目录
- 如何快速调试链表习题
- 链表习题
- 移除链表元素
- 链表的中间节点
- 反转链表
- 链表中倒数第k个结点
- 合并两个有序链表
- 链表分割
- 链表的回文结构
- 相交链表
- 环形链表
- slow和fast一定会相遇吗?如果fast一次走(3、4、5)步呢?
- 环形链表 Ⅱ
- 思路1:
- 推论
- 思路2:
- 复制带随机指针的链表
如何快速调试链表习题
int main()
{
struct ListNode* n1 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
assert(n1);
struct ListNode* n2 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
assert(n2);
struct ListNode* n3 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
assert(n3);
struct ListNode* n4 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
assert(n4);
n1->val = 7;
n2->val = 7;
n3->val = 7;
n4->val = 7;
n1->next = n2;
n2->next = n3;
n3->next = n4;
n4->next = NULL;
n1 = removeElements(n1, 7);
return 0;
}
链表习题
移除链表元素
OJ链接
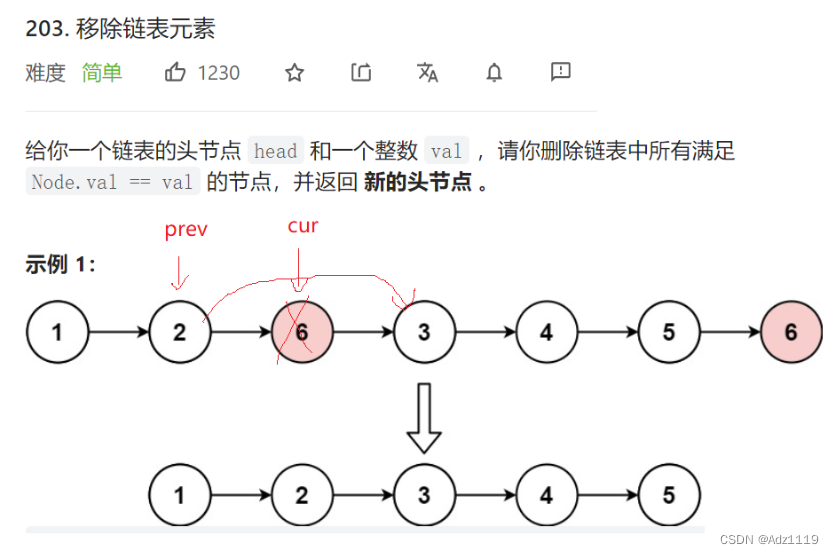
方法1:遇到val就删除
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* prev = NULL, * cur = head;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val == val)
{
if(prev==NULL)
{
cur=head->next;
free(head);
head=cur;
}
else
{
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = prev->next;
}
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
方法2:遍历当前链表,把不是val的拿下来尾插
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
struct ListNode*phead=NULL,*tail=NULL;
while(head)
{
if(head->val!=val)
{
if(tail==NULL)
{
phead=tail=head;
}
else
{
tail->next=head;
tail=tail->next;
}
}
//printf("%d\n",head->val);
head=head->next;
if(tail)
tail->next=NULL;
}
return phead;
}
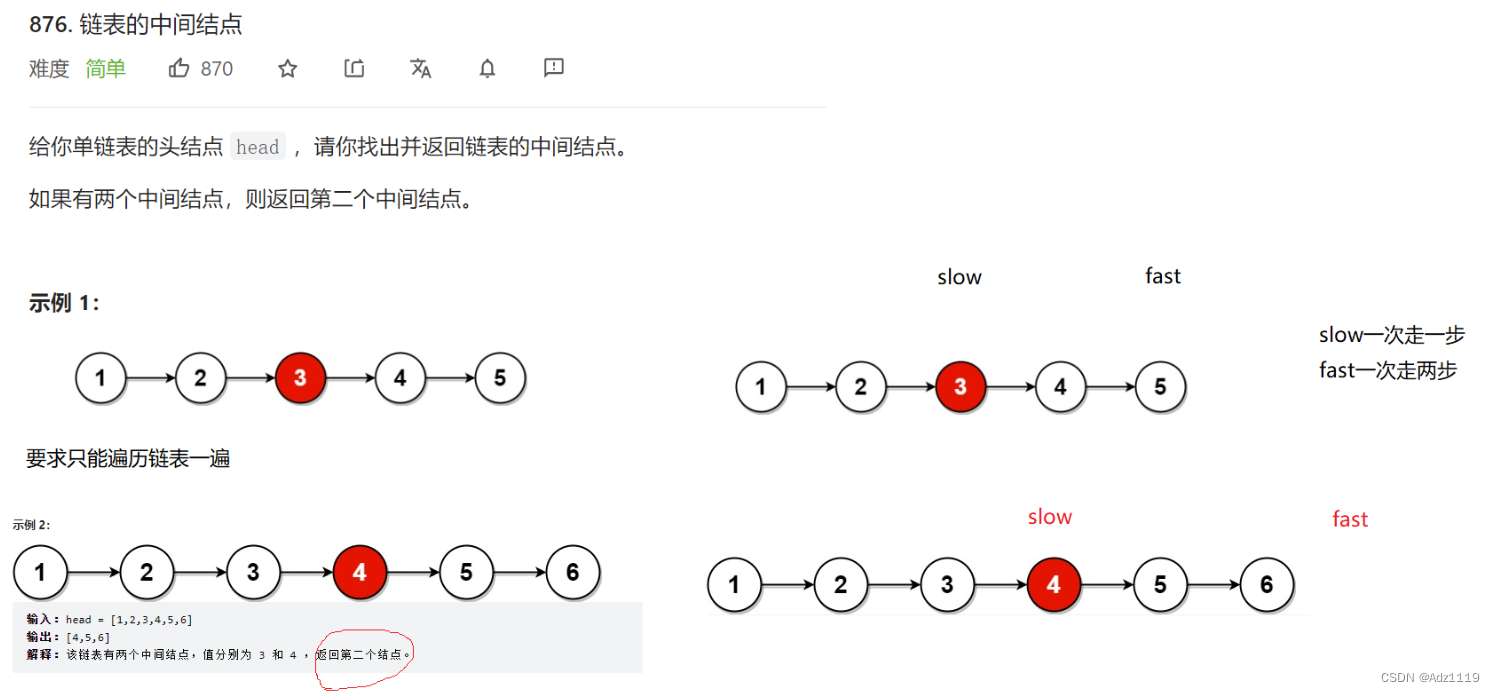
链表的中间节点
OJ链接
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode*slow=head,*fast=head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
反转链表
OJ链接
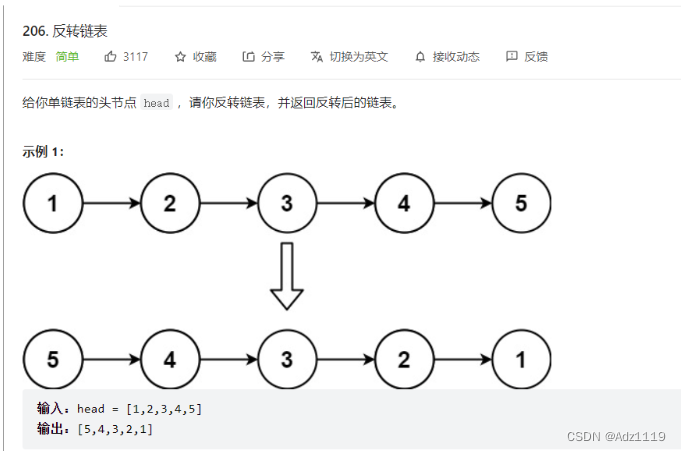
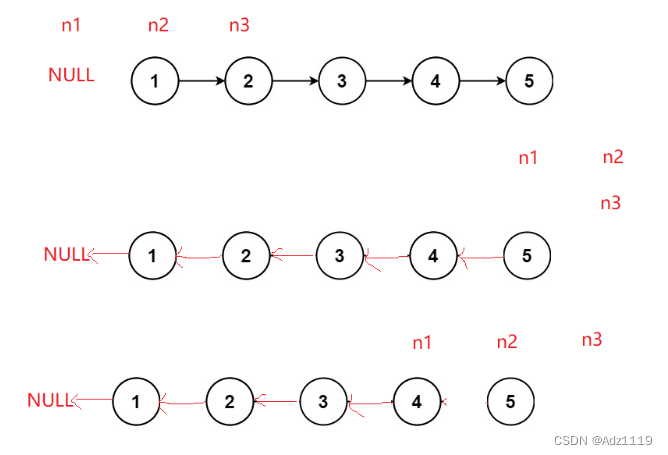
用prev,cur,next也可以
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(head==NULL || head->next==NULL)
return head;
struct ListNode*prev=head,*cur=head->next,*next=head->next->next;
prev->next=NULL;
while(cur)
{
cur->next=prev;
prev=cur;
cur=next;
if(next)
next=next->next;
}
return prev;
}
链表中倒数第k个结点
OJ链接
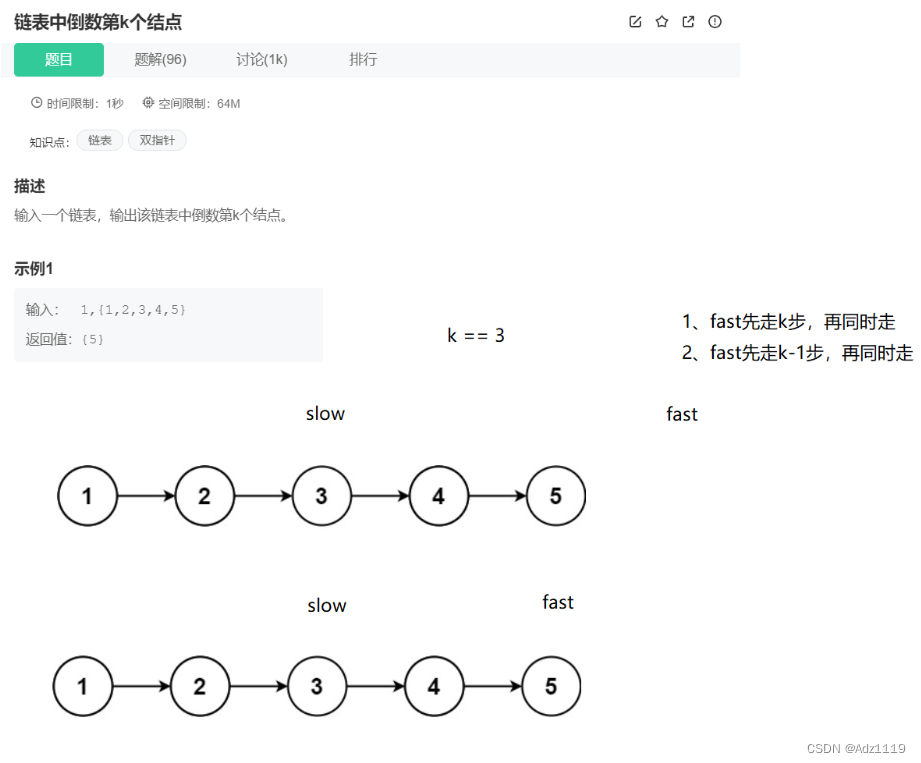
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
/**
*
* @param pListHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
struct ListNode*cur=pListHead;
struct ListNode*next=pListHead;
while(k-- && next)
{
next=next->next;
}
if(k!=-1)
return NULL;
while(next!=NULL)
{
cur=cur->next;
next=next->next;
}
//printf("%d\n\n",cur->val);
return cur;
}
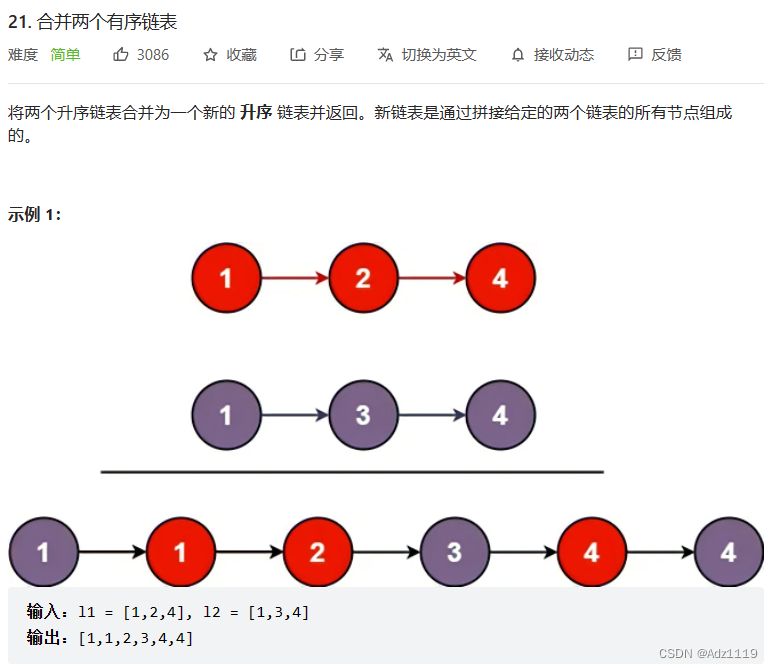
合并两个有序链表
OJ链接
不创建哨兵位的头节点的话:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
struct ListNode*head=NULL,*tail=NULL;
if(list1==NULL)
return list2;
if(list2==NULL)
return list1;
while(list1 && list2)
{
if(list1->val>list2->val)
{
if(tail==NULL)
{
head=tail=list2;
}
else
{
tail->next=list2;
tail=tail->next;
}
list2=list2->next;
}
else
{
if(tail==NULL)
{
head=tail=list1;
}
else
{
tail->next=list1;
tail=tail->next;
}
list1=list1->next;
}
}
if(list1)
tail->next=list1;
if(list2)
tail->next=list2;
return head;
}
也可以选择创建一个哨兵位的头节点来方便处理尾插
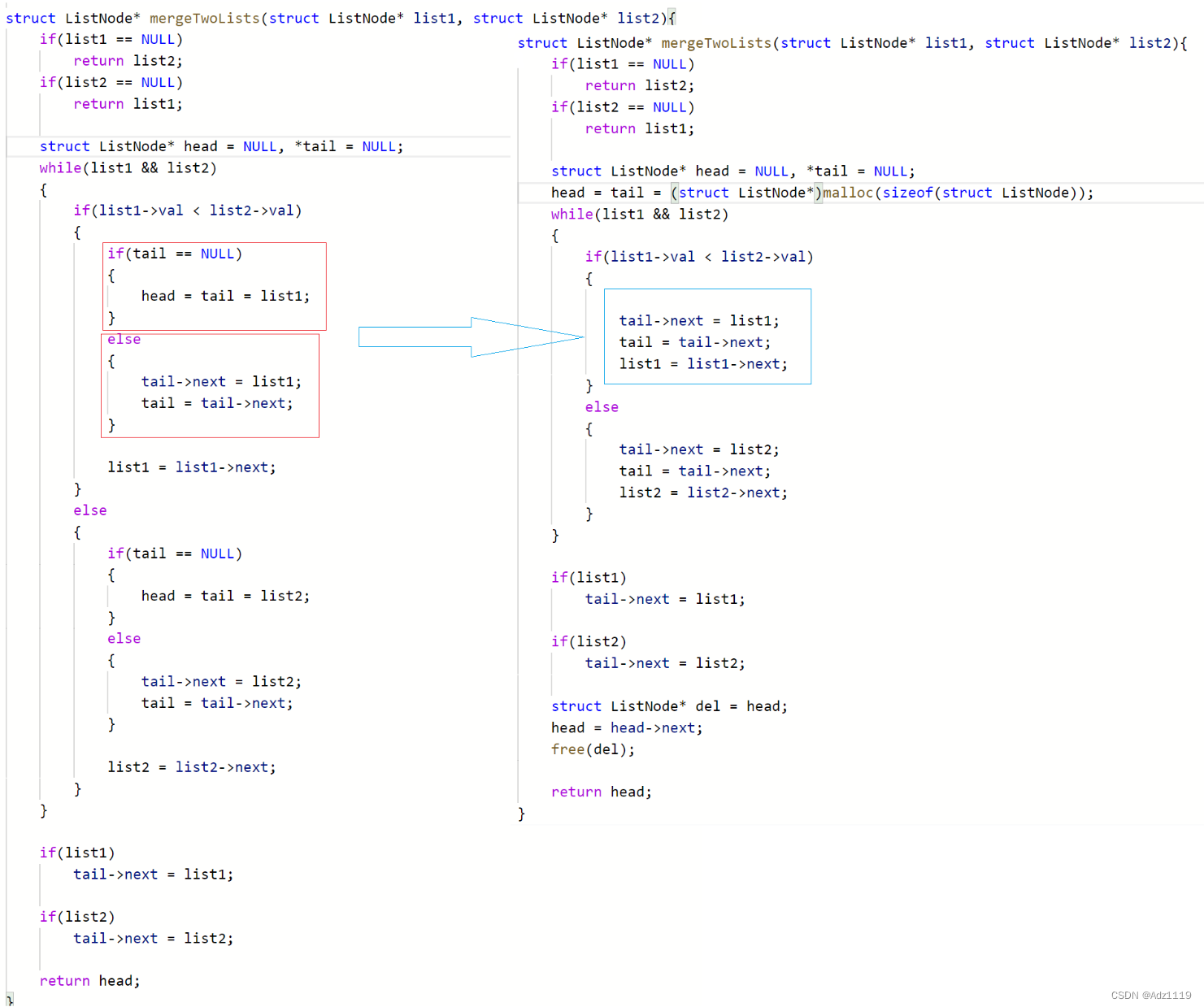
从图可以看出我们尾插的时候会记录尾tail,不然每次找尾效率太低,那么写单链表时为什么没有用tail呢?因为加尾指针也是有代价的,传给函数的时候就不是单单传头指针了,需要传结构体,结构体中有头指针和尾指针,结构复杂的话不利于学习链表。而且加了尾指针也只是方便了尾插,但对尾删没有帮助。
哨兵位的头节点一般不存储有效数据
有一些地方可能会用头节点存链表长度,其实是不好的,如果链表的数据类型是整形那么是好的,但当数据类型不是int,是char的时候,链表长度超过128的时候,记录的链表的长度就离谱起来了
当写单链表时用带哨兵位的头节点会写的更容易,不需要二级指针,因为头指针一直指向的是哨兵位,头指针的指向不需要更改了。
链表分割
OJ链接
思路:

易错点:
6的指向记得要指向NULL,否则会死循环
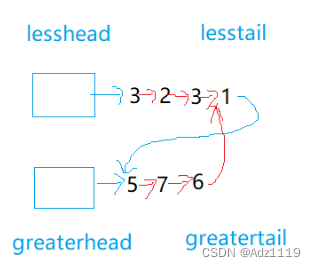
推荐使用带哨兵位的头节点,这样会方便很多
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
struct ListNode*lesshead,*lesstail,*greaterhead,*greatertail,*cur;
lesshead=NULL;
lesstail=NULL;
greaterhead=NULL;
greatertail=NULL;
if(pHead==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
cur=pHead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val<x)
{
if(lesshead==NULL)
{
lesshead=lesstail=cur;
}
else
{
lesstail->next=cur;
lesstail=cur;
}
}
else
{
if(greaterhead==NULL)
{
greaterhead=greatertail=cur;
}
else
{
greatertail->next=cur;
greatertail=cur;
}
}
cur=cur->next;
}
if(lesstail!=NULL)
{
lesstail->next=greaterhead;
}
if(greatertail!=NULL)
{
greatertail->next=NULL;
}
if(lesshead!=NULL)
return lesshead;
else
return greaterhead;
}
};
如果不使用带哨兵位的头节点,会有点麻烦,遇到第一个链表为空时,第二个链表为空时,尾插时都要多注意。
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
struct ListNode* headleft = pHead, * headright = pHead, * tailleft = NULL, * tailright = NULL;
//printf("%d\n", headleft->val);
while (pHead)
{
if (pHead->val < x)
{
if (tailleft == NULL)
{
headleft = tailleft = pHead;
}
else
{
tailleft->next = pHead;
tailleft = tailleft->next;
}
pHead = pHead->next;
if (tailleft)
tailleft->next = NULL;
}
else
{
if (tailright == NULL)
{
headright = tailright = pHead;
}
else
{
tailright->next = pHead;
tailright = tailright->next;
}
pHead = pHead->next;
if (tailright)
tailright->next = NULL;
}
}
if (tailleft)
{
if(tailright)
tailleft->next = headright;
return headleft;
}
else
{
return headright;
}
}
};
链表的回文结构
OJ链接
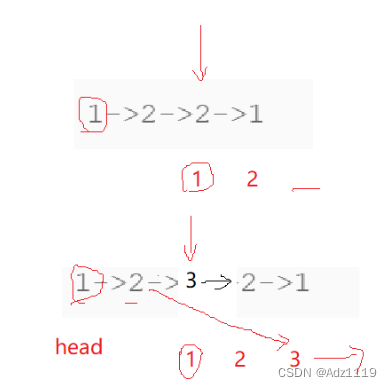
思路:找中间结点,然后以中间结点为头,将后面链表逆置
注意:逆置后3是指向NULL,但2的next还是3
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
if(A==NULL)
return false;
//快慢指针找中间
struct ListNode*slow=A,*fast=A;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
//将中间结点和后面结点逆置
//1->2->3->2->1
//逆置后:3中间结点的next会为NULL,2的next没有变,还是指向3
//1->2->1->2->3
struct ListNode*prev=NULL,*cur=slow,*next=slow->next;
while(cur)
{
cur->next=prev;
prev=cur;
cur=next;
if(next)
next=next->next;
}
struct ListNode*head=A;
while(prev)//不能用head作为结束条件,因为head为空时prev就会存在空指针访问
{
if(head->val!=prev->val)
{
return false;
}
else
{
head=head->next;
prev=prev->next;
}
}
return true;
}
};
相交链表
OJ链接
思路:

struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
struct ListNode*curA=headA,*curB=headB;
int lenA=1;
int lenB=1;
while(curA->next)
{
curA=curA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(curB->next)
{
curB=curB->next;
lenB++;
}
if(curA!=curB)
return NULL;
//长链表先走差距步
struct ListNode*longList=headA;
struct ListNode*shortList=headB;
if(lenB>lenA)
{
longList=headB;
shortList=headA;
}
int gap=abs(lenA-lenB);
while(gap--)
{
longList=longList->next;
}
while(longList!=shortList)
{
longList=longList->next;
shortList=shortList->next;
}
return longList;
}
环形链表
OJ链接
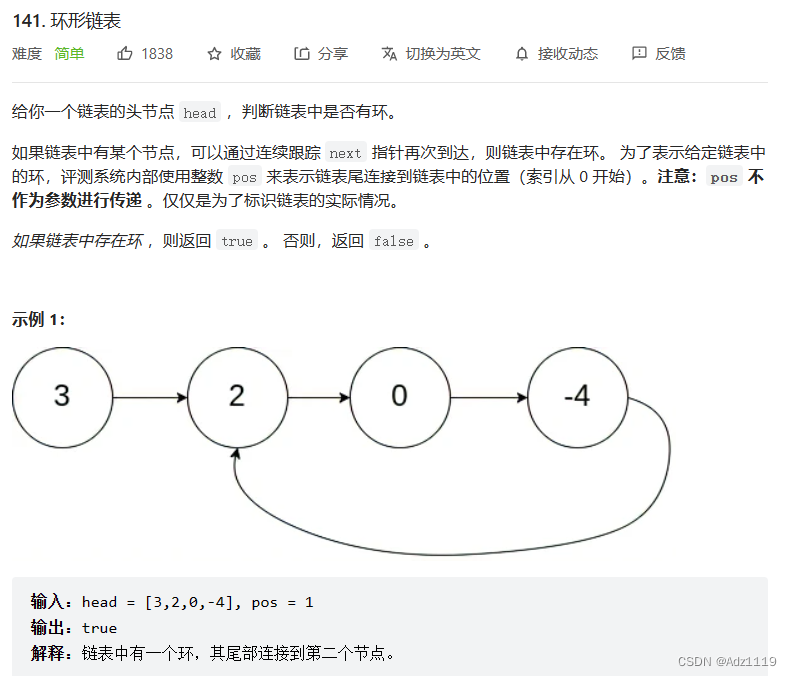
思路:
fast一次走两步,slow一次走一步,fast和slow相遇,就说明存在环
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode*slow=head,*fast=head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(fast==slow)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
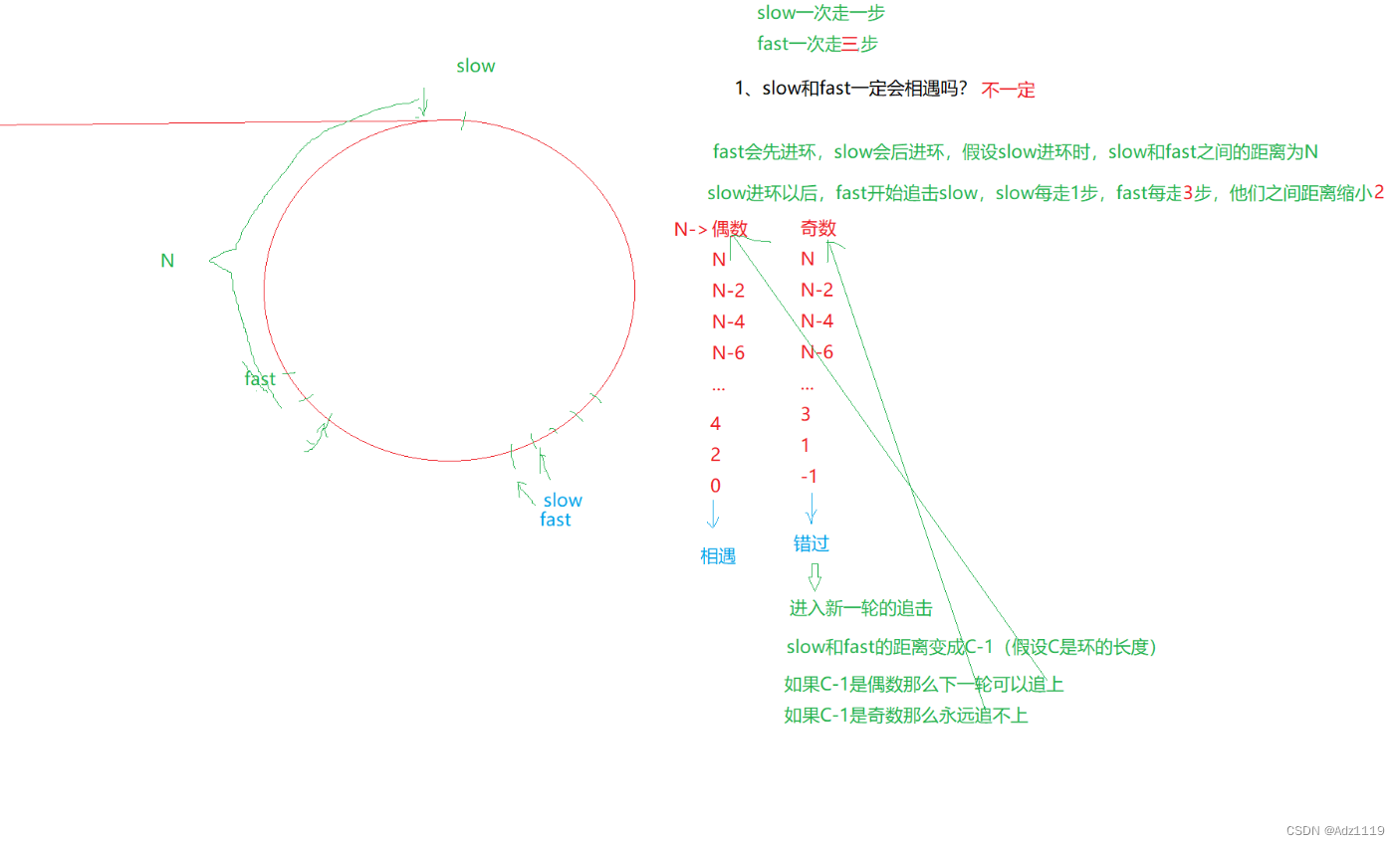
slow和fast一定会相遇吗?如果fast一次走(3、4、5)步呢?
看fast一次走几步
fast一次走两步则一定相遇

fast一次走三步则不一定相遇
环形链表 Ⅱ
OJ链接
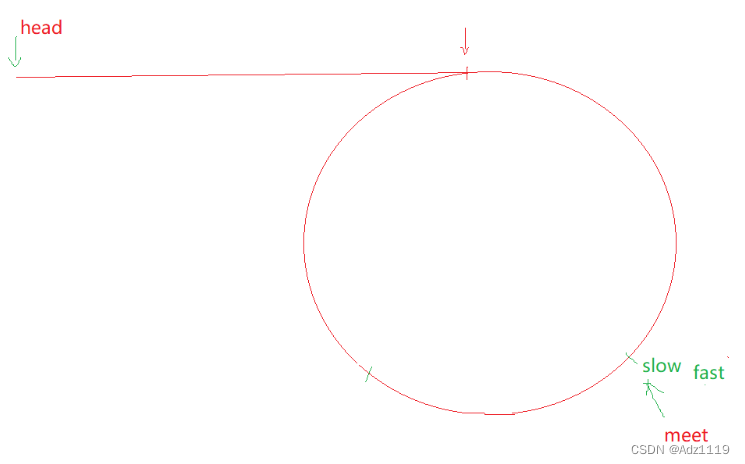
思路1:
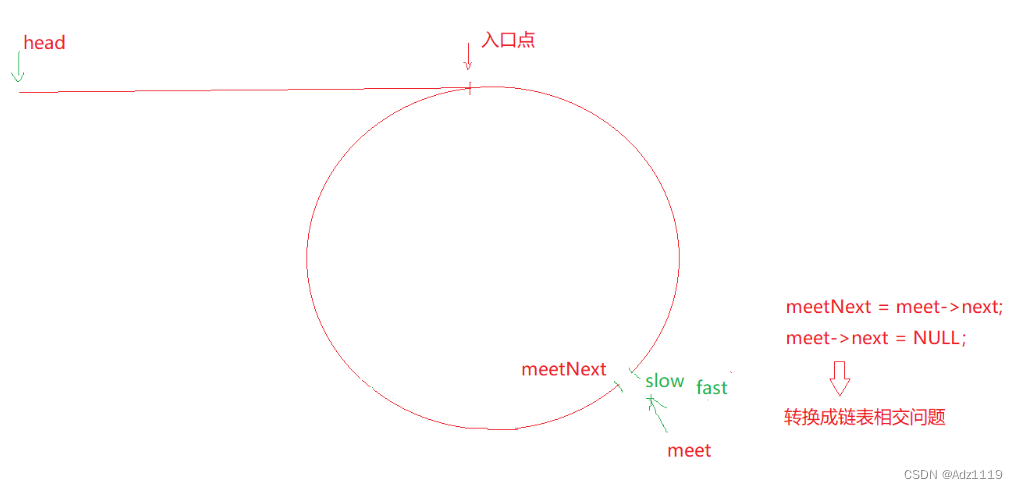
一个指针从相遇点走,一个指针从链表头开始走,他们会在入口点相遇
推论
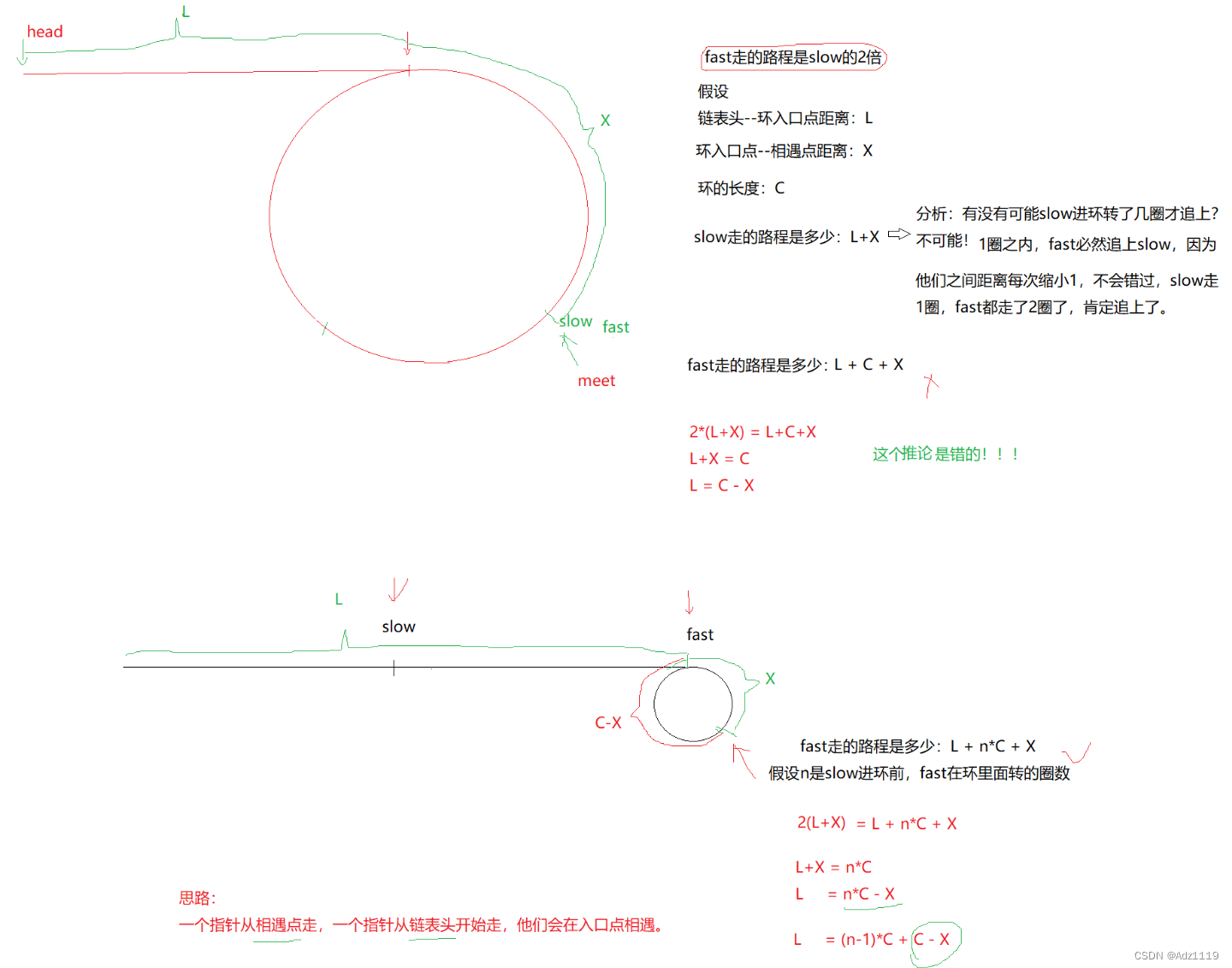
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode*slow=head,*fast=head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(fast==slow)
{
struct ListNode*phead=head;
while(slow!=phead)
{
slow=slow->next;
phead=phead->next;
}
return phead;
}
}
return NULL;
}
思路2:
复制带随机指针的链表
OJ链接
思路
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
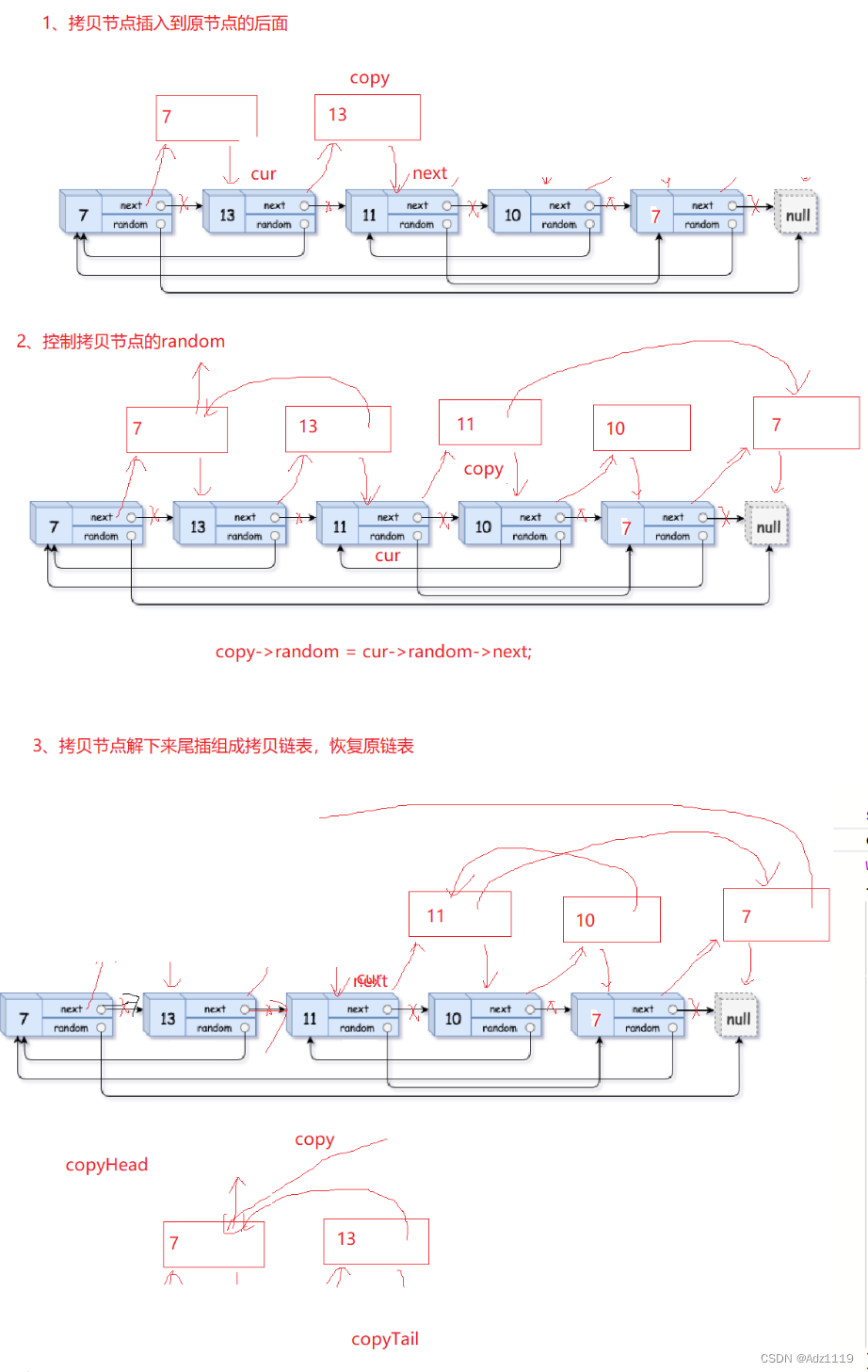
//拷贝节点到原节点的后面
struct Node*cur=head;
struct Node*copy=NULL;
while(cur)
{
copy=(struct Node*)malloc((sizeof(struct Node)));
copy->val=cur->val;
copy->next=cur->next;
cur->next=copy;
cur=copy->next;
}
//控制拷贝节点的random使其指向原节点random的next
cur=head;
copy=cur->next;
while(cur)
{
copy=cur->next;
if(cur->random!=NULL)
copy->random=cur->random->next;
else
copy->random=NULL;
cur=copy->next;
}
//恢复原链表
cur=head;
struct Node*copyhead=copy,*copytail=NULL;
while(cur)
{
copy=cur->next;
if(copytail==NULL)
{
copytail=copyhead=copy;
}
else
{
copytail->next=copy;
copytail=copytail->next;
}
cur->next=copy->next;
cur=copy->next;
}
return copyhead;
}