🎉实战项目:负载均衡式在线OJ
博主主页:桑榆非晚ᴷ
博主能力有限,如果有出错的地方希望大家不吝赐教
给自己打气:成功没有快车道,幸福没有高速路。所有的成功,都来自不倦地努力和奔跑,所有的幸福都来自平凡的奋斗和坚持🥰🎉✨
负载均衡式在线OJ
- 🎉实战项目:负载均衡式在线OJ
- 一、`compile_runner_server`模块
- 1.1 、`compile`子模块
- 1.1.1、`compile`子模块介绍
- 1.1.2、程序编写
- 1.1.3 、测试`compile`子模块
- 1.2、`runner`子模块
- 1.2.1、`runner`子模块介绍
- 1.2.2、程序编写
- 1.2.3 、测试`runner`子模块
- 1.2.4 防止恶意用户
- 1.3 `compile_runner`子模块
- 1.3.1、`compile_runner`子模块介绍
- 1.3.2、程序编写
- 1.3.3、测试`compile_runner`子模块
- 1.4 `compile_runner_server`
- 1.4.1、`compile_runner_server`子模块介绍
- 1.4.2、程序编写
- 1.4.3、 测试`compile_runner_server`子模块
一、compile_runner_server模块
1.1 、compile子模块
1.1.1、compile子模块介绍
该子模块只负责把浏览器提交上来的代码进行编译。如果编译出错,则形成临时文件,把编译报错写入到临时文件当中。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ARIa4GLF-1682861111512)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429145115572.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/960086db26a449339b7bafab63944927.png)
1.1.2、程序编写
compile.hpp
#pragma once
// 只负责代码的编译
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
using std::cerr;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
namespace ns_compile
{
// 引入工具模块
using namespace ns_util;
// 引入日志模块
using namespace ns_log;
class Compiler
{
public:
// 返回值:编译成功 true,否则 false
// 输出参数:编译文件的文件名
// 编译函数
static bool Compile(const std::string &file_name)
{
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
LOG(ERROE) << "内部错误,创建子进程失败"
<< "\n";
return false;
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
// 子进程
// 子进程调用编译器->exec系列函数进程程序替换
// file_name(123)
// 123 -> ./temp/123.cc
// 123 -> ./temp/123.exe
// 123 -> ./temp/123.err
umask(0);
int err_fd = open(PathMontageUtil::Err(file_name).c_str(), O_RDONLY | O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0644);
if (err_fd == -1)
{
LOG(WARNING) << "打开.err文件失败"
<< "\n";
exit(-1);
}
// cout << "open and creat file fail" << endl, exit(1);
// 重定向标准错误到err_fd,使得错误信息输出到err_fd指向的文件
dup2(err_fd, STDERR_FILENO);
// g++ src -o dest -std=c++11
execlp("g++", "g++", PathMontageUtil::Src(file_name).c_str(), "-o",
PathMontageUtil::Exe(file_name).c_str(), "-std=c++11", nullptr);
// 如果程序替换失败直接退出
LOG(WARNING) << "g++可能没有安装或传参错误"
<< "\n";
exit(1);
}
else
{
// 父进程
if (waitpid(pid, nullptr, 0) == -1)
{
LOG(ERROE) << "等待子进程失败"
<< "\n";
exit(1);
}
// 如果.exe文件存在,说明编译成功
if (FileUtil::IsFileExists(PathMontageUtil::Exe(file_name).c_str()))
{
LOG(INFO) << PathMontageUtil::Src(file_name) << " 编译成功"
<< "\n";
return true;
}
else
{
LOG(ERROR) << PathMontageUtil::Src(file_name) << " 编译失败"
<< "\n";
return false;
}
}
}
};
}
util.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
namespace ns_util
{
const std::string src_path = "./temp/";
// 路径拼接的类
class PathMontageUtil
{
public:
// 构建源文件路径 + 完整后缀名
static const std::string Src(const std::string &file_name)
{
return AddSuffix(file_name, ".cpp");
}
// 构建可执行程序路径 + 完整后缀名
static const std::string Exe(const std::string &file_name)
{
return AddSuffix(file_name, ".exe");
}
// 构建标准错误文件路径 + 完整后缀名
static const std::string Err(const std::string &file_name)
{
return AddSuffix(file_name, ".err");
}
private:
static std::string AddSuffix(const std::string &file_name, const std::string &suffix)
{
std::string path_name = src_path;
path_name += file_name;
path_name += suffix;
return path_name;
}
};
// 文件操作的类
class FileUtil
{
public:
static bool IsFileExists(const std::string &path_name)
{
struct stat st;
int ret = stat(path_name.c_str(), &st);
if(ret == -1) return false;
else return true;
}
};
// 获取时间戳的类
class TimeUtil
{
public:
static const std::string GetTimeStamp()
{
struct timeval time;
gettimeofday(&time, nullptr);
return std::to_string(time.tv_sec);
}
};
}
Log.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "util.hpp"
using std::cout;
namespace ns_log
{
// 引入工具模块
using namespace ns_util;
// 日志等级
enum
{
INFO = 0,
DEBUG,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL
};
inline std::ostream &Log(const std::string &level, const std::string &file_name, int line)
{
// 添加日志等级
std::string logMessage = "[";
logMessage += level;
logMessage += "]";
// 添加报错文件名
logMessage += "[";
logMessage += file_name;
logMessage += "]";
// 添加报错行
logMessage += "[";
logMessage += std::to_string(line);
logMessage += "]";
// 添加日志时间戳
logMessage += "[";
logMessage += TimeUtil::GetTimeStamp();
logMessage += "]";
// cout 本质是把内部缓存区刷新的显示器上 行刷新
// 将logMessage写入到cout的缓存区当中
cout << logMessage;
return cout;
}
// LOG(level) << "message" ->开方式的日志功能
#define LOG(level) Log(#level, __FILE__, __LINE__)
}
1.1.3 、测试compile子模块
在当前目录下创建temp子目录,在子目录下编译一个简单的程序输出 hello c++。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-laKFwwNw-1682861111513)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429151219227.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7ed93fe7a7534b1c9bb13183c49333fe.png)
code.cpp测试用例1:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "hello c++" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
code.cpp测试用例2:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
hello world
std::cout << "hello c++" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
compile_server.cc
#include "compile.hpp"
using namespace ns_compile;
int main()
{
std::string code = "code";
// 调用Compile接口,编译"code"源文件
Compiler::Compile(code);
return 0;
}
makefile
compile_server:compile_server.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf compile_server
开始测试1:code.cpp没有任何错误
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ziQA5sZM-1682861111514)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429152223648.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b9dd047feed947ff9c36947afef778a8.png)
可编译成功,并且code.err没有任何编译报错信息
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-xMVrVkbG-1682861111514)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429152331917.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9719ebce5b0b4db6841e29119a2cce2c.png)
开始测试2:code.cpp有错误,语法错误
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-0kgqwC21-1682861111515)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429153052447.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bd79785325eb40fe8bce584d4224fcac.png)
可编译失败,并且code.err有编译报错信息
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TZpUlunw-1682861111516)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429153430108.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cc6200681623415391deaaa1201dbc20.png)
1.2、runner子模块
1.2.1、runner子模块介绍
该子模块只负责把compile子模块编译好的代码运行起来,把程序运行输出到标准输出和标准错误的内容重定向到temp路径下的指定文件当中,并获取程序运行结束后的退出信号。
1.2.2、程序编写
runner.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
namespace ns_runner
{
using namespace ns_util;
using namespace ns_log;
class Runner
{
public:
// 只需指明文件名,不许要带路径和后缀
/*******************************************
* 返回值 > 0: 程序异常了,退出时收到了信号,返回值就是对应的信号编号
* 返回值 == 0: 正常运行完毕的,结果保存到了对应的临时文件中
* 返回值 < 0: 内部错误
*
* cpu_limit: 该程序运行的时候,可以使用的最大cpu资源上限
* mem_limit: 改程序运行的时候,可以使用的最大的内存大小(KB)
* *****************************************/
static int Run(const std::string &file_name)
{
/*********************************************
* 程序运行:
* 1. 代码跑完,结果正确
* 2. 代码跑完,结果不正确
* 3. 代码没跑完,异常了
* Run需要考虑代码跑完,结果正确与否吗??不考虑!
* 结果正确与否:是由我们的测试用例决定的!
* 我们只考虑:是否正确运行完毕
*
* 我们必须知道可执行程序是谁?
* 一个程序在默认启动的时候
* 标准输入: 不处理
* 标准输出: 程序运行完成,输出结果是什么
* 标准错误: 运行时错误信息
* *******************************************/
std::string _execute_path = PathMontageUtil::Exe(file_name);
std::string _stdin_path = PathMontageUtil::Stdin(file_name);
std::string _stdout_path = PathMontageUtil::Stdout(file_name);
std::string _stderr_path = PathMontageUtil::Stderr(file_name);
umask(0);
int _stdin_fd = open(_stdin_path.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_RDONLY, 0644);
int _stdout_fd = open(_stdout_path.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
int _stderr_fd = open(_stderr_path.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
if (_stdin_fd == -1 || _stdout_fd == -1 || _stderr_fd == -1)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "运行时打开标准文件失败" << "\n";
return -1; // 代表打开文件失败
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == -1)
{
close(_stdin_fd);
close(_stdout_fd);
close(_stderr_fd);
LOG(ERROE) << "创建子进程失败" << "\n";
return -2;
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
dup2(_stdin_fd, STDIN_FILENO);
dup2(_stdout_fd, STDOUT_FILENO);
dup2(_stderr_fd, STDERR_FILENO);
execl(_execute_path.c_str(), _execute_path.c_str(), nullptr);
LOG(ERROR) << PathMontageUtil::Exe(file_name) << " 程序替换失败" << '\n';
return -3;
}
else
{
close(_stdin_fd);
close(_stdout_fd);
close(_stderr_fd);
int status = 0;
int ret = waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
if (ret == -1)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "等待子进程失败"
<< "\n";
return -4;
}
else
{
// 等待子进程成功
// 程序运行异常,一定是因为收到了信号!
LOG(INFO) << "程序运行完成, 退出信号: " << (status & 0x7F) << "\n";
return status & 0x7F;
}
}
}
};
}
1.2.3 、测试runner子模块
code.cpp测试用例1:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "hello c++" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
code.cpp测试用例2:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "hello c++" << std::endl;
std::cerr << "hello c++" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
makefile: temp路径下
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm code.co* code.s* code.e*
开始测试1:code.exe没有任何错误
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-B6nhD77S-1682861111516)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429185408442.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/249ddae731fb479fabd5a6f602fb6ee2.png)
由下图可见,退出信号为0,并且code.compile_err、code.stderr都没有任何错误信息。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-78IahXeg-1682861111517)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429185559013.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/91f2f3d351db45f8afd77f99b8d5e39b.png)
开始测试2:code.exe中向stderr输出消息
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6w5aS7yg-1682861111517)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429190229095.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/75063e820ee84c829dc6b11cc608e944.png)
由下图可见,退出信号为0,并且code.compile_err没有任何错误信息。、code.stderr输出hello c++。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Jkvcq1Je-1682861111518)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230429192730327.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/165ec7e6d9ae4256a033016b2ea3aaf9.png)
1.2.4 防止恶意用户
主要是防止恶意用户编写恶意代码吃系统的cpu和内存资源,所以在这里对cpu和内存资源进行资源受限控制。
对setrlimit系统接口进行测试:
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
int main()
{
// 设置对cpu累计运行的时长限制
// struct rlimit cpu_rlimit;
// cpu_rlimit.rlim_max = RLIM_INFINITY;
// cpu_rlimit.rlim_cur = 1;
// setrlimit(RLIMIT_CPU, &cpu_rlimit);
// while (true);
// 设置对内存地址空间的限制
// struct rlimit mem_rlimit;
// mem_rlimit.rlim_max = RLIM_INFINITY;
// mem_rlimit.rlim_cur = 1024 * 1024 * 20; // 40M
// setrlimit(RLIMIT_AS, &mem_rlimit);
int count = 0;
while (true)
{
int *p = new int[1024 * 102];
++count;
std::cout << "size: " << count << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
对cpu累计运行的时长限制进行测试:
在不做cpu时长限制式,程序理想情况下可以一直运行
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-KWcbEaGT-1682861111518)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430100331656.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/735187dd794d42859aad8a0fa2f87062.png)
在使用系统接口setrlimit对cpu使用时间加以限制式,程序只可以运行指定受限时间:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-VLVNX2bW-1682861111519)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430100420152.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5527a48bca9546e99dc572238319008a.png)
对内存地址空间的限制进行测试:
在不做内存受限控制时,一个进程可以一直开辟内存,直到内存耗尽
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-yu7fElvJ-1682861111519)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430102149899.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dec92df6cc8e407f89d9c16937a1df2f.png)
在使用系统接口setrlimit对内存使用加以限制式,程序只可以最多使用指定受限内存大小:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-DupAuyuN-1682861111519)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430102017787.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d8ad0b2487894b15be41ffddfe87f2b6.png)
把该模块引入到runner模块当中的子进程当中,execl之前
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
namespace ns_runner
{
using namespace ns_util;
using namespace ns_log;
class Runner
{
public:
// 只需指明文件名,不许要带路径和后缀
/*******************************************
* 返回值 > 0: 程序异常了,退出时收到了信号,返回值就是对应的信号编号
* 返回值 == 0: 正常运行完毕的,结果保存到了对应的临时文件中
* 返回值 < 0: 内部错误
*
* cpu_limit: 该程序运行的时候,可以使用的最大cpu资源上限
* mem_limit: 改程序运行的时候,可以使用的最大的内存大小(byte)
* *****************************************/
static int Run(const std::string &file_name, int cpu_limit, int mem_limit)
{
/*********************************************
* 程序运行:
* 1. 代码跑完,结果正确
* 2. 代码跑完,结果不正确
* 3. 代码没跑完,异常了
* Run需要考虑代码跑完,结果正确与否吗??不考虑!
* 结果正确与否:是由我们的测试用例决定的!
* 我们只考虑:是否正确运行完毕
*
* 我们必须知道可执行程序是谁?
* 一个程序在默认启动的时候
* 标准输入: 不处理
* 标准输出: 程序运行完成,输出结果是什么
* 标准错误: 运行时错误信息
* *******************************************/
std::string _execute_path = PathMontageUtil::Exe(file_name);
std::string _stdin_path = PathMontageUtil::Stdin(file_name);
std::string _stdout_path = PathMontageUtil::Stdout(file_name);
std::string _stderr_path = PathMontageUtil::Stderr(file_name);
umask(0);
int _stdin_fd = open(_stdin_path.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_RDONLY, 0644);
int _stdout_fd = open(_stdout_path.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
int _stderr_fd = open(_stderr_path.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
if (_stdin_fd == -1 || _stdout_fd == -1 || _stderr_fd == -1)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "运行时打开标准文件失败" << "\n";
return -1; // 代表打开文件失败
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == -1)
{
close(_stdin_fd);
close(_stdout_fd);
close(_stderr_fd);
LOG(ERROE) << "创建子进程失败" << "\n";
return -2;
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
dup2(_stdin_fd, STDIN_FILENO);
dup2(_stdout_fd, STDOUT_FILENO);
dup2(_stderr_fd, STDERR_FILENO);
SetProcLimit(cpu_limit, mem_limit);
execl(_execute_path.c_str(), _execute_path.c_str(), nullptr);
LOG(ERROR) << PathMontageUtil::Exe(file_name) << " 程序替换失败" << '\n';
return -3;
}
else
{
close(_stdin_fd);
close(_stdout_fd);
close(_stderr_fd);
int status = 0;
int ret = waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
if (ret == -1)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "等待子进程失败"
<< "\n";
return -4;
}
else
{
// 等待子进程成功
// 程序运行异常,一定是因为收到了信号!
LOG(INFO) << "程序运行完成, 退出信号: " << (status & 0x7F) << "\n";
return status & 0x7F;
}
}
}
private:
//提供设置进程占用资源大小的接口
static void SetProcLimit(int _cpu_limit, int _mem_limit)
{
// 设置CPU时长
struct rlimit cpu_rlimit;
cpu_rlimit.rlim_max = RLIM_INFINITY;
cpu_rlimit.rlim_cur = _cpu_limit;
setrlimit(RLIMIT_CPU, &cpu_rlimit);
// 设置内存大小
struct rlimit mem_rlimit;
mem_rlimit.rlim_max = RLIM_INFINITY;
mem_rlimit.rlim_cur = _mem_limit * 1024; //转化成为KB
setrlimit(RLIMIT_AS, &mem_rlimit);
}
};
}
1.3 compile_runner子模块
1.3.1、compile_runner子模块介绍
compile_runner子模块主要内存时对compile子模块和runner子模块进行分装,并引入jsoncpp第三方库。当compile_server子模块获取到浏览器提交上来的json字符串类型的请求时,compile_server子模块就会把提交上来的json字符串喂给compile_runner子模块进行处理。所以compile_runner子模块就是分装compile子模块和runner子模块,用来对上层提供服务的。
1.3.2、程序编写
代码框架
#pragma once
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
#include "compile.hpp"
#include "runner.hpp"
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
namespace ns_compile_and_run
{
using namespace ns_log;
using namespace ns_util;
using namespace ns_compile;
using namespace ns_runner;
class Compile_And_Run
{
public:
/***************************************
* 输入:
* code: 用户提交的代码
* input: 用户给自己提交的代码对应的输入,不做处理
* cpu_limit: 时间要求
* mem_limit: 空间要求
*
* 输出:
* 必填
* status: 状态码
* reason: 请求结果
* 选填:
* stdout: 我的程序运行完的结果
* stderr: 我的程序运行完的错误结果
*
* 参数:
* in_json: {"code": "#include...", "input": "","cpu_limit":1, "mem_limit":10240}
* out_json: {"status":"0", "reason":"","stdout":"","stderr":"",}
* ************************************/
static void Start(const std::string &in_json_str, std::string *out_json_str)
{
Json::Value in_value;
Json::Value out_value;
Json::Reader reader;
reader.parse(in_json_str, in_value); // 可能反序列化失败,后面处理
std::string code = in_value["code"].asString();
std::string input = in_value["input"].asString();
int cpu_limit = in_value["cpu_limit"].asInt();
int mem_limit = in_value["mem_limit"].asInt();
if(code.size() == 0)
{
// TODO
}
// 形成唯一文件名,没有路径没有后缀
std::string file_name = FileUtil::UniqueFileName();
// 形成临时src文件,并将用户提交的代码写入src文件当中
if(!FileUtil::WriteFile(file_name, code))
{
// TODO
}
// 编译src文件
if(!Compiler::Compile(file_name))
{
// TODO
}
// 运行可执行文件
int run_code = Runner::Run(file_name, cpu_limit, mem_limit);
// 删除用于处理用户请求所产生的所有的临时文件
FileUtil::RemoveTempFile(file_name);
}
};
}
代码实现
#pragma once
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
#include "compile.hpp"
#include "runner.hpp"
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
namespace ns_compile_and_run
{
using namespace ns_log;
using namespace ns_util;
using namespace ns_compile;
using namespace ns_runner;
class Compile_And_Run
{
public:
static void Start(const std::string &in_json_str, std::string *out_json_str)
{
Json::Value in_value;
Json::Value out_value;
Json::Reader reader;
reader.parse(in_json_str, in_value); // 可能反序列化失败,后面处理
std::string code = in_value["code"].asString();
std::string input = in_value["input"].asString();
int cpu_limit = in_value["cpu_limit"].asInt();
int mem_limit = in_value["mem_limit"].asInt();
std::string file_name;
int status_code;
int run_code;
if (code.size() == 0)
{
LOG(WARNING) << "用户提交的代码是空的";
status_code = -1;
goto END;
}
// 形成唯一文件名,没有路径没有后缀
file_name = FileUtil::UniqueFileName();
// 形成临时src文件
if (!FileUtil::WriteFile(PathMontageUtil::Src(file_name), code))
{
status_code = -2;
LOG(ERROR) << "写入临时文件失败"
<< "\n";
goto END;
}
if (!Compiler::Compile(file_name))
{
status_code = -3;
LOG(ERROR) << "编译失败"
<< "\n";
goto END;
}
run_code = Runner::Run(file_name, cpu_limit, mem_limit);
if (run_code < 0)
{
status_code = -2;
LOG(ERROR) << "发生编译时未知异常"
<< "\n";
goto END;
}
else if (run_code > 0)
{
status_code = run_code;
LOG(ERROR) << "发生运行时未知异常"
<< "\n";
goto END;
}
else
{
status_code = run_code;
LOG(INFO) << "运行成功"
<< "\n";
}
END:
out_value["status"] = status_code;
out_value["reason"] = CodeUtil::CodeToDesc(status_code, file_name);
if (status_code == 0)
{
// 整个过程全部成功
std::string _stdout;
FileUtil::ReadFile(PathMontageUtil::Stdout(file_name), &_stdout);
out_value["stdout"] = _stdout;
std::string _stderr;
FileUtil::ReadFile(PathMontageUtil::Stderr(file_name), &_stderr);
out_value["stderr"] = _stderr;
}
Json::StyledWriter writer;
*out_json_str = writer.write(out_value);
FileUtil::RemoveTempFile(file_name);
}
};
}
1.3.3、测试compile_runner子模块
test_compile_runner.cc
#include "compile_run.hpp"
// 编译服务可能随时被多个人请求,必须保证上传上来的code,形成源文件名称的时候,要具有
// 唯一性,要不然多个用户之间会互相影响
using namespace ns_compile_and_run;
int main()
{
// 通过http 让client给我们上传一个json string
// 而由于我们这里还没写网络服务,所以只能手动写一个json string,充当客户端的上传的json string
// in_json: {"code": "#include...", "input": "","cpu_limit":1, "mem_limit":10 << 20}
// out_json: {"status":"0", "reason":"","stdout":"","stderr":""}
std::string in_json_str, out_json_str;
Json::Value in_value;
// R"()" raw string
// 测试代码1
// in_value["code"] = R"(#include <iostream>\nint main()\n{\nstd::cout << "hello c++" << std::endl;\nretrun 0;\n})";
// 测试代码2
in_value["code"] = R"(
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "hello c++" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
)";
// 测试代码3
in_value["code"] = R"(
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
while(true);
return 0;
}
)";
// 测试代码4
in_value["code"] = R"(
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int *p = new int[1024 * 1024 * 50];
return 0;
}
)";
// 测试用例5:
in_value["code"] = R"(
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 0;
int c = a / b;
return 0;
}
)";
in_value["input"] = "";
in_value["cpu_limit"] = 1;
in_value["mem_limit"] = 30 << 10; // 30M
Json::FastWriter writer;
in_json_str = writer.write(in_value);
std::cout << in_json_str << std::endl;
Compile_And_Run::Start(in_json_str, &out_json_str);
std::cout << out_json_str << std::endl;
return 0;
}
测试代码1:没有解析\n,所以有语法错误,会有语法错误
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-pqP39bQU-1682861111520)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430155620063.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c2d2de733c39422bbfa00de012fcd226.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Ro2pWcJF-1682861111521)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430160103576.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ec05ddd8f87b4ccaa30e1152f4206178.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-amYniJqR-1682861111521)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430160008589.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e5fc46a2dc6a4b54a12de9dd711b43d7.png)
测试代码2:没有语法错误和逻辑错误,理想状态是正常运行完
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-NJiOpiBr-1682861111521)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430162143657.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4967804205d749fe82ef37d2c94d523f.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-rrPmWW5R-1682861111522)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430162229585.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/332e8e807c8e46fc86f3754eb741a0b4.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-lYYB0f6z-1682861111522)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430162248545.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0609790040644d2db21eb1380e8c1bf9.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-3Srw5kUf-1682861111523)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430162459828.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/97dcf73ab4174f3bbebb4885439d9000.png)
测试代码3:CPU使用超时
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-gDcBtMHn-1682861111523)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430162801177.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9733726c77c04b84a061a3fb25e1653a.png)
测试代码4:内存使用受限制
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-wXQunX6k-1682861111524)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430163500768.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/993fa99a5d0348799cf0e1688e6253cd.png)
测试用例5:浮点数错误
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-cAgYmMOC-1682861111524)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430163716360.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b9f71e28323f4684886a15e52b17db35.png)
1.4 compile_runner_server
1.4.1、compile_runner_server子模块介绍
compile_runner_server子模块是一个基于cpp-httplib网络模块,它负责与浏览器进行交互,获取客户请求json字符串并返回处理结果json字符串。
1.4.2、程序编写
#include "compile_run.hpp"
#include "../comm/httplib.h"
using namespace ns_compile_and_run;
using namespace httplib;
static void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << "\n\t" << proc << " prot" << std::endl;
}
// 编译服务可能随时被多个人请求,必须保证上传上来的code,形成源文件名称的时候,要具有
// 唯一性,要不然多个用户之间会互相影响
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2) Usage(argv[0]);
Server svr;
svr.Post("/compile_and_run", [](const Request &req, Response &resp)
{
// 用户请求的服务正文是我们想要的json string
std::string in_json = req.body;
std::string out_json;
if(!in_json.empty()){
Compile_And_Run::Start(in_json, &out_json);
resp.set_content(out_json, "application/json;charset=utf-8");
} });
svr.listen("0.0.0.0", atoi(argv[1])); // 启动http服务
return 0;
}
1.4.3、 测试compile_runner_server子模块
// 测试用例1
{
"code" : "#include <iostream>\nint main()\n{ std::cout << \"hello c++\" << std::endl;\nreturn 0;} ",
"input" : "",
"cup_limit" : 1,
"mem_limit" : 50000
}
// 测试用例2
{
"code" : "#include <iostream>\nint main()\n{ while(true);\nreturn 0;} ",
"input" : "",
"cup_limit" : 1,
"mem_limit" : 50000
}
由于我们还没有编写客户端,所以我们可以用telnet或者postman进行模拟客户端,这里我使用postman模拟客户端
测试用例1:没有语法错误和逻辑错误,理想状态是正常运行完
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-lHzTQoII-1682861111525)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430185935086.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/45a4bad5790b47db9e29b736504110e6.png)
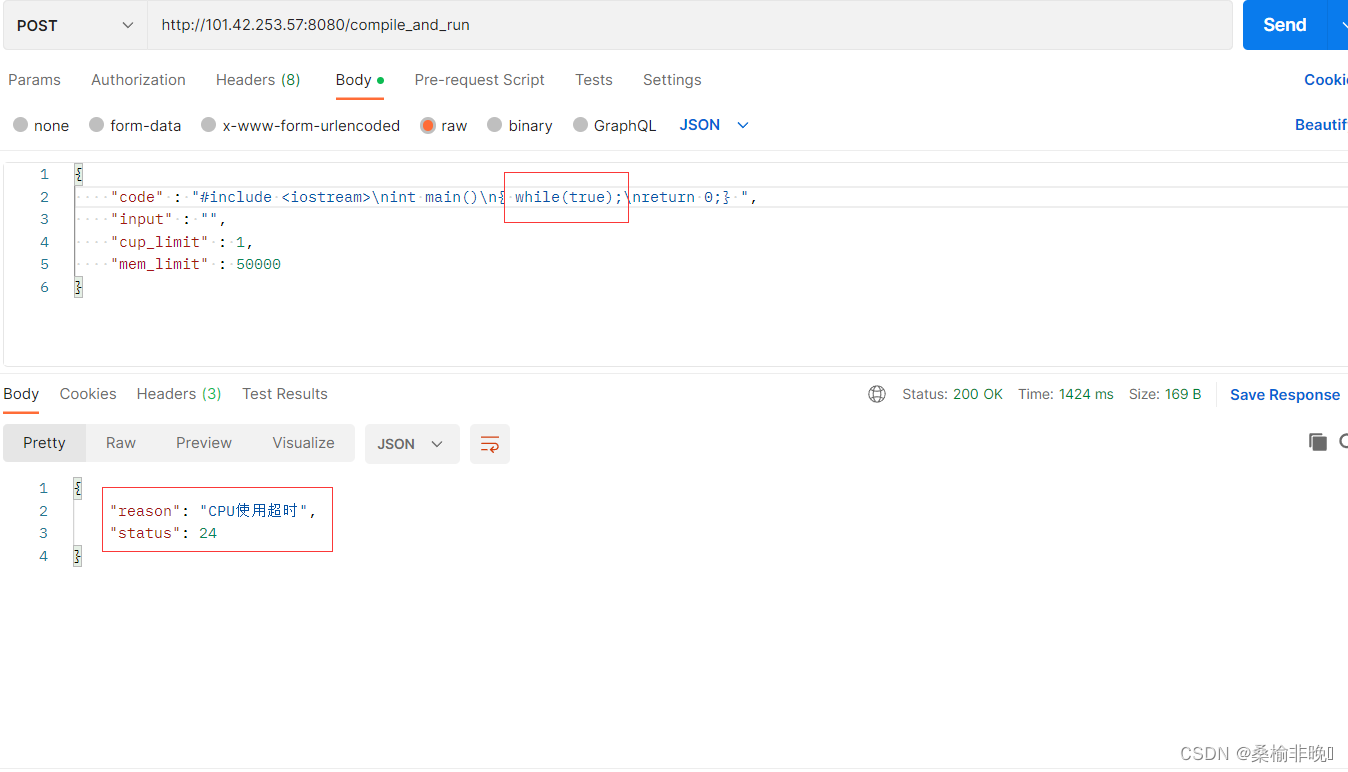
测试用例2:CPU使用超时
由于为用户提供服务会产生大量的临时文件,这样一直产生临时文件而不对进行清理,会把磁盘打满的,所以对其进行处理,具体见代码实现。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-514AP35e-1682861111526)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230430164454389.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/65d7a90891524d76950af4ac04ce7642.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传上传(imY8zj1iPfVm-1682861111511)(C:\Users\13916\Pictures\Saved Pictures\壁纸\微信图片_20221128141855.jpg)(C:\Users\13916\Pictures\Saved Pictures\壁纸\微信图片_20221128141855.jpg)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9f6b8ea0e1814bad9384d87b8377fe5f.png)

![K8S管理系统项目实战[API开发]-1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/217beb91513840f2a970b774c246a09b.png)