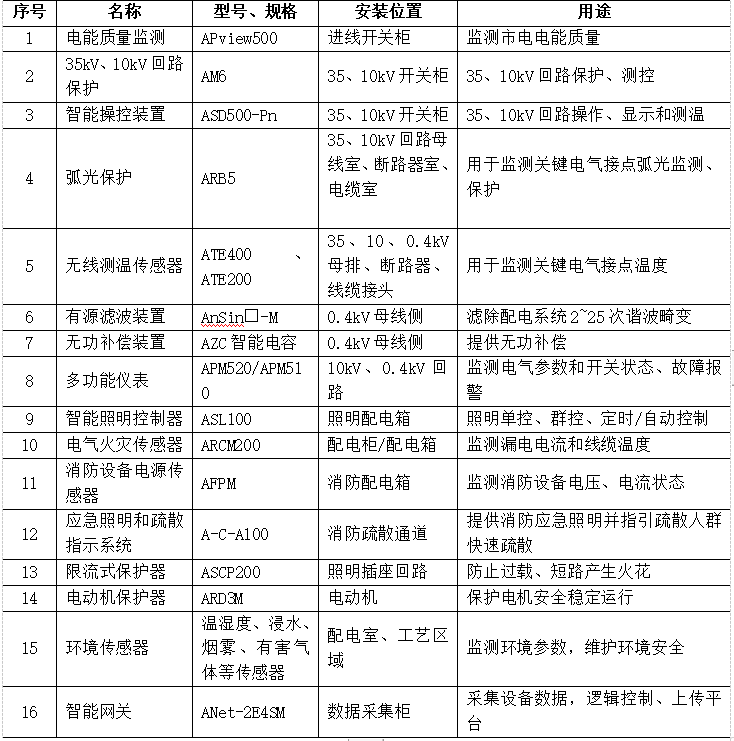
0、应用是一个有活动、布局和其他资源组成的集合。其中一个活动是应用的主活动。每个应用都有一个主活动,在文件AndroidManifest.xml中指定。
1、默认地,每个应用都在自己的进程中运行。这样有助于保证应用安全。
2、但是可以使用startActivity(intent)传入一个意图启动另一个应用中的活动。(Android系统知道设备上已安装的所有应用和它们的活动,可以使用意图启动适当的活动)。
3、需要启动一个活动时,Android会检查是否已经有一个进程在运行这个应用。(如果存在这样一个进程,Android就会在该进程中运行这个活动。如果不存在这样的进程,Android将创建一个进程)。
4、Android启动一个活动时,回调用它的onCreate()方法。(只要创建活动就会运行onCreate())。
下面通过来实现一个秒表应用,分析一下底层活动是如何工作的,应用通常会出什么问题,以及如何使用活动生命周期方法修正这些问题。秒表应用包括一个活动和一个布局。布局中有一个文本视图,显示已经过去了多少时间,另外还会显示一个Start(开始)按钮来启动秒表,一个Stop(停止)按钮停止秒表,还有一个Reset(重置)按钮可以将计时器重置为0。
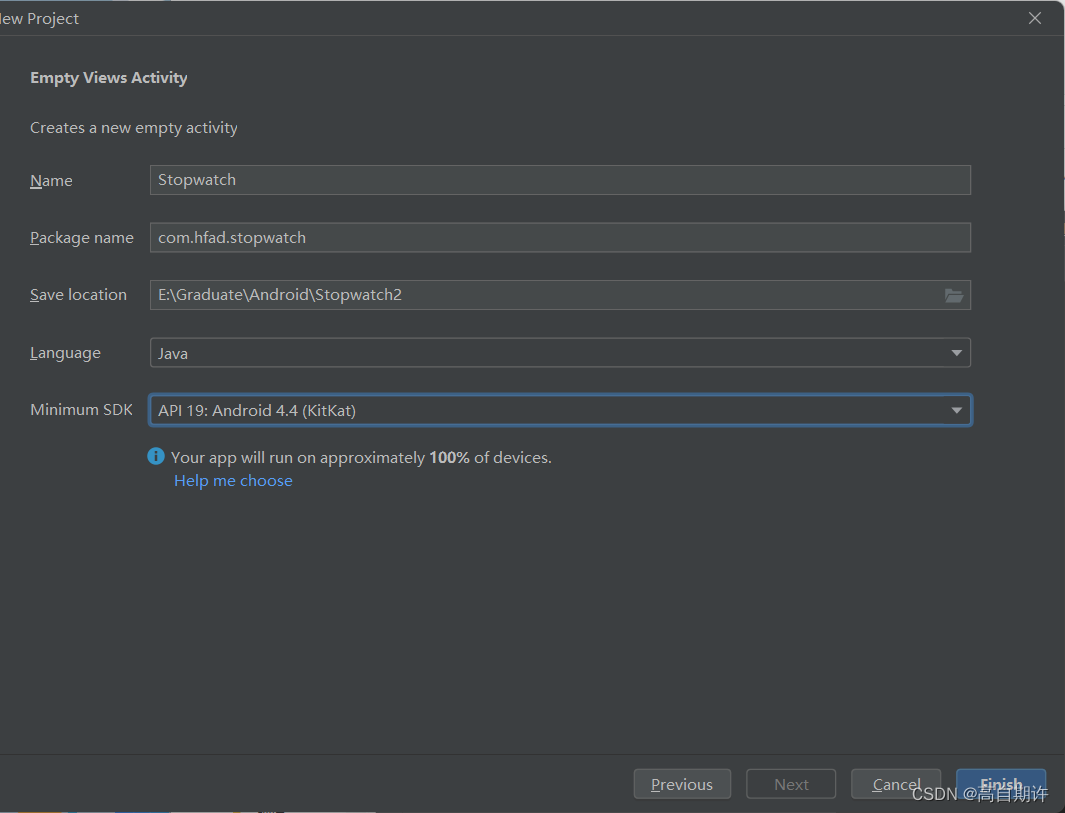
创建新Android工程,应用名为Stopwatch,选择最低的SDK,如下图所示。
另外还需要一个名为StopwatchActivity的空活动和一个activity_stopwatch的布局。
工程目录如图所示:
更新strings.xml,添加以下三行代码:
<string name="start">Start</string>
<string name="stop">Stop</string>
<string name="reset">Reset</string>
更新秒表布局代码
下面是布局的XML,这里描述了一个用来显示计时器的文本视图,另外还有三个按钮。
activity_stopwatch.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="16dp"
tools:context=".StopwatchActivity"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/time_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:textAppearance="@android:style/TextAppearance.Large"
android:textSize="56sp"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/start_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:onClick="onClickStart"
android:text="@string/start"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stop_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:onClick="onClickStop"
android:text="@string/stop"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/reset_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:onClick="onClickReset"
android:text="@string/reset"
/>
</LinearLayout>
单击Start按钮时会调用onCLickStop方法,单击Reset按钮时会调用onClickReset方法,单击Stop按钮时会调用onCLickStop方法。
我们还将使用一个名为runTimer()方法更新秒表。runTimer()方法每秒运行一次代码,检查秒表是否还在运行,如果确实还在运行,则使秒数递增,并在文本视图中显示秒数。
我们将使用两个私有变量记录秒表的状态。这里使用一个名为seconds的int变量跟踪秒表开始运行以来过去了多少秒,另一个使用一个名为running的布尔变量记录秒表目前是否还在运行。
为此,将StopwatchActivity.java的内容替换为以下代码:
package com.hfad.stopwatch;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
public class StopwatchActivity extends Activity {
private int seconds = 0;//记录已经过去的秒数
private boolean running;//秒表是否正常运行
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_stopwatch);
}
//启动秒表
public void onClickStart(View view) {
running = true;
}
//停止秒表
public void onClickStop(View view) {
running = false;
}
//单击reset按钮时会调用这个方法
public void onClickReset(View view) {
running = false;
seconds = 0;
}
}
创建runTimer方法,runTimer方法要得到布局中文视图引用,将seconds变量的内容格式化为小时,分钟和秒,然后在文本视图中显示。如果running变量设置为true,能让seconds变量递增。
private void runTimer() {
//得到文本视图
final TextView timeView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.time_view);
int hours = seconds / 3600;
int minutes = (seconds%3600)/60;
int secs = seconds % 60;
//设置显示格式
String time = String.format(Locale.getDefault(), "%d:%02d%02d", hours, minutes, secs);
//设置文本视图
timeView.setText(time);
if (running) {
++seconds;
}
}
要让这个代码一直循环,每秒递增seconds变量,并更新文本视图。而且要以一种不阻塞Android主线程的方式来实现。在非Android的Java程序中,可以使用后天线程完成类似这样的任务。不过在Android世界里,只有Android主线程可以更新用户界面,如果其他线程试图这样做,就会得到一个异常。可以使用Handler来解决这个问题。
Handler(消息处理器)是一个Android类,可以用来调度要在将来某个时间点运行的代码,还可以用它来提交需要在其他线程(非Android主线程)中运行的代码,在这里我们需要使用Handler调度秒表代码,让它每秒运行一次。
使用Handler时,可以把你想要调度的代码包装在一个Runnable对象中,然后使用Handler post()和postDelayed()方法指定希望这个代码在什么时间运行。
post()方法提交的代码要尽可能快地运行(通常几乎是立即运行),post()方法有一个参数,这是一个类型为Runnable的对象。Android世界里的Runable对象与普通Java中的Runnable很类似,就是你想要运行的一个作业。可以把想要运行的代码放在Runable的run()方法,Handler会确保这个代码尽可能快地运行。下面给出这个方法:
final Handler handler = new Handler();
handler.post(Runable);
postDelayed()方法与post()方法类似,只不过这个方法用来提交要在将来运行地代码。下面给出这个方法。
final Handler handler = new Handler();
handler.postDelayed(Runnable, long);
下面给出完整的StopwatchActivity代码:
package com.hfad.stopwatch;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.Locale;
import android.os.Handler;
public class StopwatchActivity extends Activity {
private int seconds = 0;//记录已经过去的秒数
private boolean running;//秒表是否正常运行
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_stopwatch);
runTimer();//使用单独的方法更新秒表。创建活动会调用这个方法
}
//启动秒表
public void onClickStart(View view) {
running = true;
}
//停止秒表
public void onClickStop(View view) {
running = false;
}
//单击reset按钮时会调用这个方法
public void onClickReset(View view) {
running = false;
seconds = 0;
}
private void runTimer() {
//得到文本视图
final TextView timeView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.time_view);
//创建一个新地Handler
final Handler handler = new Handler();
//调用post()方法,传入一个新的Runnable。post()方法会立即运行代码
handler.post(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
int hours = seconds / 3600;
int minutes = (seconds%3600)/60;
int secs = seconds % 60;
//设置显示格式
String time = String.format(Locale.getDefault(), "%d:%02d%02d", hours, minutes, secs);
//设置文本视图
timeView.setText(time);
if (running) {
++seconds;
}
//在1000ms后再次提交并运行Runnable中的代码,会反复调用
handler.postDelayed(this, 1000);
}
});
}
}
至此,一个基本秒表应用到此全部结束。
ps:不能直接在onCreate中写一个循环更新计时器,onCreate必须在屏幕显示之前完成,如果包含一个无线循环,这个方法将无法结束。