前面已经写了一篇Redisson的分布式限流的使用,Redisson分布式限流的简单实践,对其中的原理很好奇。
一、使用
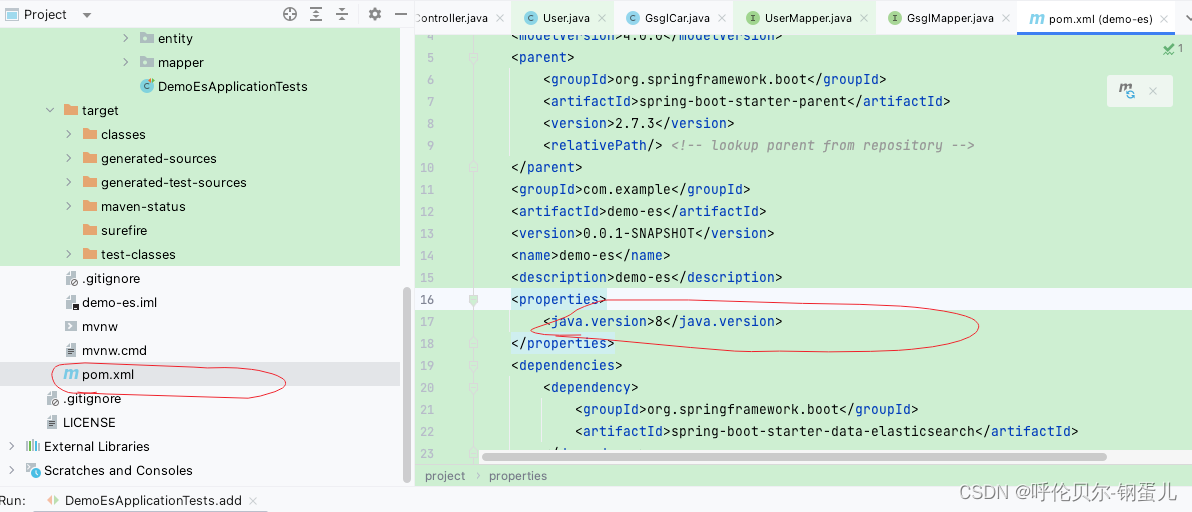
// 1、 声明一个限流器
RRateLimiter rateLimiter = redissonClient.getRateLimiter(key);
// 2、 设置速率,5秒中产生3个令牌
rateLimiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL, 3, 5, RateIntervalUnit.SECONDS);
// 3、试图获取一个令牌,获取到返回true
rateLimiter.tryAcquire(1)
二、原理
getRateLimiter
// 声明一个限流器 名称 叫key
redissonClient.getRateLimiter(key)
RedissonRateLimiter#trySetRate。5秒中产生3个令牌。rateInterval指的是时间间隔,rate指的是指定时间间隔产生的令牌数。
@Override
public boolean trySetRate(RateType type, long rate, long rateInterval, RateIntervalUnit unit) {
return get(trySetRateAsync(type, rate, rateInterval, unit));
}
@Override
public RFuture<Boolean> trySetRateAsync(RateType type, long rate, long rateInterval, RateIntervalUnit unit) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"redis.call('hsetnx', KEYS[1], 'rate', ARGV[1]);"
+ "redis.call('hsetnx', KEYS[1], 'interval', ARGV[2]);"
+ "return redis.call('hsetnx', KEYS[1], 'type', ARGV[3]);",
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()), rate, unit.toMillis(rateInterval), type.ordinal());
}
RedissonRateLimiter#tryAcquire()。- key的数组是
Arrays.asList(getRawName(), getValueName(), getClientValueName(), getPermitsName(), getClientPermitsName())。 - 如果name是
rate.limiter,那么lua脚本中的valueName是{rate.limiter}:value;permitsName是{rate.limiter}:permits。key[3]的结果是getClientValueName(),{rate.limiter}:value:4802866e-25b3-4482-aa74-61aa947d6f7a,需要拼接机器的唯一id。key[5]的结果是{rate.limiter}:permits:4802866e-25b3-4482-aa74-61aa947d6f7a。 tonumber(rate) >= tonumber(ARGV[1]),表明rate要比请求的令牌数大。- 如果首次获取,设置
valueName为rate,设置permitsName的score为当前时间戳,设置值为随机数和获取的令牌数,更新valueName,减去需要获取的令牌数。 - 第二次获取令牌执行,获取
0-(当前时间-生成令牌间隔interval)时间内的数据。获取之前所有的请求数released,如果released>0,更新valueName为当前值+释放令牌数。之前的请求令牌数 >0, 例如10s产生3个令牌,现在超过10s了,重置周期并计算剩余令牌数。 - 如果当前可提供的令牌数小于获取的令牌数,获取最近一次的记录。返回当前key的剩余过期时间。上一次请求的时间戳 - (当前时间戳 - 令牌生成的时间间隔) ,这个值表示还需要多久才能生产出足够的令牌。
- 如果当前令牌数 ≥ 请求的令牌数,表示令牌够多,直接更新zset。
- key的数组是
@Override
public boolean tryAcquire(long permits) {
return get(tryAcquireAsync(RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN, permits));
}
private <T> RFuture<T> tryAcquireAsync(RedisCommand<T> command, Long value) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"local rate = redis.call('hget', KEYS[1], 'rate');"
+ "local interval = redis.call('hget', KEYS[1], 'interval');"
+ "local type = redis.call('hget', KEYS[1], 'type');"
+ "assert(rate ~= false and interval ~= false and type ~= false, 'RateLimiter is not initialized')"
+ "local valueName = KEYS[2];"
+ "local permitsName = KEYS[4];"
+ "if type == '1' then "
+ "valueName = KEYS[3];"
+ "permitsName = KEYS[5];"
+ "end;"
+ "assert(tonumber(rate) >= tonumber(ARGV[1]), 'Requested permits amount could not exceed defined rate'); "
+ "local currentValue = redis.call('get', valueName); "
+ "if currentValue ~= false then "
+ "local expiredValues = redis.call('zrangebyscore', permitsName, 0, tonumber(ARGV[2]) - interval); "
+ "local released = 0; "
+ "for i, v in ipairs(expiredValues) do "
+ "local random, permits = struct.unpack('fI', v);"
+ "released = released + permits;"
+ "end; "
+ "if released > 0 then "
+ "redis.call('zremrangebyscore', permitsName, 0, tonumber(ARGV[2]) - interval); "
+ "currentValue = tonumber(currentValue) + released; "
+ "redis.call('set', valueName, currentValue);"
+ "end;"
+ "if tonumber(currentValue) < tonumber(ARGV[1]) then "
+ "local nearest = redis.call('zrangebyscore', permitsName, '(' .. (tonumber(ARGV[2]) - interval), '+inf', 'withscores', 'limit', 0, 1); "
+ "return tonumber(nearest[2]) - (tonumber(ARGV[2]) - interval);"
+ "else "
+ "redis.call('zadd', permitsName, ARGV[2], struct.pack('fI', ARGV[3], ARGV[1])); "
+ "redis.call('decrby', valueName, ARGV[1]); "
+ "return nil; "
+ "end; "
+ "else "
+ "redis.call('set', valueName, rate); "
+ "redis.call('zadd', permitsName, ARGV[2], struct.pack('fI', ARGV[3], ARGV[1])); "
+ "redis.call('decrby', valueName, ARGV[1]); "
+ "return nil; "
+ "end;",
Arrays.asList(getRawName(), getValueName(), getClientValueName(), getPermitsName(), getClientPermitsName()),
value, System.currentTimeMillis(), ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong());
}
RedissonRateLimiter#getValueName,生成valueName。
String getValueName() {
return suffixName(getRawName(), "value");
}
String getPermitsName() {
return suffixName(getRawName(), "permits");
}
public static String suffixName(String name, String suffix) {
if (name.contains("{")) {
return name + ":" + suffix;
}
return "{" + name + "}:" + suffix;
}
RedissonRateLimiter#tryAcquire(long, long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit),带时限的获取令牌。delay就是lua脚本返回的,还需要多久才会有令牌。如果获取令牌的时间比设置的超时时间还要大的话,直接就false了,否则会再次尝试获取令牌。
@Override
public boolean tryAcquire(long permits, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
return get(tryAcquireAsync(permits, timeout, unit));
}
@Override
public RFuture<Boolean> tryAcquireAsync(long permits, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
RPromise<Boolean> promise = new RedissonPromise<Boolean>();
long timeoutInMillis = -1;
if (timeout >= 0) {
timeoutInMillis = unit.toMillis(timeout);
}
tryAcquireAsync(permits, promise, timeoutInMillis);
return promise;
}
private void tryAcquireAsync(long permits, RPromise<Boolean> promise, long timeoutInMillis) {
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
RFuture<Long> future = tryAcquireAsync(RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG, permits);
future.onComplete((delay, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
promise.tryFailure(e);
return;
}
if (delay == null) {
promise.trySuccess(true);
return;
}
if (timeoutInMillis == -1) {
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getGroup().schedule(() -> {
tryAcquireAsync(permits, promise, timeoutInMillis);
}, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return;
}
long el = System.currentTimeMillis() - s;
long remains = timeoutInMillis - el;
if (remains <= 0) {
promise.trySuccess(false);
return;
}
if (remains < delay) {
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getGroup().schedule(() -> {
promise.trySuccess(false);
}, remains, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getGroup().schedule(() -> {
long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
if (remains <= elapsed) {
promise.trySuccess(false);
return;
}
tryAcquireAsync(permits, promise, remains - elapsed);
}, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
});
}








![二叉树的层级遍历以及[NOIP2015 普及组] 扫雷游戏、有效时间的数目](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/747ba62bd8bc461eb6cd28b7c815944a.png)


![[GFCTF 2021]文件查看器(GZ、过滤器、phar) day4](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e5117237a724436183d271832207104a.png)