只需要修改指针指向 |
| 插入 | 动态顺序表,空间不够时需要扩容 | 没有容量的概念 |
| 应用场景 | 元素高效存储+频繁访问 | 任意位置插入和删除频繁 |
| 缓存利用率 | 高 | 低 |