💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
🌈4 Python代码、数据、文章
💥1 概述
文献来源:

摘要本文提出了一种考虑冷、热、电多能负荷不确定性的区域综合能源系统鲁棒规划方法。基于改进的能源枢纽(EH)模型,建立了包括热电联产、电锅炉、燃气锅炉、电冷水机组、吸收式冷水机组、蓄电池、蓄热、冷库在内的区域综合能源系统模型。另外,引入0-1设备选择变量,对各设备的容量进行选择和优化。采用多面体集描述多能负荷的不确定性,建立鲁棒规划模型并进行等效转换。最后,通过MATLAB编程实现了容量规划模型,并利用CPLEX求解最优配置。结果表明,系统规划的稳健性可以通过鲁棒性措施来控制,最优规划能够保证系统的可靠性和经济性。这也体现了IES的多能互补集成优化效益。
关键词:综合能源系统;多能互补;不确定性
原文摘要:
Abstract—In this paper, we propose a robust planning method for regional integrated energy systems(IES) considering the uncertainty of cold, hot and electric multi-energy loads. Based on the improved energy hub (EH) model, we established a regional integrated energy system model, which includes CHP, electric boilers, gas boilers, electric chiller, absorption chiller, battery, thermal storage and cold storage. In addition, 0-1 variable of equipment selection is introduced to select and optimize the capacity of each equipment. The polyhedron set is used to describe the uncertainty of multi-energy load, and a robust planning model is formed and equivalent transformed. Finally, the capacity planning model is realized by programming in MATLAB, and the optimal configuration is solved by CPLEX. The result shows that the conservatism of system planning can be controlled by robust measure, and the optimal plan can guarantee reliability and economy of the system at the same time. It also reflects the multi energy complementary integration optimization benefits of IES.
Keywords—Integrated energy system, multi energy complementary, uncertainty, robust planning
IES的结构可分为三个主要部分:能量供应、能量转换和能量储存。每个部分由特定的能量耦合设备组成,并连接成一个整体。IES规划模型可以用图1所示的结构来描述。
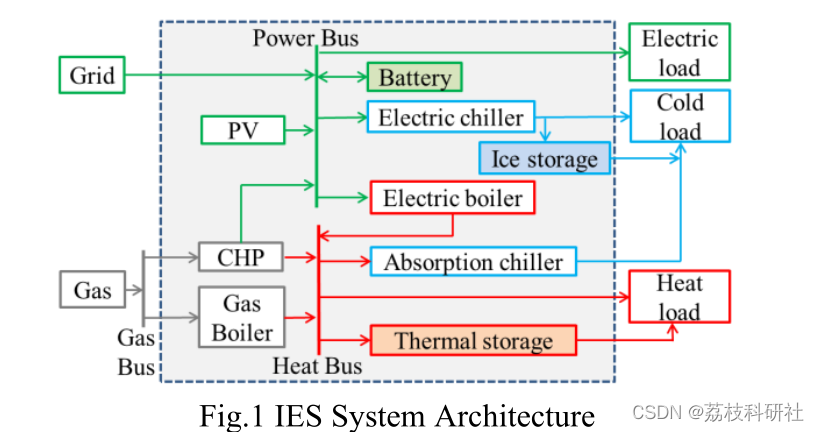
可以看到,IES与电网、燃气网和冷热网相连。它将电能、燃气和可再生能源等能源形式转化为电能、冷能和热能。由计划决定的能量流部分用虚线表示。供能部分包括光伏发电装置和电网。能量转换部分包括热电联产、燃气锅炉、电锅炉、吸收式冷水机组和电冷水机组。储能部分包括蓄电池、蓄热和冷库。这些设备的类型需要规划,不同类型的设备在容量、成本和转换效率上存在差异。
📚2 运行结果
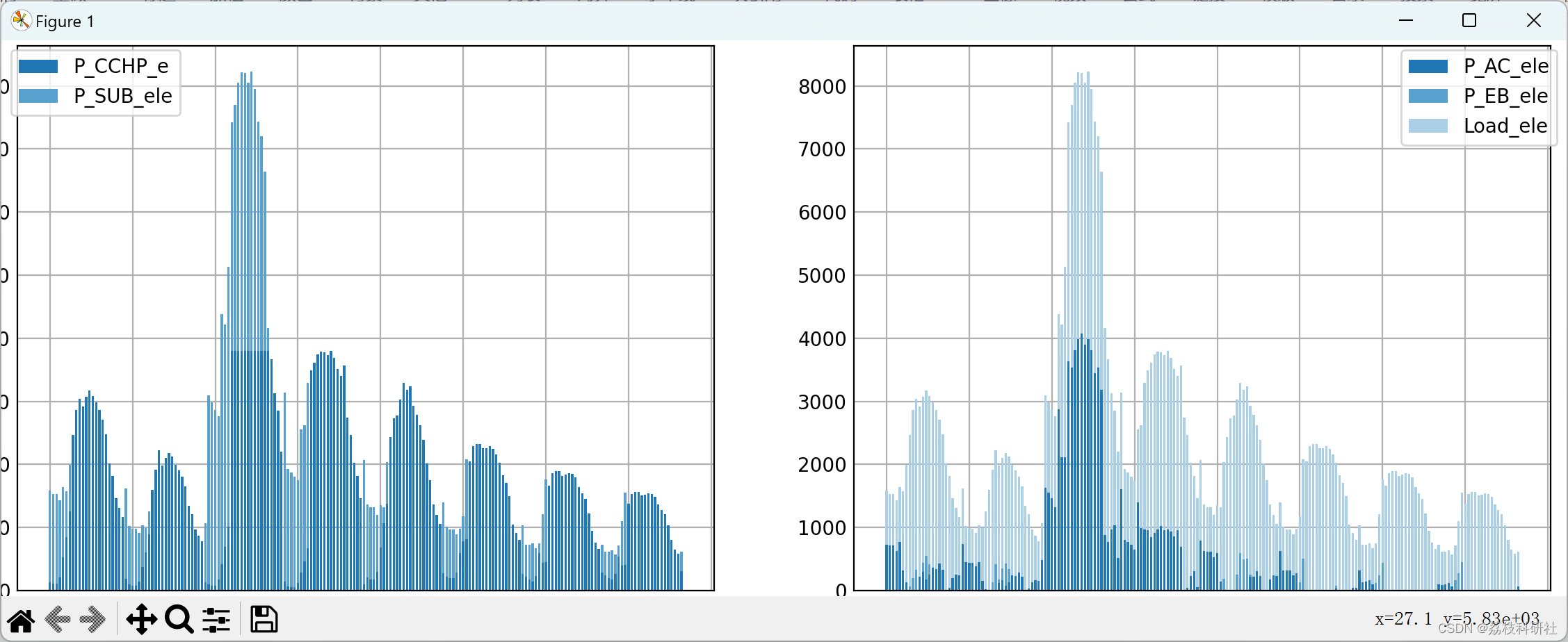


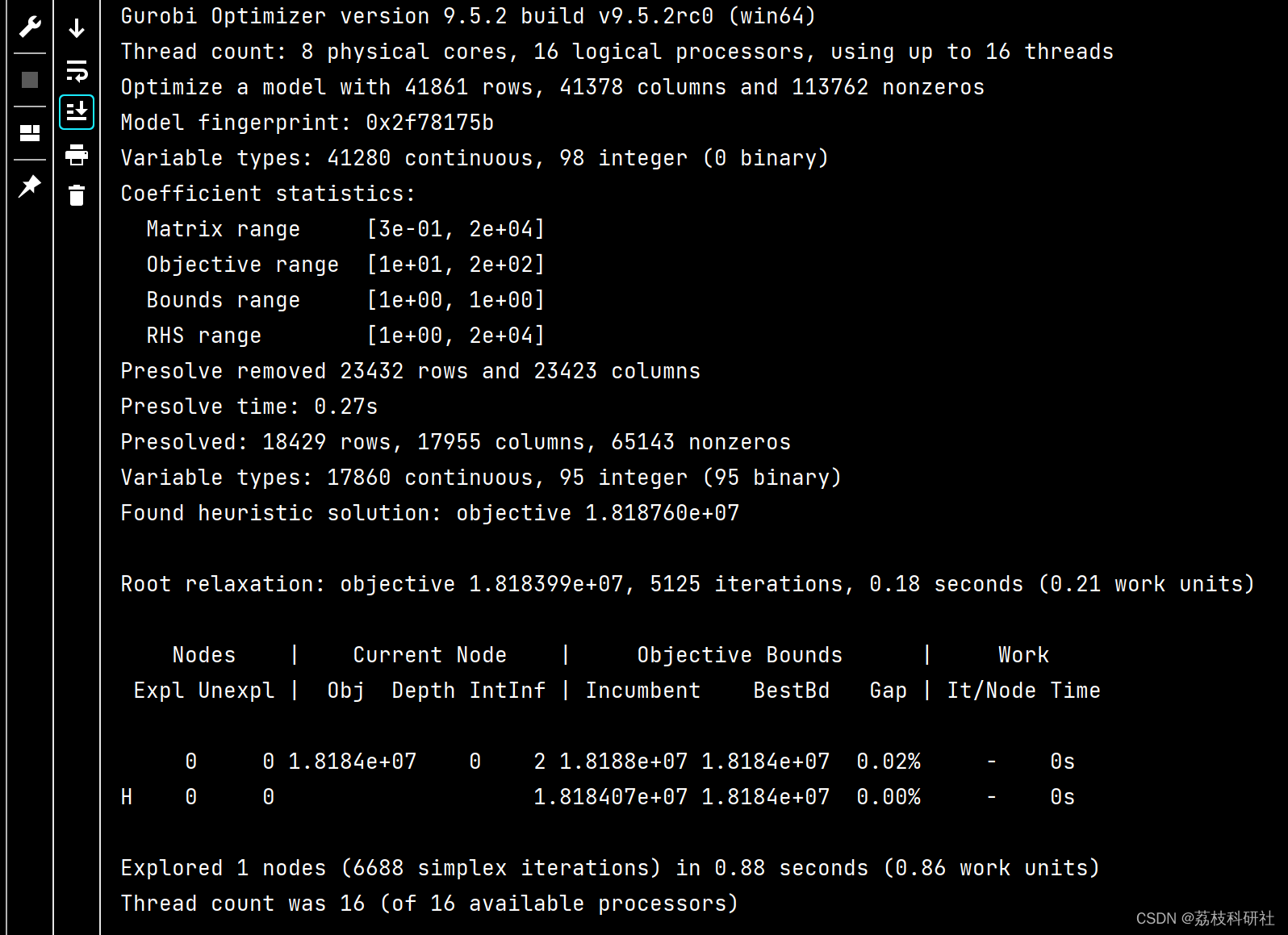
部分代码:
print('目标函数构建完成!')
print('优化计算求解中!')
# 问题选用Pulp选择的Solver进行求解
prob.solve(GUROBI()) # 目前用GLPK()求解大概要7 min+, 如果用CPLEX() 和 GUROBI() 会快很多
# 输出求解结果
for v in prob.variables():
print(v.name, "=", v.varValue)
# v.evaluate()
# np.savetxt(v.name,v.values,fmt='%.4e',delimiter=',')
print("Total Cost = ", value(prob.objective))
# 保存机组选型优化结果 到 X.values 里,是一个ndarray
X_CCHP.evaluate()
X_GB.evaluate()
X_AC.evaluate()
X_EB.evaluate()
X_SUB.evaluate()
# 保存机组耗电耗气连续变量优化结果 到 X.values 里,是一个ndarray
P_CCHP_gas.evaluate() # CCHP单位时间内所用燃气热值,单位是MW(应该修改成kw比较合适)
V_CCHP_gas.evaluate() # CCHP单位时间内所用燃气量,单位是m3/h
P_SUB_electricity.evaluate() # 变电站出力,单位是MW
P_GB_gas.evaluate() # GB单位时间内所用燃气热值,单位是MW
V_GB_gas.evaluate() # GB单位时间内所用燃气量,单位是m3/h
P_AC_electricity.evaluate() # 中央空调输入电出力,单位MW
P_EB_electricity.evaluate() # 电锅炉输入电能,单位MW
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。